About the disease
Herpetic infection is a collective concept that is used to refer to diseases that are provoked by different types of the virus of the same name.
Traditionally, in pediatric practice, pathology caused by type 1 is encountered. This is the so-called labial herpes (rash on the lips). Its peculiarity is its chronic course. It is impossible to completely get rid of the pathogen. With adequate treatment of a child with symptoms of labial herpes, stable remission can be achieved. However, at this time the virus “hides” in the nerve ganglia (ganglia), where it can remain inactive for as long as desired. When favorable conditions arise (primarily decreased appetite), it is activated again. Another common form of herpes infection that can occur in children is varicella (chickenpox). The disease is provoked by the herpes virus type 3. It is important to remember that after successful recovery, the pathogen also goes into a latent form and persists in the nerve ganglia. The risk for the patient may be a reoccurrence of the infection. The type 3 virus, when reactivated, can cause herpes zoster, which is characterized by a more pronounced clinical picture with a deterioration in the child’s well-being and the appearance of rashes along the intercostal nerves.
The specialists of the SM-Doctor clinic have extensive experience in early diagnosis and treatment of all pathologies caused by herpes viruses. Doctors provide the necessary monitoring and quality treatment for children with any form of herpetic infection.
Cytomegalovirus infection
Cytomegalovirus infection is characterized by the formation of giant cells and specific infiltrates in the affected organs, a latent (asymptomatic) course in individuals with a normal immune system and with clinical manifestations in immunodeficiency states, mainly in young children.
Clinical forms of cytomegalovirus infection (CMVI):>
Congenital CMV infection is infection from the mother during pregnancy and childbirth and acquired, which is often asymptomatic. The full clinical picture of CMV infection is characterized by:
- increase in body temperature;
- lethargy;
- drowsiness;
- adynamia;
- enlarged lymph nodes, liver, spleen, salivary glands;
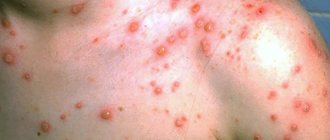
- rash;
- other organs are involved (lungs, kidneys, central nervous system).
The disease has an undulating, relapsing course, reminiscent of the clinical picture of infectious mononucleosis.
Herpes symptoms
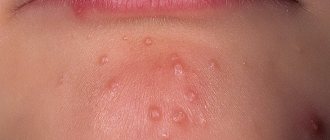
Labial herpes is the simplest and most harmless form of the disease, which occurs most often in children. Apart from discomfort for the baby and parents, in most cases the disease is not accompanied by serious consequences. Typical clinical picture:
- the formation of painful blisters filled with serous fluid in the lip area;
- itching and burning in places where skin elements appear;
- loss of appetite. Breasts may refuse to breastfeed due to pain during feeding;
- general weakness, lethargy, emotional lability;
- increase in body temperature to 37-37.5 ° C (rare).
With adequate treatment, signs of the disease can disappear after 3-4 days.
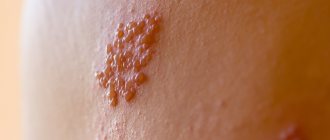
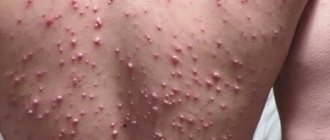
Chicken pox is a typical representative of “childhood infections”. The disease is accompanied by the appearance of rashes with serous contents throughout the body of a small patient. A characteristic feature that allows you to quickly differentiate chickenpox from other infectious pathologies is the obligatory presence of pustules on the scalp and the formation of crusts after removal of the blisters. The disease is also accompanied by a rise in body temperature to 38-39.5 ° C. The severity of the pathology depends on the individual characteristics of the child’s immune system and the aggressiveness of the pathogen.
Herpes zoster is accompanied by:
- the occurrence of rashes along the intercostal nerves;
- severe pain in the area where the pustules spread;
- high fever;
- pronounced general intoxication syndrome.
If you detect at least one of these symptoms, you should immediately consult a doctor. SM-Doctor specialists point out that chicken pox and herpes zoster are diseases that require isolation of a small patient in a hospital to monitor his condition and prevent the spread of the pathogen to other family members and the environment.
Epstein-Barr virus
Epstein-Barr viral infection (herpes type 4) is characterized by a variety of clinical manifestations and occurs in acute and chronic forms:
1. The acute form of EBV is infectious mononucleosis. Main clinical symptoms:
- acute onset of the disease;
- fever;
- enlarged lymph nodes, liver, spleen;
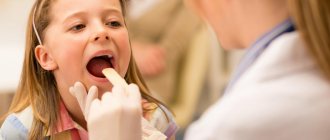
- angina;
- rash;
- difficulty nasal breathing,
- changes in the clinical blood test (increased levels of leukocytes, followed by a decrease in them, increased lymphocytes, monocytes, identification of atypical mononuclear cells).
The outcomes of infectious mononucleosis are either complete, but often long-term recovery or transition to a chronic form.
2. The manifestation of chronic EBV infection in children is:
- prolonged enlargement of lymph nodes;
- enlarged liver, spleen;
- adenoiditis;
- chronic tonsillitis;
- frequent repeated respiratory infections;
- intoxication syndrome;
- asthenic, cardiac, arthralgic syndromes;
- prolonged increase in body temperature (the so-called subfebrile body temperature - up to 38, more often it is 37 - 37.5).
Causes of herpes
All variants of herpes infection occur against the background of the activity of the virus of the same name of different types. Since upon initial penetration into the human body the pathogen no longer leaves it, it is important to know the factors that can provoke the activation of the disease:
- hypothermia;
- seasonal colds;
- any conditions that provoke a decrease in immune defense (poor nutrition, hypovitaminosis and others);
- exacerbation of chronic somatic diseases;
- contact with an infected patient.
The virus is transmitted by airborne droplets, so it is extremely difficult to completely prevent a child from encountering pathogenic particles.
Diagnosis of herpes
"SM-Doctor" is a multidisciplinary clinic specializing in providing high-quality medical services to children of any age. Diagnosis of herpetic infections in our center is carried out according to the standards used in leading clinics in Europe and the world. Our specialists establish a preliminary diagnosis at the stage of the initial examination of the child. Depending on the severity of the clinical picture, the necessary auxiliary diagnostic procedures are selected:
- a set of standard laboratory tests (general blood test, urine test, blood “biochemistry”, etc.);
- specific serological tests (ELISA) to detect antibodies to a specific type of virus in the patient’s blood;
- Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is a highly informative diagnostic method that allows you to detect the presence of a virus in a child’s body with up to 99% accuracy.
"SM-Doctor" is a multidisciplinary center. Thanks to this, if necessary (for example, if complications develop), our patients can be examined by a wide range of specialists in different fields. If the attending physician, in addition to infection, suspects a pathology of internal organs and systems, he refers the sick child for consultation with a cardiorheumatologist, ophthalmologist, neurologist and others. In a short period of time, the child receives a full range of diagnostic services aimed at identifying any abnormalities in the functioning of the body.
Herpes: symptoms, diagnosis and treatment
Itching, soreness, redness of the skin, blisters... Really again? Those who have encountered it more than once will “recognize” these symptoms as manifestations of herpes. What kind of virus is this? For what reasons does he regularly harass some people?
Our interlocutor, candidate of medical sciences, dermatovenerologist at the Expert Tula Clinic, Vladislav Leonidovich Sheinkman, told us about this and much more.
— What is herpes and how common is it among the inhabitants of our country?
This is a group of diseases caused by herpes viruses. One of the most common types is the herpes simplex virus, which is divided into herpes types 1 and 2, as well as the varicella zoster virus and herpes zoster virus.
Almost all people in Russia are infected with the herpes simplex virus. Once the virus enters the body, it never leaves it. Usually it is in the body in an inactive, “sleeping” state and does not bother a person.
— Is herpes a fungus, a virus or a bacterium?
It's a virus.
— Where does the herpes virus hide in the body?
Herpes simplex viruses are usually found in the so-called nerve ganglia (for example, in the trigeminal ganglion, sacral ganglia).
— How does infection with the herpes virus occur? Who is at risk for herpes infection?
Infection usually occurs in childhood. There are several ways of infection. This is airborne, contact household (dishes, household items, etc.), sexual.
What is immunity and how to increase it? Allergist-immunologist at Clinic Expert Smolensk tells
Chemova Ulyana Vladimirovna
The risk of virus activation occurs in the presence of so-called cofactors. These include weakened immunity, emotional distress, stress, alcohol consumption, climate change (for example, travel), menstruation, prolonged exposure to the sun or hypothermia, the presence of infection (ARVI, pneumonia, sinusitis, etc.).
Is it possible to treat sinusitis without a puncture? Otolaryngologist at the Expert Kursk Clinic, Candidate of Medical Sciences Alexandra Nikolaevna Emelyanova tells
— Tell us about the most common symptoms of herpes
Herpes occurs cyclically in the body, and its symptoms depend on the stage of the process.
The first, so-called prodromal stage, is characterized by burning, itching, and a tingling sensation in the area of future localization of herpes manifestations. The duration of this period can be several hours.
In the second stage, redness and thickening of the skin or mucous membrane appear in the form of a spot (erythematous stage). This stage of herpes lasts about a day.
At the third stage, small bubbles (2-3 mm in size) appear, which can “merge” with the serous or serous-purulent contents. Depending on the severity of the flow, the number of bubbles may vary.
In the fourth stage, the blisters break open and painful ulcers form in their place. This stage of herpes lasts several days and is the most contagious to others.
By the fifth stage, the ulcers dry out and form crusts.
And finally, at the sixth stage, the crusts fall off and the skin or mucous membrane is restored.
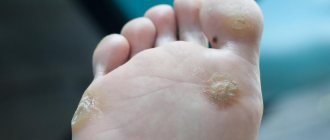
With type 1 herpes simplex virus, manifestations occur on the skin and mucous membranes of the upper half (for example, the lip area, nasolabial fold, neck), and type 2 - on the lower half of the body (otherwise it is called “genital herpes,” although Other areas may also be affected - for example, the buttock area, etc.).
In the recurrent form, the localization is usually stable.
— Is herpes on the lips contagious to others?
Absolutely yes.
— Does a herpetic infection always manifest itself with pronounced symptoms, or may a person not suspect that he is a carrier of the infection?
If a herpetic infection is also understood as a pure carrier state, then symptoms may not always be present. If a person has a strong immune system, he may not even know that he has such a virus.
The manifestations of exacerbation also vary from person to person. People with a normal but temporarily slightly weakened immune system, or those receiving some kind of antiviral treatment, may have a different severity of symptoms than a person with a severe illness (for example, tuberculosis), a severely weakened immune system (for example, HIV infection, chemotherapy, for organ transplants, etc.).
What are the symptoms of tuberculosis? Read more
— How is the herpes virus detected in humans?
Diagnosis of herpesvirus infection is primarily based on an examination by a dermatovenerologist.
To confirm the diagnosis, laboratory methods may be prescribed by the doctor. Some of them are used to detect the virus itself, while others are indicators of the immune response to the virus.
To search for the virus itself, polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is used, when material is taken from the site of the lesion and examined for the presence of virus nucleic acids.
An enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) is used to confirm the presence of an immune response against the virus. Imagine this situation. A person does not have any manifestations of herpes, and besides, he does not remember whether he ever had them or not. How to find out whether an organism has “met” the virus or not? If, when performing ELISA, specific antibodies are detected - immunoglobulins of class G (IgG) against the herpes virus, this means that there was once an infectious process, and the virus is currently in an inactive state. These antibodies are usually found throughout a person's life. If there is a suspicion of virus activation, then, in addition to PCR, an analysis for class M immunoglobulins (IgM) may be prescribed according to indications. The detection of this type of antibody indicates an exacerbation of the process. Outside of an exacerbation, only IgG is detected.
— For whom can the herpes virus be dangerous?
First of all, these are persons with serious diseases (for example, tuberculosis, oncological pathologies, immunodeficiencies). In them, the manifestation of herpes can be severe, affecting areas that are not usually found under other conditions (for example, the optic nerve).
— How to get rid of herpes? Is it enough to use only ointment or cauterize the wounds with brilliant green?
This depends on a number of factors - in particular the prevalence of the process, the frequency and severity of relapses. Often local treatment is not enough. There are certain standards and principles for the treatment of herpes, which consist in the use of antiviral drugs and agents to improve/correct the functions of the immune system.
— There are recommendations on the Internet to use tea bags or sage infusion to relieve itching from herpes. Do traditional methods really help in treating herpes infections?
The use of such methods may complicate the doctor’s work, i.e. making the correct diagnosis and prescribing effective treatment.
— What could be the consequences if herpes is not treated?
Mainly - frequent relapses, with the appearance of more common forms during exacerbations, with more severe symptoms.
— What specialty does a doctor treat herpes?
Dermatovenerologist.
You can make an appointment with a dermatovenerologist here
Please note: the service is not available in all cities
— Are effective methods of preventing herpes known to modern medicine?
Undoubtedly. It is necessary to identify and eliminate cofactors that lead to exacerbation of herpes. The main ones are stress, hypothermia or overheating, excessive alcohol intake, exposure to the sun, climate change and a number of others.
For reference:
Sheinkman Vladislav Leonidovich
Graduate of the pediatric faculty of the Smolensk State Medical Institute in 1994.
From 1994 to 1995, he completed an internship, and from 1996 to 1998, a clinical residency in the specialty “Dermatovenereology”.
Has an academic degree of Candidate of Medical Sciences.
Currently working at Clinic Expert Tula LLC as a dermatovenerologist. Provides reception at the address: st. Boldina, 74
Treatment of herpes
SM-Doctor doctors select treatment for herpetic infection for each child individually.
Our specialists prescribe medications depending on the severity of the clinical picture of the pathology and the presence of concomitant diseases. The following means are traditionally used to combat the virus:
- acyclovir is a specific drug to destroy the pathogen;
- antipyretic medications (paracetamol, ibuprofen) for fever above 38°C;
- auxiliary medications (painkillers, antiallergic and others).
Prevention of herpes
The basic rules that will help reduce the likelihood of infection with viruses of the herpes family are:
- hand washing;
- limiting contact with sick people;
- nasal instillation with saline solutions during the off-season.
There is now a vaccine against chickenpox. Vaccination helps prevent infection and/or development of severe forms of the disease. “SM-Doctor” is a multidisciplinary medical institution that provides effective treatment to children facing various diseases. Herpetic infection in any of its manifestations is not a problem. The main thing is to schedule a consultation with our specialists on time. Contact us!
Herpes type 6
Herpes type 6 - primary infection is manifested by sudden exanthema (or roseola) - the sudden appearance of a spotty rash on the skin of an allergic type with a high body temperature. It can occur in the form of infectious mononucleosis or manifest itself as chronic fatigue syndrome, prolonged enlargement of the lymph nodes. The cause of sudden exanthema and chronic fatigue syndrome can be herpes type 7, and herpes type 8 occurs in the form of Kaposi's sarcoma, and is more often recorded in people with an immunodeficiency state and HIV infection.
If you suspect or detect herpetic infections, you must contact a pediatric infectious disease specialist or pediatrician, who will determine the required volume and advisability of treatment.
Services and prices
Primary appointment (examination, consultation) with an infectious disease specialist
2,200 rub.
Repeated appointment (examination, consultation) with an infectious disease specialist
2,100 rub.