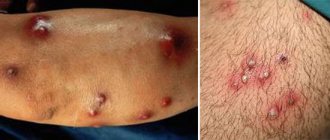
Herpes
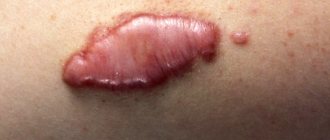
is a viral disease. One of the most well-known manifestations of a herpes infection is small, clear, painful blisters on the lips. Previously, in such a case they said “a cold on the lip popped up”, now they more often talk about “herpes on the lip”.
However, the family of herpes viruses is quite large. There are several types of herpes virus that can infect the human body. The most studied types are:
- herpes simplex virus type 1
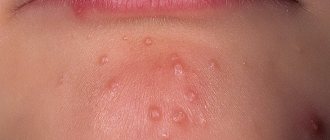
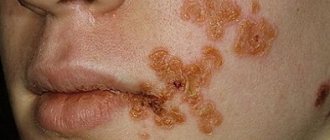
(HSV-1). It is he who is responsible for pimples on the lip. HSV-1 primarily affects the mucous membranes of the lips, oral cavity and nasopharynx. Herpetic rashes can also appear within the nasolabial triangle (in particular, on the wings of the nose), less often on the cheeks and other parts of the face. Recently, HSV-1 quite often becomes the cause of herpetic lesions of the genital area, where it is introduced through oral sex; - herpes simplex virus type 2 (HSV-2) – genital herpes
. Main manifestations: redness, the appearance in the area of redness of bubbles filled with liquid, tending to merge, the appearance of erosions and crusts at the site of the bubbles, itching, headache and muscle pain, increased urination; - chickenpox virus
(varicella) is a type 3 herpes virus. In people who have already had chickenpox, this type of virus causes herpes zoster. Therefore, this type of herpes is also called Varicella-Zoster; - Epstein-Barr virus
(Epstein-Barr viral infection - EBVI) is a type 4 herpes virus. It is the causative agent of mononucleosis, causes malignant diseases of lymphoid tissue, and is considered the cause of chronic fatigue syndrome; - cytomegalovirus
– herpes virus type 5. The virus poses a threat to children during fetal development. May affect internal organs.
Causes of herpes
Herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1) can be transmitted through household contact. Airborne transmission is also possible.
The airborne route is the main route of infection with the varicella zoster virus.
Genital herpes and cytomegalovirus are transmitted sexually.
You can also become infected with herpes through blood or saliva. The virus can be transmitted through saliva through kissing. Small children who put things in their mouths every now and then are also very vulnerable. If at least one child in a children's group is infected, a rapid spread of the infection can be expected.
Causes of herpetic rashes
Natural tears protect the visual organ well from viruses if there are no violations. Immunoglobulins contained in tear fluid block the spread of infection.
Causes of herpetic rashes:
- weakened immunity due to a stressful situation, infectious pathologies, hypothermia;
- injuries to the visual organ;
- pregnancy;
- use of immunosuppressants.
Important! You can become infected with ophthalmoherpes through contact with a source of infection (mucous mucous membranes of intimate organs, oral cavity), through household items (towels, personal hygiene items).
Herpes symptoms
Currently, most people are infected with some type of herpes virus. It is believed that antibodies to the Epstein-Barr virus can be detected in almost every adult (up to 98% of the adult population of the Earth). Antibodies to herpes simplex virus type 1 are detected in 90% of the adult population of large cities.
However, as a rule, carriage of a herpes infection does not lead to the development of the disease. The herpes virus is activated when the body's defenses decrease. The weaker the immune system, the more likely the virus is to transition from dormant to active.
That is why the herpes simplex virus type 1 is popularly called “cold on the lip.” The appearance of herpetic rashes is usually preceded by a common runny nose, that is, ARVI. The disease weakens the immune system, which is what the herpes virus takes advantage of.
Symptoms of herpes simplex
When infected with herpes simplex virus type 1, the incubation period ranges from 1 to 8 days. Typical symptoms: chills, fever up to 39-40°C, headache, general weakness and drowsiness. Then redness appears, in place of which characteristic bubbles form. When the oral mucosa is affected, blisters are usually found on the inside of the lips, tongue, and less often on the palate, palatine arches and tonsils. Bubbles appear at the site where the virus enters the mucous membrane. Subsequently, the bubbles burst, leaving behind painful erosions.
The disappearance of symptoms does not mean complete recovery. The virus remains in the body and after some time (in conditions of decreased immunity) a relapse of the disease is possible. Relapses can occur 1-3 times a year for several years and even decades.
Symptoms of genital herpes
The incubation period of genital herpes lasts from 1 to 10 days, after which itching (burning) may be observed in the areas of future rashes. After which swelling appears, and then groups of bubbles appear on the mucous membranes of the genital organs. The inguinal lymph nodes are enlarged. The blisters burst and erosions and ulcers form in their place. The process can last from two to five weeks.
Relapse of the disease is possible within two weeks after the initial lesion. Relapses occur in at least half of those who have recovered from the disease.
What is the best way to treat herpes: effective ointments and tablets for herpes infection
The most well-known antiherpetic drug is acyclovir. Its effectiveness for the treatment of types 1, 2, 3 and 4 of herpes has been proven in clinical studies. Acyclovir is recommended by the World Health Organization to combat HSV.
Acyclovir stops the reproduction of the pathogen and inhibits its activity. It is mainly used in the form of a cream, which is applied several times a day to the affected area of the skin. This drug also exists in tablet form. The rules of admission in each individual case should be discussed with the attending physician.
The drug Penciclovir is considered no less effective. It is also recommended by WHO, as this medication has successfully passed numerous clinical trials. It suppresses the activity of herpes virus types 1 and 2, and is also effective against its strains. Penciclovir can be used in patients who are resistant to acyclovir.
However, Valaciclovir is considered the most effective drug against herpes infection. It is more effective than the previous two medications. In the human body, under the influence of enzymes, valacyclovir is converted into acyclovir.
In almost all antiherpetic drugs, the main active ingredient is acyclovir, penciclovir or valacyclovir.
Drugs for the treatment of oral herpes
There are a wide variety of antiviral medications to treat the symptoms of this disease, which are available in dosage forms for topical use. They begin to act faster than drugs in tablet forms and act directly on the site of infection.
The best creams and ointments for type 1 herpes:
- Pen-Gerpevir;
- Atsik;
- Lipster;
- Gerpevir;
- Zovirax;
- Acyclostad;
- Agerp.
Acyclovir, penciclovir and valacyclovir are also included in medications that must be taken orally, that is, through the mouth.
They are included in the following herpes tablets:
- Gropivirine;
- Valavir;
- Acyclovir-Darnitsa;
- Atsik;
- Lipster.
Drugs for the treatment of genital herpes
Some of the medications listed above are suitable to combat it, but medical experts advise using drugs that contain valacyclovir. This is due to the fact that HSV type 2 has a greater number of negative symptoms and can cause complications, and valacyclovir is stronger than penciclovir and acyclovir.
Effective drugs to combat HSV type 2:
- Proteflazid drops, Proteflazid suppositories;
- Valavir tablets;
- Roller tablets;
- Lipster tablets;
- Valaciclovir-Hetero tablets.
In addition, to treat the viral infection in question, the following auxiliary agents are used:
1. Immunomodulators . They help strengthen the immune system and enhance protective responses against viruses.
Examples of these tools:
- Cycloferon;
- Anaferon.
2. Antiseptics . They are used to prevent re-infections. Antiseptics are used to treat infection sites.
The most famous medicines:
- Chlorhexedine;
- Miramistin.
3. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) . Herpes infection is accompanied by inflammatory processes that help suppress NSAIDs.
Examples of these drugs:
- Ibuprofen;
- Nimesil.
4. Analgesics-antipyretics . With genital herpes, fever may occur. It can be brought down with the help of the most famous analgesic-antipyretic paracetamol.
5. Antihistamines . During HSV, a person experiences itching sensations at the sites of infection. Ulcers and blisters are very itchy, but they should never be scratched, otherwise scars will remain in their place. Antihistamines are used to reduce itching.
Popular products of this group.
- Erius;
- Claritin;
- Eden.
The doctor must decide which remedy to choose for the treatment of herpes simplex virus and which auxiliary medications to take in each individual case. And to prevent the occurrence of the disease or its relapse, you can carry out simple prevention.
Methods for diagnosing herpes
Diagnosis of herpes is carried out, first of all, on the basis of examination of the patient, since herpetic rashes have a certain specificity. However, your doctor may order laboratory tests. Laboratory tests can detect infection even in the absence of obvious manifestations.
Herpes test
Be prepared that if you suspect a herpes infection, the doctor will write a referral for a blood test, which will determine the presence of antibodies to the herpes virus in the blood. Based on the results of the analysis, it will be possible to judge not only the presence of the pathogen, but also its activity.
More information about the diagnostic method
Sign up for diagnostics To accurately diagnose the disease, make an appointment with specialists from the Family Doctor network.
Treatment methods for herpes
Treatment of herpes is aimed at suppressing viral activity, as well as increasing immunity. Oral and topical medications may be prescribed.
The selection of drugs is carried out by a doctor depending on the type of disease (type of infection), as well as on the location of the lesion.
It is impossible to completely eliminate the herpes virus from the body. That is why it is important to always maintain the body’s defenses at a sufficiently high level, and also to prevent re-entry of the virus.
Prevention of herpes
If a person close to you has manifestations of herpes (“a cold has popped up on the lip”), try to ensure compliance with the following hygiene rules:
- use an individual towel and personal hygiene products (soap, toothbrush, etc.);
- be careful with cosmetics: do not use lipstick of a sick person;
- If you have genital herpes, avoid sexual intercourse.
Make an appointment Do not self-medicate. Contact our specialists who will correctly diagnose and prescribe treatment.
Rate how useful the material was
thank you for rating
Symptoms and signs of herpes virus
Herpes on the eyelids is characterized by increased secretion of tear fluid, redness, unpleasant discomfort and the sensation of a foreign body. With inflammation of the retina, patients complain of fogginess, convulsive twitching of the eyelids, double vision, and distortion of surrounding objects.
Depending on the form of eye herpes, the symptoms of photos that can be seen on the Internet may be different.
| Types of herpetic disease | Main features |
| Dermatitis |
|
| Conjunctivitis |
|
| Keratoiridocyclitis |
|
| Keratitis (stromal) |
|
| Ulcerative lesion of the cornea |
|
| Retinal necrosis (acute) |
|
| Keratitis |
|
| Postherpetic keratitis (trophic) |
|
Some diseases in their external signs resemble herpes eye symptoms, so they are somewhat similar. Only an ophthalmologist can diagnose pathology based on a comprehensive examination using a slit lamp and a fluorescent microscope.