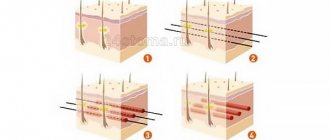
In the modern world, it is quite easy to become infected with such an unpleasant and dangerous disease as skin fungus. We all visit public places: saunas, swimming pools, shopping centers, gyms, etc., sometimes without thinking about the danger they can pose to humans. All fungal diseases can be combined under one term – mycoses. Mycoses are diseases of humans and animals caused by parasitic fungi that infect the skin and internal organs, and also parasitize food.
New mushrooms appear from the mycelium (mycelium), which consists of intertwined mycelial threads (hyphae) formed by the pathogen when it enters the layers of the skin. If mycelium is found on the skin, this is a reason to immediately begin treatment.
What is Mycelium
What is fungal mycelium is spores, that is, the very seed of the disease. Microspores can appear both on any external area and on internal organs. The question arises, what is it when you see changes in the cover in the form of thin threads - this is the mycelium of mushrooms.
Once the pathogenic grain enters the body, it begins to gradually stretch out, forming a hollow tube. Then its walls become thinner and scattered over a large area, the mycelium first transforms into a hypha. A simple and clear example of hyphae is mold. And after this, mushrooms begin to appear in rich scattering.
Depth of the mycelium of forest mushrooms
It’s not always possible to go out into the forest to pick mushrooms, but you can plant them on your site. If you like to do everything yourself, then you will like the idea of growing wild mushrooms: this way you will always know where to look for them.
Methods for growing wild mushrooms on the site
1. Transplanting mushrooms from the forest To plant using this method, you should dig up the mycelium and transfer it to your site. You need to move the mycelium very carefully, without shaking the soil from the excavated layer. Before replanting, prepare the soil under the tree. At a distance of about 0.5 m from the trunk, remove the top ball of soil 30-40 cm thick. Place compost of leaves and wood dust on the bottom, water and sprinkle with soil. Place the dug mycelium on the prepared place, water it and cover it with a layer of fallen leaves. For the first two weeks, if there is no rain, water the planting site daily using the drip method.
To plant wild mushrooms, choose a shaded, moist place. It is better to replant the mycelium under the same tree as the mother one: if you took the mycelium under a birch, it means it is better to replant it under a birch. Be careful when choosing mushrooms for transplanting - do not bring poisonous ones to your site.
2. Reproduction by mycelium The mycelium of forest mushrooms is sold in garden centers. Manufacturers offer detailed planting instructions on the packaging. Planting mycelium requires site preparation.
Choose a place in the shade of a tree, at a distance of 50-60cm from the trunk. Remove the top ball of soil by 50cm. The area of the sowing area depends on the amount of mycelium in the package and is indicated by the manufacturer. Place 20 cm of forest substrate at the bottom: fallen leaves, pine needles, dust and sawdust. Cover evenly with a layer of soil 10 cm thick. For the next layer, mix the soil with the substrate and add 10 cm. Next, mix the mycelium with soil and a growth enhancer (can be purchased at a garden center or specialized stores). Distribute the mixture, lightly tamping with your hands. The last layer is soil. Immediately after planting, carefully water the seeded area and cover with fallen leaves.
In order not to prepare such a complex substrate for mycelium, you can purchase a ready-made substrate for mushrooms - it can be purchased at garden centers and stores specializing in seeds and fertilizers.
For the first two weeks, strictly follow the watering schedule. In the future, make sure that the soil at the sowing site does not dry out. Mushrooms planted this way will grow the next year, and the mycelium will bear full fruit two years after planting. The mycelium will bear fruit in the period from 2 to 5 years from the first harvest.
Gently loosen the soil above the planted mycelium regularly.
3. Mushroom seedlings The easiest way to grow wild mushrooms on your site. Chop the caps and pieces of wild mushrooms or grind them in a meat grinder, and soak them in water for a day. Around the tree near which you plan to grow mushrooms, dig up the soil and add forest substrate to it. Water the prepared area with infused water and pieces of mushrooms and cover with fallen leaves.
Experts disagree on when the first mushrooms planted in this way will appear. Some claim that they will be in the first year of planting, others - after a year.
The listed methods differ in level of complexity, but all of them are most effective for growing wild mushrooms. You can try planting porcini mushrooms, chanterelles and saffron milk caps using these methods.
Useful tips Whatever method you choose to plant wild mushrooms, you should follow a few tips:
• choose a place for planting in dense shade • make sure that the soil is moist, add drip irrigation if necessary • add a growth activator to the soil in spring • plant mushrooms no more than half a meter from the tree • plant in the cool part of the day the best time to plant mushrooms – period from May to September
Remember that wild mushrooms do not take root very well near fruit trees. It’s good if there are several forest trees, deciduous or coniferous, on your site. If there are no such plants on your site, experiment with planting them near wooden buildings on the shaded side.
You can transplant several young trees with mycelium in the roots to the site. This method is very labor-intensive and complex. It is not suitable for owners of small plots.
Advice on how to grow wild mushrooms on your property is quite controversial. The fact is that the result depends on many factors: time, weather, watering, soil, mycelium, etc., but it is worth it. Mushrooms grown on the site are almost undamaged by insects and taste no different from their forest brothers. You will also be 100% confident in their environmental friendliness, unlike mushrooms purchased on the market and collected from nowhere.
Types of Mycelium
The species of the pathology is determined by a fragment taken from the carbohydrate material that makes up the growth.
The following groups are distinguished:
- Ascomycetes are varieties of:
- yeast-like
- moldy,
- dermatophytes.
- Zygomycetes.
- Basidiomycetes.
- Deutremycetes.
These are four groups out of eight, but they are the ones that pose the greatest threat to health.
And it doesn’t matter where any classification of fungi in the form of mycelium appears, the occurrence of pathology cannot be traced on the internal organs, but the changes seen on the nails are a signal of distress.
Interpretation of smears and test norms
To take a smear from men, a special probe is used, which is inserted into the urethra to a depth of 30-50 mm. Then make light rotational movements with the probe and remove it. The material for research is placed on glass. After receiving the results, the doctor interprets them.
If we talk about Candida in a smear, the norm for this indicator is as follows:
- normally, Candida albicans fungi should not exceed 10³ CFU;
- if the number of colony-forming units is 10³, then they speak of a slight excess in the number of fungi;
- if Candida fungi are detected, the norm in the smear is exceeded by up to 10⁴, then this indicates a moderate excess of the normal value;
- a value of 10⁵ or more indicates a large number of mushrooms.
The test results also describe the category of sensitivity of fungi to antimycotic agents. These indicators are deciphered as follows:
- H – means the sensitivity of the fungus to the drug;
- DZ - this abbreviation stands for dose-dependent sensitivity;
- R(U) – resistance or resistance of fungi to an antifungal agent.
Important! Different laboratories may have different reference values and a set of indicators in analyses.
Detection of Candida fungi in a smear in single values is a variant of the norm. The diagnosis of urogenital candidiasis is made only when indicators are in the range of 10⁴-10⁵ CFU per milliliter or higher.
Mycelium threads on nails, what are they?
Mycelial threads on the nails are a sign that the immune system is weakened and the functional system was unable to repel the attack of pathogens. Because a phenomenon such as mycelium has free access to its target, in most cases, the internal rapid response team does not work properly.
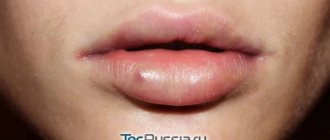
Read also: Fungus on the face: photos of symptoms, characteristic features, treatment methods
And so that the nail layer is not destroyed, the nail plate should be saved immediately.
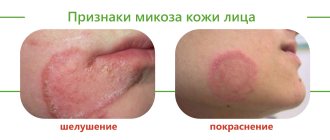
Diagnosis of mycosis
The diagnosis is made based on:
- Clinical manifestations;
- Microscopy of skin scales;
- Glow from a Voodoo fluorescent lamp;
- Inoculating the pathogen on a nutrient medium to determine the type of fungal infection;
- DNA diagnostics.
In the diagnosis of systemic fungal infections the following are used:
- X-ray of the chest organs;
- CT scan;
- Ultrasound;
- Serological research method.
Mechanism of transmission of nail fungus
Infection with pathogenic fungal spores can occur through any contact with an infected object. The mycelia of the fungus, getting on the nails, begin to conduct active occupying activities, trying to settle in a new place as soon as possible.
Infection can occur even with a normal handshake if basic hygiene is not observed. Although the danger of disease also arises when a person works for a long period in a humid environment. To minimize the risk of acquiring long and difficult treatment, it is necessary to follow sanitary recommendations.
How does infection occur?
All mycoses, according to the source of infection, can be divided into two groups:
- Contagious. Infection occurs through contact with spores of fungi living in the external environment.
- Opportunistic. Under normal conditions, pathogens are harmless to humans; the disease develops due to immunodeficiency, an imbalance of microflora.
Contagious fungi are divided into three categories:
- Anthroponoses. The source of infection is humans.
- Zoonoses. The carriers of fungi are representatives of the animal world.
- Geophilic mycoses. The natural habitat of pathogens is soil, organic residues. When spores enter human tissue, they are able to live in them.
Penetration of fungal pathogens into the body occurs through aerogenic, contact and nutritional (through the digestive tract) mechanisms. Aerogenic routes of infection are represented by airborne droplets and airborne dust. Nutritional – water, food, fecal-oral.
- Cyst on the cervix - what is it, why is it dangerous. Treatment of cysts on the cervix
- Treatment of high cholesterol - lowering drugs. How to treat high cholesterol using traditional methods
- Tongue salad: delicious recipes
Fungi that infect humans especially often include pathogens of dermatomycosis and mycoses of the mucous membranes. The latter include:
- Candida albicans is the causative agent of local and generalized forms of candidiasis (thrush), a typical opportunistic disease. The mycelial structure is characterized by the absence of partitions in the filaments.
- Cryptococcus neoformans is a saprophyte that lives in the soil and bird feces. The route of infection is aerogenic. The disease is typical for HIV carriers
Dermatomycosis fungi:
- Genus Microsporum: M.canis is a zoonotic species that causes microsporia of smooth skin, scalp and face.
- M. gypseum is a geophilic fungus that causes microsporia on smooth skin and scalp.
- M. audouinii is the causative agent of anthroponotic microsporia of the body and scalp.
- M. ferrugineum is an anthropophile and causes microsporia of the scalp.
- Tr. rubrum is the causative agent of rubromycosis, most often affecting the nails and spaces between the fingers.
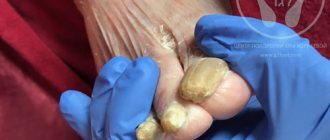
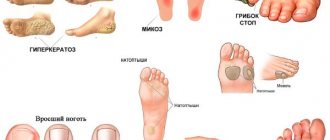
The main signs of mycelium on nails
The most common signs of the appearance of mycelium threads on nails are as follows:
- characteristic longitudinal change in the structure of the nail plate,
- plate fragility increases,
- the color changes dramatically, turning to shades of brown and yellow; in advanced cases, it becomes black,
- stripes and spots stretching to the level of the cuticle,
- unpleasant smell,
- burning and severe itching.
Such changes indicate that the fungus has settled on the body.
The degree of purity of the vaginal microflora
Based on the results of the smear, the degree of vaginal cleanliness is assessed:
- Leukocytes are normal . The main content is lactobacilli. Moderate amount of epithelium, moderate mucus. These indicators indicate the normal state of the microflora and good immunity.
- Along with lactobacilli, yeast and coccal flora . Leukocytes are normal. Epithelium, mucus – moderate. This state of the microflora is close to normal, but indicates reduced immunity and the possibility of the onset of an inflammatory process.
- Increased white blood cell count . The number of pathogenic bacteria (cocci, yeast fungi) predominates, lactobacilli are in minimal quantities. This state of the microflora indicates an inflammatory process.
- Exceeding the norm of leukocytes , pathogenic bacteria. There are no lactobacilli. Lots of mucus and epithelium. This result indicates severe inflammation and the need for immediate treatment.
Treatment of fungal diseases
In most cases, there is a practice of using complex therapy, which includes combined treatment of the fungus. This effect ranges from the use of special drugs to surgical removal of the affected area of the plate. The use of special-purpose patches, such as salicylic and trichloroacetic patches, is also encouraged.
If it is not possible to neutralize the pathology with medication, then after surgical removal of the nail, postoperative care is prescribed, which consists of using products that quickly help the wound heal and create a clean place for the appearance of a healthy nail.
Read also: What does foot fungus look like and how to treat it?
Rules for female intimate hygiene
Treatment of candidiasis involves observing special rules of intimate hygiene:
- Before inserting suppositories, the vagina is freed from cheesy masses by douching, and then by high-quality washing. Before the procedure, wash your hands thoroughly using antiseptic solutions.
- Washing is carried out using an intimate gel, foam with an acidity level of pH 4-5. Regular soap dries out the vaginal mucosa and causes irritation, so it should not be used.
- Antibacterial drugs are not used for vaginal hygiene, since they aggravate local dysbiosis and prevent the colonization of tissues with beneficial microflora.
- Douching is carried out with a weak solution of soda, no more than twice a day. Abuse of douching will lead to aggravation of the fungal disease.
- You should not take baths, which wash out beneficial microorganisms from the vagina and spread the fungus to neighboring organs. A shower is enough.
- Intimate hygiene for a woman involves the use of individual products and towels. After the procedures, the plumbing equipment is washed with antiseptic solutions to prevent secondary infection.
- It is recommended to change underwear at least 2 times a day or after each hygiene procedure. Linen is disinfected by ironing.
- The pads are changed every 2 hours. Tampons are contraindicated for candidiasis.
- It is recommended to iron bed linen daily or change it.
Treatment of candidiasis requires careful adherence to the doctor’s recommendations and intimate hygiene rules. Only a set of procedures will rid the body of pathogens and restore the beneficial microflora of the vagina.
Traditional methods
If the disease has only touched the mycelium with pathogenic tentacles, then the methods that have helped our ancestors for centuries can work effectively. What helps with this successfully:
- celandine,
- iodine,
- garlic,
- hydrogen peroxide,
- tea tree oil.
All procedures are carried out on the outer skin, without taking plant components internally.