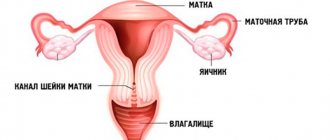
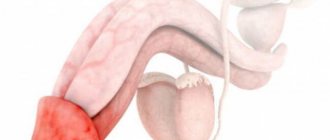
The most common diseases in gynecology are fungal infections of the genital organs in women.
As a result of a weakened immune system, the fungus begins to multiply uncontrollably, infecting the mucous membranes of the gastrointestinal tract and female genital organs. In gynecology, yeast fungus causes a disease called urogenital candidiasis or thrush. In addition, the fungus can cause vaginitis and vulvovaginitis, when in addition to the vagina, the colony affects the mucous membranes of the vulva, causing severe burning and itching.
How does genital fungus manifest?
If a woman notices the appearance of abundant cheesy white discharge on her underwear, she should immediately seek help from a gynecologist. Perhaps it is a fungus on the genitals.
By affecting the external genitalia, vaginal fungal infections can penetrate into the internal organs of the genitourinary system, thereby leading to serious complications - diseases of the genitourinary system and infertility.
Fungal diseases in women extend to:
- uterus;
- ovaries;
- fallopian tubes.
Thus, they provoke more and more new foci of infection.
Fungal genital infections cause such diseases of internal organs in women as:
- colpitis;
- endometritis;
- bartholinitis and others.
In addition, fungus in gynecology is one of the main reasons for the development of cervical erosion, and this in turn leads to infertility, i.e. inability to have children.
Prevention
Excess weight is one of the provoking factors for the development of fungus in the groin
Inguinal fungus in women develops due to a decrease in local immunity. This is associated with excessive sweating, endocrine disorders and excess weight. Careful attention to your own health and timely treatment of any diseases will help prevent the development of the disease.
It is important to avoid constantly wearing synthetic underwear, in which the skin does not breathe. In hot weather, you should give preference to products made from natural fabrics with a loose fit. You should also wipe the groin folds with an antiseptic or alcohol-containing wipes several times a day to prevent sweat from accumulating.
Types of fungal diseases
Gynecological fungal diseases are most often caused by fungi of the genus Candida, which has about 170 species. For example, Candida Parapsilosis, Candida Glabrata, Candida Albicans and Candida Tropicalis. More than 75% of women of childbearing age experience a vaginal infection caused by fungi at least once in their lives. Basically, these are thrush (candidiasis) and candidal vaginitis, most often caused by the fungus Candida Albicans.
Fungi of the genus Candida belong to the normal microflora of the vagina. However, under the influence of various factors, favorable conditions for fungal parasitism are created in the female body. World statistics show that candidiasis is diagnosed in 24-36% of cases of visits to a gynecologist.
Diagnostics
Tests and diagnostics will reveal the presence of a fungal pathogen
Having figured out what fungus looks like in the groin in women, you should consult a doctor at the first suspicion of fungal flora on the skin. Despite the specific symptoms, it is necessary to undergo an examination and tests to accurately determine the pathogen. To do this, a skin scraping is taken and examined under a microscope.
Differential diagnosis is required to exclude other dermatological diseases. This is due to the fact that groin fungus visually resembles dermatitis and some types of eczema.
What causes thrush?
Thrush or fungus in women can occur for various reasons. Doctors call alkalization of the vagina one of the common reasons for the development of candidiasis - a change from the normal (acidic) environment of the vagina to an alkaline one due to hormonal disorders, infectious and gynecological diseases. The alkaline environment in the vagina becomes an impetus for the proliferation of fungi due to the death of microorganisms that make up the natural microflora of the vagina. The disease can be caused by taking corticosteroids or antibacterial drugs. Thrush can also develop:
- against the background of decreased immunity;
- due to wearing underwear made of synthetic materials;
- due to unprotected sexual intercourse, use of intrauterine contraceptives.
Causes and symptoms
Damage to the epidermis in the groin area (tinea groin) is caused by pathogenic fungi that, for various reasons, get on the skin.
Under favorable conditions (skin folds, moist, warm environment, etc.), they begin active growth and reproduction, capturing an increasingly larger area. The following factors can provoke the development of pathology:
- Frequent visits to the swimming pool, sauna, bathhouse;
- using other people's personal hygiene items when exercising in gyms, sports complexes, etc.;
- living in hot and humid climate zones;
- irregular change of underwear and insufficient hygiene of the genitals.
The risk group includes the following categories of people:
- People suffering from mycosis of the feet;
- patients with obesity, diabetes mellitus, and those with metabolic disorders;
- persons who have been in stressful situations for a long time;
- people with cardiovascular and endocrine pathologies;
- persons who are forced to sit for a long time due to their profession (train drivers, vehicle drivers, crane operators, office employees, etc.);
- patients with excessive sweating.
According to statistics, inguinal fungus affects men more often than women.
Symptoms of the disease
Inguinal athlete's foot has quite characteristic symptoms. The area of the affected area is determined by the stage of the disease: its size can vary from 1 cm to the area of the palm.
A fungal infection may have the following external signs:
- At the initial stage, flaky pink rashes with clear boundaries are noted in the inguinal folds. Basically, the affected areas look like oval single spots of irregular shape.
- In severe cases, the affected areas acquire a dark, reddish-brown hue and are covered with pustules or papules. Often pigmented rashes merge into one red itchy spot.
The initial stage of the disease is characterized by the appearance of itching in the groin and genital area, which intensifies over time.
Gradually, the itching spreads to the skin located near the anus. At the same time, the penis remains free from rashes. Then the skin in the groin area becomes covered with a red rash, which marks the boundaries of the affected area.
If such symptoms are ignored, the rash takes the form of small blisters with watery contents. The skin wrinkles, peeling appears, the epidermis begins to dry out and crack.
After some time, a clear delineation of the boundaries of the affected and healthy zones is observed.
Incorrect or untimely treatment can lead to further spread of the fungus, primarily to the anal area and buttocks.
The waste products of the fungus cause intoxication of the body, deterioration of well-being, and decreased immunity. The patient experiences irritability and nervousness.
Diagnosis of fungus
To establish an accurate diagnosis, you need to contact a dermatologist who will carry out the following measures:
- Examination of the patient, during which a scraping of the epidermis is taken from the affected area;
- Examination of the contents under a microscope to detect mycelium threads.
- If suspicions are confirmed, the doctor prescribes appropriate treatment.
Vaginal smear - what infections does it show?
A vaginal smear allows you to identify pathogenic microflora in the vagina (bacteria, fungi). This is the simplest and most effective laboratory method for diagnosing the inflammatory process in the female genital organs. Based on the results of the analysis, the gynecologist makes a diagnosis (vaginal candidiasis, vaginitis or other gynecological disease).
A vaginal smear shows:
- number of leukocytes, lactobacilli, squamous epithelial cells;
- Is the ratio of “beneficial”, pathogenic and opportunistic microorganisms, the number of which must be balanced, disturbed?
Epidermophyton floccosum - the causative agent of athlete's foot
The fungi Epidermophyton flocosum are anthropophylls. They cause disease only in humans. Most often, the superficial layer of smooth skin is affected: most often the inguinal folds, less often the intergluteal folds, folds in the lower abdomen and under the mammary glands.
Microscopy of skin scales taken from the affected areas reveals short (2 - 4 µm) branching intertwined mycelium and rectangular arthrospores arranged in chains.
When growing on Sabouraud's nutrient medium, the colonies are round in shape, initially flat or dome-shaped, later folded-lumpy with depressions in the center. The surface is velvety-mealy or leathery with radial folds. Initially grayish-brown, lemon-olive or yellowish-green, later white.
Under microscopy, in mature cultures one can see septate mycelium with blunt-pointed macroconidia, which are arranged in the form of clubs or banana bunches in bunches of 3-5 pieces, growing directly from hyphae. Chlamydospores appear in old crops. Microconidia are absent.
Rice. 4 and 5. View of colonies of the fungus Epidermophyton flocosum at different stages of growth.
Rice. 6 and 7. Microscopy of mature fungal cultures.
How to get rid of fungi in the body using folk remedies?
Fungal diseases of the female organs should be treated only as prescribed by a gynecologist. Self-medication can lead to the development of a chronic form of candidiasis, the appearance of concomitant diseases (cervical erosion, diseases of internal organs due to fungal infection of the kidneys, intestines or bladder).
If untimely or improperly treated, fungal infections can enter the bloodstream. This is called candidemia. According to the US Centers for Disease Prevention and Control, candidemia is one of the most common fungal infections in the United States. In addition, yeast infections can lead to other health problems, such as dermatological diseases, as the area around the vagina becomes inflamed due to yeast infections. Prolonged inflammation threatens skin infections and increases the chance of infection spreading to other parts of the body.
At-risk groups
Since there are patterns of fungal infection, doctors have identified risk groups of people most often susceptible to this disease. Find out if you are at risk by answering these questions:
- Do you shower less than once a day?
- Do you go to a gym?
- Do you visit public baths, saunas, swimming pools, water parks?
- Do you often spend the night in hotels, rented apartments, hotels?
- Does it happen that you use someone else’s hygiene products (washcloth, towel, etc.)?
- Do you wear synthetic underwear, tight jeans, or uncomfortable clothes?
- Does your job involve long periods of driving?
- Do you have spontaneous sex?
- Do you do physical labor and sweat a lot?
- Do you often fail to change your underwear on time (once a day)?
If you answered yes to at least 3 of these questions, you have the opportunity to become infected with groin fungus. Therefore, you must definitely carry out prevention of this disease, which consists not only of observing hygiene rules, but also of using traditional medicine.
How to treat fungal infections?
Treatment of fungal diseases of the genital organs is based on the use of antifungal drugs, which can be prescribed externally (vaginal ointments) or internally (tablets). The gynecologist selects treatment depending on the type of fungal infection, the patient’s medical history and the course of the disease.
During the treatment period, we recommend that women abstain from sexual activity. If you have sexual intercourse during treatment, use contraception so as not to aggravate the inflammatory process in the vagina. However, in this case, it must be taken into account that vaginal creams and suppositories for the treatment of fungal infections can weaken the properties of latex condoms. This may cause it to slip or break.
Therapy methods
Treatment should not be postponed to the future; the disease will develop into a chronic stage, and it is much more difficult to get rid of it. You will have to treat the disease yourself after consulting a doctor and prescribing special medications. Most often these are local medications, sometimes in advanced cases tablets are prescribed. There are no major differences in treatment methods between men and women.
You should undergo tests so that the doctor makes the correct diagnosis:
- General analysis of urine and blood.
- Checking your sugar level.
- Biochemistry.
- Scraping areas of skin affected by the disease.
After the tests, the doctor will specify the diagnosis and prescribe treatment.
The list of possible medications looks like this:
- Ointment.
- Cream.
- Pills.
- Anti-inflammatory drugs.
Ointments
They are a common way to treat fungus. Before applying, wash your hands and apply the ointment to the affected area of the skin and a healthy area nearby. You should also change sheets and pillowcases, as well as underwear, in a timely manner. If the infection has spread to additional areas of your body, then treatment of these areas must be carried out simultaneously.
A course of ointments is prescribed for half a month, it all depends on the condition of the body. If there are no noticeable improvements, be sure to consult with a specialist again to prescribe new medications. Usually Burov's liquid is additionally prescribed in the form of compresses. One ointment is enough for the treatment to be successful.
An approximate list of drugs against fungus:
- Ketoconazole.
- Clotrimazole.
- Lamisil.
- Mycozoral.
- Nystatin.
- Nitrofungin.