General information
Every day a person is faced with many factors that can negatively affect his health.
Not everyone realizes that simple actions, such as visiting a sauna or getting a manicure in a salon, can lead to a fungal infection, which can subsequently cause numerous problems. Fungus on the hands - this is how this disease is usually called in everyday life - or mycosis very often develops precisely because of a banal failure to comply with the rules of personal hygiene and a person’s inattention. It is important to understand that fungus on the hands, as in other places on the body, spreads very quickly. Therefore, if alarming symptoms appear in both adults and children, you should definitely consult a doctor and follow the treatment regimen that he prescribes. How exactly to treat mycosis on the hands and how to recognize this disease will be discussed in this article.
Clinical manifestations
The picture of clinical manifestations depends on the strain of the fungus, as well as on its location. The fungus most often occupies 3 locations on the hands:
- Interdigital space.
- Nails.
- Palms and wrists.
The initial stage of fungus on the hands
The interdigital space is a popular location for the fungus. The reason for this is thinner and more delicate skin, as well as its susceptibility to sweating. When washing your hands, these areas are not always completely cleaned. The fungus usually begins with itching, which intensifies. Then scratching and severe redness appear. At this stage, painful manifestations are added to the itching. The skin becomes dry, crusts and scabs appear, and pustular inflammation may occur. Skin flakes peel off, becoming a source of infection for many people.
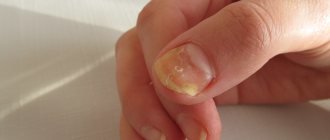
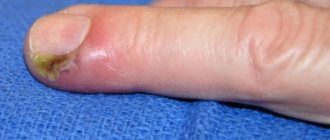
On nails, fungus manifests itself somewhat differently. As a rule, infection begins with the thumb or little finger, and then begins to spread to neighboring fingers. The nail changes color, becomes transparent, then turns yellow. A brown or black nail indicates advanced disease. The nail fold begins to swell and hangs over the nail. The nail may become mobile and not hold firmly in the nail bed. The nail thickens and becomes covered with growths. When infected with certain types of parasites, the nail, on the contrary, becomes thinner, splits, and breaks. Furrows and depressions appear, and the structure of the nail itself changes.
Pathogenesis
Photo of fungus on hands
Fungal infections of the hands can be caused by pathogenic fungi: Trichophyton mentagrophytes, Trichophyton rubrum, var. Interdigitale, less often - Epidermophyton floccosum, Candida.
A person can become infected with the fungus if he comes into direct contact with someone who is sick. Infection can also occur through contact with household items, shoes, clothes of the patient, when visiting public places - gyms, baths, etc.
The pathogenic organism penetrates the skin through damage - cracks between the fingers, abrasions. Often cracks between people's fingers occur due to heavy sweating, abrasions, poor drying of hands after washing, etc.
Since the breeding ground for fungi is keratin , they primarily affect areas with a large amount of this protein - skin, nails, hair. In the presence of concomitant diseases, deterioration in the function of the immune system, or the use of certain drugs (antibacterial, cytostatic, corticosteroid), mycosis can become widespread. Endocrine disorders and impaired microcirculation in the area of the distal parts of the upper extremities also play an important role in the development of the disease. This is typical for Raynaud's syndrome and atherosclerosis . The fungus can affect not only external areas, but also internal organs.
Ways of infection by fungus
A collision with fungal pathogens is almost inevitable for every person, but not everyone gets sick.
The main reason for the development of onychomycosis is a decrease in the body’s natural defenses - at some point the immune system simply stops coping with the infections that attack it, and pest microorganisms begin to multiply, forming colonies (see photo of nail fungus).
There are many factors that provoke the rapid development of the disease:
- Neglect of personal hygiene;
- Wearing uncomfortable and too tight shoes that prevent normal breathing of the skin of the feet;
- Foot injuries, including minor scratches, calluses;
- Vascular diseases and diabetes;
- Increased sweating of the feet.
Love of saunas, public baths and swimming pools also plays a role, increasing the risk of infection significantly, especially since a humid, warm atmosphere promotes the proliferation of pathogenic microflora.
Also dangerous are hotels, gyms, and beauty salons whose staff are careless about disinfection.
A problem can arise from trying on shoes in a store, walking barefoot on the beach, or coming into contact with the belongings of a person with fungus.
Classification
Fungal pathogenic organisms are divided into several groups:
- Anthropophilic - they only affect people.
- Zoophilic - affects exclusively animals.
- Zooanthropphilic - affects all representatives of the fauna.
In medicine, fungal diseases are divided into five groups:
- Keratomycosis (trichosporia nodosum, lichen versicolor ).
- Dermatomycosis (athlete's foot, athlete's foot, rubromycosis, trichophytosis , microsporia).
- Candidiasis (superficial candidiasis, chronic generalized candidiasis, visceral candidiasis)
- Deep mycoses (blastomycosis, histoplasmosis, sporotrichosis, coccidioidosis, etc.).
- Pseudomycosis (superficial and deep pseudomycosis).
Causes
A fungus on the skin of the hands may appear if infection occurs from an infected person. Most often, fungus on the skin of the hands develops some time after a person has visited a public sauna, swimming pool, gym, or nail salon. In fact, fungal infections of the hands are very common, because throughout the day a person goes to different places and touches a variety of objects.
Photo of skin fungus on hands
Factors contributing to fungal infection and its spread are:
- The presence of injuries on the hands - microcracks, abrasions.
- A number of diseases - diabetes mellitus , endocrine disorders, inflammatory diseases, etc.
Hand skin candidiasis
Yeast-like fungi of the genus Candida most often affect the palms of women, and dermatophyte fungi in men. The disease affects people whose hands are exposed to a humid environment for a long time - housewives, people working in food factories, confectionery shops, when working with vegetables and fruits, etc. The disease in men is more often occupational.
Rice. 18. Candida albicans fungi under a microscope. Round pathogen cells and filaments of pseudomycelium are visible.
Damage to interdigital folds
The disease begins with the appearance of very small blisters on the skin of the contacting surfaces (usually 3 and 4 interdigital folds). Hyperemia of the transitional fold and maceration are noted. The rejected epidermis becomes white. A hyperemic, shiny, smooth surface is exposed underneath. The boundaries of the lesion are clear, surrounded at the periphery by a rim of exfoliating epithelium, rarely extending to the back of the hand. Subjectively, the patient experiences itching and burning.
Rice. 19. Damage to interdigital folds due to candidiasis.
Rice. 20. Candidiasis of interdigital folds.
Damage to the skin of the palms
This form of the disease is rare and has several forms of manifestation:
- In some cases, the disease occurs as dry lamellar dyshidrosis (superficial ring-shaped, garland-shaped or lamellar peeling is noted). The disease should be distinguished from dyshidrotic eczema.
- The vesicular-pustular form is characterized by the appearance of vesicles and pustules against the background of hyperemia and edema.
- Hyperkeratotic eczema is characterized by the appearance of wide skin furrows of a dirty brown color in areas of keratinized skin.
Rice. 21. Candidiasis of the palms. Dry lamellar dyshidrosis.
Candidiasis of the periungual fold
Prolonged stay in a humid environment and trauma contribute to the development of candidal inflammation of the periungual ridges. The disease begins with hyperemia and edema. The skin becomes thinner and becomes shiny. The nail skin disappears. When pressed, ichor, a crumbly white mass, or a drop of pus may be released. In some cases, the nail plates are affected. Patients are bothered by pain.
Rice. 22. Candida paronychia - inflammation of the periungual fold.
Rice. 23. Candidiasis of the hands (photo on the left) should be distinguished from eczema (photo on the right).
Rice. 24. Interdigital candidiasis (photo on the left) and skin lesions on the hands due to rubrophytosis (photo on the right).
Symptoms of fungus on hands
Photos of fungus symptoms
When the fungus gets on the skin of the hands, it first of all “populates” closed areas - the space between the fingers. The initial stage of a fungal infection already causes unpleasant symptoms - the patient is forced to scratch the affected areas, as itching occurs.
The more the patient itches, the more irritated the affected skin. The disease most often begins in the summer, when humidity is high and people's hands sweat a lot. After this, small bubbles appear at the affected areas, which then burst, thereby creating favorable conditions for the penetration and spread of fungi. The wounds do not heal for a long time, swelling and erosion . In severe cases, typical symptoms can be aggravated by an increase in temperature to subfebrile levels, which indicates the presence of a sluggish inflammatory process.
If adequate treatment is not provided during this period, the fungus between the fingers will gradually spread to wider areas - affecting the palms, nails, etc. In this case, it will be more difficult to cure mycosis between the fingers and in other places.
Thus, the symptoms of mycosis on the hands may be as follows:
- dry skin;
- change in the color of the affected areas (blueness, redness), while the affected areas have clear boundaries and increase over time;
- the skin becomes thicker as its surface layers thicken;
- peeling characteristic of the fungus appears - the cells begin to exfoliate not like on healthy skin, but in clusters in the form of lumps or plates;
- the appearance of a specific odor (it is more pronounced when the feet are affected);
- itching in the affected areas.
The fungus is chronic if left untreated and worsens in the warm season. In the chronic course of the disease, fungus may also appear on the palms, between the fingers, and on the elbows. Mycosis on the palms of the hands is manifested by dry skin of the palms, peeling, keratosis (thickening of the stratum corneum). You can see signs of fungus in the photo.
The disease can occur both acutely and chronically. Often, after infection with mycosis of the nails, the fungal infection spreads to the fingers, as well as to the interdigital space.
Manifestation of candidiasis (defeat by Candida):
- minor peeling;
- intense itching or burning sensations in areas of the hand, especially the rib;
- dryness and whitish areas on the skin;
- itching and redness in the interdigital areas;
- swelling and inflammation of the cuticle with the formation of discharge;
- formation of cracks and erosion areas on the fingers;
- dulling of the nail plate and loss of its top layer;
- vesicular interdigital formations extending to the palm.
In most cases, the little finger, as well as the middle and ring fingers are affected. The thumb and index finger are less likely to suffer. Candidiasis occurs unevenly. If not treated correctly, symptoms always return.
Symptoms of dermatophyte damage:
- skin peeling with the formation of a large number of scales;
- roughening of the skin;
- cracks on the pads and in the interdigital areas;
- intense itching;
- watery blisters that burst when irritated;
- nail deformations (waviness and depressions, grooves, bulges, breaking);
- yellowness, whitening and dullness of the nails (if fungus on the fingernails is suspected, photos of the symptoms can be found on the Internet);
- fragility of nails (severely peeling or crumbling);
- nail peeling from the bed.
The skin in the flexion areas cracks, the wounds do not heal and cause discomfort. Inflammation is possible, as well as the appearance of pus and swelling due to additional infection.
Sometimes dermatophytosis can be confused with eczema or psoriasis.
Signs of mold mycosis:
- skin peeling and roughening, cracking;
- intense itching;
- bubble formations;
- nail deformities;
- problems with the color of the nails, their clouding (regardless of the type of fungus on the fingernails, the symptoms and treatment are similar).
The symptoms resemble the clinical picture of dermatophyte infections. If you do not immediately diagnose what exactly the patient has, the diseases may be confused. This will lead to incorrect therapy, since the drugs for dermatophytes and mold microorganisms are different.
However, molds are a less common problem. As a rule, they affect people with weakened immune systems (for example, after long-term aggressive treatment with antibiotics) or people with serious pathologies such as HIV, tuberculosis and disorders in the hematopoietic system.
Tests and diagnostics
what fungus looks like on hands photo of the initial stage
If a person shows signs of a fungal infection, he should immediately contact a dermatologist and undergo an examination.
The doctor conducts an examination, assessing the signs of the disease, and also interviews the patient.
The study requires scraping of scales from foci of disease on the skin. Analyzes are carried out using the following methods:
- Microscopic examination - biomaterial is examined under a microscope.
- Sowing - allows you to obtain more accurate information about the causative agent of the disease. This analysis takes longer - from several days to several weeks. To carry it out, the biomaterial is placed in a nutrient medium. If there is a fungus in it, characteristic colonies appear after a certain time.
- Enzyme immunoassay - used for the diagnosis of deep mycoses. It is used to determine the titer of antibodies to a specific fungus. For ELISA, blood is taken from a vein.
- PCR method - with this test you can determine the type of fungus. This is a fast and reliable, but narrowly focused research method. That is, to carry out this analysis you need to know what exactly to look for.
In addition, other studies are carried out during the diagnostic process. Before prescribing systemic antimycotic drugs, a biochemical blood test is performed to determine a number of indicators.
Preparing for treatment
Preparation for treatment is especially important for hand fungus that affects the nail plates. This is due to the fact that the nails themselves are very hard, and in order for the drug to penetrate to the source of the fungus, which is often located in the center of the nail plate or even under it, the dermis should be steamed. Nail growths also interfere with the penetration of ointments and creams, so they should be filed down or removed with scissors.
Hands should be washed thoroughly, for which it is best to use laundry soap. Thanks to its alkaline composition, it itself helps to cope with mycosis on the hands.
Remove all crusts from the surface, which must be disposed of after the procedure - they are a source of infection. Also disinfect manicure accessories - wipe with alcohol. Apply the cream as directed and try not to wash your hands for the next few hours.
It is also worth strengthening your immune system, since its weakening can provoke fungal infection. Take a course of strengthening vitamins or other remedies that your doctor may recommend to you.
Treatment with folk remedies
There are many different traditional medicine recipes used to treat fungal infections of the skin of the hands. But, before using such remedies, you need to take into account that self-medication may be ineffective and subsequently aggravate the problem. Therefore, it is better to rely on the recommendations of specialists and use traditional methods as auxiliary ones.
- Blue clay. Dilute a little blue clay to the consistency of sour cream and apply lotions to the affected areas. Clay should be applied in a 1 cm layer and secured with a cloth bandage on top. Leave for about half an hour, then wipe with heavily diluted lemon juice. Do it several times every day.
- Tea compresses. Brew strong tea and apply compresses to the affected areas of the skin. You can also use tea essential oil for wiping - dilute it and gently wipe the skin.
- Vinegar. Take a glove made of natural fabric, blot it in wine vinegar and put it on, putting on another clean glove on top. An acidic environment is detrimental to fungi, so you can use lemon juice instead of vinegar. You can take baths with wine vinegar or lemon juice several times a day.
- Oak bark. Grind and apply powder to sore areas, fixing them with a glove or cloth. You can also make lotions from a decoction of oak bark. This remedy will prevent the active progression of mycosis, but should not be used as the primary treatment.
- Baths with sea salt. Dilute 2 tbsp. l. salt in 1 liter of water and hold the solution in your hands for 15-20 minutes. Sea salt helps to destroy the protective membrane of fungal cells, as a result of which their vital activity is inhibited. Such baths should be performed 2-3 times a day.
- Coffee grounds. It is recommended to apply both coffee grounds and chilled coffee to areas affected by mycosis. Coffee slows down the proliferation of fungal cells.
- Decoctions of medicinal herbs. Applying decoctions of chamomile, calendula, echinacea, mint, burdock root, etc. to the skin helps to slow down the process. To prepare the decoction, you need to pour boiling water over the herbs and leave in the dark for 1-2 days.
- Ointment with Vaseline. To prepare it, take a decoction of hop cones, honey, onion juice and petroleum jelly in equal proportions, mix everything thoroughly and apply to the affected skin of the hands. The ointment prevents air from entering the fungal cells, which causes their death.
- Tar soap. It is necessary to use it to wash your hands several times a day. You can also mix grated soap with a few drops of Kalanchoe juice and eucalyptus oil and apply this mixture as a mask. Soap should be used for a long time - at least a month.
- Garlic maca. Crush a fresh clove of garlic and mix it with a little butter. Stir and add 3 drops of verbena essential oil. Apply to the skin once every 2 days for half an hour.
- Propolis with alcohol. Mix propolis with alcohol in a ratio of 1:3, apply to the skin and put on gloves. Make the mask at night, and in the morning wash it off with water and lemon juice.
Prevention
Photo of fungus on fingers
To prevent the development of fungal infection and prevent re-infection, you should follow simple rules for preventing the disease. To prevent fungus from appearing on your fingers, you must do the following:
- Do not use the personal belongings of other people, including relatives. Using someone else's stockings, socks, gloves, towels, or handkerchiefs is unacceptable.
- It is important to carefully monitor personal hygiene. You should wash your feet with soap every day, and your hands should be washed every time after returning from public places.
- Fungus on the fingers may appear after visiting saunas, baths, and swimming pools. Therefore, it is better to go only to places where cleaning and disinfection are carried out in a timely manner. But still, people visiting such places increase the likelihood of becoming infected with a fungus. To reduce this risk, do not share mats or other equipment. At home, it is better to take a shower immediately using bactericidal soap.
- It is worth visiting only proven nail salons, where disinfection rules are strictly followed.
- If infection does occur, the fungus should be completely cured by completing the course of treatment.
Preventive measures
Manual mycosis is difficult to cure. It’s easier to insure yourself and minimize the likelihood of defeat.
Here are the conditions that will help prevent the occurrence of the disease. Necessary:
- Avoid damage to nails and skin. When cuts, wounds, cracks and other open injuries form, it is necessary to treat your hands with an antiseptic.
- Be careful when interacting with water. It is recommended to wear gloves when cleaning and washing dishes. The skin should remain dry.
- Use antiseptic in public places. Doors or handrails in caravans may contain fungus. An antiseptic will help immediately destroy harmful microorganisms.
- Immediately begin the fight against foot fungus. It can move to the hands. Both hands and feet should be treated with antimycotic agents. Hands - for preventive purposes.
- Watch your diet. It should contain enough vitamins.
- Remove bad habits. Alcohol and cigarettes weaken all body systems, especially its protective function.
- Take care of your skin. Nourish and moisturize it. Such activities will strengthen the skin structure and improve barrier functions.
- Strengthen immunity. The body's defenses must be in order.
Thus, the optimal strategy for combating hand fungus is complex therapy, which is carried out in accordance with the doctor’s indications.
In children
In children, such a disease is not uncommon due to non-compliance with hygiene rules, active contacts with peers, pets, etc. But since children may develop other skin lesions associated with allergic reactions, infectious diseases, etc., parents should definitely contact see a dermatologist so that the doctor can determine the diagnosis. In no case should you practice self-medication, since you must initially establish an accurate diagnosis. In addition, many antifungal agents cannot be used to treat children. Parents must not only ensure proper treatment of the disease, but also teach their children the basic rules of personal hygiene.
Pathogens
Fungus on the palms and fingers is caused by two pathogens:
- Dermatophytes . The disease is common among the male population. Initially, lesions appear between the fingers, after which the infection spreads further. Most often it is Trichophyton mentcigrophytes or Trichophyton rubrum.
- Yeast-like fungi . The female half often suffers from such a pathogen. Albicans are usually the causative agents.
Diet
Antifungal Diet
- Efficacy: no data
- Terms: 3-6 months
- Cost of products: 1500-1600 rubles. in Week
In the process of treating a fungal disease, doctors recommend following some recommendations. Proper nutrition promotes a speedy recovery and helps fight fungal infections. The antifungal diet requires the following rules:
- Do not consume foods that contain yeast.
- Minimize, or better yet completely eliminate, the consumption of sweets, since carbohydrates are a breeding ground for fungus.
- The use of dishes made by fermentation (kvass, etc.) is contraindicated.
- It is recommended to eat freshly prepared food and consume as many raw vegetables and fruits as possible. It is important to introduce more greens, carrot and orange juice into your diet.
- It is prohibited to consume alcohol.
- During the treatment process, it is important to consume as much fermented milk products as possible in order to normalize intestinal functions.
- It is recommended to drink rosehip decoction, green tea, herbal teas, and mineral water. You need to drink as much fluid as possible.
Consequences and complications
If fungus on the hands is not treated promptly, it can lead to complications. After all, the fungus can continue to spread and affect a wider area of the hands, nails and other areas of the body.
- As a fungal infection develops, the deeper layers under the skin may become infected. If the infection penetrates deeper, the internal organs of a person are affected. As a result, immune system function may deteriorate. Allergic manifestations may develop - rhinitis , urticaria , conjunctivitis , bronchial asthma .
- In the absence of timely treatment for a fungal infection, the patient’s psycho-emotional state may be disrupted. neuroses and depression develop .
- Relapses of diseases may also become more frequent and their course becomes more severe.
- Fungal diseases are complicated by secondary bacterial infection. Subsequently, this can lead to the development of warts on the soles and palms, and erysipelas.
- Therefore, it is extremely important to treat the disease in a timely manner.
Reviews
- Oleg: “I work at a construction site, constantly working with cement and other materials. I noticed that my thumb on my hand began to break out constantly. I went to the doctor and was diagnosed with mycosis of the hands. I tried to be treated with creams, it helped for a while, and then everything came back. Constantly cold hands in construction chemicals are the best way to catch fungus. I read on the Internet that bleach helps. I applied the bath cleaner to my finger and held it for 3 minutes. I did not experience any pain or other unpleasant sensations. How surprised I was when after a day or two the wounds began to heal. The finger healed in just a week. Overall, an excellent, strong remedy."
- Natalya: “The initial stage of fungus on my hands appeared in the form of flaky, dry palms. I was prescribed clotrimazole ointment. I lubricated my hands morning and evening. Very quickly the disease began to recede, and I completely got rid of it after about 3 weeks. I don’t know where I caught the fungus, most likely on public transport.”