A fungal infection often appears on the nails or skin of girls, and if detected, you should immediately contact a dermatologist or mycologist. However, the doctor cannot always correctly prescribe a treatment regimen, which is due to the presence of strict contraindications for many antifungal drugs.
Because of this, it is quite difficult to choose how to treat nail fungus during pregnancy, especially its advanced form, since most antimycotics are not recommended for use during pregnancy.
Table of contents
- Etiology and pathogenesis
- Clinical manifestations
- Principles of treatment
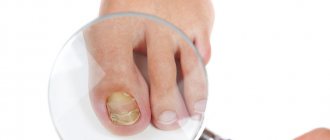
Onychomycosis (fingernail fungus, toenail fungus) is a fungal infection of the toenails or fingernails that affects any component of the nail complex, including the base, bed or plate. The disease can be accompanied by pain, discomfort, and changes in the appearance of the nails, which in some cases leads to serious physical and professional limitations, anxiety for patients and a decrease in their quality of life.
In our company you can purchase the following equipment for the treatment of onychomycosis:
- AcuPulse (Lumenis)
In the USA, onychomycosis of the nails occurs in approximately 2–13% of the population, in Canada - in 6.5%, in England, Spain and Finland - in 3-8%. According to a systematic review of 1914 articles, the prevalence of onychomycosis is as follows:
- general population - 3.22%;
- children - 0.14%;
- elderly people - 10.28%;
- patients with diabetes mellitus - 8.75%;
- patients with psoriasis - 10.22%;
- HIV-positive patients - 10.40%;
- patients on dialysis - 11.93%;
- after kidney transplant - 5.17%.
Onychomycosis accounts for about half of all nail pathologies and is the most common nail disease in adults. As for the affected areas, statistically, the legs are affected much more often than the arms.
The main forms of onychomycosis are:
- Distal lateral subungual onychomycosis
- Proximal subungual onychomycosis
- White superficial onychomycosis
- Endonyx-onychomycosis
- Candidal onychomycosis
Often patients have a combination of these subtypes, or total dystrophic onychomycosis - damage to the entire nail complex.
What is the danger
Having discovered symptoms of fungus, pregnant women wonder whether the unborn baby will suffer from this. Affected nails serve as a source of rapid proliferation of infection. If an unpleasant disease is not cured, pathogenic microorganisms will penetrate into the deep layers of the skin. Foot fungus is dangerous because it significantly suppresses the immune system of a pregnant woman. To treat onychomycosis, only antifungal antibiotics are suitable, which are harmful to the baby’s health because they cause developmental defects.
It is strictly forbidden to ignore the symptoms of fungal infections or try to get rid of them on your own, since there is a possibility of infecting the baby through the blood coming from the mother to the fetus. It is necessary to consult a dermatologist for an accurate diagnosis. The doctor will develop a treatment regimen and prescribe a set of safe drugs that are active against mycosis.
- Crochet rugs with diagrams and descriptions
- How to freeze eggplants for the winter
- General complication in people who have recovered from coronavirus
Etiology and pathogenesis of onychomycosis
Onychomycosis is caused by three main classes of fungi: dermatophytes, yeasts, and nondermatophytic molds.
Dermatophytes are the most common cause of the disease. Two main pathogens are responsible for 90% of all cases of onychomycosis: Trichophyton rubrum (70%) and Trichophyton mentagrophytes (20%). Onychomycosis, caused by non-dermatophytic mold fungi of the genera Fusarium and Aspergillus, as well as Scopulariopsis brevicaulis, is an anamorphic (asexual) representative of the genus Ascomycota, is gradually spreading throughout the world. Today they are responsible for 10% of cases of the disease. As for candidal onychomycosis, it is caused by Candida albicans and is quite rare.
In distal lateral subungual onychomycosis, Trichophyton rubrum is usually detected. Proximal subungual onychomycosis is typical in immunocompromised patients . The same type of onychomycosis, but with periungual inflammation, is caused by non-dermatophytic molds. White superficial onychomycosis of the nails is caused by Trichophyton mentagrophytes, and its deeper forms are caused by non-dermatophytic molds. Candida nail infection is often observed in premature infants, immunocompromised patients, and individuals with chronic mucosal candidiasis.
Risk factors for developing onychomycosis:
- family history;
- elderly age;
- warm and humid climate;
- weakened body;
- nail injury;
- regular fitness classes;
- immunosuppression (drug, HIV, etc.);
- visiting public swimming pools, baths and saunas;
- tight shoes.
Repeated microtrauma of the nails in tight and uncomfortable shoes provokes onycholysis (detachment of the nail from the soft tissues of the finger) and other degenerative conditions that contribute to the penetration of fungi into the nails.
Traditional methods
Having decided to turn to alternative medicine, the expectant mother should know that many folk remedies have a lot of contraindications. Tea tree oil, which has an antiseptic, anti-inflammatory and antifungal effect, acts as a safe component that helps cope with fungus . The treatment procedure is carried out as follows:
- The affected areas are thoroughly cleaned with laundry soap.
- A foot bath is made with the addition of salt, soda or vinegar.
- The limbs are well dried with a clean towel.
- The nail plate eaten by mycosis is cut off as much as possible.
- Using a cotton swab, 1-2 times a day, lubricate the sore nails with 1 drop of oil, rubbing in the medicine. The course of treatment is 12 weeks.
Propolis solution
According to user reviews, propolis solution has proven itself well in the treatment of nail fungus. The drug is moistened at the pest's location, applying a swab with the solution for several minutes. This should be done daily, 2-3 procedures. Propolis relieves itching, flaking, softens the skin, has a regenerative effect, and prevents the proliferation of pathogenic flora.
Clinical manifestations of nail onychomycosis
At first, onychomycosis is asymptomatic - patients can see a doctor because of visible cosmetic defects of the nail plate, but without any discomfort. As the disease progresses, paresthesia, pain and discomfort occur in the affected area. This makes walking difficult and interferes with sports and everyday life.
Clinical manifestations of onychomycosis depend on its type:
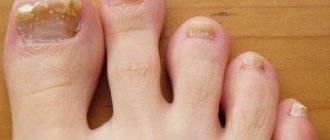
- Distal lateral subungual onychomycosis - there is subungual hyperkeratosis and onycholysis, the plate becomes yellow-white. In its central part, yellow stripes and/or yellowish onycholytic areas are visible.
- Proximal subungual onychomycosis - represented by leukonychia (white spots and stripes) in the proximal parts of the nail plate, which move distally (towards the edge) as the nail grows. If mold fungi are among the pathogens, periungual inflammation occurs.
- White superficial onychomycosis - small white speckled spots form on the toenails, the nail plate becomes rough and crumbles easily. Variations are possible with a deeper spread of the pathological process into the nail, depending on the causative agent of the disease.
- Endonyx-onychomycosis - the color of the nail plate becomes milky white. Unlike distal onychomycosis, there are no signs of subungual hyperkeratosis or onycholysis.
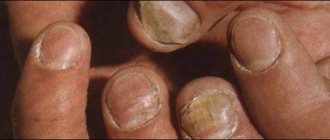
- Candidal onychomycosis of the nails is associated with chronic mucocutaneous candidiasis or immunosuppression, in which several or all nails are affected at once with the presence of periungual inflammation. The fingers of such patients often take on the shape of a bulb or drumsticks.
To assess the severity of the disease, the Onychomycosis Severity Index (OSI) has been developed. The result is obtained by multiplying the lesion area scores by the proximity scores of the lesion to the nail growth zone. Mild degree – 1–5 points, moderate – 6–15, severe – 16–35. Dermatophytoma (spots or longitudinal stripes) more than 2 mm with subungual hyperkeratosis is scored 10 points.
In its manifestations, onychomycosis is similar to many other nail pathologies. For example, leukonychia (stripes) resemble trauma to the nail plate. To confirm the diagnosis, it is necessary to perform a laboratory mycological study. Interestingly, a negative result does not rule out onychomycosis, since microscopy can be false negative in 10% of cases and culture in 30% of cases. A more reliable, although more expensive, method is PCR research (polymerase chain reaction).
Rice. 1. Distal lateral subungual onychomycosis (Dr. Antonella Tosti)
Rice. 2. Proximal subungual onychomycosis (Dr. Antonella Tosti)
Rice. 3. White superficial onychomycosis (Dr. Antonella Tosti)
Rice . 4. Endonyx-onychomycosis (Piraccini B., Alessandrini A. Onychomycosis: A Review. J Fungi 2015; 1: 30–43)
Rice. 5. Candidal onychomycosis (Dr. Antonella Tosti)
List of the best drugs
Pregnant women can not use all anti-fungal products. Their use is possible only after consultation with a doctor. Remember that before applying the drug to the affected nails, they should be prepared in a special way:
- Wash your hands well and treat with an antiseptic solution.
- Next, they should be placed in a hot bath with your favorite foam composition. The nail plate and the skin around the nail will soften, and the drug will better penetrate the pores. Doctors recommend taking baths with sea salt and soda to soften. To do this, dilute 1 spoon of this composition in a large bowl of water. Keep your hands in the bath for 15-20 minutes. Next, they should be wiped well.
Popular pharmaceutical remedies for fungus:
- "Lamisil";
- "Nizoral";
- "Exoderil";
- "Clotrimazole".
Before applying them, you need to study their contraindications. During pregnancy, doctors recommend that women use cream with salicylic acid and tar: they have fewer contraindications and will not cause harm to health.
How is thrush treated during pregnancy?
The difficulty of treating thrush during pregnancy is that it is important to maintain a balance between the therapeutic effect and the safety of the fetus. In the first trimester of gestation, the formation of the internal organs of the embryo occurs, and the unborn child is not yet protected by the placenta. In this regard, only topical drugs are used that do not penetrate the systemic circulation. For example, based on natamycin. In the second and third trimesters of gestation, when most of the organs and systems of the fetus are already formed, the doctor may advise the use of a wider range of drugs.
During treatment, it is recommended to refuse intimacy or use barrier contraception during sexual intercourse.
When treating a disease, it is important to strictly adhere to the regimen prescribed by a specialist. If you do not follow it, there will be no therapeutic effect, and the disease may become chronic. It is much more difficult to cure chronic vulvovaginal candidiasis.
Online consultation with a gynecologist
Online consultation
During the consultation, you will be able to voice your problem, the doctor will clarify the situation, interpret the tests, answer your questions and give the necessary recommendations.
Some pregnant women use folk remedies to treat thrush. However, “grandmother’s” methods are not only ineffective, but can also be harmful. For example, douching with a soda solution can lead to the washing out of beneficial vaginal microflora.
Not necessarily a fungus
In addition to mycosis, there are many other diseases that affect the nails. Among them, it should be noted in particular onychodystrophy, psoriasis of the nail plates, eczema of the nail plates, etc. Their treatment is radically different from the treatment of fungus. To confirm and establish an accurate diagnosis of onychomycosis, it is necessary to do tests: microscopy and culture. These methods make it possible to identify the exact type of fungus: dermatophytes, mold or yeast. Now many doctors neglect this, and completely in vain. The prescription of the necessary treatment and the selection of the correct systemic therapy depend on the type of fungus.
Details about diagnostics
In some cases, in addition to examination and microscopic examination, additional tests may be needed. So, in especially advanced or difficult to diagnose cases, the patient needs to check the function of the liver and kidneys. To do this, you need to donate blood for biochemistry: apartate aminotransferase and anine aminotransferase, creatinine. It is also necessary to exclude hepatitis B and C. Only based on these tests (biochemistry, microscopy and culture), it is possible to prescribe the correct therapy for the patient, which will get rid of the problem once and for all and will not harm the patient. Once every 1.5 months, a biochemical blood test is repeated to monitor drug tolerance. Most often, everything remains normal, but in rare cases of an individual reaction, an increase in indicators may occur. In this case, hepaprotectors are prescribed, the dosage or frequency of administration is reduced, or a lighter drug is prescribed.