Causes of cold dermatitis
The main cause of cold dermatitis is prolonged exposure to low temperatures on exposed skin. A spasm of the capillaries occurs, as a result of which the blood supply to the upper layers of the dermis is disrupted, causing an inflammatory process.
People who have dry skin or a lack of natural fat layer are also at risk.
In addition, at low temperatures, proteins are formed that are part of the cellular structure of the skin; proteins activate the development of histamine (an organic compound, an endogenous factor in the development of allergies), which causes skin manifestations, but these compounds are not stable; when warmed, the protein disintegrates.
The reasons that may contribute to the development of the initial stage of frosty (cold) dermatitis have been identified:
- A genetic factor is a predisposition, the presence of allergies in one or both parents, which can cause the child to develop the disease or be sensitive to it.
- Tendency to allergic manifestations.
- External influence of toxic substances can very rarely become the cause.
- Avitaminosis.
- Reduced immunity.
There is a version that cold dermatitis is a complication of other diseases of internal organs or diseases of an autoimmune nature.
What is cold allergy and why does it occur?
This pathology, in its essence, is an inadequate response of the immune system to the effects of low ambient temperature or water. For what reason such changes occur is currently not known for certain. Some scientists suggest that cryoglobulins, special proteins that are produced in the cold and activate histamine, thus triggering a cascade of allergic reactions, play an important role in the mechanism of the allergic reaction.
The foundation for this pathological process is various somatic pathologies: chronic diseases of the respiratory, urinary and reproductive systems, infectious and parasitic diseases. An extremely important role is played by disturbances in the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract due to intestinal dysbiosis, gastritis, cholecystitis, enterocolitis, etc. In principle, almost any long-term health disorder can provoke an allergic reaction.
Symptoms of cold dermatitis
There are a number of characteristic symptoms for cold dermatitis:
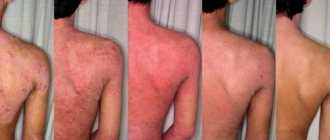
- The formation of scarlet/pink/burgundy/cyanotic spots, the size can reach five centimeters, most often occur on areas of the skin that have not been hidden from exposure to low temperatures;
- The spots peel and crack;
- Itching, burning, feeling of skin tightness in areas where dermatitis occurs;
- Rhinitis, conjunctivitis (non-infectious etiology), sneezing;
- The skin is inflamed, tissue swelling is noted;
- Rash similar to hives (blisters like insect bites);
- There may be a deterioration in the general condition, as with acute respiratory infections, acute respiratory viral infections;
- Very rarely, Quincke's edema, bronchospasm, and short-term loss of consciousness may occur; this is considered a complication; these manifestations can occur in people with immunodeficiency or prone to frequent allergic reactions.
The spots can be localized on any part of the body. It often appears on the face, due to the poor protection of this part of the body from exposure to cold temperatures. Cold dermatitis on the face appears quickly, in the form of bluish spots and a feeling of dry skin; with further exposure to cold, a rash may appear; when warmed up, they go away, and the skin acquires a pale tint.
Even children are susceptible to cold dermatitis. The main signs of frost dermatitis in children are the appearance of pink itchy blisters on exposed areas of the body, which may appear after warming up. There is a loss of strength, the development of conjunctivitis and rhinitis.
Why is cold dangerous?
Frozen skin is easier to injure, it becomes dry and prone to irritation.
- Low temperatures cause spasm of small blood vessels that nourish the epidermis. This leads to a slowdown in metabolic processes in cells.
- The sebaceous glands, which are supposed to protect the integumentary tissues from hypothermia, work worse.
- Cold air dries out the dermis, makes it less elastic, and increases the tendency of the epidermis to desquamate.
People with dry skin types, children under 10 years of age, older adults, people with diseases of the digestive system, and reduced thyroid function are more affected.
Cold dermatitis on hands
Due to the anatomical position of the hands (fingers pointing down), there is an obstacle to the outflow of blood, and the hands are less well supplied with blood. Since hands are washed frequently, the natural oil layer is washed away, which makes them sensitive and vulnerable. All this contributes to the manifestation of dermatitis more often on the hands than on other parts of the body.
Lesions appear on the back of the hands, manifesting themselves with characteristic symptoms, which are accompanied by severe pain, itching and burning; over time, crusts form, and the lesions become very flaky.
You can see what cold dermatitis on your hands looks like in the photo section.
How to distinguish from cold allergies
This hereditary disease is manifested by a rash of blisters with jagged edges - similar to urticaria. When pressed, the spots turn pale. There is severe itching, burning throughout the body, sometimes swelling of the throat, and abdominal pain along the intestines. An allergist will make a diagnosis after a specific examination.
The cause of this allergy is considered to be the instability of the membranes of mast cells (a type of white blood cell), their release of increased doses of histamine under the influence of cold.
A test with a piece of ice will help you suspect cold urticaria: if you apply ice, after 1–2 minutes a characteristic spot will appear in this place.
Treatment is carried out with antihistamines.
Treatment of cold dermatitis
Before starting treatment, it is imperative to carry out a diagnosis, since cold dermatitis has similar symptoms to other diseases - allergic urticaria, chicken pox, atopic dermatitis. The doctor uses the following diagnostic methods:
- Dermatoscopy is a device for tenfold magnification and study of tumors.
- Measuring the pH level - to exclude a fungal or bacterial infection, and determine what caused the development of dermatitis.
- General blood and urine analysis.
Additionally, additional examinations may be prescribed - ultrasound, smear, gastroscopy. It is quite difficult to establish a diagnosis on your own, so it is recommended to visit a dermatologist; the doctor, based on the tests obtained, will prescribe a treatment regimen taking into account the characteristics of the patient’s body.
The main treatment is to protect the skin from exposure to low temperatures and complex treatment aimed at:
- Relieving symptoms - often antihistamines (tablets or ointments) eliminate itching, swelling and redness of tissues;
- Retinoids - to heal formed cracks, accelerate tissue regeneration and normalize the functionality of dermal cells (gels, creams);
- Vitamin complexes - to boost immunity;
- Prebiotics – to eliminate dysbiosis;
- Cosmetics for skin care and protection from negative factors.
Self-prescribing and taking medications is unacceptable; any medications should be prescribed only by a doctor, this will avoid negative consequences.
Treatment of allergies to cold
Treatment regimens for cold allergies are similar to those for true allergies, and they come down mainly to preventive measures. Prevention, by and large, is aimed at preventing an allergic reaction by eliminating contact with the provoking factor - cold. Medications only help relieve symptoms.
Patients prone to this pathology should give preference to clothing made from natural fabrics and try to avoid hypothermia. If this fails in some situations, you should try to warm up immediately upon arriving home. Be sure to moisturize your lips with a special hygienic lipstick. If lacrimation and runny nose appear, you need to periodically massage your nose and cheeks.
In addition, it must be emphasized that any allergy, including allergy to cold, very often appears against the background of any chronic pathologies accompanied by decreased immunity and frequent stress, which also requires adequate preventive measures. If signs of a cold allergy appear, you should seek help from an allergist as soon as possible.
Treatment of cold dermatitis with folk remedies
In folk (alternative) medicine, there are many recipes to combat many skin pathologies. Ointments, tinctures, lotions or decoctions are made based on herbs or other natural ingredients. Almost all of these remedies are ineffective against cold dermatitis, and are sometimes dangerous, especially when treating children. The possibility of using any folk remedy as an addition to the main drug treatment should be discussed with your doctor.
Only the attending physician can advise the remedy and the advisability of its use.
Diagnostics
In HD diagnostics, the main attention is paid to clinical signs, collection of anamnestic information, study of patient complaints and their physical examination.
Anamnesis data allows us to confirm or refute the connection between the occurrence of CD lesions and the influence of NVT. Simple HD pathology is characterized by local cutaneous lesions in the area of influence of the NVT factor. This is primarily the skin surface of the cheeks, nose, ears, as well as fingers and toes.
The difference between the allergenic HD form is the presence of a latent period preceding the onset of symptoms, the spread of the pathological process beyond the areas of direct exposure to the exogenous cold factor.
If difficulties arise in making a diagnosis, a number of collegial consultations with a dermatologist, allergist, and immunologist are encouraged.
Prevention of cold dermatitis
It is impossible to completely protect yourself and avoid the occurrence of cold dermatitis, but by following simple rules you can minimize the risk of developing the disease:
- During the cold season, especially during strong winds, use cosmetics aimed at protecting the skin. It is not advisable to use moisturizers, as this can cause dry skin and flaking.
- Protect your skin - use gloves, wide scarves, and a hat.
- Minimize contact with cold water, do not drink cold drinks, and avoid ice cream in winter.
- In residential areas, maintain the required air humidity.
- Take vitamin complexes and eat a balanced diet to avoid vitamin deficiency and support immunity during periods of exacerbation of respiratory diseases, especially in the autumn-spring period.
- Pay attention to the functioning of the stomach and intestines; if there are any malfunctions in the functioning of these organs, contact a specialist to eliminate complaints.
- Eliminate sources of allergies - food, synthetic clothing, detergents, household chemicals, and, if possible, select hypoallergenic medications.
- Hardening is acceptable for cold dermatitis, and an effective way to combat it.
- Contrast shower is a training for blood vessels, increases their resistance and elasticity.
- Do not ignore any diseases and treat them completely, following the advice of your doctor.
Cold dermatitis is a dangerous disease, so if you notice characteristic signs, you should consult a doctor; timely treatment is the key to a speedy recovery.
Diet for cold dermatitis
Poor nutrition, stomach and intestinal diseases are a common cause of the development of cold dermatitis. To get rid of the disease and prevent its recurrence, you should follow a diet and try to give up the following foods:
- Fast food and quick snack: chips, crackers, nuts, etc.;
- Citrus fruits often cause allergies;
- Store-bought juices and sweet sodas contain dyes and preservatives;
- Limit baked goods (especially rich ones);
- Chocolate, candy, cakes, honey;
- Any mushrooms;
- Seasonings;
- Store-bought sauces;
- Eggs are considered a strong allergen;
- Milk – many people are allergic to lactose;
- Seafood - except fish, whose meat is considered dietary;
- Fatty foods and fatty meats.
Can be used:
- Poultry meat – chicken, turkey;
- Dairy products;
- Greens – parsley/dill, etc.;
- Vegetables - zucchini, cabbage, and pumpkin are especially useful.
- Cereals.
Steam cooking is recommended. It is acceptable to add a small amount of olive oil and salt for taste.
By adhering to the basics of proper nutrition and a healthy lifestyle, you can avoid many dermatological diseases or alleviate their course, avoiding complications.