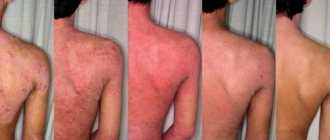
Irritant genital dermatitis (irritative dermatitis) is a rash or redness on the genitals that occurs in sensitive people after contact with a specific irritant. Irritants can be any drugs applied to the skin of the genital organs. The most common ones are soap, detergents and condoms.
The rash appears as redness of the penis or redness of the vulva (a woman's external genitalia), which causes genital itching in men or genital itching in women, discomfort and pain. After redness, blisters and scabs appear on the genitals - places where a genital infection can develop.
Treatment of genital irritative dermatitis is based on recognizing the irritant and avoiding it. Corticosteroid creams and cool baths relieve symptoms.
Genital irritant dermatitis - causes
Genital irritant contact dermatitis is an inflammation of the skin. It manifests itself as redness (genital rash) and mild swelling of the skin resulting from a nonspecific reaction to direct chemical injury. The agent, which acts as a strong irritant, causes damage to the epidermal skin cells and an inflammatory response, leading to redness, swelling and ulceration of the skin.
Chemicals that remove the lipid layer of the skin or damage the cell membrane cause irritation.
Common irritants:
- soap and detergents;
- hygiene products (for example, tampons, sanitary pads, wet wipes);
- baths, shower gel, oils, perfumes;
- toilet paper;
- condoms (latex);
- washing the genitals too often;
- wearing synthetic and colored underwear.
Why does trophic venous eczema occur?
Venous eczema is most often observed in middle-aged and elderly patients - according to leading European dermatologists, it affects up to 20% of patients over 70 years of age. This is due to the following reasons:
- Phlebeurysm.
- Previous deep vein thrombosis of the affected limb.
- The presence of venous trophic ulcers.
- Previous cellulitis on the affected limb.
- Chronic swelling of the lower leg, aggravated by hot weather and prolonged static position (standing).
The main cause of the pathology is varicose veins, which is why you can sometimes come across the term “Varicose eczema”.
Venous eczema of atypical localization
Quite often, signs of eczema can be found in young patients with a long history of varicose veins. There is no doctor, both in public and private clinics, who would not observe venous eczema in patients under 40 years of age.
Irritant genital dermatitis - symptoms
Symptoms may appear minutes to hours after exposure to the irritant. In rare cases, symptoms may appear even after several weeks or months (cumulative contact dermatitis). This type of dermatitis usually occurs after exposure to mild irritants, such as detergents, for an extended period of time.
Patients complain of redness, itching, burning, pain and discomfort in the genitals.
There are several stages:
- Erythematous stage - redness of the genitals;
- Vesicular stage - formation of blisters on the genitals;
- erosive stage - the appearance of ulcers on the genitals;
- squamous stage - the formation of a thicker stratum corneum.
The typical presentation of irritant contact dermatitis includes diffuse redness of the affected skin with crusting.
The damaged skin may develop furrows, causing genital pain and itching.
Damaged genital skin is a place where inflammation and infection easily develop.
In men, diseases of the genital organs are not uncommon. Inflammation of the glans penis is most often caused by infection or chronic skin changes resulting from poor hygiene and irritation. Untreated sexually transmitted diseases can lead to balanitis (inflammation of the head of the penis).
Irritation of the glans penis can be caused by insufficient rinsing of soap after showering, using washes that are not suitable for the genitals, or other inappropriate preparations (lotions, fragrances).
Symptoms of balanitis:
- redness on the foreskin around the glans;
- redness on the penis,
- itching of the genitals in men;
- thickening of the foreskin;
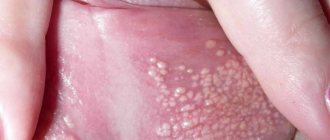
- white round plaques on the head of the penis;
- painful skin on the penis;
- difficulty urinating.
Treatment of inflammation of the glans penis depends on the cause that caused it.
Non-infectious causes of scarlet spots and spots on the phallus:
- Allergic reactions. They can appear both when the allergen gets inside and from local exposure. If red spots appear on the penis, you need to rule out allergies to the medications or lubricants used, latex included in the condom, or food products that have recently appeared in the diet. It is important not to wear synthetic underwear. During treatment, avoid washing powder and soap with fragrances (you can use household or children's hypoallergenic soap).
- Failure to comply with personal hygiene rules. A scarlet rash appears in those men who rarely change their underwear and wash their penis poorly or rarely.
- Decreased immunity. Stress, alcohol abuse, and the presence of chronic diseases worsen immune defense. Against this background, opportunistic flora is activated, which leads to the formation of rashes.
- Damage to the head of the phallus. During intense coitus, wearing tight underwear, riding a bicycle for long periods of time, or riding a horse for many hours, capillaries and other small blood vessels can burst. In addition, it is possible to injure the delicate skin on the head. In this case, the spots that appear do not itch, but touching the penis causes discomfort.
- Autoimmune pathologies. The most common is psoriasis. It can manifest itself in different ways, which sometimes makes diagnosis difficult. Localization of spots - in the groin, on the head or body of the penis.
- Precancerous condition. With Bowen's disease, a red-brown spot appears in the pathological area, which turns into a plaque. This lesion peels off and becomes covered with crusts that are easy to remove. When the disease progresses to oncology, an ulcer forms.
- Cancer. It is characterized by the appearance of a small malignant neoplasm of a spot that does not hurt or bleed. Gradually increases in size, becomes denser, similar to a tubercle. Purulent discharge, itching and the appearance of blood from the pathological focus are observed as the disease progresses.
As you can see, there are many reasons why red spots appear on the head of the penis or its body. And it is not recommended to diagnose yourself by looking at photos on the Internet and reading information about possible diseases; it is inappropriate. So the man will only worsen the course of the pathology, and the disease will become chronic. Remember: the sooner you start fighting the disease, the easier it is to kill the infection and achieve a complete recovery.
Inflammation of the vulva (vulvitis) and vagina (vaginitis)
Vulvitis is an inflammation of the vulva, that is, inflammation of the external female genital organs. If the vagina is also affected, then we are talking about vulvovaginitis.
Causes of vulvitis include infections, irritants, medications and hormonal changes. Poor intimate hygiene can promote the growth of fungi and bacteria and also cause irritation.
Based on the causes of occurrence, vaginitis can be divided into several groups:
- non-infectious vaginitis - a consequence of contact dermatitis;
- atrophic vaginitis - in women during menopause, due to a lack of estrogen, the vagina becomes thinner and becomes susceptible to infections;
- infectious vaginitis - infection by microorganisms;
- bacterial vaginosis is a consequence of an imbalance in the bacterial flora of the vagina;
- fungal infection of the genital organs - vaginal candidiasis.
The most common symptoms in women are unusual discharge, genital irritation and itching. The skin becomes red and swollen. An unpleasant vaginal odor emanates from the vagina, and a burning sensation is felt when urinating.
The diagnosis is very easy to make based on the history and clinical picture.
Allergic contact dermatitis must be distinguished from irritant contact dermatitis by performing an epicutaneous skin test for allergens.
When diagnosing irritative dermatitis, a skin test is negative.
Causes that should be excluded when diagnosing irritant dermatitis:
- allergic contact dermatitis;
- genital psoriasis;
- genital fungus in men (penile fungus);
- genital fungus in women (vaginal candidiasis);
- genital herpes;
- syphilis;
- inflammation of the glans penis (balanitis);
- inflammation of the foreskin (balanoposthitis);
- inflammation of the vagina (vaginitis);
- inflammation of the vulva (vulvitis);
- inflamed sebaceous glands;
- hair folliculitis.
Complications
You should not listen to the opinions and advice of loved ones when trying to cure genital eczema on your own. This is dangerous for the patient’s health and can also aggravate the situation.
The disease can become chronic and cause various adverse consequences.
Despite the fact that genital eczema in men and women is a serious disease, by contacting a specialist in time and following all his instructions, it is possible to get rid of the disease and avoid subsequent relapses and the spread of infection.
Irritant dermatitis on the genitals - treatment
The most important step in treating genital irritant dermatitis is recognizing the irritant and avoiding it.
Cold compresses and baths can help relieve symptoms, and topical corticosteroid creams can be used in the short term.
The patient should reduce frequent washing of the genitals with scented soaps and stop wearing tight synthetic clothing, which may cause irritation. Women should stop using wet sanitary napkins, panty liners, and scented and colored toilet paper.
Trophic venous eczema is very bad
Varicose eczema has a chronic, relapsing course and a tendency to progress. Quite often you can encounter a situation, especially in public hospitals, when only dermatologists treat venous eczema. Considering the main etiological component of the pathology, impaired venous outflow, treatment of such patients takes years.
Chronic recurrent eczema on the right lower limb
The disease slowly recedes, but invariably appears again. Moreover, trophic changes in the lower extremities progress, lipodermatosclerosis occurs, and then an ulcer appears.
Frequently asked questions from patients on the Internet about trophic venous eczema
How to treat venous eczema of the legs in Moscow?
For good treatment of venous eczema of the lower extremities in Moscow, you need to contact a competent specialist, a phlebologist. The doctor will conduct a detailed diagnosis, including an ultrasound examination. Only after this can we talk about modern treatment. The best solution would be to find a good city phlebological center, where the ultrasound will be performed by the phlebologist himself.
What is the modern treatment for venous eczema of the legs in Moscow?
In Moscow, good modern treatment of venous eczema that meets European standards includes innovative technologies for both diagnosis and treatment. Leading city phlebological centers, including our Moscow Innovative Phlebological Center, successfully treat venous eczema. First, a detailed duplex angioscanning of the venous system of the lower extremities is performed. Only then is treatment prescribed, including the fight against local inflammation and modern treatment of the true cause of eczema, varicose veins.
How to treat venous eczema with folk remedies?
Specialists of the Moscow City Phlebological Center have good experience in working with various trophic disorders in venous diseases, including venous eczema. Leading phlebologists at our center do not recommend treating venous eczema with folk remedies. The disease responds well to treatment using modern technologies, but we often encountered serious complications after treatment with folk remedies.
My mother has venous eczema on her legs, which doctor is best to see?
If you suspect that your mother has venous eczema, it is better to first contact a good phlebologist, a doctor specializing in the diagnosis and treatment of venous pathology. First you need to understand the cause of inflammation in the lower extremities. You may need the help of a dermatologist. If eczema is of venous origin, then now there are modern European technologies with the help of which curing your mother will not present any special problems.
Results of treatment of trophic venous eczema. Photos before and after treatment
The result of treatment of trophic eczema using endovenous laser coagulation (EVLC) using German Biolitec technology in our center
Photos before and after treatment of trophic eczema on the left lower limb
The result of treatment of trophic venous eczema using radiofrequency ablation (RFA) in our patient
Photos before and after treatment of trophic venous eczema on the left lower limb
Trophic venous eczema - diagnosis
Diagnosis of venous eczema in public and private urban medical institutions often begins in a dermatologist’s office, where a specialist evaluates local changes in the skin. It is very important here that the patient is referred to a good phlebologist in a timely manner. If eczematous changes are associated with venous pathology, then treatment of skin manifestations only is likely to be ineffective. Even a visual examination by a phlebologist using all kinds of functional tests often does not reveal the true cause of the pathology. At this stage, the best solution would be a good ultrasound examination of the veins of the lower extremities.
Ultrasound diagnosis of trophic venous eczema
Only competent modern diagnostics of the venous system will help determine the correct treatment tactics.
Why does trophic venous eczema almost always appear on the lower extremities?
The answer to this question lies in the pathogenesis of varicose veins, the dominant cause of venous eczema. Varicose veins affect exclusively the lower extremities, where, according to the gravity gradient, it is in their distal parts that trophic disorders occur. One of which is venous eczema.
Trophic eczema of the lower extremities
Pathological eczematous changes in the skin of the lower extremities are most often caused by varicose veins, since they are the cause of impaired venous outflow (up to 90% according to leading experts in the region).