| Appointment with a surgeon in Moscow on the same day of treatment | Reception is strictly by appointment, make an appointment by phone: +7 | Prices for services | Reviews about the clinic |
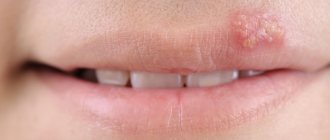
Abscess on the lip
- this is the formation of a purulent process that develops as a result of the penetration of pathogenic pathogens into the tissues of a given area. The starting mechanism for the formation of an abscess is trauma to the mucous membrane of the lips from the oral cavity or damage to the skin on the face. Another reason for the formation of deep abscesses is multiple pustular rashes on the face.
An abscess on the lip is an extremely dangerous condition, since the likelihood of its spreading throughout the cellular spaces is extremely high. Due to the intensive blood supply to the face, the spread of the purulent process to the infraorbital and buccal area occurs extremely quickly.
Make an appointment with a surgeon by phone or by filling out the online form
| Select a clinic | Abdominal ultrasound | Gastroenterologist | Calling a surgeon to your home |
Useful information on the topic:
- Abscess
- Abscess on the stomach
- Abscess of the buttocks
- Opening an abscess
- Abscess treatment
- Causes of abscess
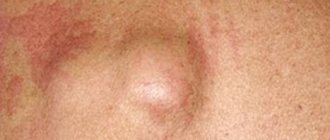
Diagnosis of an abscess on the lip
The primary stage of diagnosis is an examination of the patient and a thorough history taking. Patients are usually bothered by pain, which intensifies when:
- conversation
- chewing food
- lip movements
When examining the lower half of the face, the following is revealed:
- swelling in the area of localization of the pathological process
- skin hyperemia
- smoothness of the nasolabial fold
- palpation and any impact on the skin and mucous membranes are sharply painful
When an abscess has formed on the surface of the skin or mucous membrane, the place of greatest thinning of the tissue is outlined. Purulent masses can melt the structures of the skin or mucous membrane, causing spontaneous opening of the purulent cavity.
Subsequently, such a wound heals poorly and is constantly moistened with serous-purulent discharge. After healing of such a wound surface, a cosmetic defect remains with the formation of a scar.
Useful information on the topic:
- Calling a surgeon to your home
- Callus
- Abscess on finger
- Ingrown nail
- Felon
- Wart removal
- Removal of condylomas
- Abdominal ultrasound
- Removal of papillomas
- Treatment of bedsores
- X-ray
- Removing stitches
- Gastroscopy
- Colonoscopy
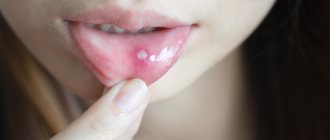
Symptoms of stomatitis and its classification
If a child has a white sore on the inside of his lip, it is better to take him to a dentist for an examination to prevent negative consequences. Most often, the disease is diagnosed in children from one to 3 years of age; it is slightly less common in infants. Preschoolers and schoolchildren encounter the disease extremely rarely. The peak incidence usually occurs in the spring, when everyone feels their immunity weakens.
Experts distinguish 4 types of stomatitis: traumatic, infectious, allergic and chronic. First, small ulcers appear on the child’s lips, and then swelling of the mouth and lips becomes noticeable. The mucous membrane takes on a bright red color. Then the marks begin to spread to the tongue, palate and cheeks. Often they are the result of tissue injury from braces, a plate or a damaged tooth.
The appearance of bubbles indicates the infectious nature of the disease. Formations can make themselves felt on the face (on the nose, cheeks and lips). Such manifestations linger for several days, and then turn into traces of erosion, bringing with them headache, joint or muscle pain, as well as enlarged lymph nodes. Additional symptoms of stomatitis are dryness and burning in the mouth. Pain occurs when eating food. In extreme cases, the papillae located on the tongue may lose sensitivity.
Kinds
Today, 8 types of stomatitis can be diagnosed:
- bacterial;
- aphthous - manifests itself when immunity decreases due to gastrointestinal diseases and anemia;
- herpetic – occurs due to the herpes virus;
- viral;
- angular;
- allergic – a reaction to an allergen entering the child’s body;
- traumatic - the cause may be an accidental bite of the lip with teeth or scratches on the gum;
- fungal – infection of the oral cavity by fungi of the genus Candida.
All types of stomatitis can occur in childhood. However, from birth to 3 years, children are especially susceptible to aphthous, candidal, herpetic and allergic types. During the period of active growth of baby teeth, traumatic stomatitis often appears, caused by rupture of the soft tissue of the gums.
Note! Stomatitis does not always occur on its own. Quite often, rashes in the mouth are a sign of other diseases, so before treatment it is necessary to carry out a series of diagnostic measures to discover the exact cause.
Symptoms
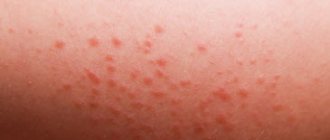
The classic clinical picture for diagnosing stomatitis includes the following symptoms:
- swelling of the mucous membrane;
- the appearance of a white or yellowish coating;
- bad breath;
- dryness or excessive salivation;
- enlarged lymph nodes and increased temperature.
Stomatitis in children has similar and different symptoms. Each type of disease has its own differences in manifestations.
With allergic stomatitis, minor ulcerative lesions appear on the palate, gums, cheeks, and lips. They pass as soon as the irritant can be identified and removed. With aphthous, even one spot with a diameter of up to 1 cm may appear in the mouth. Its outer part is covered with a film, the ulcer is yellow, and its edges are inflamed. If stomatitis is herpetic, then the mucous membrane is affected by numerous rashes that merge into one large wound. These are blisters with clear liquid and are extremely painful. Often the herpes virus causes a deterioration in the general condition of the child’s body, accompanied by body aches and high fever.
The most common type of stomatitis in a child’s mouth is candidiasis. Its common name is thrush. 9 out of 10 parents have encountered this phenomenon at least once. It is characterized by the appearance of a white cheesy coating on the tongue, gums, and cheeks of the baby. It is often observed after completing a course of antibacterial therapy or as a consequence of infection of the mother’s nipples by Candida fungus. Candidiasis can also be caused by poor hygiene.
On a note! Regardless of the type of stomatitis, its treatment should be comprehensive and begin immediately after the first signs of damage to the oral cavity are detected!
Treatment options
How to cure stomatitis in a child? It’s worth noting right away that you can’t prescribe medications to your baby yourself. Only the pediatrician makes a diagnosis and makes recommendations for therapy. Attempts to overcome the disease on your own can lead to a worsening of the little patient’s condition. To determine the causative agent of the inflammatory process, a scraping is made and a virological study is carried out.
For stomatitis in children, what treatment will be most effective? Only those therapeutic measures will help that will affect the disease comprehensively, eliminating both the cause and external manifestations.
Medicines
When an accurate diagnosis is established, dentists prescribe medications for the treatment of stomatitis in children. They are conventionally divided into symptomatic and special.
The purpose of the first is to eliminate the symptoms that accompany the disease. For this purpose the following is prescribed:
- vitamin complexes to strengthen the body;
- antiviral drugs that fight viruses;
- antipyretic and anti-inflammatory drugs;
- anesthetic gels;
- ointments and solutions for treating the oral cavity.
- need to drink plenty of fluids
- gentle diet (exclude sour, salty, spicy)
Candidal stomatitis is treated with special pharmaceuticals that contain substances that kill the fungus. Creams suitable for internal use are prescribed. If an allergic type is detected, the pediatrician will add antihistamine drops or tablets to the general list. If the rash is caused by the herpes virus, you cannot do without taking antiviral drugs, as well as local treatment of the mucous membranes with antiherpetic ointment.
Attention! The entire oral cavity needs to be treated, since pathogens are found everywhere on the mucous membrane. They are not visible to the naked eye, but if they remain in the mouth, they will continue to spread and the treatment will be delayed.
Folk remedies
Have you noticed stomatitis in a child and don’t know how to treat it? Drug therapy can be supplemented with the use of traditional medicine. Compositions prepared from natural ingredients are used to treat stomatitis in children over 2 years of age.
The following formulations are suitable for treating mouth ulcers.
Soda and salt
0.5 tsp each Dissolve the components in warm water. Rinse your mouth with the solution 3-4 times a day after meals. Baking soda relieves inflammation and disinfects well. The same composition, only diluted with water to a mushy consistency, can be used to clean off plaque from fungal stomatitis using a finger wrapped in gauze.
Honey and aloe
The leaf of the plant is ground to a puree, and the same amount of natural honey is added to it. Apply to affected areas three times a day.
Chamomile with honey
Dried flowers are brewed in the proportion of 1 tbsp. for 250 ml of boiling water. Add 2 tsp to the cooled broth. honey Rinse your mouth with warm liquid 2-3 times a day.
Rinses can be prepared from other ingredients:
- sage;
- rosehip;
- St. John's wort;
- oak bark;
- flaxseeds;
- yarrow;
- calendula;
- propolis tinctures.
Lotions of essential oils help a lot.
Important! Folk remedies can only be used after consulting a pediatrician!
How to prevent stomatitis
To reduce the risk of getting an infection in your mouth, you should:
- regularly wash toys, hands, pacifiers, bottles;
- carry out wet cleaning and ventilate the room where the baby spends his leisure time;
- strengthen the immune system: strengthen the child, give vitamins, maintain proper sleep and wakefulness;
- provide a balanced diet;
- fight the bad habit of biting nails or other objects (pencils, pens, rulers);
- Make an appointment with the dentist twice a year for a routine examination.
Any disease should be treated in a timely manner, otherwise negative consequences cannot be avoided. Carefully examine the child’s oral cavity at the first complaints. When stomatitis occurs in infants, the first symptoms include behavioral changes, crying, and refusal of the breast or bottle. Children aged 1 year and older will be able to independently point out to their parents the source of discomfort. Get treated promptly and be healthy!
Periandibular abscess
Treatment of maxillary abscesses
The ultimate goal in treating patients with maxillary abscesses will always be to eliminate the source of infection and completely restore the impaired functionality of the body as soon as possible.
It can only be achieved with the help of complex therapy. Before choosing a specific treatment regimen, you must consider:
- stage of the disease;
- features of the inflammatory process;
- the ability of an infectious focus to infect other tissues and organs;
- type of body response;
- prevalence of inflammation;
- patient's age;
- presence of concomitant diseases.
From the very beginning, the main essence of treatment of acute stages of perimandibular abscesses comes down to limiting the spread of infection throughout the body. The odontogenic infectious process should not progress in the area of the upper jaw, which covers the following sections:
- infraorbital;
- zygomatic;
- orbital;
- temporal;
- infratemporal;
- pterygopalatine fossae;
- soft and hard palate.
Surgical dissection procedure
Opening the perimaxillary abscess of the infraorbital region (levels 1,2,3 teeth) begins with an incision of the mucous membrane along the transitional fold and with spreading the muscle. In addition, it should be taken into account that classical drainage with a cellophane or rubber strip is sometimes not enough, since in the abscess cavity the purulent focus is continuously filled with purulent exudate. This process is associated with the infringement of the drainage strip by reducing expression wrinkles. The most effective drainage will be after using a narrow perforated rubber tube. Complex clinical cases force the opening of the perimandibular abscess through the skin.
If a surgical incision is made in the area of the zygomatic region along the lower edge on the side of the skin, then the entire area of localization of the abscess is taken into account, including the adjacent cellular spaces. In this case, it would be rational to make a wide excision of the lower part of the purulent formation with the simultaneous use of counter-aperture. Gauze bandages and turundas with antiseptic, hypertonic solutions are also used.
Treatment with medications
Drug treatment is mandatory; advanced stages of perimandibular abscess require complex therapy. If surgical intervention is not necessary, the patient is prescribed antibiotics, which come in both tablet form and in the form of injections.
Doctors strongly recommend immediately seeking qualified help from dentists at the first symptoms and signs of a perimaxillary abscess, because in case of inflammation, the main role is played by the timely elimination of the purulent focus and the causative tooth (if necessary). After opening, it is necessary to ensure the outflow of exudate. All medical procedures are performed under general anesthesia, taking into account the characteristics of the blood supply, innervation and structural nuances of the maxillofacial area.
The following is prescribed parenterally or internally:
- broad-spectrum antibiotics;
- anti-inflammatory and painkillers (amidopyrine, phenacetin, analgin);
- sulfa drugs;
- restorative and antihistamine.
During the treatment of perimandibular abscesses, it is important for the patient to provide adequate nutrition with additional vitamins; we should not forget about the general detoxification of the body with the help of large amounts of fluid. The procedure for sanitation of the oral cavity is carried out only after the final elimination of the inflammatory process.
Causes
Stomatitis is a disease that affects the mucous surfaces of the oral cavity. This is an acute inflammatory process of various etiologies, which is manifested by the appearance of yellowish or whitish pimples with liquid and ulcers. It can occur in children and adults, but children are much more likely to suffer from the disease.
The rash affects the inside of the cheeks, gums, and tongue. Their appearance causes discomfort, since ulcerative wounds itch, hurt, and there is a constant burning sensation in the mouth.
Young children have extremely delicate oral mucous membranes. The body’s insufficiently developed defense system is not able to quickly cope with infectious agents, so the natural reaction of the immune system to their entry into the body is inflammation. Common causes of the disease are:
- insufficient oral hygiene;
- chronic gastrointestinal diseases;
- mucosal injuries;
- burn;
- ingestion of pathogenic bacteria from hands or toys.
Important! Treatment of stomatitis in children is possible at home. However, in order to choose the right treatment regimen, you cannot do without consulting a specialist.