August 16, 2020
Dermatitis is an inflammation of the skin that can occur due to a variety of irritants: allergens, aggressive chemicals, fungi, and adverse weather factors. Chronic inflammation of the skin also occurs with psoriasis, but in this case the condition is distinguished as a separate disease, and dermatitis is a collective concept, a syndrome that may not relate to any specific disease, occurring periodically.
Causes of dermatitis
The disease develops due to three main reasons:
- exposure to an irritating factor;
- decreased general immunity;
- deterioration of the protective properties of the skin.
Factors that cause dermatitis can be divided into two large groups: external (exogenous) and internal (endogenous).
External factors:
- mechanical impact - prolonged compression, friction;
- physical impact - high and low temperatures, sun rays, radioactive radiation;
- contact with chemicals - cosmetics, household chemicals, alkalis, acids, salts of heavy metals;
- contact with poisonous, burning plants, pollen, biological fluids;
- bacteria, viruses, fungi.
Internal factors:
- errors in nutrition, metabolic disorders, hypo- and avitaminosis;
- internal diseases – endocrine disorders, gastrointestinal pathologies;
- neuropsychiatric disorders;
- taking medications (antibiotics, hormones, drugs with novocaine).
Knowing the causes of dermatitis, you can understand that in most cases it is not a contagious disease. Only dermatitis of an infectious nature is contagious - those caused by various microorganisms (herpetic, scabies).
Complications of microbial eczema
If this type of eczema is not treated correctly, complications can occur. As a result of the use of ineffective drugs and after a violation of the integrity of the inflammation, the following occurs:
- Edema spots of a reddish hue (polymorphism);
- Characteristic rashes in the form of vesicles, papules and pustules;
- Spreading areas of weeping nature to healthy areas of the skin. The disease becomes true;
- Diseases of the endocrine system;
- Infections of a bacterial, pyoccal nature;
- Clear signs of erythroderma;
- Herpes virus symptoms;
- Foci of inflammation that are characteristic of neurodermatitis.
General symptoms
Characteristic signs for all dermatitis are hyperemia (redness) of the skin, swelling, local increase in temperature, feeling of heat and itching at the site of the lesion. After prolonged contact with the provoking factor or as the disease develops, a vesicular rash, blisters of various types, skin cracks, scabs, and areas of necrosis appear.
Is microbial eczema contagious?
This type of bacterial disease cannot be transmitted by shaking hands or kissing. This disease is not considered one hundred percent contagious. It can occur in the body of a healthy person only with the simultaneous occurrence of infections of a bacterial or fungal nature.
| Appointment with a dermatologist at the clinic. Call a dermatologist at home. | Reception is strictly by appointment, make an appointment by phone: +7 | Prices for services | Reviews about the clinic |
Classification of types of dermatitis
Allergic contact dermatitis
Develops as a result of contact with an allergen in people with a family history and a history of allergic diseases (hay fever, bronchial asthma). The risk group also includes people who are forced to constantly come into contact with sensitizing factors due to their professional activities.
This type of disease can develop acutely, immediately after interaction with the allergen, or after some time. With constant contact with an irritating substance, the disease becomes chronic.
Allergic dermatitis is characterized by redness, itching, and swelling of the affected areas. Symptoms are more severe in younger patients.
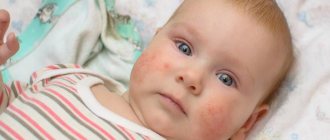
Atopic dermatitis
Most often it develops in childhood and is caused by a hereditary predisposition to allergies and dietary errors. In adults, atopic dermatitis mainly appears due to inspiratory allergens, most often house dust, or medications. The disease is chronic and difficult to cure.
Distinctive features are the localization of lesions on the face, neck, in the elbow and popliteal fossae, armpits, in the groin area, on the scalp, under the earlobes. There is no sharp hyperemia, the lesions peel off, and ichthyosis and keratosis may develop. One of the features of this species is the high probability of secondary infection with bacteria, viruses or fungi.
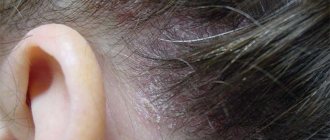
Seborrheic dermatitis
This is a chronic inflammatory process in areas of the skin with a large number of sebaceous glands. The glands produce excess secretion, which becomes a favorable environment for the pathological reproduction of microorganisms that live on the skin under normal conditions - the fungi Pityrosporumovale and Malassezia. Provoking factors for uncontrolled proliferation of fungi can be hormonal disorders, stress, and disruption of the gastrointestinal tract. This type is characterized by seasonal spring and autumn exacerbations.
The lesions are mainly located on the scalp, chest, back, and certain areas of the face. The disease is divided into oily, dry and mixed types. A characteristic symptom is symmetrical areas of inflammation in the form of pink-red plaques covered with whitish scales. With the oily type, the affected areas become wet and yellowish crusts appear on them. Damage to the scalp leads to hair loss.
Toxic-allergic (food) dermatitis
It develops in response to the introduction of an allergen into the body through food, drinks, air, and medications. Additional factors that provoke its occurrence are some chronic diseases.
In the toxic-allergic form, local symptoms (itching, hyperemia, burning) are accompanied by general symptoms of intoxication - weakness, chills, lack of appetite, nausea.
If you are allergic to medications, a severe course of toxic-allergic dermatitis - toxicdermia, the extreme degree of which requires emergency medical care, cannot be ruled out.
Traumatic dermatitis
Inflammatory reaction of the skin in response to mechanical stress. It is local in nature (damage at the site of impact), as a rule, goes away when the traumatic factor is eliminated.
The clinical picture of this type of dermatitis depends on the degree and time of exposure to the damaging factor and the initial condition of the skin. More often it occurs in people with sensitive, dry skin, or, on the contrary, prone to hyperhidrosis, in patients with chronic diseases that are characterized by impaired microcirculation (diabetes mellitus, atherosclerosis).
Manifests itself in the form of abrasions, calluses, including water calluses, calluses, and diaper rash. These manifestations may be accompanied by a secondary infection.
Thermal (cold) dermatitis
Skin reaction to cooling. It manifests itself as inflammatory changes that look like red itchy spots with a surface prone to peeling and cracking. Most often, lesions are located on open parts of the body - face, ears, neck, or closed, but sensitive to cold, hips and knees. External manifestations are often accompanied by a runny nose and conjunctivitis.
Increased sensitivity of the skin to low temperatures is observed in people with diseases of the ENT organs, gastrointestinal tract, and genitourinary tract.
Infectious dermatitis
Caused by bacteria, viruses or fungi. The entrance gates for the entry of microorganisms are microdamage to the skin, abrasions, scratching. It manifests itself in the form of pyoderma - pustular rashes.
In another case, infectious dermatitis is one of the symptoms of various infectious diseases - herpes, rubella, measles, chickenpox. In these situations, the clinical picture will be different, depending on the underlying pathology.
Types of microbial eczema
In medicine, five types of microbial eczema are defined:
- Coin-shaped or plaque-shaped;
- Varicose;
- Sycosiform;
- Post-traumatic;
- Nipple.
In the first type of disease, small round plaques appear in the area of the upper extremities. The boundaries of the inflammation focus are clear. The patient feels a strong blood flow. Swelling and purulent formations appear on the surface of the skin.
The second type is accompanied by varicose veins or venous insufficiency. Swelling appears around the formed ulcer. The body is itchy and itchy, especially at the end of the day. In the third form, the follicles become inflamed. On the body you can see weeping spots of a bright red hue. Lesions are most often found in the chin area and on the lip.
If the healing process of a wound after surgery or an abrasion is disrupted, then the fourth form of the disease occurs. The latter type is most common in women. The nipples become inflamed and itchy. The lesion becomes wet, its boundaries are clearly defined. The disease is very painful.
Common symptoms and manipulations in dermatology:
- Skin rashes
- Calling a dermatologist to your home
- Itching in the urethra
- Itchy skin
- Skin rash
- Prevention of casual sex
- Skin neoplasms
- Pyoderma
- Pityriasis rosea
- Streptoderma
- Scabies
- Peeling skin
- Fungal infections
- Skin infection
- Pus on the skin
- Blisters on the skin
- Papillomas on the foreskin
- Sexually transmitted diseases
- Skin structure
Diagnosis and treatment principles
The diagnosis is made based on the clinical picture, the patient’s medical history, and laboratory tests. If characteristic signs appear - redness of the skin, itching, rashes, you should immediately consult a doctor for timely diagnosis and successful treatment. Depending on the cause of its occurrence, dermatitis should be treated by a dermatologist or allergist. You should not self-medicate, as this can lead to the disease becoming chronic, which will be much more difficult to get rid of.
Basic principles of dermatitis treatment:
- elimination of the irritating factor;
- hypoallergenic diet;
- correct daily routine;
- exclusion of hot baths;
- detoxification of the body;
- antihistamines;
- local treatment - treatment with antiseptics, ointments;
- mild sedatives;
- physical therapy;
- therapy of chronic diseases.
Prevention of microbial eczema
Timely preventive measures can prevent this disease. To do this you need:
- During hygiene procedures, use products that contain substances with a neutral pH value;
- Constantly follow standard rules of personal hygiene;
- Buy and wear clothes based on only natural, safe ingredients;
- Constantly treat your fingernails and toenails with a cosmetic file;
- Eat right, introduce environmentally friendly products into your diet;
- Do not develop chronic infectious diseases. Treat them strictly according to the recommendations of doctors.
These simple requirements can protect the body from inflammation and eliminate even minor painful signs without consequences.
Diet
Diet is very important for the prevention of dermatitis and their treatment in both adults and children. Foods that provoke allergies should be excluded from the menu: citrus fruits, nuts, red fish, eggs, chocolate, honey. It is recommended to limit irritating foods as much as possible - spices, vinegar, salty, spicy and smoked foods. Patients are advised to take light soups, low-fat foods, and fermented milk products. It is necessary to drink enough water.
For infants suffering from atopic dermatitis, it is advisable to continue breastfeeding. At the same time, the mother should exclude allergens from her food as much as possible. If breastfeeding is not possible, the child is prescribed special formulas with a minimum content of cow's milk protein. Complementary feeding is introduced to such children as late as possible, with extreme caution. Each new product and the reaction to it should be recorded in a food diary.
Article sources:
- Characteristics of seborrheic dermatitis. Shukurov I.B., Yakhshieva M.F., Rustamov M.K. Scientific journal, 2018
- Atopic dermatitis of adults. Dvoryankova E., Denisova E., Piruzyan A., Korsunskaya I. Doctor No. 3, 2022. p. 9-13
- Maintenance pharmacotherapy for atopic dermatitis. Petrova I.V., Omarov N.N., Sargsyan M.S., Khamroeva S.A., Osmanova Z.S., Proshin S.N. Reviews on clinical pharmacology and drug therapy, 2022. p. 60-63
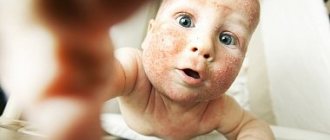
Microbial eczema in children
Infants aged two months to six months, as well as children and teenagers, can develop microbial eczema. Painful signs may appear:
- For hereditary reasons;
- Due to weak immunity;
- For diabetes mellitus;
- In children with a disrupted endocrine system;
- Against the background of ongoing allergic diseases.
The above reasons are associated with hormonal fluctuations. A baby who feeds on mother's milk is not afraid of this disease. Those who are healthy, kept clean, do not suffer from dermatosis.
What to do if microbial eczema appears?
The formation of a weeping, purulent ulcer on the skin can cause serious concern for anyone. In this case, the main thing is not to panic, but to make an appointment with a dermatologist for an examination as soon as possible.
And the easiest way to do this is using the “Your Doctor” service, which provides data from most private clinics in Moscow. You can find out which of them you can call a dermatologist at home or simply make an appointment with him, and then make an appointment directly on the website.
Publication date: 2020-01-07
Answers to frequently asked questions to a dermatologist:
- Treatment of skin diseases
- Consultation with a dermatologist
- Prevention of skin diseases
- Dermatologist appointment
- Examination by a dermatologist
- Pediatric dermatologist
- Skin doctor
- Paid dermatologist
- How to prepare for an appointment with a dermatologist?
- How to get checked for skin diseases?
- What diseases does a dermatologist treat?
- What tests should be taken by a dermatologist?
- What diagnostics can a dermatologist perform in the clinic?
- Where to go with a skin disease?
- What symptoms should you consult a dermatologist for?
- What equipment does your clinic have for diagnosing skin diseases?
- How to call a dermatologist at home?
- What skin diseases are contagious?
- Help from a dermatologist in the clinic
- Dermatologist help at home
- How to make an appointment with a dermatologist?
This article is posted for educational purposes only and does not constitute scientific material or professional medical advice.
Physiotherapy for eczema
Physiotherapeutic procedures have a good effect. They reduce itching and burning. The inflamed areas become smaller. The immune system is being adjusted. Metabolism is restored. The central nervous system calms down and is less excited.
The patient is prescribed the following procedures:
- Light therapy with ultraviolet rays (UVR);
- High frequency electromagnetic field (UHF) therapy;
- Laser therapy;
- Ozone treatment;
- Treatment sessions based on the action of a magnetic field.
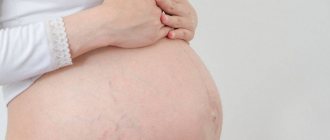
Microbial eczema in pregnant women
Often pregnant women can suffer from dermatosis. Their body undergoes certain changes. The immune system is weakened and hormonal levels are disrupted. There are no particular risks for the fetus or woman. But unpleasant sensations such as itching and a constant desire to scratch create some discomfort. If painful symptoms occur, you should immediately visit a dermatologist.
Methods for diagnosing skin diseases:
- Diagnosis of skin diseases
- Diagnosis of skin diseases at home
- Diagnosis of allergic skin diseases
- Diagnosis of bacterial skin diseases
- Diagnosis of viral skin diseases
- Diagnosis of hair diseases
- Diagnosis of nail diseases
- Diagnosis of skin tumors
- Blisters on the skin
- Dermatoscopy
- Demodex tests
- Diagnosis of sexually transmitted infections
- Mushroom tests
- Skin scraping
Calling a dermatologist to your home for eczema
Calling a doctor to your home depends on the form of the disease. The severity also plays a role. At home, the patient experiences psychological comfort. The doctor can find out all the signs in more detail and draw up a picture of the course of the disease. Prescribe drugs that will have a more powerful effect on the body.
There are cases when the disease is systemic in nature. This requires the participation of other specialists. Consultation with a nutritionist and allergist is necessary. The patient must be in a hospital. Undergo a full examination and course of therapeutic therapy.
Ointments used for microbial eczema
To eliminate pain, patients are prescribed ointments:
- Removing swelling and itching (clobetasol, advantan);
- Which reduce the inflammatory process (triamcinolone, prednisolone);
- Having anti-allergenic, hormonal qualities (hydrocortisone, acriderm);
- Enhancing healing and enzymatic processes (dexpanthenol, ichthyol);
- Necessary for the treatment of hard crusts (fucorcin, boron, sulfur, zinc mixtures);
- Containing antibiotics (tetracycline, erythromycin, etc.).