What is seborrhea?
Seborrheic dermatitis, or seborrhea, is a chronic disorder of the skin epithelium and sebaceous glands, which causes inflammation, pain, itching and flaking of the skin. The disease can develop in different parts of the body, most often on the scalp and face.
Upon examination, areas of inflammation and peeling are observed on the skin. If seborrheic dermatitis is left untreated, the skin and hair follicles suffer, and foci of inflammation with clear boundaries form. The disease leads to excessive hair loss.
Reasons for development
The natural chemical composition of the secretion of the sebaceous glands of the skin contains linolenic acid. It prevents the proliferation of fungi. When the function of the sebaceous glands is impaired (hypo- or hyperfunction), pathogenic microorganisms, including fungi, begin to develop on the skin. They are present on the surface of the skin and are normal, but in small quantities. When the pH of the skin changes, fungi begin to multiply and negatively affect the skin epithelium.
The reasons for the development of seborrheic dermatitis include the following factors:
- proliferation of the yeast-like fungus Malassezia, which changes the composition of the skin microflora;
- prolonged exposure to stress;
- hormonal disorders, which often occur in adolescence, with malfunctions of the thyroid gland;
- adverse environmental influences (for example, water quality, dry indoor air during the heating season, sudden changes in climatic conditions);
- taking certain medications, using cosmetics that cause skin irritation;
- dysfunction of the gastrointestinal tract
- hereditary predisposition.
In addition, the development of seborrheic dermatitis is facilitated by factors such as poor personal hygiene, obesity, and frequent consumption of spicy, salty, and sweet foods.
Scalp dermatitis in conditions caused by immunodeficiency
With an active decrease in the protective properties of the immune system, the fungus rapidly multiplies, moving into the pathogenic phase.
Conditions caused by decreased immunity can be primary or secondary.
In the first case, we are talking about the human immunodeficiency virus.
In the second - about a decrease in immunity in acute respiratory infections, acute respiratory viral infections, diabetes mellitus, and chronic pathologies.
In the case of persistent and prolonged immunodeficiency, dermatitis progresses to a chronic form.
It is extremely difficult to treat effectively.
Usually, medications can reduce the severity of the symptoms of the disease.
But they rarely eliminate it completely.
Symptoms
Fungi on the skin provoke the production of histamine, which causes skin itching and pain. This in turn leads to scratching of the skin and a more severe course of the disease.
With seborrheic dermatitis, skin cells die en masse ahead of schedule, which leads to epithelial detachment and peeling of the skin. Unfavorable skin condition negatively affects the hair structure.
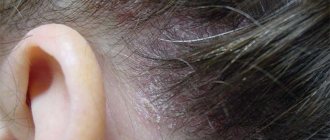
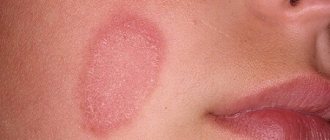
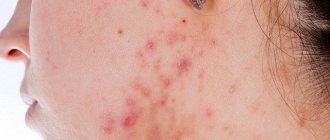
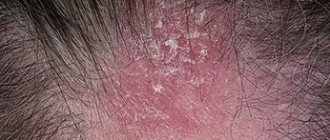
With seborrheic dermatitis, irregularly shaped foci of inflammation with flakes of keratinized cells are observed on the skin. Similar spots of fungus-affected skin can also be observed on the scalp. In severe cases of the disease, dense crusts form on the inflamed skin.
In the case of seborrheic dermatitis on the face, the skin between the eyebrows, in the area of the bridge of the nose, and nasolabial folds is affected. Small yellowish-pink papules merge and form inflammatory plaques covered with grayish-white or yellow greasy scales.
Seborrheic dermatitis has several clinical forms:
| Marginal blepharitis | Dermatitis affects the eyelids, which become yellow-pinkish in color and covered with pityriasis-like whitish scales. Patients complain of a burning sensation in the eyes, moderate itching, slight swelling and redness of the conjunctiva. They are also concerned about photophobia and lacrimation. |
| Seborrheic dermatitis of the external auditory canal | Its manifestations are similar to external otitis. Redness, peeling and itching appear in the area of the external auditory canal. Swelling and cracks are also observed behind the ears. |
| Patchy seborrheic dermatitis | It usually has a chronic course. The skin in the middle third of the forehead, eyebrows and scalp is affected. |
| Lichen asbestos | On the skin of the scalp there is an abundance of white crusts and scales that glue the hair together. When attempting to remove the scales, normal or reddened and swollen skin is exposed. |
Methods of therapy
With seborrheic dermatitis, hair can fall out both on the entire surface of the head and in certain areas (on the back of the head, temples, frontal part). It is better to prevent the problem from developing; it is very important to intervene at an early stage. The treatment is simple. However, the process is very lengthy and requires patience, an integrated approach and consistency. Work is being carried out in a number of areas:
- organization of proper nutrition;
- use of special hair care products;
- physiotherapy;
- drug treatment.
Diagnostics
The symptoms of seborrheic dermatitis are similar to atopic dermatitis, psoriasis, and allergies. To make an accurate diagnosis, you need to consult a specialist. Consultations with a neurologist, gastroenterologist, and endocrinologist may be necessary.
To diagnose this disease, it is necessary to examine the biochemical composition of the blood and hormonal levels. If necessary, ultrasound examination of internal organs, spectral analysis of hair, and skin dermatoscopy are prescribed. A comprehensive diagnosis will help identify the causes of seborrheic dermatitis and prescribe the correct treatment.
Types of seborrhea
Depending on the location of the lesion, seborrheic dermatitis is distinguished:
- faces;
- scalp;
- widespread (face, scalp, upper back and chest are affected).
Depending on the duration of the disease, the following forms of seborrheic dermatitis are distinguished:
- acute;
- chronic.
At the initial stage, dry seborrheic dermatitis develops. It is characterized by brittle hair and excessive flaking of the skin, which falls off onto clothing in the form of dandruff. At this stage, there is a decrease in the secretory function of the sebaceous glands and the disease is not difficult to cure.
In oily seborrheic dermatitis, the sebaceous glands produce excessive amounts of sebum. Dandruff has a yellowish tint, and red inflammatory lesions form on the skin. Oily dandruff quickly makes hair greasy. This disrupts the protective function of the skin. Layered scales cover the inflamed skin. Pain with oily seborrhea is less pronounced than with dry seborrhea. However, skin irritation causes itching and scratching, which further traumatizes the skin.
If the causes of oily seborrhea are not identified and eliminated, then frequent washing will tidy up the hair for a short time. Under the influence of hyperfunction of the sebaceous glands, skin cells quickly die and form areas of flaking and dandruff.
The wrong choice of skin and hair care products aggravates the course of the disease. As a result, the skin is dry, dehydrated, prone to injury and infection.
With a mixed form of the disease, there are signs of dry and oily seborrhea.
Treatment
For any type of seborrhea, it is important to correctly diagnose and choose treatment. To do this, you need to contact a dermatologist or trichologist. Only after a comprehensive examination can a treatment plan for seborrheic dermatitis be drawn up.
It is necessary to wisely choose cosmetic products for the care of the scalp, as well as products with antifungal effects and normalizing the function of the sebaceous glands.
For seborrhea of the scalp, shampoos with antifungal components (zinc pyriton, ketoconazole, naftalan oil, tar) are indicated. These shampoos not only eliminate fungi, but also reduce inflammation, swelling and itching.
Antihistamines are used to eliminate skin irritation and itching.
If there are dense layers of scales on the skin, then drugs are used to soften them. Then apply external agents with antifungal components. For severe seborrheic dermatitis, antifungal drugs are prescribed orally for 1-2 weeks.
Depending on the location of seborrhea, gels, ointments, shampoos, aerosols, and tonics are used to cure it. In this case, the individual tolerance of certain drugs is taken into account.
A good effect is observed from taking combination drugs that include glucocorticosteroids, antibiotics and antifungals. Medicines with this composition act on several causes of the disease at once:
- glucocorticosteroids have anti-inflammatory, antiallergic, antipruritic effects and reduce the secretion of exudate;
- the antifungal component suppresses the development of the Malassezia fungus;
- An antibiotic destroys pathogenic bacteria.
Additional recommendations
During the treatment period, you must adhere to the following recommendations:
- Avoid cosmetics, as they can lead to skin irritation and allergies.
- Men who have seborrheic dermatitis on their face should not shave with blades. To remove hair, it is better to use a gentle method - use an electric razor once every 2-3 days.
- Instead of washing your face every day, it is useful to wipe your face with special lotions designed for people with skin diseases. Lotions based on micellar water cleanse the skin and enhance its recovery processes.
- It is not recommended to use soap to cleanse the skin, as it disrupts the activity of the sebaceous glands. It is better to use medicated washing gels and shampoos that do not contain soap, dyes and fragrances. Preparations based on deresined naphthalan, extracts of burdock, Japanese Sophora, and vegetable oils are effective.
- Physiotherapy is useful for improving blood circulation in the skin, normalizing metabolism and rapid healing of inflammation. A good effect is observed from the use of cryotherapy, cryomassage, laser and magnetic therapy of skin lesions, as well as darsonvalization.
- To achieve stable remission, it is necessary to treat diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. Avoid foods that contribute to the development of seborrheic dermatitis. These are fatty, fried, sweet foods and dishes. Lean meat, vegetables, fruits, and dairy products are healthy. The diet includes foods with a high content of vitamins B, A, C, as well as zinc and selenium.
- The environment has a significant impact on the condition of the skin. In hot and humid climates, the activity of the sebaceous glands increases, which contributes to the proliferation of fungi on the skin. At home, it is recommended to use dehumidifiers. Patients with seborrheic dermatitis should not visit saunas and steam baths.
Complications
Without treatment, seborrheic dermatitis can spread throughout the scalp and may affect the eye and eyebrow areas. Over time, foci of layered keratinized cells form on the skin and the development of streptoderma is possible. Crusts in places of inflammation tend to crack, which leads to the formation of wounds and their infection.
With seborrhea, increased hair loss is possible, and patchy baldness (alopecia) may appear.
When the foci of seborrheic dermatitis merge, seborrheic erythroderma is formed. Reddened, scaly areas merge, there may be an increase in body temperature to 37.1 ° C - 38 ° C.
If the signs of seborrheic dermatitis are accompanied by weeping and cracking of the skin, then seborrheic eczema develops.
In order not to encounter complications of seborrheic dermatitis, it is necessary to strictly follow the treatment prescribed by the doctor and not replace it with traditional medicine.
Prevention
To prevent seborrheic dermatitis, you need to monitor your health and follow the following recommendations:
- Select hair care products according to the characteristics of your skin and hair.
- Maintain good hygiene. Regular hair washing eliminates favorable conditions for the proliferation of pathogenic bacteria and fungi.
- Consult a specialist who will select a shampoo with the optimal pH for hair care. To do this, you need to understand the composition of their components. Therapeutic shampoos gently cleanse the skin of dandruff and have a beneficial effect on the condition of the hair.
- Nutrition has a great influence on the condition of the skin and hair. Sufficient amounts of fiber, vegetables and fruits in the diet help improve digestion, strengthen the immune system, and improve skin condition.
- You should also pay attention to hair styling products. They should not cause allergies and should match your hair type. It is not recommended to frequently dry your hair with a hairdryer, as drying your hair and skin contributes to the development of seborrheic dermatitis.
If you notice signs of seborrheic dermatitis, contact a professional. RTH specialists will determine the cause of the disease and draw up an individual treatment plan.
Necessary prevention
Unfortunately, not all types of alopecia can be prevented. But in some cases, prevention can be a salvation from baldness.
Necessary preventive measures:
normalization of hormonal levels
· stress reduction
· normalization of sleep and rest patterns, proper nutrition
· performing physical exercises that improve blood circulation and lymph flow
· use of high-quality cosmetics
· preventive examinations and exclusion of diseases that indirectly affect the condition of the hair
The Nanoesthetic Center for Medicine and Aesthetic Cosmetology offers a number of procedures that improve the condition and growth of hair.