What are the most common warts?
Most often (up to 70% of all cases), patients report warts that bother them, and the majority of patients are school-age children. Warts are also found in 20% of students. Plantar warts are more common in adults (34% of cases), as opposed to flat warts, which are again more common in children (4% of all warts).
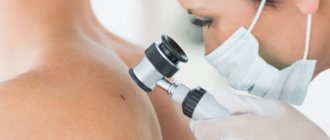
An experienced dermatologist can easily determine the type of wart during a consultation. However, in rare cases, especially if the wart is injured, it is difficult to diagnose it only by examination, and then the doctor can perform a biopsy of the derivative and histological examination.
general information
Such formations can have different shapes and sizes. They often appear on the knees, elbows, fingers; It is not uncommon to see warts on the face and scalp.
These benign neoplasms do not change their appearance for a long time, but can spontaneously disappear without treatment and just as suddenly appear again.
Warts cause aesthetic discomfort. In addition, they can be constantly injured when shaving, clothing, or a comb. This increases the risk of inflammation and bleeding.
To learn how to get rid of warts, you must first determine their type. It is difficult to do this on your own, so you will need the help of a doctor.
Can warts cause complications?
Warts usually do not cause complications unless they grow, become painful when walking, and cause psychological discomfort for aesthetic reasons. In rare cases, injuries can spread to adjacent areas.
Patients with a significant defect in the immune system (for example, immunodeficiency of various origins) retain the theoretical possibility of malignant formation of a simple wart, although this does not occur in everyday practice. This is in contrast to genital warts, which can also be caused by oncogenic types of human papillomavirus (HPV). Thus, to avoid the complications listed above, radical removal of warts is recommended in all cases.
Wart removal
Although scientific literature suggests that with a good immune system, warts can disappear on their own within a few years, medical practice shows the opposite. The main problem with treating warts is that there is currently no method or medicine to remove the virus itself, so a doctor cannot guarantee a 100% cure. All treatment is aimed at removing the wart itself, but does not prevent HPV recurrence.
Basic ways to remove warts:
- Laser;
- Cryodestruction with liquid nitrogen;
- Medicines;
- Removing warts surgically.
Ideally, wart removal should be carried out by an experienced dermatologist, since incorrectly prescribed treatment may not only not help, but also worsen the situation. Warts are treated only by radical removal, which, as already mentioned, can be carried out with a surgical laser, liquid nitrogen or special drugs.
Our center uses any of the above methods for removing warts. In each case, the treatment method is selected individually.
Zolotov Sergey Alexandrovich
- Candidate of Medical Sciences, surgeon, specialist in laser surgery.
- From 2003 to 2009 completed training at the State Budgetary Educational Institution of Higher Professional Education "Russian National Research Medical University" named after. N.I.Pirogov Ministry of Health of Russia.
- From 2009 to 2011, he completed his residency at the Moscow State Budgetary Healthcare Institution, Research Institute of Emergency Pediatric Surgery and Traumatology, specializing in Pediatric Surgery.
- In 2011, he completed training under the program of additional professional education of doctors in laser medicine at the State Scientific Center for Laser Medicine of the Federal Medical and Biological Agency of Russia. From 2011 to 2014, he studied full-time graduate school at the Moscow State Budgetary Healthcare Institution Research Institute of Emergency Pediatric Surgery and Traumatology.
He has extensive experience in removing various benign formations of the skin and subcutaneous tissue using laser surgical methods.
More than 5 years of experience in surgery.
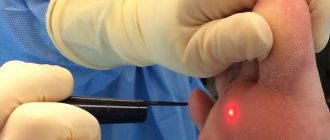
Laser wart removal
The procedure is performed under local anesthesia after the doctor has administered painkillers. Depending on the size of the derivative, laser removal of warts takes up to 15 minutes. After the procedure, a bandage is applied and medications are prescribed to lubricate the wound as it heals.
Laser wart removal
The main advantage of laser wart removal is that just one procedure is enough to make the wart that bothers you disappear forever. In addition, this treatment method is the most common among patients and has the best reviews, since laser warts are removed from:
- faces;
- palms and feet;
- genitals.
Human papillomavirus infection of the skin (papillomatosis, or warts) is caused by human papillomaviruses (HPV). The HPV group is the DNA-containing papovaviruses ( Papovaviridae
) size 40-50 nm.
More than 100 types of HPV are known, of which more than 40 can cause damage to the anogenital tract (genitals and anus) and the appearance of genital warts.
Warts are one of the most characteristic clinical manifestations of HPV infection. The histological picture is characterized by proliferation of the epidermis with impaired keratinization, vacuolization of cells and hypertrophy of the papillary dermis [1].
There are vulgar, flat, plantar, filiform and genital warts.
Types of warts
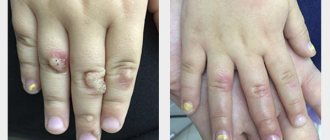
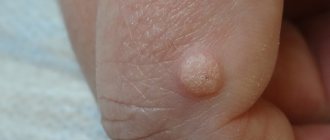
Vulgar (simple) warts
account for up to 70% of all skin warts and occur mainly in school-age children. These are round papules the size of a pinhead to a pea, with an uneven, keratinized surface, grayish, yellowish-brown or flesh-colored, which can merge with each other. The favorite localization is the hands, but they can appear on the face, red border of the lips and, extremely rarely, on the mucous membrane of the mouth. Usually among the warts there is the largest one - the “maternal” one. When the mother's wart is removed, all the others often disappear as well.
Flat (juvenile) warts
are less common (4%) and are observed mainly in children and young people. They are small in size, have a smooth surface, the color of normal skin or are slightly yellowish, and rise above the skin level. The shape can be round or polygonal. Flat warts are characterized by multiple rashes of elements, mainly on the back of the hands and feet, face, and oral mucosa. Flat warts can be localized on the skin of the penis, cervix, and rectum.
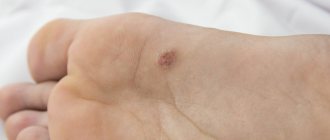
Palmoplantar warts
common among adults and young people and occur in 34% of skin warts. They appear in the form of dense formations with horny layers. Plantar warts are the most difficult to diagnose: they must be distinguished from calluses, calluses, and horny syphilitic papules of the soles.
Palmoplantar warts are most often observed on areas of pressure from ill-fitting shoes and can cause pain when walking. In patients with excessive sweating of the hands and feet, warts spread quickly and are difficult to treat.
Filiform warts
They are soft papules, flesh-colored to dark brown, often pedunculated. They are often located on the neck, skin of the eyelids, in the armpit, groin area, and under the mammary glands. Their size is usually 1-4 mm, but sometimes reaches 3 cm or more in diameter.
A pronounced tendency to autoinoculation (self-infection) proves the viral origin of filamentous warts, and the frequent combination with diabetes mellitus, obesity, pregnancy, and menopause indicates that they are hormonally determined.
Genital warts (genital warts)
are usually localized in the intergluteal folds, on the skin of the perineum, and external genitalia. The appearance of genital warts is promoted by secretions that occur during inflammatory diseases of the genital organs. Sexual transmission is also possible. At first, genital warts appear as soft, papule-like, pointed nodules that tend to coalesce into tumor-like conglomerates with a surface resembling a cockscomb or cauliflower (giant genital warts). In genital warts, the hyperplastic epidermis retains its typical structure, although keratinization is disrupted (parakeratosis). Typically, condylomas are caused by HPV types 6-11; their malignant degeneration occurs rarely.
Causes of warts
HPV is transmitted through contact from people or animals suffering from diseases caused by HPV, as well as through contact with a virus carrier who does not have clinical manifestations of the disease. Intensive reproduction of HPV occurs in the superficial layers of the skin. Another type of infection spread is autoinoculation (self-infection). For example, warts in the periungual area are observed mainly in people who have the habit of biting their nails, and the appearance of flat warts on the cheeks, chin and legs can be caused by shaving, hair removal, and cosmetic peeling.
The “gate” for virus penetration is microtrauma of the skin (abrasions, cracks). Infection can occur in swimming pools, baths, and gyms. People who cut meat, fish and poultry often suffer from warts on the hand and forearm (“butcher’s warts”).
The incidence of warts has not been studied, but, according to various sources [2, 3], they occur in 10% of children and adolescents, most often in the age group of 12-16 years.
Treatment methods
Therapy for HPV infection is reduced to treatment aimed at removing areas of altered epithelium along with viruses. For this purpose, along with surgical methods, podophyllin, podophyllotoxin, liquid nitrogen, laser, electrocoagulation, acids and mixtures of acids are used.
Surgical methods
Cold treatment (cryodestruction).
The advantage of the method is the ability to treat extensive lesions. Side effects include pain during treatment, the formation of erosions and ulcers, and the occurrence of hyperpigmentation (darkening) of the skin.
Coagulation
using electrosurgical instruments or laser. In recent years, this method has been increasingly abandoned, since the smoke can be potentially dangerous, more for the doctor than for the patient. A high risk of HPV infection for a surgeon through smoke generated by tissue evaporation has been proven. A mask of any density is not effective. Unfortunately, unpleasant localizations of warts when infected through smoke are the pharynx, larynx, respiratory tract, mouth and nose.
Surgical excision
effective, but has a certain relapse rate. 63-91% of patients are cured.
Local drug treatment
In modern conditions, local drug treatment is most preferable.
Podophyllin
(podophyllin). A resin obtained from plants that has a cytotoxic effect. Usually a 10-25% solution is used on an outpatient basis 1-2 times a week for no more than 5 weeks.
Podophyllotoxin
(podophyllotoxin) is the most active substance in podophyllin. It is the active ingredient of several well-known old drugs, including those prepared in pharmacies.
Oxolinic ointment 3%
(unguentum oxolini 3%). Has virucidal activity. To remove genital warts, apply 3% ointment 2-3 times a day for 2 weeks to 2 months. Wax paper is placed on top. In general, this treatment method is complex and not effective enough.
Feresol
is a mixture of phenol (60%) and tricresol (40%). Condylomas are treated with a break of 1 week. The mechanism of action of this drug is a chemical burn, so its use is possible only in medical institutions and not in all patients. At the same time, effectiveness is balanced with safety, since there is always a risk of under-treatment or excessively deep or extensive exposure, including scarring.
Trichloroacetic acid
at a concentration of 80-90% it is a weak destructive chemical that causes the formation of local necrosis. Recommended for mild cases and pregnancy. Unfortunately, the relapse rate with this treatment method is quite high.
Various mixtures of organic and inorganic acids
, produced by pharmacies (nowadays rare). They have a coagulating effect on altered tissues. Treatment of condylomas with such drugs is carried out using a special applicator, which allows the drug to be applied locally to the formation, preventing it from spreading to surrounding tissues. The procedure is painless. The break between sessions can be 1-4 weeks, the scab disappears on the 3-5th day.
Apparently, the best known method of combating HPV infection, both in terms of simplicity and effectiveness, is modification of the acid treatment method
- in the form of finished preparations containing both salicylic and lactic acids.
Salicylic acid has a keratolytic effect and has antimicrobial activity. Lactic acid causes chemical destruction of warts.
In practice, salicylic acid has been used for many years in different concentrations - from 15 to 60% (most often 15-26%; without lactic acid). According to numerous data [4], the effectiveness of such treatment reaches approximately 60-75%.
To treat warts in modern conditions, special varnishes are used in the form of elastic collodion, into which a combination of salicylic and lactic acids is introduced. This varnish is used to remove calluses, warts, etc. When applied to the skin, the varnish hardens in the form of a thin film, which is quite strong and prolongs the medicinal effect.
If necessary, the film from the skin can be removed by intense mechanical action or easily - with gasoline. The varnish has the ability to penetrate deeply into the skin, which has a positive effect on the effectiveness of treatment.
This varnish can be made ex tempore, according to a doctor's prescription. But currently there is a ready-made dosage form in the form of Collomac varnish.
Collomak
is a modern multicomponent drug that contains active ingredients: keratolytics - salicylic (20%) and lactic (5%) acids, emulsifier polidocanol 600 (2%), as well as special fillers that form the basis of the varnish dosage form, a film-forming substance ( ethylcellulose 5.5%), plasticizer (dibutyl phthalate 1%), solvents (acetone 6.65%).
Polidocanol, a component of Collomac
, plays another important role: it causes sclerosis and obliteration of small veins and arteries at the base of the papilloma.
Collomak
applied to a wart or callus, after which the horny layers are easily removed.
If necessary, this treatment is repeated several times. To avoid damage to the surrounding skin when applying Collomac
, it is protected with indifferent zinc paste.
You can protect the surrounding skin with adhesive tape by cutting a hole in the middle. The duration of treatment is determined depending on the effectiveness of the drug. For adults, the maximum dose of Collomac
is 10 ml/day, which corresponds to 2 g of salicylic acid;
for children - 1 ml, which corresponds to 0.2 g of salicylic acid. It is not recommended to exceed this dose and treat several areas of the skin and mucous membranes at the same time. During pregnancy, the use of Collomak
is permissible only when applied to a limited surface (no more than 5 cm).
When using the drug in the maximum daily dose in adults and children, the duration of treatment should not exceed 1 week. Positive experience with the use of Collomac
allows us to recommend this drug for widespread use in gynecological and dermatological practice in the treatment of warts, including genital warts [5].
Modern local drugs for the treatment of HPV have undoubtedly made a big step forward compared to the methods used previously. This progress is a consequence of perfecting finished dosage forms from previously known ingredients. In combination preparations, the effective properties of their predecessors - single preparations - are preserved and enhanced and the disadvantages are eliminated, primarily excessive resorption and fairly extensive local irritation.
This is exactly how we see the emergence of modern combination drugs for the treatment of HPV, which are now undoubtedly the drugs of choice.
Removing warts with nitrogen
This is an alternative to laser wart removal. The method is also quite popular, but usually requires several procedures, they are quite painful, and after cryodestruction with liquid nitrogen a painful bubble forms. Therefore, removal of condylomas with liquid nitrogen is recommended only for older children and adults.
Removing warts with nitrogen
Cryodestruction is repeated every 2-3 weeks until the final disappearance of condylomas. Usually 6 sessions of liquid nitrogen treatment are sufficient, but if the wart still persists, other treatment options are considered. In addition, destruction with liquid nitrogen is not suitable in cases where the wart affects the area of the fingers and thighs.
Removing warts with medication
Destroying acids such as salicylic acid, trichloroacetic acid, urea and other special medicines are also wart removers. Any pharmacy offers a fairly wide selection of such drugs.
Salicylic acid, urea softens the top layer of the wart, in addition, stimulates the local immune response, and hence the disappearance of the wart. But when choosing to treat warts with medications, you need to be patient, because even if you use the product in strict accordance with the instructions, the effect becomes noticeable only after a few months.
Removing warts with medication
In addition, constant use of the drug is required according to a special scheme in compliance with certain skin care rules. Sometimes it causes discomfort to the patient and also the medicine has side effects such as skin irritation, redness, etc.
Therefore, many patients make a better decision - see a dermatologist and remove warts in faster and safer ways.
Diagnostic methods
Before starting home treatment, you need to consult a dermatologist to confirm the diagnosis. Self-medication can be dangerous, especially if it is misdiagnosed. The doctor will carefully examine the tumor and, if necessary, prescribe tests to exclude a malignant process.
What additional diagnostic methods may be prescribed:
| Research method | Explanation |
| Dermatoscopy | Primary method for diagnosing dermatological diseases. Under 10x magnification, you can examine the edges, color and shape of the formation in detail. Dermatoscopy is indicated for all patients before starting treatment. |
| Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) | Allows you to identify the causative agent of the disease. Using the test, you can determine the type of HPV. |
| Histological examination | It is carried out when a malignant nature of the formation is suspected, as well as during surgical removal of a wart. |