Pathogenesis
Comedones occur as a result of excess sebum synthesis and disruption of the keratinization process - the formation and exfoliation of cells in the stratum corneum of the skin. As a result, characteristic plugs are formed at the mouth of the hair follicles, which fill them. Thus, sebum loses the opportunity to leave the follicle and begins to accumulate in it, forming cysts.
The removal of toxins through the pores of the skin is also impaired. They interact with sebum, forming a thick, glue-like mass. A mixture of toxins, sebum, partially released from the narrowed mouth of the follicle, as well as skin bacteria and dust, becomes dark under the influence of oxygen. This is manifested by the formation of black dots on the skin. When the orifice is completely blocked, the follicle greatly increases in volume, which leads to the formation of a white nodule.
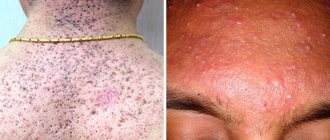
Open comedones on the back and acne on the face. Photo: Chinese Medical Journal / Open-i (CC BY-NC-SA 3.0) and Roshu Bangal / Wikipedia (CC BY-SA 4.0)
Classification of comedones
In clinical practice, comedones are divided into 2 types:
- Open. They are plugs of sebum and skin cells that block the entrance to the hair follicle. Oxidizing upon contact with air, they become black, which is why they look like black dots with a diameter of 0.5-1.0 mm.
- Closed. Clogged hair follicles, which, due to the secretion accumulated in them, expand, forming small cysts. On the skin they look like nodules about 1 mm in diameter, white or reddish.
Since comedones are one of the manifestations of acne, in clinical practice the American Academy of Dermatology classification is used to assess skin lesions. It includes 4 degrees of disease severity:
- I degree. The presence of comedones and up to ten papules - small pink blisters, sometimes with a black dot in the center.
- II degree. A combination of comedones and papules, with the appearance of no more than 5 pustules - pustules.
- III degree. Combination of comedones and papulopustular rash. In this case, no more than five nodes appear on the skin.
- IV degree. Severe inflammation of the skin with the formation of painful nodes and cysts.
Also, to assess the severity of comedonal lesions, the Cook scale² can be used, which evaluates the severity of the pathological process in points:
- 0 points. The presence of several small comedones or papules, which are noticeable only upon careful examination.
- 2 points. There are 1-2 open or 20-30 closed comedones on the skin. At the same time, up to ¼ of the surface of the facial skin is covered with small papules in a total number of up to 6-12 pieces.
- 4 points. Small papules or comedones are observed on more than ½ of the facial skin. There may also be several pustules and large comedones protruding above the surface of the skin.
- 6 points. About ¾ of the face is covered with papules and/or large open comedones, which are combined with many pustules.
- 8 points. Skin rashes are located on almost the entire surface of the face, large pustules appear.
Figure 1. Open and closed comedones. Image: mikrostoker/Depositphotos
Closed comedones32
They are also called whiteheads. In a closed comedone, the SVF is filled and slightly swollen. The outlet is almost invisible. The diameter of acne elements varies from 0.1 to 3 mm. Such formations can already be palpated, that is, if you run your hand over them, they can be felt.
Sometimes small closed comedones can resolve spontaneously in 3-4 days. Large formations can remain on the skin for a long time without causing discomfort or developing into another form of acne. But the risk of transforming closed comedones into inflammatory acne is present, and it is much higher than that of open comedones. In bright light and under a magnifying glass, such acne elements are clearly visible, especially when the skin is stretched.
A type of closed comedones are macrocomedones, which are often localized above the joints, on the cheeks. They can reach a size of 3 mm or more.
Symptoms of comedones
Early signs of comedones are roughening of the skin and visually noticeable enlargement of pores, which is often combined with increased oiliness and a tendency to peeling. In this case, the color of the skin often changes - it may acquire a grayish or greenish tint.
Next, comedones are formed directly. Externally, depending on the type, they appear as black dots or white nodules. The last few protrude above the skin level and are prone to inflammation, which leads to redness of the skin and moderate pain when touched.
Most often, comedones are located on the skin of the face, upper chest and back. The quantity depends on the individual characteristics of the body, concomitant diseases and can range from 3-7 to 100-150 pieces.
Treatment: general points
The abundance of factors contributing to the occurrence of acne directly affects the nature of effective treatment for this disease. To solve the problem in this case, an integrated approach is required, including the use of a number of acne products from the pharmacy range.
To begin with, here are some general recommendations that can be briefly mentioned in a conversation with a buyer. They can not only help him fight the disease, but also increase his loyalty to the pharmacy.
The first is advice to treat concomitant diseases and sanitize infectious foci. To do this, it is necessary to undergo an examination by an endocrinologist, gynecologist, dermatologist, gastroenterologist, therapist, dentist or otolaryngologist - depending on the patient’s medical history.
The second is a recommendation to follow a diet. The appearance of acne and comedones is promoted by foods rich in carbohydrates. You should limit easily digestible sugars (cakes, cakes, sweets, chocolate), spicy foods and marinades. Food should contain enough vegetables and fruits. As a supplement to the diet, specialized foods containing fiber (for example, bran) can be recommended.
The third is an offer to undergo physiotherapeutic procedures. In particular, the UFO course has a good effect. Ultraviolet irradiation has a drying and bactericidal effect. Additionally, cryotherapy, darsonvalization and laser therapy are used.
Risk factors
In addition to the main reasons, there are a number of factors that increase the risk of developing comedones. The most significant include:
- Hereditary predisposition.
- Frequent stress and emotional overstrain, lack of sleep.
- Natural fluctuations in hormonal levels, including during puberty and the transition to menopause.
- Endocrine diseases: hyperthyroidism, diabetes mellitus type 1 and 2, polycystic ovary syndrome, hyperandrogenism.
- Poor nutrition: excessive consumption of flour and confectionery products, whole milk products, fatty and fried foods.
- Smoking and excessive consumption of alcoholic beverages.
- Pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract: gastritis, peptic ulcer of the stomach and duodenum, dysbacteriosis.
- Friction or pressure on the skin, such as the use of mobile phones, helmets, tight collars and backpacks.
Pregnancy and the onset of menopause
One of the important triggering factors for comedones is hormonal imbalance.
Quite often this is due to a change in the ratio between male and female sex hormones (androgens and estrogens). Natural hormonal changes in the body, for example, occur during pregnancy and at the beginning of menopause. The sebaceous glands are also part of the endocrine system and are controlled by androgen receptors. Steroid sex hormones (dihydrotestosterone) are responsible for the synthesis of sebum. As a result of sharp fluctuations in the ratio of androgens and estrogens, the synthesis of sebum is stimulated, and the division of cells in the stratum corneum of the skin increases, which often leads to the formation of comedones.
Development mechanism
The development of acne is promoted by a huge number of factors, which can be divided into several groups.
Physiological factors:
- The proliferation of acne-causing bacteria is Propionibacterium acnes. The contents of the sebaceous glands with keratinized epithelium serve as a suitable environment for this.
- Hormonal disorders. This is why acne often appears during hormonal changes in the body (adolescence, premenstrual period, pregnancy, abortion). Increased levels of the male sex hormone, testosterone, also contribute to the appearance of acne. Therefore, acne often develops with hyperandrogenism.
- Diseases of the digestive system. More than half of the cases of acne are associated with the presence of chronic diseases of the stomach and intestines, especially with a violation of the intestinal biocenosis.
- Increased production of sebaceous glands. Increased production of sebum leads to its thickening and weakening of its bactericidal properties. As a result, blockage of the excretory ducts occurs.
- Hyperkeratosis is increased keratinization of skin cells. Dead cells further clog the ducts of the sebaceous glands.
- Disturbances of the microbial flora of the skin.
- Hereditary predisposition.
- Immune disorders.
- Chronic foci of infection.
Lifestyle factors:
- A state of prolonged stress.
- Nutrition. The appearance of acne is promoted by a diet with a predominance of carbohydrate foods, seasonings and spices.
- Long-term use of cosmetics that clog the pores of the sebaceous glands: powder, foundation, blush and fatty creams.
- Violation of personal hygiene rules - insufficient cleansing of the skin and squeezing out blackheads.
Other factors:
- Prolonged contact with toxic and polluting substances.
- Taking certain medications (for example, glucocorticoid hormones).
- Humid and hot climate.
Complications of comedones
With prolonged exposure to trigger factors, as well as improper treatment, comedones can lead to various dermatological complications. The most common among them are:
- Ostiofolliculitis. Inflammation of the hair follicle or sebaceous gland. Externally it resembles a subcutaneous node. In this case, the skin over the boil becomes thinner, becomes bluish, and a white dot appears in the center - a purulent core.
- Intradermal cysts. They are a subcutaneous cavity formation and are the result of purulent melting of inflamed comedones. After healing, a rough connective tissue scar is left.
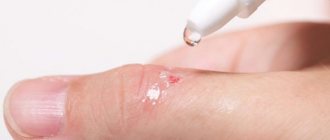
Is it possible to squeeze out comedones?
Despite the fact that one of the treatment options for this pathology is facial cleansing with mechanical removal of comedones, you cannot squeeze them out yourself. Possible complications:
- Post-inflammatory erythema. Redness of the skin, a residual phenomenon after inflammatory skin lesions. It occurs as a result of damage to local blood vessels or due to strong pressure on the skin, including when trying to squeeze out a comedone on your own.
- Pyoderma. When manually removing a comedonal rash, there is a high risk of introducing infection (pathogenic staphylococci and streptococci) into the damaged follicles. In addition to ostiofolliculitis, such actions can provoke the appearance of a boil, carbuncle, various forms of impetigo and other variants of pyoderma.
- Scarring. Rough mechanical impact on comedones, especially closed forms, often leads to deep skin damage and the formation of persistent connective tissue scars that look like pink or whitish stripes or spots.
Diagnostics of comedones
The diagnosis is established by external examination of the affected areas of the skin by a dermatologist. If necessary, dermatoscopy is performed - examination using magnifying glasses of a dermatoscope.
Interviewing the patient also plays an important role, helping to identify existing risk factors and concomitant diseases. If the latter are present, additional consultations with related specialists (for example, an endocrinologist), laboratory or instrumental studies may be prescribed.
Differential diagnosis of comedones is carried out with other skin diseases that may have similar manifestations. These include:
- Hyperplasia of the sebaceous glands.
- Warts.
- Milia.
Treatment of comedones
Therapy must be comprehensive. This involves treating not only skin lesions, but also eliminating the cause of their appearance, for example, prescribing hormonal therapy for endocrine pathologies. The fight against comedones directly includes the use of medications and mechanical removal of acne.
Drug therapy
An effective method of treating comedones is the use of comedolytics (retinol, retinoic acid, zinc, salicylic acid). These are medications that can prevent blockage of the hair ducts, normalizing the growth of skin cells and the secretion of sebum.
Mechanical removal of comedones
A dermatologist or cosmetologist can remove comedones mechanically. In this case, a Uno spoon or a Vidal needle is used. As a preliminary preparation, skin cleansing can be carried out - chemical peeling and microdermabrasion. Their goal is to remove particles of dust, bacteria and sebum from the surface of the skin, thereby preventing the development of complications. After the procedure, special cosmetics with anti-comedogenic properties are applied to the skin.
Other methods of cleaning the skin are also used:
- Disincrustation. It involves removing comedones using weak current discharges.
- Ultrasonic cleaning. The technique is based on the use of ultrasonic waves that gently cleanse pores. Helps improve the overall condition of the skin.
- Vacuum cleaning. The essence of the technique is to remove plugs using a vacuum.
You can’t squeeze out comedones yourself! Only a cosmetologist or dermatologist can remove comedones. Photo: kukuruzaphoto / freepik.com
Causes of acne
All causes of acne development can be divided into exogenous and endogenous.
Exogenous ones include41,50,29:
- Skin injury. Wearing uncomfortable, tight, chafing clothing can cause skin irritation and acne. Squeezing pimples also promotes inflammation, infection, and triggers the proliferation of pimples.
- Wrong choice of cosmetics. The content of comedogenic components in cosmetics can cause a rash. Constantly drying out the skin with lotions containing alcohol can cause the skin to produce more sebum for hydration.
- Taking medications. Systemic glucocorticosteroids, anabolic steroids, and cytostatics can provoke acne.
- Poor nutrition. Dairy, sweet products, coffee, fatty foods, as well as those rich in iodine, bromine, glucose, sucrose - the presence of all this in the diet will have to be reconsidered, since these are the main food provocateurs of acne.
Endogenous factors are identified through additional diagnostics and testing41,50,29:
- Endocrine pathologies. These include thyroid diseases, PCOS, pituitary adenoma, etc.
- Vegetovascular dystonia. If the autonomic innervation of precapillaries, microvasculature, arterioles, and capillaries is disrupted, then this pathology can also be considered as an acne trigger.
- Chronic diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. Chronic gastritis, ulcers caused by H. pylori, gastroduodenitis can lead to the appearance of acne on the skin.
Acne can also be caused by stress, genetic factors, immunodeficiency and other conditions41, 29.
Alternative therapy
In the fight against comedones, especially against the background of acne, the following natural remedies can be an effective addition to the main treatment³:
Tea tree oil. Gels containing at least 5% tea tree oil can be as effective as benzoyl peroxide lotions. Possible side effects include mild itching, burning, redness and dry skin.
Brewer's yeast. When taken internally, a strain of brewer's yeast called Hansen CBS may help reduce acne. A common side effect is increased gas production in the intestines (flatulence).
Why retinol?
Retinoids are a group of drugs based on vitamin A, represented by retinol and its derivatives.
The Global Alliance of Dermatologists and Cosmetologists, based on many years of research, clinical observations and treatment of patients with problem skin, has come to the conclusion that
Retinoids are the N1 substance in acne therapy.
Russian experts classify retinoids as first-line drugs for the treatment of problem skin with acne.
The term “1st line” means that they are recognized as the most effective and it is worth starting therapy with their prescription.
One of the main goals of acne treatment is not just to stop the process and get rid of acne, it is important to prevent the appearance of scarring. After all, getting rid of scars is almost impossible!
For a detailed understanding of the reasons for which the Global Alliance of Dermatologists and Cosmetologists made this conclusion, let’s begin the analysis by listing the points where retinol works for acne.
Features of nutrition and skin care
Nutritional correction for comedones involves excluding from the diet foods that increase sebum production. First of all, these are foods with a high glycemic index or fast carbohydrates. These include:
- Confectionery.
- Chocolate.
- White bread and pastries.
- Sweet carbonated drinks.
- Dairy and fermented milk products: milk, kefir, yogurt, fermented baked milk, cottage cheese, cheese.
- Trans fats: fast food and processed foods.
- Alcohol, coffee.
Why do comedones “love” those with a sweet tooth?
Consumption of large quantities of confectionery products is associated with a sharp increase in blood glucose levels, which entails a response increase in the production of insulin by the pancreas.
The hormone insulin takes part in the activation of androgen receptors in the sebaceous glands, while simultaneously increasing the level of dihydrotestosterone. As a result, sebum production increases, which is one of the provoking factors for the appearance of comedones. Whole milk and refined foods also contribute to a sharp increase in glucose and insulin levels. Figure 2. Products that provoke the appearance of comedones. Image: artcherich/freepik.com
We also note a number of products that can help to cleanse the skin faster and prevent the appearance of new comedones. This list includes:
- Products rich in zinc: chicken and beef liver, boiled beef tongue, roast beef, pumpkin and watermelon seeds, pine nuts.
- Fatty varieties of sea fish rich in omega-3 fatty acids: mackerel, tuna, sardines, salmon, cod liver.
- Vegetables and berries: carrots, sea buckthorn, parsley, celery, raspberries, blueberries, black currants.
Caring for problem skin at home should take into account the following tips and recommendations:
- Regular cleansing of the skin with special products for excessive oiliness. At the same time, cosmetics should not foam, contain alcohol or surfactants. You can also use toners containing comedolytics for additional cleansing and moisturizing.
- When using creams, you should give preference to products with a more liquid texture, without intense fatty components.
- Application of peelings and polishing agents. These procedures and medications allow you to maintain the effects of the treatment at home. In this case, you should choose products with a low concentration of active ingredients and avoid harsh scrubs.
Hollywood Secrets
Many people, including world-famous people, are prone to skin problems. They use different approaches to combat acne and comedones. For example, Megan Fox makes oxygenating and restorative face masks and cleanses her skin daily morning and evening. Cameron Diaz gave up fast food, and Rihanna gave up alcoholic drinks (these products provoke acne). Victoria Beckham eats salmon every day, Scarlett Johansson washes her makeup brushes once a week and never goes to bed with makeup on her face.
How to get rid of comedones?
In case of comedonal acne, facial cleansing can be performed. The most primitive is the mechanical one, when a specialist removes comedones with his hands or an instrument. But this is a traumatic procedure, which is better replaced by an ultrasound, atraumatic technique. Peels can also be carried out with fruit acids; they act as a means to “dissolve” comedones. But only a specialist should carry out the procedures in a clinical setting.
Acne can be treated at home. For mild to moderate acne, Azelik® gel, which contains azelaic acid, can be used for this purpose.5
An effective remedy against acne is considered to be one that affects several parts of its pathogenesis. The main ones include: inflammation, follicular hyperkeratosis, increased colonization of propionibacteria, increased sebum production. For mild acne, as a rule, the use of topical medications is sufficient; for moderate and severe acne, systemic medications are added to them.
Prevention
You can prevent the appearance of new comedones by paying attention to the following preventive recommendations:
- Do not squeeze out any skin rash yourself.
- Follow the rules of personal hygiene and skin care.
- Refuse excessive use of cosmetics, avoid using low-quality cosmetic products.
- Normalize your diet, avoid foods that increase sebum production.
- Avoid stress, overwork, lack of sleep.
- Give up bad habits: smoking, alcohol abuse.
- Treat endocrine and somatic diseases in a timely manner.
- Regularly visit a dermatologist or cosmetologist to promptly identify skin changes and correct them.