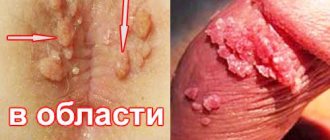
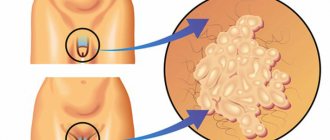
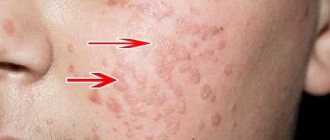
A pressing problem in modern gynecology that many girls and young women face is papillomas on the labia. In these intimate areas on the mucous membrane from some types of HPV, the so-called appear. "genital warts". If a wart on the genital organs is detected or suspected, each patient should know how the disease manifests itself, what treatment should be carried out and what tests should be taken for diagnosis.
These formations are very common. Warts on the labia minora and majora in girls are mainly represented by genital warts, the causative agents of which are types 6 and 11 of the virus. These types of HPV are of low oncogenic risk, that is, the risk of their degeneration into a malignant tumor is low. Children, teenage girls and girls with virgin status cannot be excluded from possible risk groups for the presence of these formations, because sexual is not the only way of transmitting the virus (see more details).
Condylomas in the labia (vulva) area
Vulvar condylomas appear as a result of infection with the human papillomavirus. This virus enters the female body more often during sexual intercourse. If the immune system is in good condition, this disease may not manifest itself for years, and a woman, not knowing that she is sick, can infect her partners with it if their local immune defense is insufficient. When immunity decreases, the virus can make itself felt. Condylomas may appear on the labia, internal genital organs, perineum, and anus.
Genital condylomas of the vulva must be removed without fail, and not only due to their lack of aesthetics, but given their growth and spread. This disease can progress and spread to the vaginal mucosa and cervix and to the skin of the anogenital area.
Treatment of condylomas should be carried out by a gynecologist, who will determine the treatment regimen.
Treatment methods for condylomas in the labia (vulva) area
If you have condylomas on the vulva, you should immediately consult a gynecologist. Today, there are several approaches to the treatment of this disease, and an experienced professional, having established the correct diagnosis and assessed the extent of damage to the body, will be able to choose the correct treatment regimen.
As a rule, condylomas in the vulvar area are treated in the clinic in the following ways:
· excision with a scalpel;
· cryodestruction – cold treatment;
· the excision procedure is performed using laser or electrosurgical devices (radio wave apparatus with argon-enhanced coagulation).
Examination for papillomatosis
The first thing to do with any type of papillomatosis is to establish its nature.
To do this, doctors analyze the clinical picture (features of the course) of the disease.
The most important stage of diagnosis is analysis: biopsy and histological examination of a tissue sample.
This is the only way to ensure that the process is truly benign.
Considering the prevalence of HPV, papilloma tissue is analyzed to determine the type of pathogen using PCR.
If it turns out to be HPV of high oncogenicity (type 6, 11, 16,18), then treatment must be taken with the utmost seriousness.
Especially for women with cervical papillomatosis.
Vaginal condylomas
Condylomas in the vagina are also a consequence of infection with the human papillomavirus (HPV). The diagnosis is established by a gynecologist upon examination of the speculum of the vaginal mucosa, clarified during colposcopy, and confirmed by performing a PCR test for HPV and, in doubtful cases, taking a biopsy of the formation.
Condylomas in the vagina bring a lot of problems to a woman and can affect sexual behavior. Symptoms may include: the presence of growths in the vagina palpated by the woman herself during genital hygiene, an inflammatory reaction, itching, the appearance of cracks in the mucous membrane, pain during sexual intercourse.
This disease can progress and spread to the cervix, although it does not lead to cancer. Therefore, experts recommend treating condylomas in the vagina immediately after they are detected.
Symptoms
After infection with HPV, it may take several years for the first genital warts to appear. Often the infection occurs without symptoms, so it is impossible to confirm HPV infection without a laboratory test.
Symptoms of the development of viral warts:
- at the initial stage - redness of the skin, small rash;
- the appearance of flat warts on the mucous membranes of the genital organs;
- discomfort during sex (pain, itching, burning);
- the appearance of erosions and cracks in the genital area;
- change in skin color of the perineum, hyperemia;
- the appearance of single papillae on a filiform stalk.
After the first condylomas appear, the disease can develop according to the following scenarios:
- self-healing after restoration of immunity (extremely rare);
- active reproduction of warts;
- stable remission (the number and size of formations are unchanged);
- malignant transformation.
Any of these symptoms is a good reason for urgent consultation with a gynecologist and venereologist.
Treatment methods for vaginal condylomas
To remove tumors, the following destructive treatment methods are available:
· cryodestruction;
· laser removal, the most optimal destructive method;
Argon plasma ablation;
· radio wave (high frequency) removal, preferably with argon-enhanced coagulation.
Destructive methods of influence do not guarantee relapse of the disease, which is why the use of antiviral drugs is practiced in our country. Immunotherapy is not always justifiably used; more often it is prescribed blindly, without appropriate examination. This method sometimes gives side effects in the presence of condylomas, and as monotherapy it is ineffective, but in some cases it can give a good result, but this is impossible to predict. The best effect is achieved in a combination of destructive and conservative treatment.
Key points:
Treatment of condylomas of the external genitalia and vagina produces positive results in most patients within 1 to 6 months. At the same time, the virus can remain and be detected in 30% of women, without clinical manifestations, which no longer requires treatment, but observation.
It is important to note that condylomas that appear on new areas of the skin or mucous membrane during treatment or after completion of treatment do not require a change in treatment method. The appearance of new formations in the area where the treatment was carried out requires a change in the treatment method.
Patients should be informed about maintaining sexual rest during treatment and undergo examinations until the condylomas completely disappear.
Sexual partners should be examined and treated only if there are condylomas on the penis.
Methods to combat papillomatosis
The first thing people do when they notice papillomatosis in themselves or their child is to turn to folk remedies.
These conspiracies, the red thread and all sorts of rituals sometimes really give results: the placebo effect is well known to doctors.
But most patients are not successful.
Moreover: the process progresses, the number of papillomas and their size increase, the quality of life decreases.
Complications often occur in the form of secondary infections, the appearance of ulcers and scars.
And then people do what should have been done right away: they come to see a dermatologist.
Cervical condylomas
Cervical condyloma is one of the types of HPV manifestations. Infection with this disease also occurs during sexual intercourse with an infected partner. In the absence of exophytic (visible) condylomas on the penis, the sexual partner may not be aware of the carriage of this virus.
Cervical condyloma is not always a consequence of HPV types 6 or 11. The cervix is also affected by other types of viruses, which also have an oncogenic risk.
A special feature of condyloma on the neck is its shape. Condyloma can be flat and not visible when examined in a mirror, or it can be protruding (typical). Flat condyloma of the cervix is detected during colposcopy. This painless technique involves examining the vulva, vagina and cervix under a microscope, stained with special solutions. Areas affected by flat condyloma are highlighted after staining with solutions.
To finally confirm the diagnosis, in addition to a cytological examination (Pap test), a PCR test for HPV and a biopsy or removal of the altered area with histological confirmation are performed.
It should be noted that any formation on the cervix, even a typical genital wart, after removal must undergo histological examination. If the gynecologist has no doubts about the diagnosis of cervical condyloma, then when using treatment methods after which it is not possible to conduct histology, it is necessary to take a biopsy before treatment.
What is the relationship between HPV and human cancer?
The clearest causal role of HPV has been demonstrated in cervical cancer. Thus, high-risk HPV types (see Table 1) were found in 93 - 99% of women with cervical cancer. Previously, it was found that the most susceptible to cervical cancer are women who began sexual activity early, had an STI, and also had a large number of sexual partners, as well as those who were in contact with men whose partners had cervical cancer. It turned out that high-risk HPVs contain regions with high oncogenic activity (E6 and E7) in their genome. When HPV invades the genome of cells in the cervical mucosa, regions of the genome E6 and E7 stimulate the synthesis of corresponding proteins, which in turn interact with proteins that regulate cell division and cell death. The E6 protein suppresses the activity of the P53 gene (and the corresponding protein), and the E7 protein of the retinoblastoma gene, which stimulates the process of apoptosis (programmed cell death). This leads to the predominance of cell reproduction over cell death, which stimulates the uncontrolled malignant growth of cervical epithelial cells and the development of cervical cancer. Thus, the International Agency for Research on Cancer has concluded that high-risk HPV types are the leading cause of cervical cancer.
However, it is known that most women infected with HPV do not develop cervical cancer and the presence of HPV is “necessary” but not “sufficient” for the development of this disease. The development of cervical cancer in people infected with HPV is facilitated by smoking, long-term use of hormonal contraceptives, and the presence of other STIs, such as chlamydia, namely Chlamydia trachomatis, herpes simplex virus type 2. In addition, vitamin A deficiency, genetic predisposition and immunodeficiency contribute to the development of cervical cancer in the presence of HPV. In addition to cervical cancer, the causative role of HPV has been established in cancer of the anal area (especially in homosexuals), and in cancer of the vulva, vagina and penis. Some cases of cancer of the mouth, larynx and esophagus are also possibly related to HPV.
Every year, up to half a million new cases of cervical cancer occur worldwide. Most of these cases are registered in developing countries, where preventive programs of annual screening examinations for HPV, dysplasia and cervical cancer do not work or work poorly. The introduction of similar preventive programs in developed Western countries has reduced the incidence of cervical cancer by 75%. Although the incidence of other HPV-related cancers is much lower, the incidence of anal cancer among gay men is estimated to be 4 times higher than the incidence of cervical cancer in women (35 cases per 100,000 homosexuals per year, versus 8.3 cases per 100,000 women). population per year).
Treatment of cervical condylomas
Removal of condylomas on the cervix is a mandatory procedure in terms of the spread of infection and the prevention of cervical cancer.
Cervical condylomas can be removed in the following ways:
· laser vaporization is an effective technique with a low relapse rate and does not affect the reproductive function of nulliparous patients;
· argon plasma ablation – a good effect, especially in nulliparous patients;
· radio wave removal - a technique that allows a histological examination to be carried out after removal;
· cryodestruction is a popular method, but it is effective for small lesions;
· Solkovagin – cauterization of single genital warts using a chemical preparation.
Each of the listed methods has its own advantages and disadvantages. In each specific case, the choice of treatment remains with the doctor and depends on the availability of equipment and the qualifications of the specialist.
Using destructive treatment methods, part of the affected cervical tissue that is visible or detectable by colposcopy is removed, but not the virus itself. Therefore, along with removal, gynecologists recommend antiviral or immunomodulatory drugs of local or general action to prevent relapse and fight the virus. We cannot predict the effect of this treatment, but in some cases there is a positive result. It is incorrect to believe that antiviral drugs are the main ones in the fight against HPV. These medications activate the immune system, and it already resists viral aggression. In the practice of treating condylomas of any location, these drugs have their own niche of use. Clear evidence of the effectiveness of these dosage forms has not been obtained, so they are practically not used in world practice.
Vulvar condylomas during pregnancy
Pregnancy can provoke the development of exophytic condylomas (visible), which previously did not bother and did not make themselves felt. Condylomatosis is the result of the presence of the human papillomavirus in the body. This virus, having entered a woman’s body, may not manifest itself in any way if the immune system is strong. However, during pregnancy there is a temporary decrease in immunity due to the presence of a fetus, which half consists of foreign genetic material (protein) belonging to the husband. The papilloma virus, if present and in an inactive state, may begin to manifest itself in the form of neoplasms on the external and internal genital organs of a woman, in the perineum, and in the vicinity of the anus.
Condylomas during pregnancy must be removed due to their active growth and the sooner this is done, the better.
Treatment of condylomas during pregnancy should be carried out by an obstetrician-gynecologist who is fluent in removal techniques. Treatment of exophytic condylomas is preferable using the most effective modern laser and radio wave equipment with argon-enhanced coagulation. These operations are usually performed in a hospital under intravenous or epidural anesthesia. With extensive condylomatosis, removal is sometimes carried out in several stages. Epithelization of the wound surface in pregnant women occurs quite quickly, due to increased blood circulation in the genital area. Therefore, removal of condylomas can be carried out from early pregnancy up to 36 weeks of pregnancy. Before the planned removal of condylomas, it is necessary to conduct an examination to exclude possible complications occurring during pregnancy (for example, the threat of miscarriage, gestosis, etc.). Carry out sanitation in case of an inflammatory reaction in the genital area.
During pregnancy, only external condylomas should be removed. It is better not to touch condylomas in the vagina and cervix, as this is associated with an increased risk of bleeding and the threat of miscarriage. As practice shows, condylomas regress on their own after childbirth, especially in the vagina.
In pregnant women with condylomas, only local immunotherapy is performed. Virus carriage, without clinical manifestations (presence of visible condylomas), is not a basis for therapy. It is better to start treatment before removal and continue after surgery. The goal is to reduce the risk of recurrence of condylomas.
To ensure that you are not burdened by treatment for condylomas during pregnancy, it is preferable to undergo testing for the presence of HPV before planning a pregnancy. If this virus is detected, it is necessary to first improve the body’s defenses and only then plan a pregnancy. If this is not done, then there is a chance that you will develop condylomas during pregnancy.
It is not possible to guarantee that a woman will be cured of the virus before a planned pregnancy using modern medications. Treatment of the identified inflammatory process of the reproductive tract, before a planned pregnancy, is a sufficient measure to prevent exacerbation of HPV.
It should be emphasized that carriage of HPV of any type, without clinical manifestations (presence of exophytic condylomas), is not a contraindication to pregnancy.
What are the goals of treatment for diseases caused by HPV, and how is it carried out?
Diagnosis, treatment and prevention of genital diseases caused by HPV in men is carried out by urologists, in women - by gynecologists. Unfortunately, there are currently no methods of systemic action on HPV in the human body (antiviral agents) that could be used to completely destroy the virus. The main goal of treatment for OCs is their removal using electro- or laser coagulation, excision, cryodestruction (destruction by cold), as well as using chemicals, cell toxins (podophyllin) or immunomodulators applied topically. Removing OK solves mainly a cosmetic problem; there is no data confirming that removing OK helps to completely remove HPV from the body or reduce the risk of its sexual transmission or infection of the fetus during childbirth. There is no evidence that OC treatment has any effect on the likelihood of developing cancer. However, from a common sense point of view, removal of OCs should reduce the risk of development and recurrence of diseases caused by HPV.
The main goal of treatment of squamous epithelial lesions of the cervix is the prevention of cervical cancer. If a cytological Pap smear shows the presence of a lesion of unknown significance at the risk of malignancy, dynamic observation with Pap smears performed every 4 to 6 months for 2 years is indicated until there are 3 consecutive negative (without any pathological changes) smears. Women with high-risk intraepithelial lesions require immediate colposcopy and possibly biopsy of the detected lesions for more detailed histological evaluation. If CIN 1 is identified as a result of histological examination, dynamic observation is indicated, because the vast majority of such lesions undergo spontaneous regression to normal. For lesions of CIN 2/3, active treatment is required, which consists of cryodestruction, laser evaporation or loop electrosurgical excision (conical excision or conization) of the cervix.
Recent randomized clinical trials have shown that all three methods have similar rates of complications (2 - 8%), persistence (3 - 5%) and recurrence (13 - 19%) of lesions. Risk factors for persistence (lack of treatment effect) were a large affected area, relapse - older age, the presence of oncogenic HPV types 16 and 18, as well as previous treatment.
Childbirth with condylomatosis
I would like to remind you that condylomas themselves are a manifestation of the human papillomavirus (HPV). This virus may pose a risk of fetal infection and laryngeal papillomatosis in the unborn child. Research does not confirm that 100% of women who carry the virus become infected in the fetus. Unfortunately, it is impossible to predict whether a child will become infected with the virus during pregnancy and childbirth. Undoubtedly, the presence of condylomas increases the risk of infection, so it is better to remove the tumors.
The need for delivery by cesarean section in women with condylomatosis is decided individually. It is preferable to give birth on your own, even despite the presence of formations in the area of the external or internal genital organs that are present before childbirth. There are cases that children born by cesarean section from pregnant women with HPV carriage suffer from laryngeal papillomatosis. Caesarean section is performed on pregnant women in the presence of extensive condylomatosis of the external genitalia, when this prevents vaginal delivery, or in combination with other complications and diseases during pregnancy.
It should be noted that termination of pregnancy for condylomatosis of the anogenital area is usually not performed.
Condylomas in the rectum (anus) area
Anal condylomas, like other types of similar neoplasms, are the result of infection of the body with the human papillomavirus. Condylomas in the anus are a rather complex disease, which is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- the appearance of a formation in the anus;
- an increase in the number of warts in this area;
- traumatization of warts due to mechanical impact.
Condylomas of the rectum must be treated without fail. A specialized doctor who is able to correctly diagnose this disease is a proctologist. As soon as you experience one of the above unpleasant sensations, you should immediately consult a doctor. Condylomas in the anal area are also called perianal by experts.
Papillomavirus is transmitted through sexual intercourse. In this case, anal sex plays a role.
Papillomatosis in children
Infection with viral papillomatosis in childhood occurs during childbirth through the mother's birth canal infected with HPV.
Or when using shared towels or washcloths.
Because of these features, in infancy and early childhood, papillomas are more often found on the epithelium of the larynx and ENT organs (respiratory forms).
Older children in organized groups are already more prone to the appearance of papillomatosis of the skin of the torso, face and extremities.
Clinical manifestations are normal, the appearance of the neoplasms is the same as those described above.
Treatment of anal warts
Perianal condylomas require immediate treatment due to the many inconveniences they cause to the patient and the likely progression of the disease. Modern specialists, along with excision of formations using various methods, simultaneously influence the patient’s immune system.
Treatment of condyloma in the anal area will be effective if you contact a specialized specialist in a timely manner and strictly follow all his recommendations. Proper influence on the immune system of a patient with condylomatosis activates the body's defenses and directs all their efforts to fight the papilloma virus.
Factors of HPV progression are:
- acute and exacerbation of chronic inflammatory diseases of the genital organs (trichomoniasis, chlamydia, mycoplasma genitalium, herpes simplex virus, etc.);
- the presence and exacerbation of systemic diseases (diabetes mellitus, systemic lupus erythematosus, thyroid disease, etc.);
- immunosuppressive therapy (for example, after organ transplantation);
- hormonal disorders;
- contraception (taking COCs for >5 years);
- smoking;
- stressful situations.
Treatment of condylomatosis at home
The main disadvantage of various destructive treatment methods is the recurrence of the disease, which varies, depending on the technique, from 20 to 50% of cases.
Imiquimod cream, commercial name Aldara, is a highly effective remedy in the fight against genital warts. This cream, when applied topically to the skin, acts as an immunomodulator, stimulating the production of interferons. This leads to a decrease and then to the disappearance of condylomas and a decrease in the amount of HPV in the tissue.
Aldara cream, available in sachets (sachets) for one-time use, is applied to condylomas and the skin near them 3 times a week before bed, and the next morning the area of application is cleaned with soap and water. Treatment continues until the condylomas disappear, on average 4 weeks, but not more than 16 weeks. When used, a local skin reaction in the form of redness (erythema) may occur. In this situation, you can pause until the reaction disappears and continue treatment. More details about the method of use are described in the instructions for the Aldara cream.
Numerous clinical studies show that imiquimod (Aldara cream) can achieve significant improvement within 8-10 weeks of use. There is a low relapse rate of 13%. Additionally, it should be noted that the drug stimulates the regeneration of the skin and improves its appearance in case of actinic (senile) keratosis.
Complications of condylomatosis
Given that both sexes are equally susceptible to condylomatosis, this disease poses a greater danger for women than for men. Benign anogenital warts (condylomas), in 90% of cases are caused by HPV types 6 and 11 and are benign. Patients with visible warts can also be infected with highly oncogenic HPV types 16 and 18, which may be flat and not visible during routine examination. These last 2 types can cause cancer of the lower reproductive organs (cervix, vagina and vulva).
Genital warts caused by HPV types 6 and 11 are benign growths. Such neoplasms are not dangerous and cannot lead to oncological degeneration. They cause a lot of inconvenience to humans and pose a danger to sexual partners due to the high probability of infection.
Experts consider flat lesions more dangerous due to the difficulty of their timely diagnosis. It is viral lesions of the flat type that can cause tissue degeneration.
Buschke-Levenshtein condyloma is a fairly rare disease. Medical science does not have accurate statistical data due to the external similarity of this formation with epidermoid cancer.
In the initial stages, giant Buschke-Levenshtein condyloma appears in the form of elements similar to papillomas, wart-like nodules and genital warts. All elements of the neoplasm grow quickly, merge together, and form a tumor with a specific wide base. The surface of such a giant condyloma is characterized by growths and vegetations. All surface elements are separated by grooves. As the tumor grows, individual parts become more pronounced, becoming superficially covered with horny scales.
This is a rare type of disease associated with HPV types 6 and 11, characterized by aggressive growth.
Giant condylomas are usually localized in the anogenital area.
Radio wave surgery method
Radio wave surgery is the optimal method for removing tumors in the anogenital area due to good aesthetic results and wound healing without scarring.
The method is based on the effect of radio frequency waves on biological tissues. This leads to increased molecular vibrations, local heating and evaporation of neoplasm cells. Due to the high temperature, blood vessels are immediately sealed, which prevents bleeding.
At the site of removal, a dry crust forms, under which epithelization of the wound occurs. After the scab falls off, a pink skin forms in its place, which over time transforms into normal integumentary tissue. In our clinic, for radio wave removal of condylomas, we use the latest generation Surgitron device Surgitron DF-120 (USA) with an innovative “fulgurate” mode specifically for the removal of condylomas.
Features and diagnosis of giant condylomas
Giant Buschke-Levenshtein condyloma has a characteristic clinical feature: progressive growth. There is a pronounced tendency for recurrence of this disease, even after complete excision of the existing formation. Predominantly exophytic growth is observed against the background of the presence of invasive growth. The result is the fusion of individual parts of the new growth, which forms its external similarity to the cauliflower inflorescence.
Buschke-Levenshtein's condyloma, from the point of view of histological picture, is diverse: areas of benign condylomas alternate with areas of atypical cells or squamous cell carcinoma.
To confirm this diagnosis, specialists must carry out differential diagnosis, the purpose of which is to exclude the following probable diagnoses:
- squamous cell carcinoma;
- condyloma lata, which accompanies syphilis;
- ordinary genital warts.
Difficulties in diagnosis may arise due to the transformation of giant or ordinary condyloma acuminata into an atypical tumor. The disease requires multiple sectional biopsies and computed tomography (CT) or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).
To completely exclude oncology, complete excision of the tumor is performed with histological examination.
The difference between papilloma and condyloma
During life, a variety of formations appear on the human body. The most common benign formations include the following:
- nevi;
- papillomas;
- warts;
- others.
It should be understood that not all formations are safe. It is always preferable to consult a dermatologist to determine the danger of a particular skin formation.
Papillomas are delicate papillary formations on human skin that appear as a result of infection of the skin, most often with certain strains of the human papillomavirus (HPV). The virus is transmitted by contact from the skin of an infected person to the skin of an uninfected person. Papillomas can remain on a person’s body throughout his life; these tumors are considered safe. Dermatologists still strongly recommend removing papillomas due to the possibility of damaging them or accidentally tearing them off, which can lead to negative consequences.
Condyloma is a rough scallop formation on the skin and mucous membranes of the genital organs, anogenital area and oral cavity. Condylomatosis is a disease that is caused mainly by HPV types 6 and 11. In this case, the mode of transmission is sexual (sexual transmission). Condylomas (warts) develop as a result of a decrease in the body’s protective abilities, and are subject to mandatory removal, which is one of the stages of complex treatment of this problem.
The main difference between condyloma and papilloma is their location on the human body. Also, these neoplasms have different structural features. In any case, you should not engage in self-diagnosis and self-medication. If you are interested in an effective solution to the problem, it is preferable to contact a specialized specialist: in the genital area, this is a gynecologist, on the skin of another area, a dermatologist.
Prevention of condylomatosis
Condylomatosis is a consequence of infection of the body with the human papillomavirus (HPV), which is mainly transmitted through sexual contact. It appears in the form of warts called condylomas. Such formations can appear on the external and internal genital organs, in the anal area, and oral cavity.
Therefore, to prevent condylomatosis, you should avoid:
· presence of sexually transmitted infections;
· neglect of protective equipment during sexual intercourse;
· smoking;
· mechanical trauma to the skin or mucous membrane of the genital organs.
Self-regression of condylomas
The sexually active population can become infected with HPV during their lifetime; according to statistics, 80% of people are susceptible to this. The majority self-heal from HPV without clinical manifestations and without treatment. This occurs due to the activation of the local and general immunity of the infected person. In approximately 10% of patients, the virus has clinical manifestations, these include anogenital condylomas and patients with precancer and cervical cancer.
As practice shows, condylomas in pregnant women regress on their own after childbirth, especially in the vagina.
Prevention
To avoid HPV infection and the formation of papillomas in the vagina, women should adhere to preventive measures and recommendations.
- maintaining intimate hygiene;
- maintaining a healthy lifestyle;
- no abuse of tobacco and alcohol products;
- regular examinations by a gynecologist;
- use of barrier methods of contraception during sexual intercourse;
- increasing immunity (regular consumption of vitamin complexes, minerals and trace elements);
- maintaining a proper balanced diet.
Behavior after removal of condylomas
Inform the patient that it may take 1 to 6 months for condylomas to disappear. During this time, relapses of the disease are possible, but a complete cure will still occur.
Reassure the patient that due to the long persistence of the virus after infection (the presence of the virus in the body in an inactive state), the appearance of condylomas in only one sexual partner in a permanent relationship does not mean sexual contact on the side of the other partner.
Smokers who do not respond well to treatment should quit smoking, as there is a link between smoking and genital warts.
Advise the use of a condom to reduce the risk of recurrent or additional infection.
It is recommended to avoid excessive solar radiation (tanning) and use sunscreen while vacationing in the south, since excessive sun exposure stimulates the development of the virus, if present in the body tissues.
Warn about the inappropriateness of various warm-ups (sauna, steam bath, hot bath), this can also provoke the activity of the human papillomavirus when carrying the virus.
Why do vaginal papillomas occur?
The main cause of papilloma in the vagina is the papilloma virus. It enters the body through unprotected sexual contact with a carrier. However, there are a number of factors that increase the likelihood of infection. These include sexually transmitted diseases (for example, gonorrhea and chlamydia).
Also, the reasons that contribute to the development of papillomas are:
- frequent change of sexual partners;
- disruption of the normal vaginal microflora (dysbiosis);
- low immunity;
- inflammation of the ovaries;
- severe stressful situations;
- pregnancy;
- deviations from the endocrine system;
- lack of vitamins in the body.
If several of the reasons described above are present, the risk of infection increases significantly. The incubation period is no more than 3 months, but under the influence of unfavorable circumstances for the immune system, this time can be reduced to 14-20 days.
Healing after removal of condylomas
After removal of condylomas, the resulting wounds are usually recommended to be treated with Baneocin powder. Accordingly, for some time there may be profuse serous or minor bleeding after removal of condylomas, which is absolutely normal and should not frighten the patient.
After removal of condylomas, swelling and pain may occur, which can last from two to five days. Their duration is related to the size of the removed tumors and the individual sensitivity of the person.
In most cases, during the healing process, itching may occur after removal of condylomas, which is also absolutely normal, as for the healing of any other area of the skin.
After removal of condylomas, limit physical activity and exclude sexual activity for about 2-3 weeks until epithelization (healing) of the wound surface.