Any dermatitis is a reaction to some external or internal factors. In the case of seborrheic dermatitis, skin manifestations are a response to excessive activity of a yeast-like fungus caused by improper functioning of the sebaceous glands. The causes of malfunction of the sebaceous glands are different, but among them are diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, as well as unhealthy diet. Seborrhea is treated with medications and cosmetics. But the condition is also greatly influenced by diet as a type of rational nutrition with the exclusion of allergens and substances that cause excessive sebum secretion.
The diet for dermatitis has two goals:
- exclusion of foods that cause the onset or exacerbation of the disease;
- formation of proper nutrition, which helps the patient cope with the disease, and the skin to recover and be protected from the development of the disease.
When the first symptoms of seborrheic dermatitis appear, you should consult a doctor for an accurate diagnosis and selection of drug therapy, if required. It is also necessary to choose skin care cosmetics. For treatment to be effective, you need to follow a diet. The menu can be compiled by a nutritionist in a specialized center. But you can simply follow the general recommendations that are suitable for everyone suffering from dermatitis.
Seborrheic dermatitis in the photo
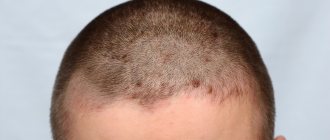
Photo 1. Seborrheic dermatitis of the scalp.
Photo 2. Seborrheic dermatitis of the head.
Photo 3. Photo of seborrheic dermatitis before treatment.
Photo 4. Photo of seborrheic dermatitis after treatment.
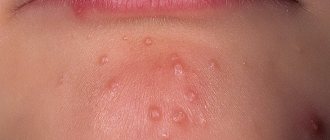
Photo 5. Symptoms of seborrheic dermatitis: redness and peeling.
Photo 6. Symptoms of seborrheic dermatitis: the appearance of crusts.
Hair care during the treatment of seborrheic loss
Homemade masks and decoctions, selected together with a doctor, are a good help in the treatment of seborrheic hair loss. For example, you can use these tips:
- infusions and decoctions of oak bark and chamomile are suitable for disinfecting the skin;
- softening and nutrition - burdock root;
- drying - lemon water, soda water, a decoction of string;
- softening - a decoction of celandine or onion peels.
Warming masks have a beneficial effect. They stimulate blood circulation and accelerate hair growth. For such masks, take red pepper, onion, and mustard.
It is not recommended to wash your hair every day, as this can dry out your skin. If your hair quickly becomes oily at the roots, then you need to wash it 2-3 times a week, and dry hair once is enough.
Seborrheic dermatitis on the scalp and sebaceous glands
The secretion of the sebaceous glands is a mixture of lipids and is called sebum. It is necessary for the healthy functioning of the skin: moisturizing it, maintaining elasticity, creating an antimicrobial protective barrier.
The skin is covered unevenly with sebaceous glands; there can be from 4 to 380 ducts per 1 cm2. They lie in the middle layer of the skin - the dermis, between its papillary and reticular layers. The largest number of sebaceous glands are located in the so-called “seborrheic zones”: on the skin of the face and body (back, neck, scalp, pubis, chest, abdomen, shoulders, forearms, legs). There are no sebaceous glands on the skin of the soles and palms.
For the most part, the ducts of the sebaceous glands open at the mouths of the hair follicles. In smaller numbers, the excretory ducts open directly onto the surface of the epidermis - in the area of the eyelids, borders of the lips, external auditory canal, nipple halos, and anus.
The size of the glands and the amount of lipid secretion depends on various factors: the functioning of the endocrine, nervous, reproductive systems of the body, age. In young children, the sebaceous glands secrete very little secretion. By adolescence, their work increases sharply, but as they grow older, their activity decreases. In adult men, sebum is constantly secreted in approximately the same amount; in women, this process is often associated with the menstrual cycle. In old age, the amount of secretion released decreases.
Seborrheic dermatitis. Varieties
Oily seborrhea is the most common type of disease. It is characterized by increased secretion of sebum and changes in skin microflora. With oily seborrhea, redness of the skin or small reddish papules with an oily sheen and clearly defined boundaries are observed. Oily seborrhea, in turn, is divided into thick and liquid, depending on changes in the composition of the skin secretion (see photo of seborrheic dermatitis).
Oily seborrhea
Oily seborrhea
With liquid seborrhea, the level of free fatty acids in sebum increases. The skin of the face becomes shiny, rough, with enlarged pores. Comedones and acne easily form on it. If liquid seborrhea affects the scalp, the hair looks very dirty and sticks together in strands.
With thick seborrhea, there is a decrease in the level of lower fatty acids and an increase in higher fatty acids in the sebum. An imbalance in the composition of skin secretions reduces its protective properties and provokes the proliferation of microorganisms. Externally, thick seborrhea can manifest itself as pustular rashes, dilation of the mouths of the ducts of the sebaceous glands, comedones, and the separation of large yellowish scales glued together.
Dry seborrhea - often observed in young children, as they produce an insufficient amount of skin secretion. In adults, the dry form of seborrheic dermatitis occurs less frequently. It is characterized by a decrease in sebum production, dryness, cracks and excessive flaking of the skin, a feeling of tightness that intensifies after contact with water. The hair on the head becomes thinner, brittle and split. In some cases, the scales layer on top of each other, forming crusts. Acne, pink and red spots appear on the skin.
Dry seborrhea
Severe seborrhea with infection
Mixed seborrhea - characterized by the simultaneous appearance of dry seborrheic dermatitis on the scalp and oily seborrheic dermatitis on the face.
Seborrheic dermatitis. Symptoms
Seborrheic dermatitis can develop both in the head and torso. Seborrhea of the scalp can manifest itself as inflammation of the scalp, eyebrows, eyelashes, hairline, nasolabial folds, external auditory canals and the area behind the ears. In men, it is often localized in the area of beard and mustache growth.
Seborrheic rash can also affect the chest and natural folds of the body: armpits, groin, abdomen, mammary glands. Seborrhea of the face and body manifests itself as red spots, accompanied by itching and peeling, a burning sensation and even the appearance of papules, merging into ring-shaped or garland-shaped plaques. The plaques have clear boundaries, the papules are covered with fatty yellowish scales. As the disease progresses, bright yellow crusts appear on the skin, inflammation grows over a large surface area of the skin, and a bacterial infection occurs.
Seborrheic dermatitis of the scalp is characterized by the detachment of whitish scales, which can be mistaken for large dandruff. However, unlike dandruff, seborrhea is accompanied by itchy skin, and the lesions are clearly visible. Many patients associate dry scalp with the appearance of “dandruff”, so they wash their hair less often. Unfortunately, such tactics, instead of the desired result, only lead to the accumulation of seborrheic scales, the formation of dense crusts and pathological inflammation of the scalp and sebaceous glands. Refusal of treatment leads to thinning hair and baldness.
Seborrhea of the scalp in infants usually appears at the age of 3 months. It consists of thick yellow crusts that can be easily removed with vegetable oil and does not bother children. However, the combination of skin rash with diarrhea and underweight in newborns requires urgent medical attention, as it may indicate the presence of such a serious disease as Leiner's erythroderma.
Complications of seborrhea
Alopecia does not begin to manifest itself immediately. First, redness and dandruff appear on the scalp. At the next stage, the nutrition of the hair follicles is disrupted. This is due to roughening of the skin and sebaceous layers. At the last stage, hair follicles begin to die, hair thinning is noticeable and its growth stops, and restoration becomes difficult.
With seborrhea, hair rarely falls out completely. However, the remnants of hair look very unpresentable. This appearance causes psychological disorders and makes it difficult to communicate with people.
Seborrheic dermatitis. Causes
The main reason for the development of seborrhea is the effect on the skin of opportunistic yeast-like lipophilic fungi Malassezia furfur, which are present in varying quantities in most people. The oval form of the fungus (Pityrosporum ovale) is responsible for the development of inflammation of the scalp. Lesions on the skin of the body are caused by the round form of Malassezia furfur – Pityrosporum orbiculare. Fungi create colonies around the ducts of the sebaceous glands, feeding on lipid secretions and actively multiplying.
However, seborrheic dermatitis does not affect everyone. Thanks to the immune system, a healthy body inhibits the growth of fungi. If the body's metabolism is disrupted, Malassezia furfur begins to multiply uncontrollably, which breaks down sebum into free fatty acids, which causes inflammation.
The development of pathology can occur due to the following factors:
- puberty - due to hormonal changes in adolescents, the composition of sebum changes, and the sebaceous glands begin to work with greater intensity. In this case, the disease goes away on its own as the patient grows older;
- hereditary predisposition explaining the hyperfunction of the sebaceous glands;
- hormonal imbalance, in which there is an increase in the level of androgen and progesterone and a decrease in estrogen levels. Hormone-dependent seborrheic dermatitis is observed in women in menopause or with ovarian diseases, in men with testicular tumors, and in obesity;
- unhealthy diet with an abundance of spicy, salty and fatty foods;
- presence of bad habits (alcohol, tobacco smoking);
- infectious diseases, weakened immunity;
- stress and overwork;
- non-infectious diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, endocrine system and metabolism. Painful conditions are accompanied not only by increased work of the sebaceous glands, but also by excessive sweating and cardiac arrhythmia;
- psychological and mental diseases (for example, Itsenko-Cushing syndrome, schizophrenia, epilepsy, manic-depressive disorder), in which the functions of the pituitary gland and hypothalamus are disrupted.
But despite the extensive list of possible reasons, none of them are absolute. The exact reason contributing to the excessively active activity of Malassezia fungi has not yet been identified.
Prevention
To minimize the risk of disease, you need to adhere to a healthy lifestyle, eat well and properly care for your hair. If you do not want to provoke the development of dry seborrhea of the scalp, follow these rules:
- Maintain personal hygiene regularly;
- Take special care to rinse any remaining styling products from your hair;
- choose products that suit your curl type;
- do not use foams, varnishes, mousses, gels too often;
- When styling with hot tools, do not forget about thermal protection;
- try to at least sometimes dry your hair naturally, without a hair dryer;
- do not abuse the use of curling irons or straightening irons;
- if you have a tendency to dry seborrhea, periodically take preventive measures : change your regular shampoo to a medicinal one against dry seborrhea of the scalp;
- do not ignore hair rinses;
- cover your hair with a weather-appropriate hat so that your hair does not suffer from ultraviolet radiation or precipitation, extreme cold or heat;
- Do not forget to take off your hat indoors;
- Avoid stress, and if you cannot cope with it on your own, consult a neurologist. He will prescribe you sedatives;
- make time for sports, do not forget about physical activity;
- be sure to walk in the fresh air;
- Allow sufficient time for sleep (7.5–9 hours). Lack of sleep also affects hair health;
- take vitamin complexes a couple of times a year;
- give up bad habits;
- Monitor your overall health, get examined and tested once a year;
- eat right.
The issue of food quality is one of the most important for the prevention and treatment of dry seborrhea and many other ailments, including those related to skin and hair. The diet for dry seborrhea does not have any special features, but is designed taking into account the principles of a healthy diet. The priority is fermented milk products, fresh vegetables, fruits, eggs, fish. Avoid salty, sweet, fatty, starchy, spicy, and canned foods. This is especially true for acute periods of the disease. The rest of the time, you can treat yourself to so-called junk food, but in moderation.
Treatment of dry seborrhea is always a comprehensive approach. You are unlikely to be able to get rid of white flakes and itching if you continue to be nervous a lot, smoke, or develop any serious illness. It’s not for nothing that they say that health comes from within. Hair is a reflection of the state of your body. The more attentively you react to changes associated with your curls, the more healthy, beautiful and well-groomed they will be.