Share:
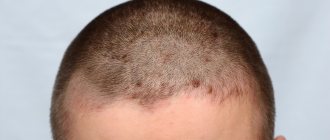
Total alopecia is a disease that causes severe hair loss. For various reasons, baldness occurs in men, women and even children. A very unpleasant result of the disease, in addition to baldness, is that the person’s hair remains everywhere.
After some time, if the hair loss is higher than normal (for everyone, the normal hair loss rate is determined individually, but general standards can be found in online sources), unpleasant bald patches appear. If the problem of partial baldness is not resolved in time, then complete baldness occurs. Everyone chooses for themselves how to live with total alopecia. This disease forces people to hide their illness in various ways (scarves, baseball caps, wigs). However, you can try to solve this problem with the help of known types of treatment.
Features of total alopecia
The peculiarities of total alopecia are that complete hair loss occurs, and sometimes hair is lost throughout the entire body. It can occur not only in those who have undergone chemotherapy courses, but also in people who are at risk.
It has been proven that total alopecia is much more common in men than in women. This is due to changes in the hormonal system and occurs at different times for everyone. Baldness occurs in 20% of cases in people with a genetic predisposition. However, the occurrence of the disease is not necessarily associated with hereditary characteristics. It can be provoked by poor nutrition, severe stress, as well as the use of antibiotics and hormonal drugs.
1.What is baldness or alopecia?
Hair grows on human skin all over the body, with the exception of the palms and soles of the feet. But many hairs are so thin and short that they are practically invisible. Hair is made up of a protein called keratin, which is formed in hair follicles in the outer layer of the skin. As follicles create new hair cells, the old ones are literally pushed through the surface of the skin. And visible hair is formed, which grows at a rate of approximately 15 centimeters per year. It turns out that hair is essentially a chain of dead keratin cells. The average adult has between 100,000 and 150,000 hairs on the head, and 100 of them are lost every day. Therefore, a few lost hairs on a comb are not a cause for alarm.
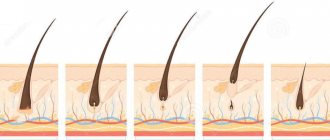
About 90% of all hair on the scalp is in the growing stage at any given time. Each follicle has its own life cycle, which is influenced by many factors - age, disease and others. The life cycle of a follicle is divided into three stages:
- The anagen phase
is active hair growth, which lasts from two to six years; - The catagen phase
is a transition period lasting two to three weeks; - The telogen phase
is a resting phase that lasts two to three months. At the end of the telogen phase, hair falls out and the growth cycle begins again.
The older a person is, the slower hair grows. As they age, some people face the problem of hair loss - baldness, or in medical terms - alopecia. There are many types of hair loss, or types of alopecia.
A must read! Help with treatment and hospitalization!
Symptoms
The first signs of total alopecia are rapid hair loss in men, women and children, as well as changes in the nail plates. There are cases when the disease quickly covers areas of the skin and in 3-4 months you can become almost completely bald. Hair falls out gradually, usually starting from the scalp, then moving to the groin, armpits and eyebrows, gradually affecting the entire body.
Complete baldness begins with a focal form. There is a special risk group: it includes teenagers (due to changes in the hormonal system), children under 1 year of age, men over 40 years of age, and women during menopause.
Types of baldness
Today there is no unified classification of alopecia. In our country, it is customary to classify alopecia based on its development and the nature of baldness.
Due to the development of the disease, there are:
- Androgenic, or androgenetic alopecia, associated with high levels of masculinizing steroid hormones and genetically determined increased sensitivity of the papilla to male hormones. This is the most common form of baldness and involves thinning and gradual loss of hair. In this case, in men, the condition of the front hairline initially worsens, gradually turning into baldness and moving towards the parietal part, often forming a horseshoe shape. In women, the disease begins to develop from the crown, in the area of the central parting, and gradually spreads to the side surfaces of the head.
- Seborrheic alopecia is baldness that develops against the background of seborrhea, associated with a violation of the neuroendocrine regulation of the sebaceous glands, leading to increased sebum secretion. The disease is characterized by diffuse hair thinning and subsequent baldness.
- Symptomatic baldness develops as a symptom of some pathology. In this case, alopecia is considered not as a separate nosological disease, but as a manifestation of other ailments, such as syphilis, vitamin deficiencies, connective tissue diseases, consequences of poisoning or radiation. In this case, various forms of baldness can develop: diffuse, focal, scarring or total. In most cases, when the underlying disease is cured, alopecia also goes away.
- Traumatic baldness develops as a result of physical or chemical damage to the hair and/or hair follicles, such as chemical or thermal burns. This also includes trichotillomania, a mental disorder in which the patient pulls out hair on his head or other parts of the body.
- Premature or hereditary alopecia is baldness that develops at a young age, while the patient’s history shows a familial nature of the disease. This form of baldness is often accompanied by a hormonal disorder in the direction of increasing male hormones, so it is often referred to as androgenetic alopecia. However, there are cases of hereditary alopecia occurring against the background of normal hormonal balance, so it is advisable to distinguish this form of baldness as a separate type.
- Presenile and senile alopecia (presenile and senile) develops against the background of aging of the body and is natural. With proper care and nutrition of the skin and hair follicles, this process can be significantly slowed down.
- Alopecia of unknown etiology and pathogenesis is baldness, the causes of which could not be determined.
According to the nature and form of baldness, they are distinguished:
- Focal or patchy baldness is the formation of bald spots, especially noticeable on the head. The disease develops as a result of autoimmune pathological processes in which cells of the own immune system attack the cells of the hair follicles. The exact causes of the development of the disease are still unknown; it is believed that heredity plays an important role in this case. There are several subtypes of alopecia areata: focal, multifocal, subtotal and total baldness, as well as ophiasis - hair loss in tortuously spreading foci, with the formation of a smooth skin surface.
- Diffuse alopecia is a uniform thinning of hair over the entire head followed by baldness. Diffuse alopecia occurs as a result of disruption of the entire body, usually due to the development or exacerbation of some general diseases or stress, so sometimes this form of baldness is classified as symptomatic. Diffuse alopecia is the second most common of all types of baldness. There are two subtypes of diffuse baldness: telogen effluvium (telogen miasma), when, as a result of some factor, such as stress, poor diet, hormonal imbalances, up to 80% of the hair follicles on the head enter the resting phase (telogen) ahead of schedule.
- anagen alopecia (anagen miasma), when under the influence of some factors, usually more aggressive than with telogen effluvium, such as radiation, chemotherapy, poisoning with certain poisons, hair follicles do not have time to enter the telogen state and hair falls out in the anagen phase, that is, at the growth stage.
The Small Medical Encyclopedia distinguishes seborrheic, premature, symptomatic and focal forms of baldness, as well as:
- Scarring alopecia is baldness that develops as a result of the formation of scar tissue in the area of the hair follicle. The cause of scarring may be trauma, an inflammatory process that leads to the formation of a scar in its place. Scarring alopecia accounts for 1-2% of all cases of baldness. It is impossible to restore the hair follicle at the site where the scar has been forced; only surgical transplantation of healthy follicles can be an effective treatment.
- Congenital alopecia is a rare form of baldness, which is manifested by partial thinning or, less commonly, complete absence of hair. Usually the condition is combined with cutaneous or ectodermal symptoms, such as thinning or dystrophy of the nails, pathology of dental development, and so on. In most cases, the disease has a hereditary or genetic etiology.
According to the course of the disease, they are distinguished:
- temporary alopecia (anagen and telogen miasma);
- chronic (androgenic);
- malignant (ophiasis) should not be confused with malignant tumors.
Causes
Scientists have not yet figured out the causes of total alopecia. However, there are factors that help the disease develop, for example:
- taking strong antibiotics, medications, hormonal drugs;
- congenital underdevelopment of hair follicles;
- genetic predisposition or autoimmune diseases (the body's cells are perceived as foreign, then the immune system puts all its efforts into getting rid of them, and as a result the body kills its own cells);
- previous severe infectious diseases, diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, failure of the endocrine system or thyroid system;
- severe shock, depression, stress.
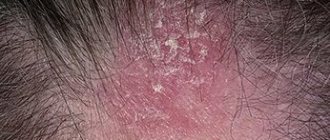
Symptoms of alopecia areata
| Disease stage | Characteristic |
| Acute | · Inflammation and swelling appear in places on the skin; · the process is accompanied by burning, itching, tingling in the baldness area; hair breaks easily; · the bald spot expands, in the border areas the hair can be pulled out painlessly; · the diameter of the lesion is from 0.3 to 1 cm |
| Subacute | · Areas of baldness are formed; · no longer bothered by redness and swelling; · itching disappears; · normal skin tone returns; Hair loss stops |
| Regression stage | · Thin vellus hair appears on the bald spot; · hair follicles are strengthened; Pigmentation is restored |
Stages
Total alopecia is the final stage of alopecia and develops in stages:
- Hair begins to shrink, becomes more brittle and falls out more than usual.
- The appearance of bald patches and the appearance of fuzz in those places where there was previously hair.
- Complete baldness. With rare exceptions, the disease progresses quickly; complete baldness is possible in 2 to 4 months.
Complete baldness occurs after focal baldness, since the bald patches seem to unite with each other, thereby increasing the area of baldness. Seeing a doctor is necessary if:
- excessive hair loss has been noticed;
- bald patches appear;
- intense hair loss lasts more than two weeks.
Tips for caring for different hair types
Proper hair care will help avoid the development of alopecia or significantly help in its treatment if the disease has already appeared. Please understand that different hair types require different care. Ideally, an individual hair care complex should be selected by a trichologist. However, there are some general rules for different hair types.
All hair can be divided into four types:
- normal;
- fat;
- dry;
- mixed.
Caring for normal hair
Even healthy hair of normal type requires proper care, which includes the following basic principles:
- comb no more than 4-5 times a day, do not pull the hair when combing, use a massage brush for combing;
- Wash when soiled with warm water;
- all skincare products should be intended for normal hair;
- Before going to bed, you should remove all styling products from your hair;
- Do not use very tight elastic bands or hair clips.
- do not comb wet hair
Oily hair care
- You can wash your hair as needed (even every day) with fertile or cool water, but not hot or cold;
- You can rinse oily hair with an infusion of nettle, coltsfoot, horsetail or sage;
- you should use products specifically designed for oily hair;
- It is necessary to comb your hair from the ends of the hair, without touching the roots;
- You should avoid using styling products, so it is better to choose a simple hairstyle.
Dry hair care
- It is better to comb your hair from the roots, as this stimulates the sebaceous glands;
- for combing, you must use any gentle comb, for example with a ceramic coating;
- You need to wash your hair as rarely as possible, but without allowing your hair to get too dirty;
- You should use warm water to wash your hair;
- It is better to avoid hot styling, the use of hair dryers and curling irons;
- all products used must be intended for dry hair;
- At least once a week you need to make special masks for dry hair.
Care for mixed hair
As a rule, this type of hair is characteristic of women with long hair. Their hair roots are oily and the ends are dry. In this case, it is recommended:
- wash your hair as needed with two types of shampoos at once, using shampoo for oily hair to wash the hair roots, and shampoo for dry hair to wash the entire length of the hair;
- do not blow-dry your hair, avoid heat styling;
- trim split ends;
- Apply special products to the ends of your hair to constantly additionally nourish and moisturize them;
- Apply masks to the hair roots once every 1-2 weeks to eliminate excess oil;
- Do not use tight hairpins, clips or elastic bands.
Hair can also be hard, soft, thin, thick, damaged, dyed, permed and keratin straightened. Thus, there are actually many more types of hair, and general recommendations do not always apply even to people with the same type. That is why it is important that a specialist develop a care package.
Mesotherapy
Mesotherapy is one of the most effective ways to treat alopecia. Using the mesotherapy method, the drug is injected under the skin. The serum contained in the drug helps awaken dormant hair follicles and also stimulate the growth of the hair shaft.
Mesotherapy is very often used to increase hair thickness, improve its strength, and give it shine and shine. After mesotherapy, even clients with total alopecia experience improvements. Therefore, this procedure can be used both for the treatment and prevention of various scalp diseases.
The composition, as well as the concentration of the active ingredients of the serums differ. Almost every serum includes components such as hyaluronic acid, vitamins, plant extracts, extracts, minerals, amino acids, and glucocorticoid hormones. All these components help increase hair growth, as well as improve their quality and quantity.
The entire medicinal cocktail is injected under the skin in several ways:
- Manual – the doctor performs mesotherapy himself.
- Hardware – the supply of the drug is carried out by a special device.
The number of punctures, as well as the depth of insertion, is strictly regulated by the doctor and is done under his strict supervision.
Photochemotherapy
The most famous method of photochemotherapy is PUVA therapy. This method is common in the treatment of many skin diseases. For quite a long time, it was believed that PUVA therapy was ineffective for total baldness. However, new studies have proven that PUVA therapy in combination with EHF therapy shows a high cure rate of 39.4%. Photochemotherapy together with medications, as well as measures aimed at restoring hair growth, helps achieve such results.
To treat the disease, a special comb with phytoactive enhancers is used. The course consists of 10 procedures, and they need to be repeated every three months until positive dynamics appear, which is confirmed by a trichologist.
Laser therapy
Laser therapy is actively used in therapy to treat diseases. It is used in various conditions of alopecia, including total alopecia. If laser therapy is carried out comprehensively, the following improvements appear:
- Metabolic activation.
- Increased regenerative and reparative properties of the scalp, which affect not only hair growth, but also its quality.
- Increasing local immunity.
- Increasing the proliferative capacity of skin cells (proliferation of skin cells by dividing them).
Complete treatment, in which visible improvements appear, consists of 12-15 procedures, the interval between which should not exceed 48 hours. Secondary courses are carried out no earlier than 60-90 days from the date of previous treatment.
Diathermy or pulsed currents
An outstanding and effective method of electrotherapy is a targeted effect on the scalp with pulsed currents. Improvement in the scalp of the skin occurs during the acupressure procedure not only with partial, but even with complete baldness.
The treatment is carried out as follows: the doctor moves a special electrode along the surface of the patient’s scalp, through which weak pulsed high-frequency currents are supplied. They activate skin cells and also have a beneficial effect on hair follicles.
This effect is achieved by improving lymph and blood circulation, normalizing tissue nutrition, and activating immune function.
It is most effective to use not only the pulsed current method, but also combine it with other methods of physiotherapy, for example, ultraviolet or laser irradiation.
EHF therapy
EHF therapy is one of the most effective methods for treating various stages of baldness. The technique involves irradiating the scalp with low-intensity electromagnetic waves.
The spectrum of therapeutic activity of EHF therapy is huge, its results:
- Restoration and improvement of the activity of the autonomic and neuroendocrine systems. They are responsible for regulating the hair cycle; after normalizing these systems, the stages of their growth are improved and normalized.
- Nonspecific resistance increases.
- The rheological properties of blood improve and homeostasis normalizes.
- The opiatergic regulatory system is activated.
However, EHF therapy has a drawback - the time that needs to be spent on the procedure. The course consists of 20 procedures that must be performed daily, and a repeat course must be completed after 3 months.
Diagnostics
While alopecia can be successfully treated in many cases, the key to effectively treating hair loss is identifying the cause and making an accurate diagnosis.
Diagnosis of alopecia includes a medical history, examination of the scalp and other areas of the skin, a hair loss test, examination of the scalp and hair under magnification (using a trichoscope), and in some cases a scalp biopsy. Laboratory tests help rule out or identify diseases that may cause hair loss.
In the future, depending on the results of diagnostic studies, a dermatologist (or trichologist) may recommend that the patient consult a therapist, endocrinologist, gynecologist, rheumatologist and other specialists.
What other methods are used to treat total hair loss?
Modern hair experts have a large number of techniques that allow them to treat total alopecia, achieving excellent results.
In addition to the methods listed above, the patient may be offered the following procedures:
- mud therapy;
- halotherapy;
- ultraviolet irradiation with medium and short wavelengths;
- balneotherapy;
- paraffin applications;
- massage, cryomassage with liquid nitrogen;
- vacuum therapy;
- hydrotherapy;
- infrared irradiation.
In addition to treatment, various serums, organic shampoos, as well as solutions with active substances, tablets, and sprays containing minoxidil, which helps stimulate hair growth, can serve.
Treatment prognosis
Patients undergoing treatment for total alopecia must normalize their daily routine, eat properly and establish a diet necessary for the patient’s age, and normalize their rest regimen.
Patients are advised to walk a lot in the fresh air, eat plenty of fruits and vegetables, and drink vitamins. To prevent recurrence of the disease, it is recommended to consume foods that contain natural sources of collagen and hyaluronic acid.
It is necessary to avoid situations that can cause stress and inadequate physical activity. It is also necessary to normalize sleep so that the body feels rested and stress does not arise due to chronic lack of sleep.
If the patient regularly monitors his own health, regularly monitors the condition of his hair, and does not forget to consult a doctor in case of symptoms, then the problem of baldness is solved at the initial stage of its appearance. If the patient has a genetic predisposition to total alopecia, then it is necessary to regularly visit a doctor (trichologist). After identifying the problem, the specialist will prescribe the correct treatment, as well as the correct hair care in a specific situation.
Treatment of androgenetic alopecia with traditional methods
Since ancient times, traditional medicine has offered various ways to strengthen hair, increase the density of curls, and reduce the rate of baldness. But all of them will give the expected effect only when used together with medications.
- Onion rub. At the first signs of thinning, it is recommended to rub a mixture of chopped onion into the hair roots. Leave the mask on for an hour and a half, then wash off with strengthening or regular shampoo. If you add crushed garlic and a little honey to the onion mass, the procedure will be even more effective.
- Pepper tincture. Grind the pepper, pour in 100 ml of vodka and leave for 24 hours. Then rub the tincture into the scalp and after an hour and a half, wash your hair thoroughly.
- Onion-cognac tincture. Grind a medium onion through a meat grinder and pour 200 ml of cognac into it. The mixture should sit for several hours. To achieve a positive result, the tincture must be rubbed into balding areas of the head daily.
- Mustard mask with castor oil. Take one tablespoon of dry mustard, mix it thoroughly with 30 ml of castor oil and let it brew for 20-30 minutes. To reduce the amount of hair falling out, a mustard mask should be applied to the scalp for 40–50 minutes. The session is carried out before each hair wash 1-2 times a week.
- Nettle lotion. The therapeutic effect is obtained by using nettle for androgenetic alopecia. In a saucepan with 5 tbsp. spoon leaves, pour 450 ml of water, add 2 tbsp. spoons of vinegar and put on the stove. Bring the mixture to a boil, keep on low heat for half an hour, then remove and cool. The product should be rubbed into the scalp every day before bed.
- Salt mask. Good results are obtained by rubbing regular or sea salt into the scalp 30–40 minutes before washing it.
- Mask with vitamins and Dimexide. Mix 2 tbsp. spoons of castor and burdock oil, add to them 1 teaspoon of vitamins A, E and 1 tbsp. spoon of Dimexide. The prepared mixture is rubbed into the roots of thinning hair and left for one hour.
- Tincture to strengthen follicles. Pour 1 tbsp into a jar. spoon of nettle and crushed burdock root, pour a glass of alcohol, add 1 bottle of alcohol tincture of mint and propolis. Close the jar tightly and put it in a cool place for a week. Then filter the composition and pour into a container with an airtight lid. Rub the resulting lotion daily before bed.
- Mask with sea buckthorn oil. Mix 1 teaspoon of sea buckthorn oil with 6–8 drops of grapefruit oil, 1 teaspoon of vitamins A, E and heat in a water bath. Then add 1 spoon of Dimexide to the mixture. Apply the mixture to the hair roots and leave for an hour.
Due to the fact that androgenetic alopecia is difficult to treat, some medications will have to be used throughout life, taking short breaks between courses. Otherwise, baldness will progress.
Why clients choose Veronika Herba Beauty and Health Center:
- This is a beauty center where you can take care of yourself at a reasonable cost, while your face and/or body will be treated not by an ordinary specialist, but by one of the best in Moscow. This is a completely different, higher level of service!
- You can receive qualified help at any time convenient for you. The beauty center is open from 9:00 to 21:00, seven days a week. The main thing is to agree with your doctor in advance on the date and time of your appointment.
Sign up for a consultation with a specialist by phone +7 (495) 085-15-13
, and you will see for yourself!