Types of abscesses on fingers or toes
Paronychia
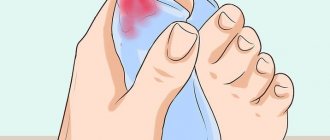
A mild form of finger ulcer, or paronychia, occurs when pathogens enter the skin. During the course of the disease, infiltrative and purulent stages .
Paronychia begins with redness and swelling of the skin around the nail. Then a pain syndrome occurs, the appearance of intercellular fluid containing microbes. As the infiltrate accumulates, a vesicle is formed, the contents of which become purulent. The following types of paronychia are distinguished: 1 . Paronychia of acute and chronic nature - depending on the duration.
Subepidermal paronychia
Acute paronychia occurs suddenly and is characterized by severe pain in the area of suppuration. Typically, this type of paronychia is caused by a bacterial infection - Staphylococcus aureus after injury to the upper phalanx (damage to the cuticle).
The chronic form manifests itself gradually : first, the skin around the nail turns red, the finger swells, and pain in this area occurs. 2. Paronychia is superficial (subepidermal) and deep , affecting the thickness of the nail fold near the base of the nail.
These varieties differ in localization and clinical course. With subepidermal paronychia, pus accumulates under the epidermis near the edge of the nail fold. Panaritium occurs when paronychia is treated incorrectly.
The following varieties are distinguished:
| Type of panaritium | description |
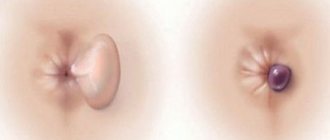
| Cutaneous panaritium | Occurs on the back of the finger. With this disease, pus accumulates under the epidermis, resulting in the formation of a vesicle with a cloudy liquid, often mixed with blood. The skin turns red, the pain syndrome is mild, and sometimes a burning sensation is felt. An enlarged vesicle indicates that the inflammatory process is developing in deeper tissues and the disease is progressing. |
| Periungual felon (paronychia). | described above |
| Subungual panaritium | Inflammatory process in the tissues under the nail plate. It develops when pus penetrates under the nail. The cause of the development of such a disease may be a splinter getting under the nail plate or an injection. |
| Localization of subcutaneous panaritium | Palmar surface of the finger. Inflammation occurs under the skin. The pus formed there cannot break through the thick enough skin in this part of the finger and come out, so the inflammatory process goes deeper - tendons, joints and bone tissue are affected. |
| Bone panaritium occurs when the bone of the finger is affected. | This occurs when the infection directly penetrates into the bone tissue (open fractures with infection) or when the purulent process spreads to the bone from the tissues surrounding it. |
| Articular felon is called purulent arthritis of the interphalangeal joint | This disease occurs due to the direct penetration of infectious agents into the joint cavity, as well as due to the prolonged course of subcutaneous panaritium. This type of panaritium is manifested by a sharp limitation of the motor functions of the joint, pain during palpation and movement of the finger. |
| Tendon panaritium is also called tenosynovitis. | This is a rather serious disease that leads to long-term limitation of the functioning of the hand. With such panaritium, swelling occurs, the finger takes a bent position, and movements are limited. Tendon panaritium differs from its other varieties in its severe pain syndrome. |
How does it manifest?
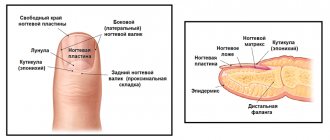
Symptoms of paronychia depend on the form of the disease. When the protective barrier between the nail and the nail fold is broken, pathogenic microorganisms or aggressive substances enter there, which triggers the growth of pathogenic microflora and the inflammatory process.
In acute paronychia, inflammation develops quickly. The first signs appear 1 to 2 days after the injury. These include redness of the damaged area, swelling, pain when pressed, and a local increase in temperature. Subsequently, purulent masses accumulate under the skin, which appear yellow or yellow-green. At the same time, swelling increases, the nail fold rises, and the finger becomes painful not only when pressed, but also at rest. Bending the upper phalanx of the finger causes difficulty; there is a feeling of fullness inside. With strong pressure, pus may be released from the nail sinus, the gap between the nail bed and the nail fold.
Paronychia in a small child initially causes moodiness and problems sleeping. Then the baby’s finger turns red and swells. The inflamed area becomes hot to the touch, touching it is very painful. The child cries, pulls away his sore finger when the parents try to look at him, and cannot bend it.
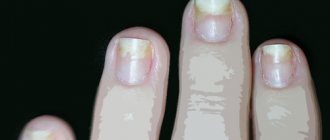
The chronic form of inflammation develops slowly and does not cause severe pain. The nail fold may be red and swollen. There is no throbbing pain. Accumulation of pus is possible only during exacerbations. The skin on the nail fold may peel and flake. Long-term chronic inflammatory processes lead to dystrophic changes in the nail and the disappearance of the cuticle. The shape and structure of the nail plate changes, its thickening and discoloration are observed.
Fungal and bacterial forms of infection differ in intensity and localization of the inflammatory process. With fungal paronychia caused by infection with a fungus of the genus Candida, redness and swelling are observed. There is pain when pressing on the roller. With prolonged flow, transverse grooves form on the nail, and the periungual skin peels off. The inflammatory focus is located between the nail skin itself and the outer surface of the nail plate. A bacterial infection is characterized by severe throbbing pain; the inflammatory focus is located in the soft tissues of the nail fold and does not affect the nail plate.
Causes of a sore finger near a toenail or hand nail
Improper manicure as a cause of paronychia
One of the most common causes of inflammation of the finger in the nail area is incorrect performance of pedicure and manicure.
Careless actions can damage the cuticle and provoke an inflammatory process with further accumulation of pus around the nail. Typically, such inflammation is caused by streptococcal and staphylococcal microorganisms that live on the skin of every person.
The development of the inflammatory process is influenced by certain conditions, such as:
- decrease in the body's immune forces
- presence of severe concomitant blood diseases
- metabolic disorders.
- fungus on the feet or nails.
Most cases of felon development occur after injury to the skin on the fingers. Moreover, the inflammatory process can occur even due to minor injuries - abrasions, scratches or splinters, cracks due to the skin being too dry and flaking. An infection penetrates the skin, which gives rise to purulent inflammation. For this reason, even minor wounds should be immediately treated with alcohol-containing solutions or iodine. Hangnails can also cause inflammation and the formation of pus in the tissues of the finger near the nail.
Classification of the pathological process
An abscess on the big toe can be acute or chronic. Acute panaritium begins suddenly and develops quickly, characterized by severe pain in the affected area. Often provoked by high sensitivity of the skin. The finger near the nail can become sharply inflamed, which provokes vivid clinical symptoms - pain, swelling. The affected area may fester and become swollen.
Chronic panaritium is characterized by a slow course of the inflammatory process. The pain syndrome increases gradually, first the affected area swells, then suppuration forms near the nail. This condition can last for quite a long time, but you should not let it get worse; it is better to consult a doctor as soon as possible.
Inflammation of the toe from an ingrown toenail
An ingrown toenail is also often the cause of inflammation and suppuration of the area around the nail plate.
Inflammation from an ingrown toenail
There are people prone to this problem. The most susceptible to ingrown toenails is the big toe. This is influenced by the special location and size of the periungual fold, as well as the growth of the nail itself. Also, an incorrectly done pedicure on the feet can contribute to ingrowth: if the corners of the nail plate on both sides are prevented from growing by the periungual ridge, they grow into the soft tissue. Therefore, it is necessary to properly treat the nail plates during a pedicure:
- control the length of your nails and do not grow them;
- do not give your nails a square shape or file off the corners;
- regularly carry out foot baths to soften the skin and nails;
- remove dead skin particles in areas of possible ingrown nails.
The first sign of an ingrown nail is pain in the periungual fold near the edge of the nail plate . Then the pain spreads to the entire phalanx. Due to the fact that such sensations are tolerable, most people do not pay much attention to this problem. But then they notice that the skin around the nail is inflamed. If measures are not taken, the situation will become more serious and suppuration will begin around the nail plate. If an abscess forms, it is better to consult a doctor to avoid complications.
Causes
A common cause of purulent inflammation is trauma to the periungual tissues, which can occur as a result of a carelessly performed pedicure procedure, when splinters and microtraumas appear.
Violation of the upper layer of skin (epidermis) serves as an “entry gate” for the penetration of an infectious pathogen.
In turn, inflammation of the toe of septic origin can be caused by:
- fungus of the Candida type, which is a type of opportunistic pathogen that lives on the skin;
- pyogenic cocci that produce pus;
- ulcerative paronychia, which results in ulcerations on the periungual fold.
Parasitic fungi, as well as staphylococci and streptococci, live everywhere, including on the skin of human feet. In the absence of damage to the epidermis, good immunity and the absence of severe chronic diseases, the microflora does not pose a danger to humans.
When deviations occur, pathogenic microorganisms can lead to suppuration.
Provoking factors that cause the formation of an abscess on the finger include:
- the appearance of scratches, cuts, abrasions on the skin near the nail;
- exposure to chemicals;
- ingrown nail;
- frequent overheating of the feet.
Endocrine pathologies – diabetes mellitus, dysfunction of the thyroid gland – increase the incidence of abscess on the finger. Improper metabolic reactions, hormonal imbalances, and chronic diseases of internal organs contribute to a decrease in the body's defenses.
Wearing low-quality shoes, incorrectly selected for the size or season, and poor personal hygiene lead to the development of inflammation of the big toe.
Splinter as a cause of nail abscess
A splinter is the cause of inflammation of the fingernail.
A splinter can cause an abscess under the nail if it gets into this area.
In this area, small splinters are difficult to notice. They are not exposed to mechanical stress, so in such situations a strong inflammatory process develops. If it is possible to remove the splinter on your own, after removing it, you should use means to relieve inflammation. This way the situation will quickly return to normal. In some cases, removing a splinter may require the help of a doctor.
Signs of a nail abscess
In most cases, the big toe is affected by paronychia and panaritium; any finger on the hands can become inflamed.
By the damage to several nails at the same time, one can judge the work of the body’s immune forces - its decrease. Also, an inflammatory process on more than two toes may indicate the presence of foot or nail fungus. But no matter what causes felon, the characteristic symptoms will be:
|
If you find these signs in yourself, it is better to contact a surgeon to prescribe the correct treatment and avoid complications.
Clinical manifestations of purulent inflammation
A complex of local symptoms of phlegmon of the left or right foot develops within several days from the moment of infection.
- Within two to three days, a tumor appears on the back of the foot in the form of a dense infiltrate, tissue edema forms, and bursting pain appears.
- Over time, the infiltrate softens in the direction from the center to the periphery.
- The skin in the affected area acquires a beet-red color with a local increase in tissue temperature.
- Palpation during examination causes pain; it is difficult for the patient to localize the source of inflammation.
- Attempts to move the leg, much less walk, are met with attacks of acute pain.
- The motor function of the foot is limited.
- The popliteal lymph nodes are enlarged.
In addition, clinical manifestations characteristic of most inflammatory processes develop quite quickly - an increase in body temperature to 39-40°C, decreased performance, weakness, headaches. If the process quickly spreads deeper, the patient’s condition worsens: shortness of breath and palpitations appear, intoxication syndrome develops, and urinary function is impaired. The patient needs immediate hospitalization.
Complications of finger inflammation
An abscess in an advanced form is very dangerous : the purulent inflammatory process can spread deeper: to the tendons, bone tissue, and finger joint. The finger may partially or completely lose its function. Moreover, inflammation can affect the hand and forearm. A severe form of panaritium with concomitant diseases, such as diabetes, can lead to the following complications:
more complicated than nail inflammation
- sepsis (blood poisoning) - a rather dangerous condition that can lead to death without qualified help;
- phlegmon of the hand - acute purulent inflammation of the cellular tissue of the hand;
- tenosynovitis - a purulent inflammatory process in the tendon sheaths, the most severe condition in which there is a long-term loss of mobility of the affected finger;
- osteomyelitis - a severe purulent process of bone tissue that requires immediate surgical intervention, sometimes complete amputation of the finger.
First aid for a nail abscess
In order to normalize the situation when the first symptoms of an abscess appear on a toe or hand, you should know the rules of first aid, as well as warnings. What you should not do under any circumstances is to pierce a bubble with pus in order to get rid of it, because in a greater degree of probability, it will not be possible to completely remove all the purulent fluid, and such an effect will not have any effect.
This is quite dangerous - if you insert the needle too deeply, you can provoke blood poisoning and the infection will spread throughout the body, and this is fraught with serious consequences.
What you can do: a warm bath with substances that have anti-inflammatory properties: salt, soap or chamomile decoction. The foot should be immersed in this liquid several times a day, which will significantly reduce the occurrence of unpleasant symptoms. After the procedure, you should blot the limb with a towel, then you are allowed to make an onion compress or use aloe leaves instead.
Healing properties for treating wounds
The high effectiveness of saline solution is due to a fairly wide pharmacological spectrum:
- Adsorbent - salt particles retain water, oil and foreign particles, and then bring them to the surface of the wound. This allows you to heal even the deepest wounds, while all the contents of the wound will be extracted. Syringes can be used to conveniently treat deep wounds.
- Disinfection - in a salt environment, all pathogenic microorganisms die, because salt disrupts all metabolic processes, which leads to their death. Saline solution can also compete with other disinfectants.
- Anti-inflammatory and anti-edematous effect - salt removes fluid from the wound, prevents swelling, redness and itching. The inflammatory process occurs in a less pronounced and painful form.
- Accelerated regeneration processes - after removing exudation, the wound dries faster, the crust shrinks, which prevents bacteria from penetrating inside.
- Complete safety - while iodine and varnish cause soft tissue burns, saline solution is gentle on the wound without drying it out. Only dead and damaged cells that cannot recover are removed. Salt does not affect the quantitative and qualitative composition of blood.
- It does not cause adverse reactions - although medications can cause allergic reactions, salt is a natural ingredient needed by the body.
Saline solution for wounds is an excellent remedy
Saline solution is easy to prepare and use
There is no need to buy special products at the pharmacy or study the instructions. The solution will be ready in 1 minute, until the salt is completely dissolved in the water. However, you should pay attention to such an important indicator as salt concentration. If you prepare the solution “by eye”, you can forget about the effectiveness of the procedure for two reasons:
- Lack of salt does not allow removing excess fluid from the wound and speeding up metabolic processes.
- Excess salt can negatively affect the condition of newly formed epithelial cells, making regeneration difficult.
The appropriate amount of salt in the solution provides a disinfectant, anti-inflammatory and decongestant effect.
Treatment of paronychia and panaritium
For abscesses on the toe and hand, medications are more effective than traditional methods of treatment.
- One such medicine is Dimexide . It is prescribed when the patient cannot use warm baths. This drug has powerful antiseptic properties and good penetration through the skin. Dimexide is often used by doctors for purulent dressings.
The solution is applied to a cotton swab and applied to the inflamed area of the finger. If adverse reactions occur, the drug is discontinued.
- For moderately severe inflammation, your doctor may prescribe antibiotics taken by mouth .
- If pus accumulates near the nail plate, the surgeon will numb the area and remove the fluid.
- For chronic paronychia caused by a fungal infection, the doctor will prescribe topical medications against this type of fungus. These drugs include Clotrimazole, Ketonazole and others.
Treatment can be quite long - from several weeks to several months. In complicated cases, oral antifungal drugs or steroids will be required.
| If treatment for a chronic abscess on the finger is ineffective, it is necessary to exclude various neoplasms, since the signs of these conditions may be similar. |
Foot baths
How to treat panaritium? The appointment is made by the doctor after examining the wound and conducting tests. For example, pus from under the nail is cultured to identify a specific pathogen. If a person is determined to cure himself, then he should know that he cannot open an abscess on his own. This is doubly dangerous when it comes to felon in a child. An abscess can only be removed by a specialist under appropriate conditions and with a sterile instrument.
Traditional medicine offers many methods for treating finger abscess, which in some cases turn out to be very effective and efficient for any form of the disease. These are compresses, baths, ointments and tinctures.
To quickly get rid of the existing problem, it is recommended to use several methods at once.
Baths for an abscess of the finger near the toenail:
- Soda. Add baking soda to warm water in a ratio of 100 g per 1 liter of water. The foot with the sore toe is placed in it for 10 minutes. If necessary, repeat the bath after 2-3 hours.
- With potassium permanganate. The water should have a pale pink color. The duration of the procedure is 10-15 minutes.
- With garlic. To prepare such a bath you will need a head of garlic, 25 g of soda and 10 g of sea buckthorn oil. Chop the vegetable, add a little warm water, oil and soda and mix. Leave the mixture for 3 minutes and pour into a container with warm water. The foot is immersed in the liquid for half an hour, and you need to periodically add hot water to prevent the bath from getting cold.
- With soda and salt. This foot bath is recommended for ingrown toenails and skin tags. Pour warm water into a basin, pour 2 tsp into it. soda and salt, mix. The duration of the procedure is 20 minutes.
Antibiotics for the treatment of abscess on the finger
When treating suppuration caused by streptococci or staphylococci, antibacterial drugs are always prescribed.
- With subcutaneous panaritium, antibiotics are used when the inflammatory process moves deeper, but in the absence of purulent tissue decomposition.
The greatest effect is observed from drugs of the cephalosporin or penicillin series.
- At the beginning of the development of articular panaritium, intra-articular injections with broad-spectrum antibacterial drugs are used. But in severe cases of this disease and in the absence of effect from injections, the only treatment method will be surgery, which also uses antibiotics.
This group of drugs is also prescribed for phlegmon of the hand or finger, if after surgery there are foci of inflammation and pus. In such cases, antibiotics are used to prevent infection of adjacent tissues. Broad-spectrum drugs for this condition are prescribed in fairly high doses.
inflammation surgery
These are antibiotics such as Ampicillin, Oxacillin, Cloxacillin, Erythromycin, Methicillin, Chloramphenicol . For local exposure, the affected area is pierced with a penicillin solution containing novocaine. The dosage is determined by the doctor individually.
Drug treatment
Anti-inflammatory ointments will help relieve suppuration of the finger at the nail. You can buy them at the pharmacy without a prescription. If a finger on your hand breaks out near the nail, most doctors prescribe these medications:
- Levomekol. Antimicrobial ointment, relieves inflammation, easily penetrates tissue.
- Vishnevsky ointment. Antibacterial balsamic liniment that accelerates regeneration and relieves inflammation.
- Dioxidine. A broad-spectrum antibacterial agent, prescribed only to adult patients.
If your finger near the nail is seriously festering, and the inflammatory process is accompanied by general weakness and fever, the doctor may prescribe antibiotics. They are taken orally (orally or by injection) and are based on penicillin or cephalosporin. Can be assigned:
- Ampicillin.
- Chloramphenicol.
- Oxacillin.
- Erythromycin.
Your doctor will tell you how to treat serious inflammation. You cannot take antibiotics on your own. The dosage and method of administration are also determined individually.
Surgery to treat nail inflammation
If conservative treatment was started late and did not bring results, complications arise that can only be eliminated through surgery. To do this, drainage of purulent fluid is performed under local anesthesia . If the skin in the area of the abscess has acquired a white or yellow color, local anesthesia is not performed, since this sign indicates damage to the nerve fibers. Surgical options:
| 1. Surgical intervention for superficial paronychia is carried out by cutting without the use of local anesthesia of the exfoliated skin, followed by its excision and removal of the purulent mass. Then an antiseptic bandage is applied for 5 days. This time is necessary for epithelization of the wound area. |
| 2. In case of deep paronychia, a 10 mm incision is made in the direction of the palm at the marginal part of the base of the nail. The skin covering the base of the nail plate is not cut, but is pushed back, cleaned and turned away from the damaged side. If the nail plate at the base peels off due to a purulent mass, it is carefully excised. If this area is accidentally damaged, the growing nail will become deformed. |
| 3. If the entire nail bed or its middle part is damaged Two 10-15 mm incisions are made. A trapezoid-shaped area of skin is turned away from the base. The part of the nail that is peeled off due to pus is removed and the pus is eliminated. A special rubber strip is placed under the skin flap, onto which Vaseline is applied, and the skin returns to its place. An antiseptic bandage is applied to the finger. After a day after the operation, the finger is dipped in a warm solution with the addition of potassium permanganate, the rubber gasket is changed and left for another day. If the purulent inflammatory process ceases, the rubber strip is no longer used, and a bandage with ointment is applied to the wound surface. |
For faster healing of incisions and to prevent secondary infection, a course of antibiotics and antiseptics is prescribed.
Requirements and features of using saline solution for treating wounds
There are a number of requirements, the fulfillment of which guarantees the achievement of the desired result in the shortest possible time:
- The optimal salt concentration in water is a 9% solution, the content of which is identical to natural human tears. A 10% solution is also allowed, but no more. Too much salt in the water can cause chafing and excessive drying of the open wound, which will slow down and complicate the regeneration process.
- Type of salt - Do not use flavored sea salt or fine table salt. The best option is medium-ground table salt without various additives, flavors and dyes.
- Ventilation - When applying a dressing to a wound, do not cover it with a piece of plastic, thick cloth or other objects to prevent the solution from spreading over the body. Ventilation must be provided under the bandage. Otherwise, increased humidity and heat from the wound will become excellent conditions for the development of pathogens.
- There is no need to isolate the compress - the bandage should be attached to the wound for maximum fixation. There is no need to keep warm with scarves, scarves and blankets; body temperature is sufficient to activate natural regenerative processes.
- Use only sterile dressings - the dressing material should be made from natural fabrics. Sterile dressings and gauze soaked in boiling water are preferred. It is not recommended to reuse dressing material, even if it is almost clean. Compliance with the rules of asepsis is the main guarantee of rapid wound healing.
- Bandage temperature - to achieve maximum therapeutic effect, it is recommended to set the bandage at a temperature slightly above body temperature. The cold saline solution and bandage will cause the blood vessels to constrict, making it difficult to remove fluid from the wound.
- Duration of application of the compress - the bandage cannot be kept on for more than 5 hours. Dressings should be done at least 3 times a day. After applying the bandage, the wound is washed with boiled water and fixed with an antiseptic.
To prepare a saline solution for wounds, it is best to use salt with a medium degree of disintegration, without any additives or additives.
Not all saline solutions can be used to treat wounds:
- Isotonic is the closest thing to saline in the body. It contains 9% salt in water. It does not irritate the wound and does not cause changes in the quantitative and qualitative composition of cells at the wound site.
- Hypertonic - salt concentration is more than 9%. It reduces cell size by removing large amounts of fluid. Most effective in the treatment of purulent and ulcerative wounds.
- Hypotonic - the concentration of salt in the solution is minimal, so it is practically not used for treating wounds.
All actions related to applying a salt dressing and dressing a wound should be performed with sterile gloves, which will reduce the number of pathogens on the surface of the wound. For convenience, you can use tweezers that have been previously disinfected with alcohol.
Home treatment for nail abscess
Treatment of nail and subcutaneous panaritium at home is possible only at the onset of the disease and under the close supervision of a doctor. If there is no effect from ointments, baths and the signs of the disease intensify, the only way to get rid of purulent inflammation will be surgery. Treatment in the clinic can be carried out for such types of panaritium as subcutaneous, cutaneous and nail. When purulent inflammation spreads to the joints, tendons and bone tissue, the patient is referred
Herpes infection on toe
to the surgical department of the hospital.
Herpes infection of sore finger
If there are blisters on the inflamed finger or toe , filled with clear liquid or mixed with pus and blood, the cause of panaritium is most likely caused by herpes pathogens. Most often, herpes infection on the fingers occurs in children , but such blisters are also present on other parts of the body - in the mouth, on the lips.
| The difference between herpes inflammation on the fingers and others is that it does not respond to treatment with antibacterial drugs. For abscesses caused by these pathogens, surgical intervention is not performed, as there is a risk of infection spreading throughout the body and causing serious complications. |
If you suspect herpes inflammation of the finger, treatment should be carried out as follows: 1. Apply Acyclovir ointment to the inflamed area for a week. After this treatment, the skin will return to normal in 1 or 2 weeks. 2. A bandage can be applied to the site of inflammation in order to reduce the risk of the herpes infection spreading to healthy parts of the body, especially the mucous membranes. If the use of the ointment does not bring results and the inflammatory process only intensifies, you need to make an appointment with a doctor to choose further treatment tactics.
If a child's finger is torn
An abscess on a finger in children is a common phenomenon. A splinter that is not removed in time or a cut that has festered leads to a similar problem. The infection quickly penetrates the wounds through dirty hands or feet and begins to quickly spread inside.
A child picks a nail
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=eaXqPMbdPKo
If a child begins to complain of pain in a finger, you need to take measures:
- prepare a herbal solution from chamomile, St. John's wort and calendula;
- ask the child to hold the inflamed area of the finger in the solution for 15-20 minutes. The solution can be prepared from potassium permanganate, after which the inflamed area should be wiped dry and treated with brilliant green. After 3-4 hours, check the condition of the finger.
If the inflammation does not go away and the swelling does not subside, you need to apply Vishnevsky ointment. Despite the pungent odor, the ointment actively fights bacteria, destroying their flora, and the abscess matures faster. You need to check the condition of your finger the next day.
Note If the ointment does not help, there is no improvement, the swelling of the finger quickly spreads to neighboring areas, then you need to consult a surgeon urgently.
It is worth considering that during the first day after a cut and suppuration, only a small abscess on the finger can be eliminated. If after a day there is no improvement, the abscess does not go away, self-medication is unlikely to help, it is better to go to the doctor.
Folk remedies for the treatment of felon on the arm or leg
Traditional methods are effective only at the initial stage of inflammation and abscess on the toes and hands.
- For this, lotions with an infusion of herbs that have antiseptic properties are used: chamomile, calendula.
To obtain the product you will need 200 ml of boiling water and 1 spoon of dry raw materials. The grass is poured into a container with liquid and left for a while. A cotton swab is soaked in the cooled infusion and applied to the affected area and fixed.
- potassium permanganate or soda and salt are no less effective . Bath with potassium permanganate
The amount of potassium permanganate should be such that the liquid acquires a pale pink color. The finger with the abscess is dipped into this solution, after a while it is removed, blotted with a towel and ointment is applied to the affected area, followed by a bandage.
- To obtain a salt-soda bath, you need to dissolve a spoonful of soda and salt in 200 ml of water. Such baths are allowed to be performed alternately.
- Onion compress
A compress with onions is a fairly effective remedy in the treatment of panaritium. In order to prepare it, you need to take ¼ of the onion, grate it on a coarse grater and place it on gauze to form a layer 1 cm thick. The compress is applied to the finger, covered with film, and then secured with a bandage. You should keep such a compress on the affected area for 2 hours, then take a bath with soda and salt and replace the onion mass with fresh one. This alternation should be carried out 2 times a day. If there is no effect within 3 days, consult a doctor.
ethnoscience
For mild pathologies, it is possible to use products with natural ingredients as an addition to traditional therapeutic measures. To treat suppuration, medicinal baths and compresses can be used.
Before using the recipe, a sensitivity test is performed by applying a small amount of the product to the inner surface of the forearm. It should be remembered that each action must be approved by the attending physician.
Foot baths
- In 250 ml of water brought to a temperature of 60 degrees, dissolve 15 grams of soda and the same amount of salt. Keep the foot with the affected toe in the solution three times a day for 15 minutes.
- Chop a few cloves of garlic, add 15 ml of sea buckthorn oil. Dilute the resulting mixture with hot water to the consistency of liquid sour cream. Exposure time is 5 minutes until the liquid cools down.
- A bath with a decoction of calamus has an antiseptic effect. Dry raw materials are poured with boiling water and infused for half an hour. The sore finger is kept in the decoction for 15-20 minutes.
Effective compresses
Treatment with compresses is carried out after water procedures. Baked onions are used for the medicinal base. Apply half a baked onion to the affected finger, secure it with cling film and wrap it in a warm scarf. It is recommended to leave the compress for 2-3 hours.
White cabbage has anti-inflammatory and analgesic effects. The leaf is washed, smeared with honey and applied to the abscess. You can secure the cabbage using loose bandaging.
Panaritium in a child
Finger abscess in a child
You need to watch your child’s fingers especially carefully, since children, more often than adults, have the habit of biting their nails and tearing off hangnails, which can lead to an inflammatory process on the hands. If a red spot appears near a child’s fingernail, you should immediately smear it with iodine solution . You can also apply a cotton pad soaked in calendula tincture. Lotions will also help. This is necessary to stop the inflammatory process at the very beginning of its development. If an abscess appears, you should never try to treat it yourself or pierce it with a needle. The best solution would be to consult a doctor, he will carry out the necessary manipulations. Since in children the inflammatory process and the formation of pus occurs very quickly , surgical treatment is usually used.
In order to prevent the development of felon in a child, you need to:
|
Recommendations
To prevent the appearance of paronychia in a child or adult, it is necessary to trim nails using special tools that undergo antiseptic treatment before use. If tissue integrity is compromised, the damaged area should be treated and a bandage applied.
Using protective gloves will help reduce the likelihood of developing an inflammatory process on your fingers. Timely manicure and pedicure will help prevent ingrown nails.
Regardless of whether there are damaged areas on the skin, you should always ensure that your hands and feet are clean. Pathogenic microflora (with reduced immunity) can penetrate microcracks in the epidermis and cause the development of an inflammatory process.
Prevention of paronychia and panaritium
The main preventive measure for such conditions is to avoid damage and injury to the skin on the fingers: bruises, cuts. It is also important to maintain daily foot hygiene . More information about paronychia can be found in the video.
Using the services of a professional pedicurist will protect you from improper treatment of the nail plates and its consequences: damage to the skin, ingrown nails and inflammation.
Wearing comfortable shoes will also eliminate these unpleasant situations. Treatment of chronic diseases that can cause inflammation of the toes is also important. Diabetes requires constant monitoring of blood sugar levels. Increasing immunity will strengthen the body and activate forces to fight infections.