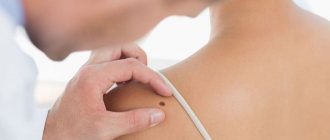
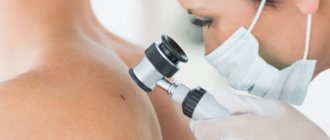
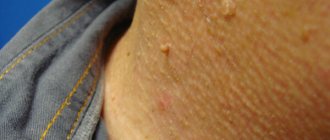
Anal warts are just one of the types of manifestations of HPV (human papillomavirus), which is very common these days. In this case, the disease manifests itself in the form of dry growths or genital warts, concentrated around the anus and in the adjacent area of the rectum.
Often, such neoplasms merge with each other, forming conglomerates, which in exceptional cases completely block the anus and complicate the process of defecation. As a rule, this happens if, in addition to HPV, the infected person suffers from diabetes mellitus or an immunodeficiency virus.
What happens if you tear off a papilloma on a leg?
When a pedunculated papilloma is detached from the base, the benign neoplasm begins to become inflamed.
This creates a wound surface.
All this is accompanied by itching and increased body temperature.
There is suppuration and swelling due to the inflammatory reaction.
Remains of papilloma must be removed in a hospital setting.
Such injuries threaten the degeneration of a benign papilloma into a malignant neoplasm.
Sometimes, with good immunity, papillomas come off and new ones do not grow.
There is no negative impact.
The recovery is complete.
Symptoms of anal warts
A burning sensation in the anus is a symptom of the appearance of anal warts.
Although many people infected with HPV are asymptomatic, doctors have long known the full list of “classic” manifestations of this disease. In addition to anal warts, carriers of the papilloma virus often voice the following complaints:
- itching and burning in the anus;
- hyperemia;
- cracks and suppuration in the anal area;
- discharge from the anus;
- uncharacteristic pain that appears during anal sex.
In the presence of concomitant diseases (for example, HIV), HPV symptoms can increase many times over.
Some side signs of the virus may also begin to appear. For example, wart growths, when infected, begin to emit an unpleasant odor and provoke the formation of fistulas in the anus, starting the process of intoxication of the entire body.
This, in turn, leads to discharge from the anus of ichor mixed with pus and the appearance of sharp, almost unbearable pain during defecation.
How to distinguish a papilloma from a mole
The papilloma is colorless and pedunculated.
A nevus or wart does not have a stalk and is brown in color.
It is advisable to remove papillomas, since they are most often located in areas of increased trauma and are not very aesthetic.
As a rule, moles do not pose any danger.
They do not have a special function and in their structure contain various pigments in large quantities.
About the prevention of anal warts
It is important to understand that there is no 100% guarantee of avoiding infection with HPV (and, in particular, anal warts). However, certain measures can help minimize this risk. Doctors give the following recommendations on this matter:
- It is important to regularly undergo complete medical examinations, including examination by a proctologist, dermatovenerologist, as well as a gynecologist or urologist.
- Timely vaccination against HPV helps reduce the risk of contracting this disease several times.
- During each sexual intercourse (especially not with a regular sexual partner), you should use condoms.
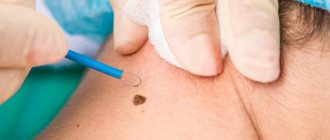
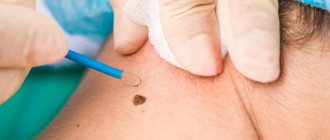
Pedicled papilloma: diagnosis, histology
Pedicled papillomas, like other papillomas, must be subjected to histological examination.
This will complement the cytological examination.
The histological examination method consists of analyzing a biopsy specimen - a part of the papilloma obtained during its removal.
A microscope is used for this.
We evaluate the nature of the benign tumor and determine the degree of oncogenicity of the papilloma.
Within three days after the study, we have the result.
The diagnosis of papillomatosis when infected with HPV occurs on the basis of laboratory diagnostics:
- cytological analysis (to determine changes in the cellular material of the test sample);
- carrying out a polymerase chain reaction (to find viral DNA in the material under study);
- obtaining a biopsy specimen for histological examination;
- carrying out the histological examination itself;
- conducting a daijin test.
The Daijin test is carried out to determine the type of HPV, its quantity and degree of oncogenicity.
Without laboratory research methods, based only on the clinical picture, even an experienced doctor has difficulty in making a correct and accurate diagnosis.
Medications
A good alternative to traditional treatment can be drug therapy prescribed by a specialist. There are many ways to treat this disease. However, none of the options for removing skin tumors guarantees getting rid of virus cells, so the growths may appear again. A third of patients cannot completely get rid of HPV, so their papillomas appear again, but they must be removed each time.
Surgitron device: principle of operation and areas of application of the radioknife
Complex treatment of the disease is carried out using the following medications for internal and external use:
- The use of antiviral drugs is indicated. Doctors usually prescribe Isoprinosine as an antiviral agent and Panavir or Genferon to stimulate the immune system response.
- To cauterize small and single formations, use a solution of Solcoderm or Condilin. These drugs allow you to remove papillomas using non-hardware and non-surgical methods. To prevent the growth of tumors, the drug Podophyllin is prescribed.
Despite the abundance of methods for treating papillomas, various methods for their removal are very popular.
Complications of papillomas
The most important complication is the degeneration of benign neoplasms into malignant tumors.
It is necessary to determine as quickly as possible the type of HPV that caused the formation of papillomas.
If it is a highly oncogenic type 16 or 18, constantly monitor the development and changes in the condition of papillomas.
These pedunculated papillomas also threaten traumatization and relapse.
You should always remember this and avoid injury, and after removing papillomas, prevent their occurrence.
What types of anal warts are there?
Genital warts are a type of anal wart.
Depending on their appearance, manifestations of HPV in the form of anal warts can be divided into several large groups. Their classification will look like this:
- Genital warts. These formations look like elongated “papillae”. When several warts are concentrated in one place, they resemble a cockscomb in appearance.
- Papules. Such formations are characterized by small sizes and the absence of “finger-like” (in other words, elongated) elements. In small quantities, often almost invisible above the skin.
- Common warts. As a rule, these neoplasms look like flat spots and are distinguished by a wide variety of shapes, colors and sizes.
- Buschke-Lowenstein condylomas. These formations are quite rare in practice. They differ from ordinary condylomas by their unusually large, almost gigantic size.
- Bowen's disease. With this diagnosis, neoplasms affect the entire area of the mucous membrane in the anus. The second name for this disease is intraepithelial neoplasia.
Despite the fact that HPV (especially types 16 and 18) often provokes the development of malignant tumors and other serious diseases, the appearance of anal warts in itself is not a cause for alarm. Typically, such reactions are caused by the entry into the body of subtypes of the virus numbered 6 or 11, each of which is known for its low oncogenic activity.
Degeneration of papillomas into malignant pathology
We must always remember that HPV poses a risk of cancer.
Especially highly oncogenic types, for example, 16 and 18.
Typically, malignant degeneration of papillomas cells takes ten to twenty years from the moment of infection.
The process is accelerated by smoking, drinking alcohol, obesity and hormonal disorders that reduce immunity.
It is the decrease in immunity, which occurs for various reasons, that contributes to the activation of HPV and the transition of the benign state of papillomas to a malignant pathology.
The destruction of papillomas is enhanced by cytomegalovirus, genital herpes, chlamydia, syphilis, gonorrhea, and trichomoniasis.
And of course, you need to avoid frequent trauma to papillomas, which contributes to their malignancy.
A direct indication for removal of papillomas is the presence of large papillomas.
They are often hurt and hurt.
Methods for removing papillomas
There are quite a lot of methods for removing papillomas.
Let's consider everything.
Firstly, it is the destruction of papillomas using a special liquid containing alkali.
They are purchased in pharmacies with prescriptions from the attending physician.
The disadvantage is considered:
- the need for precise local application of liquid to papillomas,
- risk of chemical burns to adjacent tissues,
- painful procedure,
- the possibility of scars appearing at the site of papillomas removal.
Usually, the method is used to remove single vulgar papillomas (warts) of the hands.
It is not suitable for filamentous papillomas.
Refrigerants are used for cryodestruction.
Basically, liquid nitrogen is used.
Although other refrigerants are possible.
The application of the coolant is painless; acute pain occurs later when “defrosting” occurs.
After a certain time, the surrounding tissues turn red and swell.
There is an active formation of a subcutaneous bladder filled with fluid.
After a week (maximum one and a half months), everything heals and is restored.
It takes three weeks for the tissue under the crust to die, while the infected tissue is reliably destroyed.
There are no scars, and any traces disappear within six months.
The intimate area and face are not treated with this method.
Firstly, the genital area is very sensitive.
And secondly, it is not suitable for the face due to post-operative swelling and redness of the surrounding tissues.
Using a special device, papillomas are removed using radio wave coagulation.
Most often they use Surgitron.
The method does not cause pain.
Several radioknives in the kit allow you to choose the most convenient one for papilloma of a given location.
The radioknife provides directed high-frequency radiation, which cuts off the papilloma, “evaporating” its tissue.
There is no rehabilitation period.
The operation is quick, painless and leaves no traces of the intervention.
But if there are acute inflammatory processes or worsened chronic ones, then radio wave coagulation is not used.
Diabetes mellitus, pregnancy, lactation and any cancer pathology in the body are also contraindications for using the method.
But if there are no contraindications, the method can be successfully used anywhere.
Patients say that the only drawback of the method is the discomfort at the time of administration of the anesthetic.
Laser beams are also used to remove papillomas without contact.
Healthy tissues are not damaged.
Infected papilloma tissues seem to “evaporate” under the action of a laser beam.
A session of laser removal of papillomas does not take long, just a few minutes.
Complete rehabilitation takes place in two weeks.
Side effects include prolonged redness of the skin and swelling of adjacent tissues.
Problems with the thyroid gland contribute to the formation of keloid scars.
Contraindications for the use of laser coagulation are the presence of:
- diabetes mellitus;
- acute inflammatory processes;
- epilepsy;
- disorders of endocrine and immune status;
- photoderomatosis;
- thrombocytopenia.
Patients who have undergone laser coagulation report pain and an unpleasant “burnt meat” smell.
Long-term rehabilitation, pain and tendency to relapse with this method.
Small papillomas are removed by electrocoagulation or cauterization.
Rehabilitation takes place within a week.
Reliable and inexpensive method.
Any localization of papillomas is suitable for its use.
To remove large papillomas or malignant neoplasms, a scalpel is used.
Reasons for appearance
Papillomas and condylomas appear due to the penetration of the human papillomavirus (HPV) into the body. There are about a hundred varieties of this virus. When an infection enters the skin, it penetrates the cells of the basal layer of the epidermis. The degeneration of a human cell occurs after the virus removes the protein shell of a healthy cell.
Important! In a person with a strong immune system, HPV DNA cannot penetrate the chromosome of the cell nucleus, so there are no signs of the disease.
Infection occurs when the immune system is weakened. The infected, modified cell contributes to the further spread of the virus, which causes the appearance of papillomas on the buttock, thigh and other parts of the body. Since the virus cannot infect blood cells, it appears only in certain areas of the skin, and not throughout the body.
There are several ways of transmitting the virus:
- HPV is most often transmitted sexually, since the mucous membranes are more susceptible to infection;
- contact infection is possible both in a public place and when using common household items at home;
- infection of the child can occur during childbirth;
- self-infection is possible when the virus lives on the skin.
Papillomas can appear when immunity decreases due to stress, illness, during hormonal changes, alcoholism and other conditions that provoke immunodeficiency.