Papilloma is a growth on the skin or mucous membrane. Their formation is associated with the human papillomavirus (HPV). Such formations are classified as benign. But there is a risk that in the future they will transform into malignant ones. This disease is widespread and chronic with relapses. There are many different strains of HPV known. They lead to formations of different sizes, shapes, and colors. Papillomas do not hurt or itch, but if placed poorly they cause discomfort or rub.
Are you worried about papillomas on your body? Laser No. 1 for removing papillomas!
Causes of papillomas
The main reason for the occurrence of papillomas on the body is the penetration of a virus into the body. This is often associated with unprotected sexual intercourse. Less commonly, microorganisms enter through small wounds on the skin, during childbirth from mother to baby, as well as during cosmetic procedures and operations. It can take a couple of years from the moment the virus enters the body until formations appear. The fact is that its activity increases greatly when the immune system is weakened.
The rapid growth rate of viral formations may be associated with the following factors:
- Metabolic disorder.
- Chronic gastrointestinal diseases.
- Diseases of the endocrine system.
- Drinking large quantities of alcohol, drugs, smoking.
The development of papillomas can occur in any part of the body, even on the mucous membrane.
Is human papillomavirus (HPV) a sexually transmitted disease?
HPV can be deciphered as a virus that causes a benign tumor of epithelial origin in the form of a papilla. Papilloma is classified as a sexually transmitted disease (STD). Unfortunately, today this concept has expanded significantly. If previously only a few, as it seemed then, “frightening” classical diseases of Venus were known, which in fact are easily treated and detected quickly (gonorrhea, syphilis, trichomoniasis, chancroid), today the list of STDs includes many dangerous, severe detectable, and sometimes difficult to treat and completely incurable (HIV) diseases. Moreover, their number is constantly growing.
Today, the list of “new” STDs includes mycoplasmosis, chlamydia, gardnerellosis, ureaplasmosis, candidiasis, genital herpes and human papillomavirus. Growths from papillomavirus identified in the genital or perianal areas are called genital warts. In fact, both condyloma and papillomavirus are the same virus, just different strains (varieties).
Genital condylomas in the perineal area can appear either one at a time or as whole growths that look similar to cauliflower. In some cases, such formations cause itching, irritation when touched, and bleeding.
Types of papillomas
The most common types of skin formations are:
Regular or vulgar
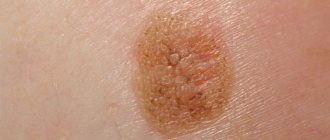
This is a large papule. At first it is small, as it grows its surface becomes rough. Papilloma does not differ in color from healthy tissue. Several small ones often appear around one wart.
Chords
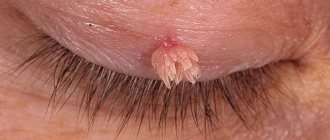
Papillomas in the form of threads. First, a yellow compaction appears on the skin, which stretches out and acquires a thin stalk. It often forms in the area of the eyelids, neck, and chest.
Flat
Such seals protrude slightly above the body. Outwardly they resemble moles, but are denser in structure. Can form in groups in the genital area, back, anal area
Condylomas
In most cases, a number of papillomas appear in one place, which grow and take on the shape of a “cauliflower”. Locations: labia, vagina, penis.
Warts on the sole
Their main part grows inside tissues and nerve endings, which causes discomfort. The papilloma looks flat and yellow.
Most often, papillomas that are located on the mucous membrane are oncogenic in nature. In any case, if they occur, it is better to consult a specialist.
Papillomatosis in the throat
There is also papillomatosis of the respiratory tract, when the tissue lining the nasopharynx begins to grow from the nose to the lungs, also often affecting the larynx. This is also one of the types of disease caused by the papilloma virus; the formations in this case are considered benign. SM-Clinic doctors are good at diagnosing this type of HPV and successfully treating it, while the disease is not always recognized by local or ENT doctors, who at best shrug their shoulders and prescribe rinses.
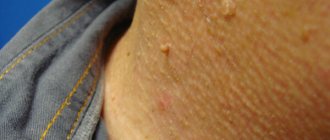
Papillomas on the body
Papillomas on the body can occur in the body in various forms. Their size ranges from 1 mm to several centimeters. The rashes can be single or multiple, the color ranges from white to brown.
There are three forms of manifestation of HPV:
- Clinical – papillomas, condylomas, flat formations, warts appear on the skin.
- Subclinical - the appearance of rashes that are not noticeable during a medical examination.
- Latent – there are no symptoms or manifestations. To make a diagnosis, scraping of the epithelium is necessary.
VRF is insidious. Some papillomas can develop into malignant tumors.
Who is at risk of getting the papilloma virus?
Papillomas and condylomas can appear, disappear and appear again, because they are manifestations of a viral infection, and their presence depends on the state of the body’s defenses at the moment, that is, immunity. Infection is most likely among smokers and alcoholics, and among those who are indiscriminate in sexual relations.
Women who use oral contraceptives (COCs) for a long time are also at risk of contracting the virus. The carrier of the virus can be both old and young. It is enough for your body to experience internal stress of various origins: you have had the flu or ARVI, gastrointestinal problems have worsened, your body cannot cope with long-term medication use - and here you have a weakened immune system, and with it the papillomavirus.
It is enough to be in close contact or live next to a person carrying the virus, take a swim in a “dirty” pool or shower in a public bath, or just walk along the beach - and if your immune system fails, the virus will invade your life. The papillomavirus “loves” heat and high humidity, when your skin is not protected by clothing. He immediately finds refuge on your heated skin.
Papillomas on the neck
We are accustomed to calling small nodules with a thin stalk on the neck warts, although in fact they are filiform papillomas. These formations are not life-threatening, but many people want to remove them.
Before removing a papilloma on the neck, you need to make sure that it is not a mole or other skin formation. Its characteristic features:
- The shape of a grain attached to the skin by thin threads, up to 2 mm long.
- Shade - from yellow to brown.
- They can be single (lower on the neck) or grouped up to ten pieces.
- In addition to the neck, papillomas appear on the face, eyelids, cheeks, and around the lips.
Papillomas on the neck appear due to a specific virus that penetrates in different ways - through contact with the skin, transfer to the fingertips.
Are papilloma and condyloma the same thing?
Genital condylomas in the perineal area are sometimes single, and sometimes look like growths that resemble cauliflower in appearance. Sometimes these formations cause itching, irritation when touched, and sometimes they bleed. SM-Clinic doctors are often approached by patients who, having seen enough advertising, have been treated for years with “one pill” for supposed “exacerbations” of candidiasis (thrush). Upon examination, it turns out that the smear in such patients is normal, and the often recurring itching is actually caused by condylomas.
Papillomas on the eye
Papillomas can form on the upper and lower eyelids due to the penetration of the papillomavirus. For a long time, the disease may not manifest itself in any way, but its progression can even lead to deterioration of vision. Pathology can take two forms:
- Keratomas are elongated tuberous growths.
- Fibropapillomas are flat formations of various shapes.
Removal of eyelid papilloma is not carried out using a laser; a more preferable option is electrocoagulation.
We treat papilloma
Scientists have discovered more than 100 varieties of the HPV virus, but some types of genital candyloma can lead to cervical cancer, especially HPV subtypes 16, 18, 31. And the reason for this is that often, due to an asymptomatic course, a person goes nowhere for a long time appeals! Dispensary examinations have disappeared from our lives, which is why diagnosis can be quite late.
To avoid this, you need to visit an obstetrician-gynecologist twice a year, and once a year have a cytology smear (also called a Papanicolaou test or “atypia smear”) to detect precancerous changes in the cervix. It is also necessary to undergo a blood test to determine the DNA of the virus using PCR. SM-Clinic's own laboratories use high-quality reagents to more accurately determine test results. After going through them, it will become clear what types of HPV are present or absent in your body, and whether treatment is worthwhile.
- Non-oncogenic papillomaviruses - HPV 1, 2, 3, 5.
- Oncogenic papillomaviruses of low oncogenic risk - HPV 6, 11, 42, 43, 44, 54, 61, 70, 72, 81.
- Oncogenic papillomaviruses of intermediate oncogenic risk - HPV 26, 53, 66.
- Oncogenic papillomaviruses of high oncogenic risk - HPV 16, 18, 31, 33, 35, 39, 45, 51, 52, 56, 58, 59 and 68.
Do not forget that the appearance of papillomas indicates trouble in your body: these small unpleasant skin protrusions, which are easy to get rid of, signal that you have not seen a doctor for a long time, and may have developed gynecological diseases, kidney disease, gastritis or colitis.
Under no circumstances should papillomas be torn off, tied with threads, or combed out - this provokes the virus to aggressively “seize” new territories - it will simply move to an unaffected organ.
Removal without traces or complications is carried out at SM-Clinic using painless methods that do not leave marks or scars. Immunity-boosting treatment is also carried out in parallel.
Papillomas in intimate places
In intimate parts of the body, papillomas often appear not one at a time, but several at once, resembling cauliflower. The most popular localization locations:
- pubis,
- groin and perineum,
- scrotum and penis,
- cervix, vaginal mucosa.
In women, papillomas located on the mucous membrane of the vagina or cervix often cause discomfort - itching, pain, bleeding after sexual intercourse, and unpleasant discharge.
Removal of genital papillomas
Where can you go in Moscow if a gynecologist has discovered papillomas on the genitals? Doctors at our clinic remove condylomas from women and teenage girls using the most modern, best method - radio waves. At your service are delicate gynecologists with extensive experience and positive reviews, good imported local anesthesia, which allows you to remove genital papillomas quickly and painlessly!
Prices for services
How much does it cost to remove papilloma on the genitals - the clinic’s basic range of services for women:
✘ Doctor’s appointment with examination - 2500 ₽; ✘ Consultation with a teenage doctor - 2500 ₽; ✘ High-risk HPV types - from 650 ₽; ✘ Colposcopy/vulvoscopy - 1500 0 ₽; ✘ Removal of genital papillomatosis - from 5000 ₽; ✘ Panavir dropper (with placement) - 5500 ₽; ✘ Allokin Alpha injection (with injection) - 3500 ₽; ✘ Taking a smear for viruses - 450 rubles.
Considering the widespread prevalence of genital papillomas and the various possible methods of their transmission, doctors recommend that both sexually active women, girls and adolescents undergo a medical examination and be examined for their presence (read more about condylomas in virgins).
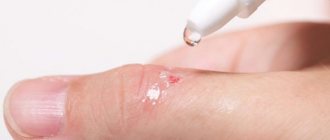
How to remove papilloma (methods)
In cosmetology, there are several methods for getting rid of papillomas in different locations:
- Surgical intervention - recently the technique is losing relevance because it is traumatic.
- Cryodestruction is the removal of tumors using liquid nitrogen.
- Laser removal is the safest and most modern method. Eliminates papillomas without the risk of relapse.
- Electrocoagulation - the procedure is carried out using electric current.
- Radio wave radiation. This technology is similar to laser removal. It not only removes the growth, but also glues the walls of the blood vessels to reduce the rehabilitation period.
Laser removal of papillomas is considered the most popular and safest today.
Transmission routes
The human papillomavirus is most often transmitted through sexual contact. People who frequently change sexual partners and neglect barrier contraception are most at risk of infection.
Another way of transmitting HPV is through household contact. Viral particles enter the body through damaged skin and mucous membranes when shaking hands, when visiting public saunas and baths, as well as when personal hygiene rules are violated (several people use the same towel, soap, underwear).
Vertical transmission of the virus from mother to child during childbirth is also possible. Infection in utero occurs extremely rarely.
Folk remedies for removing papillomas
There are several options for how to remove papillomas at home:
- Cauterize them with celandine juice.
- Apply tea tree oil to the formations every day.
- Make compresses with aloe vera gel. The substance is applied to gauze, which is then applied to the papilloma. Such compresses need to be changed every three hours.
- Constantly wipe the papilloma with a banana peel.
You can use folk remedies only if we are dealing with ordinary papilloma. If it bleeds, causes discomfort or other abnormalities, you should consult a doctor as soon as possible.
Nowadays, there are many methods to remove papilloma. But this does not solve the problem of impaired immune system and metabolism. It is necessary to undergo a full examination to determine the causes of growths and undergo full therapy.
Should I go to the doctor if my papillomas itch?
If one or more papillomas begin to itch for no reason, it is important to immediately contact a specialist to find out the cause of the discomfort and, if necessary, undergo treatment.
The appearance of itching is often associated with a decrease in the body’s immune defense, which provokes the activation of HPV and the formation of new rashes on the skin.
In the case when, after pressing the papilloma, it stops itching, then you can calm down.
If the growth is not always manifested by the presence of discomfort, does not change color, or increases in size, then these symptoms indicate that nothing terrible is happening.
However, if symptoms of itching occur frequently, then it is better to see a doctor.
If itching appears and the papilloma turns red, then this is a dangerous sign, so a visit to the doctor is inevitable.
Moreover, this must be done as soon as possible in order to avoid dangerous consequences.
If relapses occur after removal of papillomas, you should visit a doctor to undergo an examination and find out the reasons.
In this case, you will most likely have to see an oncologist.
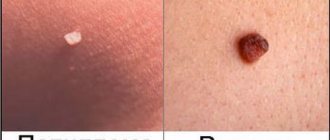
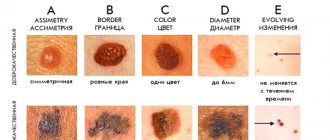
What do they really look like?
Very often, patients who come to see me ask to remove a papilloma or several of them and indicate a pigmented nevus, fibropapilloma or wart. Once I was offered a tick to remove a papilloma (I’m not kidding):
I consider it necessary to clearly define what papilloma is and how it differs from other skin neoplasms. Most often this is a small, 1-3 mm skin formation on a thin stalk. There are three main differences between papilloma and other skin formations. First, the leg is always thinner than the top. Secondly, the consistency of papilloma is always softer than the surrounding skin. Third, the size of the papilloma is usually small - no more than 5 mm. The photo below shows a typical papilloma.
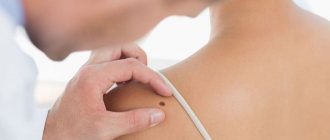
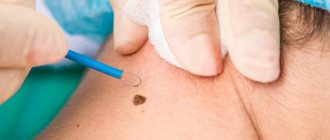
How is papilloma removed?
Removal of papillomas is carried out in a beauty salon or medical institution equipped with special equipment, as well as meeting the conditions of asepsis (measures to prevent infection of the skin or mucous membranes during medical procedures). In most cases, the medical clinic performs papillomas removal on an outpatient basis, which does not require hospitalization of the patient. Regardless of the technique, the papilloma removal procedure does not last long (on average 15-20 minutes) and does not cause significant pain or discomfort.