How and why we become infected with HPV:
- In most cases, HPV is transmitted through sexual contact.
- Infection is possible through household means, through touch, while staying in public places, such as baths, saunas, swimming pools, toilets or gyms.
- Self-infection, such as when you accidentally cut yourself while shaving.
- There are known cases of infection of a newborn during passage through the birth canal.
The danger of HPV lies in the fact that, once it enters the human body, it can remain in an inactive state for a long time, but then suddenly (during stress, a cold or other immune system failure) make itself felt in the form of the appearance of tumors on the body and growths on the tongue.
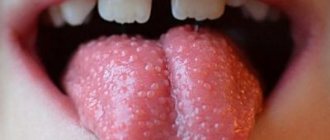
Papillomas
A benign tumor of the tongue is caused by the human papillomavirus. Favorable conditions intensify and activate the disease. Such conditions include: stress, weak immunity, lack of vitamins and minerals in the body. The shoots are formed mainly in places prone to injury.
Most often they are located:
- under the tongue;
- on the side of the tongue;
- at the root of the tongue.
There are two types of papillomas: flat and pointed.
Flat
Pronounced round growths with clear boundaries. They do not cause any particular problems to humans.
Pointed
The nipple-shaped tubercles at the base of the tongue are pinkish in color. They cause some inconvenience, especially during eating and talking.
In cases of the appearance and growth of papillomas, their removal is prescribed, as well as treatment with antiviral drugs, since the presence of infection can cause re-formation of growths. Therapy at home with folk remedies is excluded.
Which people are susceptible to papillomas?
Based on the information we provided above, we can distinguish several “risk groups”, people in which are susceptible to the development of growths and neoplasms on the tongue and body.
The appearance of a process on the tongue is possible:
- In a situation where a person has reduced immunity as a result of stress, the presence of parasites in the body or ongoing inflammatory processes.
- If a patient with a growth in the mouth suffers from autoimmune diseases.
- In a person with HIV infection.
- In people who are promiscuous.
- In the event that a person has bad habits. Smoking and drinking alcohol especially contribute to the appearance of neoplasms in the form of growths on the tongue.
- If there was any trauma to the tongue or damage to the mucous membrane occurs systematically.
Lymphangioma
Lymphangioma is a congenital benign tumor localized in the lymph nodes. The tumor can affect either one side or the entire tongue. In this case, the organ takes on an enlarged shape, which makes it difficult to close the mouth.
Such a disorder causes the formation of small bubbles on the cavity of the tongue, which can grow at high speed.
The main causes are considered to be:
- congenital pathology;
- infectious diseases;
- hereditary factor;
- previous surgical operations;
- the presence of other neoplasms of any form.
Signs of the disease:
- bubbles of different sizes with a glassy surface;
- opening and bleeding due to injury;
- white coating on the mucous membrane of the tongue;
- malocclusion ;
- disorder .
The presence of signs indicates immediate treatment, which involves complete removal of the tumor. Minimally invasive methods are considered effective removal methods.
What is the danger of developing growths on the tongue?
Often a person does not even suspect that HPV is present in his body, which manifests itself in the form of papillomas. If the growth is localized on the inside of the tongue, closer to the palate, then the patient may not notice the growth. And then the doctor accidentally finds the papilloma during an examination of the patient’s oral cavity.
Papillomas that are located on the tip of the tongue are less common, but they are always noticeable. Such growths interfere with talking and eating, so people with such growths most often seek help from a medical facility.
What else can you expect from a growth on the tongue, besides discomfort:
- Papilloma is a benign neoplasm that in itself does not pose a threat to human health. But in 1.2% of cases, malignancy of such processes occurs, i.e. The tumor goes from benign to malignant.
- The oral cavity is an extremely undesirable place for papillomas to be found. If in other parts of the body growths can “live” quietly, and the doctor will not recommend removing a tumor that does not pose a threat, then papillomas on the tongue are often injured. This can lead to inflammation.
Reasons for the appearance of a lump
A tumor can appear for various reasons. If the pain is not severe, temporary, and goes away on its own within a day, there is nothing to worry about. And when the appearance of a growth causes significant discomfort and lasts for several days, you should be alarmed. A growth under the tongue near the frenulum can be caused by the following factors:
- Condylomatosis, that is, papilloma virus. In this situation, the cell growth mechanism is disrupted. The early phases of the disease have no obvious symptoms. The virus is actively transmitted through household and sexual contact, especially with weak immunity. The nature of warts is such that they act selectively. HPV is distinguished by genotypes. There are benign and life-threatening strains. Warts may rise above the muscular organ. Keratin, which is produced in such cells, gives the balls rigidity.
- Inflammation often appears when the frenulum is short from birth. It is better to correct the problem in childhood.
- The process of inflammation appears with vitamin deficiency, gastrointestinal diseases, allergies, abscesses in the oral cavity, and injuries.
- A pimple on the frenulum under the tongue is formed during tonsillitis, when streptococci and staphylococci are activated and the lymph nodes are affected.
- The problem occurs when the salivary duct is blocked. Mineral or mucus plugs can become an obstacle. This interferes with patency. In this situation, a ranula is formed, which contains liquid exudate. The bubble may be clear or cloudy. It can burst, then build up again. Provoking factors include stomatitis, herpes, candidiasis, and lichen planus.
Since the mucous tissues of the oral cavity are sensitive, they can be damaged by hot food or drink. In the burn area, bacterial microflora feels comfortable, which contributes to the formation of salivary plugs in the ducts.
How to get rid of papillomas?
If the growths on your tongue are present in small quantities and are small in size, then the process of removing such growths is quite simple. But this does not mean that you can remove the papilloma yourself, using such “effective folk remedies” as cauterization, cutting the “leg” of the tumor with scissors, etc. To remove the growth, you should contact a professional medical institution.
Methods for removing tumors:
- Excision of papillomas with a scalpel or electric knife. This affects not only the growth itself along with the stem, but also part of the healthy tissue around it.
- Laser removal of tumors.
- By using a tool such as a conchotome, shaped like a wire cutter. After removing the papilloma with such a device, galvanoacoustics is performed (cauterization of the localization of the growth using a platinum wire).
Prevention of inflammation of the floor of the mouth
To prevent diseases of the sublingual area, dentists give recommendations on proper oral care:
- take care of your gums;
- avoid the accumulation of bacterial plaque;
- visit the dentist 2 times a year;
- prevent the occurrence of caries;
- brush your teeth 2 times a day.
But if the patient has congenital or acquired anomalies in the development of the floor of the oral cavity, such as a shortened frenulum or structural asymmetry, then you will have to be more careful to prevent injury. Some abnormalities can be treated. Come to an appointment at Family Dentistry and experienced specialists will tell you how to get rid of defects, tumors and inflammations.
How to avoid relapse of the disease?
After the growth has been removed from the patient's tongue, the person should not relax. Typically, single papillomas do not recur, but with multiple formations, the reappearance of growths on the body occurs quite often.
Therefore, after surgical removal of papillomas from the surface of the tongue, you should:
- Take precautions and limit risk factors (see above).
- Take a course of antiviral treatment as recommended by your doctor.
- Seasonally take immunomodulatory drugs and vitamin complexes, which your doctor will also help you choose.
- Maintain oral hygiene and avoid tongue injuries.
One of the main conditions for achieving a favorable outcome in the fight against papillomas is choosing the right medical center, since much in the procedure for removing a tumor depends on the actions of the doctor. We hope that the recommendations of specialists from the LeaderStom network of dental clinics helped you clarify the picture of the growth that has developed on your tongue, and now you can solve this problem without unnecessary emotional distress.
Treatment
Having established the causes of inflammation of the tongue, the specialist prescribes treatment. In case of inflammation of the salivary glands, the purulent contents are initially removed, then antibacterial agents are injected into the ducts, and the patient is also prescribed antibiotics or sulfonamide drugs orally.
As a rule, therapy is accompanied by rinsing (in each case the doctor selects the optimal solution) and physiotherapy: UHF, Sollux and others. For fever and general malaise, paracetamol or ibuprofen is prescribed.
Surgical treatment methods are used extremely rarely. The operation is performed if there are stones in the duct and they cannot be removed in any other way.
If you experience unpleasant symptoms or discover inflammation or swelling under your tongue, do not look for what it might be. Go to a qualified dentist, he will examine the oral cavity, make a diagnosis, and prescribe adequate therapy. Perhaps pain in the sublingual space is a symptom of another serious disease and consultation with an appropriate specialist will be required.
Monitor the condition of your teeth and mucous membranes, visit the dentist regularly, promptly treat inflammation of the ENT organs and ARVI - such preventive measures will minimize the possibility of inflammation and pain.
Diagnosis of diseases of the gastrointestinal tract by language
The tongue will tell you about gastrointestinal diseases.
Modern gastroenterology does not specialize in diagnosis based on the appearance of the tongue. However, an attentive person suffering from such pathologies can distinguish the symptoms of gastrointestinal diseases:
- Acute gastritis - a viscous, dense coating of white-gray color is visible on the entire surface of the tongue, with the exception of the tip and side parts. The mouth feels dry and has an unpleasant acidic taste. Perhaps, instead of dryness, increased salivation will appear. In acute gastritis, similar symptoms include heartburn and sour belching, cutting pain in the epigastric region 1-2 hours after eating, weakness, headaches, diarrhea, heaviness in the stomach. With inadequate treatment, acute gastritis becomes chronic.
- Chronic gastritis - light deposits on the tongue are replaced by occasional dark gray deposits. To the previous symptoms are added such characteristic signs of chronic gastritis as astheno-neurotic syndrome, constant irritation, aching pain that intensifies some time after eating. About 40% of all cases of acute gastritis become chronic. This condition is fraught with the spread of the process to the duodenum and the development of gastroduodenitis.
- A stomach ulcer in combination with gastritis affects the condition and appearance of the tongue - its surface becomes bright red, with gray spots of dense plaque that are difficult to clean. This picture is complemented by signs of stomatitis and cyanosis. The patient feels a burning sensation and the production of saliva increases.
- Oncological damage to the gastrointestinal tract, as well as the presence of internal circulation, is reflected in the condition of the tongue by the appearance of evenly spaced white plaque of increased viscosity, excessive saliva production, and a burning sensation in the oral cavity.
What is in the sublingual area
The tissues located on the lower jaw under the tongue are called the floor of the mouth. Due to the complexity of the structure, as well as the natural functionality of this area, a person often experiences problems accompanied by pain.
Structure of the sublingual region:
- Hyoid muscles - have an elastic structure and are responsible for the motor function of the area;
- Hyoid bone - has an anatomical shape in the form of a horseshoe, located in the muscle layer. It is the only bone in the human body that has no connections with other bones of the body;
- Nerve endings are elements of the peripheral nervous system, responsible for the sensitivity of the sublingual area to various physical, mechanical and thermal stimuli;
- Salivary glands - responsible for the production of saliva, which is involved in the process of wetting the mucous membranes of the oral cavity and the digestion process;
- Blood vessels - provide nutrition to the tissues of the sublingual area;
- Frenules are connecting folds in the sublingual area, responsible for connecting the sublingual tissues with the tongue.
Each of the above elements ensures the natural functionality of the dentofacial apparatus and participates in all physiological processes of the oral cavity.
What does a healthy tongue look like?
The tongue is pale pink - absolutely healthy.
Diagnosis by the appearance of the tongue was mastered by ancient healers, who believed that a disease could not be considered cured until the patient’s tongue regained its previous appearance. The tongue of an absolutely healthy person has the following signs:
- Pale pink color;
- Small taste buds without pronounced features;
- No bad breath;
- Be moderately moist;
- The presence of a small amount of translucent bright pink coating is allowed;
- There is no unpleasant odor.
If you deviate from these signs, you should consult a general practitioner or gastroenterologist and undergo the examination prescribed by him.
Signs of deviations from the normal state of the tongue
It is quite possible that, once you look at your tongue, you will see a rather unsightly picture. Symptoms of deviation from the norm:
- A coating of various colors, thicknesses, and with different locations of spots appears on the back of the tongue;
- The sides of the tongue are bright red;
- The taste buds look uneven, some of them increase in size and begin to disturb with unpleasant sensations, taste sensations change, their intensity weakens;
- The oral cavity becomes unusually dry;
- In some cases, the appearance of pain and burning is diagnosed;
- There is an unpleasant odor from the mouth;
- After cleaning the tongue, the plaque appears again after a short time.
In the plaque that appears on the tongue, laboratory testing can reveal leukocytes, pathogenic microflora, and exfoliated epithelial cells.
This video will tell you about plaque on the tongue due to gastritis: