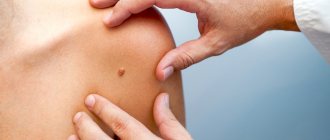
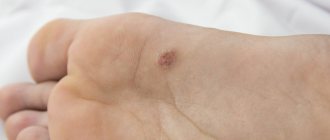
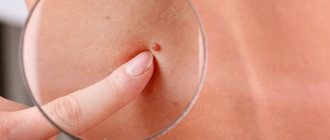
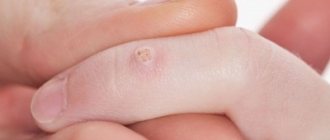
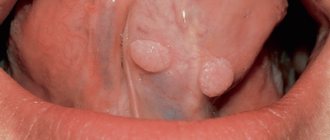
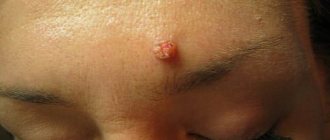
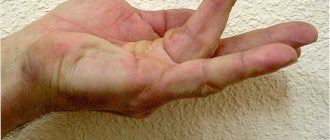
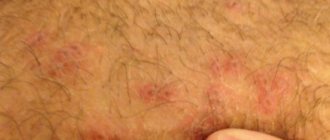
Let's start with what warts are in general. Warts, or papillomas, are dense, nodular, round or flat growths that most often form in 5 areas of the body:
- Palms
- Feet
- Armpits
- Genitals
- Face
You've probably heard many myths about warts. For example, that they arise from contact of the skin of the hands with frogs and toads, or that it is simply a superficial skin disease. In fact, papillomas of any type in children and adults have only one cause - the human papillomavirus (HPV). Warts are only an external manifestation of this disease.
HPV and warts
HPV is a whole group of viruses that infect humans. Several dozen strains of HPV can live in the body of one person, but this does not pose any threat to health if you have a strong immune system and do not have serious chronic diseases that weaken it. HPV does not manifest itself in any way until the body’s immune functions decrease to a certain level. If you notice warts on yourself, you should think first not about the aesthetic appearance of your skin, but about your health.
It is worth understanding that HPV is not some rare disease. It occurs in at least half of the world's population, it simply does not manifest itself, and is dangerous only in a number of cases.
Infection with the human papillomavirus occurs during sexual intercourse or kissing, when sharing personal hygiene items - towels, washcloths, nail scissors, etc.
External manifestations
HPV rashes can be large or tiny, intrusive and disruptive, or go unnoticed. They are typical for people of any age and gender. And they do not give discounts to children, teenagers or pregnant women.
With warts, self-infection often occurs - when the rashes are spread throughout the body by the patient themselves: if they are scratched, touched, not maintained by hygiene and not treated. For example, it all starts with a tiny dot on a leg or arm, and in the end we see warts on a child’s face and then we sound the alarm. “Children often begin to pick and tear apart elements, which will contribute to the spread of infection,” comments Dr. Yakubovskaya.
Types of warts and their location
1. Simple or vulgar warts occur mainly in children and adolescents. These are round, dense growths on the hands, face or lips. More than 65% of all skin warts are of this type. 2. Flat warts of various shapes with a smooth surface appear in adolescence on the fingers, feet, and oral mucosa and are not common - only 3-4% of all cases. 3. Palmoplantar papillomas can appear at any age. These are hard, round formations with layers of keratinized layers of skin. Most often they form on the feet and over time cause a person severe pain when walking. 4. Thread-like papillomas of flesh-colored, brown or coffee color are located in the folds of the skin of different parts of the body - genitals, armpits, eyelids, neck. These are elongated warts with a “pedicle”. 5. Soft genital warts are located on the mucous membranes in the groin, rectum or urethra. They manifest themselves in the form of a ball, pyramid or nodular cluster, and are rarely found in a single copy. Genital warts are often multiple growths with a keratinized surface.
How is the human papillomavirus transmitted: what is the danger?
Everyone should know how the human papillomavirus is transmitted. This is the only way to protect yourself from dangerous diseases. Often, papillomas are not given much importance. Many people believe that if a growth appears on the body, it will disappear on its own. This mistake haunts humanity, and the consequences may be undesirable.
Papilloma tissue tends to grow, which leads to the spread of papillomavirus throughout the body. Sometimes its individual strains can cause cancer.
What is human papillomavirus
This virus is a chronic infectious manifestation of various diseases that can appear in a person at any age. In medical practice, this virus comes in two types: one that does not carry a high risk of dangerous diseases, and a virus with a high risk.
The papilloma virus multiplies on the skin and its mucous membranes. As a result, the following growths form on the skin:
- warts;
- condylomas;
- papillomas in the mouth and larynx;
- papillomas on internal organs.
Many cases have been recorded in which papillomas become the cause of cervical cancer in women, as well as cancer of the male genital organs. To avoid such consequences, it is necessary to know about the routes of transmission of the disease.
How does the virus enter the human body?
The infection spreads through the mucous membrane or skin of a person. If there are no acute diseases, then papilloma does not manifest itself in any way, and growths do not form on the surface of the skin.
If growths of different colors have formed on the skin, then this indicates a precancerous condition, when the human skin, and the entire body, suffers a malignant disease, or the immune system is significantly reduced.
The “favorite” place for bacteria to penetrate are cuts, scratches and other skin lesions through which the virus can penetrate. The likelihood of infection increases if:
- A person has colds or other reasons for which immunity is greatly reduced.
- Dysbacteriosis of the intestines or female genital organs is observed. In this case, the beneficial microflora dies and is replaced by harmful microorganisms, in this case, papillomavirus infection.
- Presence of sexually transmitted diseases.
- Relapse of chronic diseases.
- Stress and depression, which reduce a person’s defense against viruses.
Most often, people suffering from nicotine addiction, as well as women taking birth control pills, get sick.
How the virus spreads
If a person has no symptoms, this does not mean the papilloma virus is absent. The initial stage, when there are no growths yet, can be diagnosed using the latest equipment. In medicine, there are several ways through which dangerous microorganisms are transmitted.
Both men and women can become infected with the dangerous virus. The following transmission methods are distinguished:
Sexually
This is the most common way to become infected. Just one sexual encounter, and the papillomavirus can be transmitted from an infected person to a healthy person.
Many people are interested in the question of whether papillomavirus is transmitted from woman to man. Most often, the disease is diagnosed in men, however, a large number of women can become carriers of the disease. In this case, the location of the bacteria becomes the genitals or the mucous membrane of the oral cavity, where genital warts appear. In this case, there is a 100% risk of infection.
Predisposing factors for the disease are:
- early onset of sexual activity;
- frequent change of sexual partners;
- condylomas or warts that the sexual partner has.
Reproducing in the mouth, in the absence of qualified treatment, there is a high probability of developing throat cancer. To avoid such consequences, you must use a condom.
If the localization of the virus is human skin, then a condom will not help. Papilloma is transmitted from direct contact with human skin on which condylomas and warts are located.
By everyday means
In this case, infection occurs in the following ways:
- Sharing the same towel, soap and other personal hygiene products with a person who has condylomas on their hands. Pathology occurs if there are injuries and abrasions on the body.
- Using the same toothbrush or utensils leads to infection through the patient’s saliva.
- The clothes of an infected person can also become a hotbed for the development of the virus and be transmitted to a healthy person.
- Self-infection through shaving, hair removal and other methods. The disease develops if a wart, which previously did not pose any danger, is damaged with a razor or other object. If damaged, this growth provokes the development of neoplasms, which can pose a significant danger to human health.
Infection in public places through contact with infected people
Medical practice has recorded cases where the virus was transmitted through blood transfusions, operations to remove condylomas, when doctors accidentally spread the source of infection throughout the body, and poor sterilization of manicure instruments in salons.
Mother-to-child transmission of the virus
Human papilloma is not a hereditary disease, however, the risk of transmission from mother to child still exists. When carrying a child, the risk of transmitting the virus is minimal, but still, if the placenta is damaged or other changes occur, papilloma can spread to the unborn baby.
The virus will reach him through the placenta, since the fetus has not yet formed bronchi and alveoli. In this case, the child develops respiratory papillomatosis. If after the birth of the baby he experiences breathing problems, then an examination is carried out, after which medication or surgery may be prescribed. The latter option is used much more often, as it has a greater chance of cure.
Therefore, when planning a pregnancy, it is necessary to undergo all the necessary tests to eliminate the risk of developing papilloma.
There is a very high probability that the child will become infected with the virus when passing through the birth canal. The consequence is the appearance of genital warts in the child’s mouth and larynx, which leads to various disorders of the respiratory system and decreased immunity.
If papillomas were detected in the woman’s genitals before giving birth, the birth is carried out artificially to reduce the risk of infection of the child.
Another way to infect a child from the mother is through breastfeeding. In this case, the child develops respiratory papillomatosis, which must be treated immediately.
Features of the virus in men and women
In women, the virus enters through the cervix, rectum or oral cavity. If there is a frequent change of sexual partners, the risk of infection increases to its maximum. The consequences of the disease can be infertility, cancer and many other ailments.
The papillomavirus in men most often manifests itself on the scrotum, head of the genital organ, anus or oral cavity. In men, the disease can occur without symptoms; only after severe stress or decreased immunity can the development of papillomavirus occur.
A dangerous aspect of HPV in men is the development of cancer of the male genital organs or anus.
In order to prevent the virus from entering the human body, it is necessary to follow the rules of hygiene, as well as lead a healthy lifestyle and be faithful to one sexual partner.
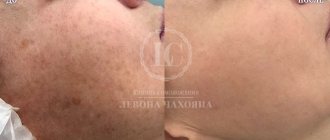
How to treat warts
Answering the question in the title of the article, we will say: you need to remove warts, but only as prescribed by a doctor. In no case on your own! In some cases, removal is contraindicated, so be examined before making a decision.
In modern medicine, warts are safely removed using surgery, electric current, laser or liquid nitrogen. Such procedures do not leave serious scars on the skin and help quickly get rid of papillomas. At the same time, the patient is prescribed specially selected antiviral and immunomodulatory therapy, which helps suppress the HPV outbreak and significantly increase immunity.
If the wart is small in size, does not grow and does not interfere with the natural movement of the body, then you can try to cure it with special ointments. Treatment takes a lot of time and is always discussed between the doctor and the patient during the examination.
Also, every patient should understand that today there are no medications or procedures that can permanently rid the body of HPV. No one is immune from relapses. But you can suppress the influence of HPV with the help of a healthy lifestyle, increasing the body’s immune functions, hygiene and barrier contraception.
How long does it take for a wart to heal after cauterization with nitrogen?
Warts are often removed with liquid nitrogen.
This is the simplest method of dealing with them.
It's also the cheapest.
But this method is also the most unpleasant and ineffective.
It often causes more suffering to the patient than the wart itself.
After cauterization with nitrogen, a focus of inflammation is formed.
With a short exposure time of the nitrogen swab, only small warts can be removed.
Medium and large ones do not pass.
To destroy them, it is necessary to increase the exposure time to nitrogen.
But increasing the exposure time leads to an increased risk of severe inflammation and scarring due to deep skin damage.
If you still have cauterization with nitrogen, you need to wait 1-2 weeks for healing.
After this, the doctor will examine the skin.
If the wart does not disappear, the procedure will have to be repeated.
Why are traditional methods of treatment dangerous?
Many people remember cauterization with celandine, iodine and vinegar from childhood. Some people removed warts using a silk thread, while others applied hot metal objects to them to burn them out! All these methods are not only ineffective in the fight against warts and HPV, but also dangerous to human health.
As a result of such “home” treatment, a child or adult can receive multiple burns, scars and welts, and removal with a thread only provokes further growth and spread of papillomas on the skin.
We live in the 21st century, where there are modern methods of treatment and correction that are safe for health. If you find papillomas on the skin or mucous membranes, first make an appointment with a dermatovenerologist or gynecologist. The doctor will prescribe treatment and, if necessary, refer you to a surgeon for quick removal of the papilloma.
The MC “Health” network welcomes doctors - gynecologists, dermatovenereologists and surgeons with extensive experience. Hundreds of patients come to appointments with external manifestations of HPV, and our specialists consider each case individually - prescribe the necessary tests and studies, adjust treatment, and help quickly cope with the disease. You can make an appointment with any doctor on the clinic’s website.
Don’t delay the examination and get treatment from professionals!
Methods of infection
The fact that many people on Earth have these growths suggests that warts are contagious. Since warts are transmitted exclusively through injured skin (cuts, abrasions, wounds, scratches), and microtraumas exist on the body of almost any person, everyone is at risk.
Since children's delicate skin is regularly injured, they encounter this problem more often than adults.
All family members may have warts on their hands, but this does not mean that the human papillomavirus is inherited. It’s just that contact with an infected person occurs more often and in a narrower circle. The virus can be transmitted in the following ways:
- when using a shared towel;
- through the doorknob and other common objects;
- through a damp rug on the bathroom floor;
- when shaking hands;
- even when using another person's office supplies.
Diagnostics
Which doctor treats warts depends on the location of the growths and their nature. Initially, if growths are detected, you will need to visit a dermatologist. He will prescribe additional examinations that will confirm or refute the presence of papillomavirus in the body, and also determine the nature of the tumors.
Treatment of malignant papillomas will need to be carried out by an oncologist, treatment of benign formations is carried out by a dermatologist, and a surgeon will undertake the removal of growths.
Can the immune system fight infection?
Killer T lymphocytes recognize cells with damaged DNA and destroy them. This is natural antitumor immunity. This prevents the development of cancer. Antitumor immunity is relevant due to the fact that some strains are capable of inducing the synthesis of oncoproteins, leading to immortalization and proliferation of keratinocytes. As a result, it is possible to avoid consequences such as cancer.
After infection, the cells of the macroorganism begin to secrete interferon, which has a dual effect. It affects the genes of neighboring cells, reducing the rate of protein synthesis, which slows down the assembly of viral particles. Interferon increases the activity of macrophages and T-killers. The rate of antigen representation to T-lymphocytes and killer cells increases, which ensures rapid recognition and destruction of infected cells and warts.
Thanks to the coordinated work of the immune system, in some cases the disease goes away on its own. The prognosis for the disease is favorable. Timely treatment will help avoid complications.
Hardware methods are aimed at removing warts to prevent the appearance of new ones and reduce the concentration of the pathogen in the tissues of the body. Medication methods are aimed at strengthening the body’s strength to fight independently. This is achieved by using immunostimulants, antiviral agents and cytostatics.