The Necklace of Venus is one of the signs of the secondary period of syphilis.
It is also called syphilitic leukoderma.
Venus Necklace photo:
What is the rash associated with syphilis?
syphilitic rash in the photo
Rashes with syphilis almost always occur in the second stage of this disease, and in appearance they are very similar to ordinary allergies, dermatitis or prickly heat. But specifically with syphilis, the rash on the patient’s body differs in certain characteristic signs, the occurrence of which requires urgent contact with a competent specialist.
The rash appears as small pink spots that are localized on the skin in the thighs, upper arms, or shoulders. But it is also possible that spots may appear on other areas of the skin of the body.
The rash is one of the main symptoms of syphilis, but it remains on the skin for no more than two months, after which it simply disappears. Many patients do not complete the course of prescribed therapy; as a result, the disease progresses to a more severe stage, in which blood and lymph become infected.
It is very important to establish a correct diagnosis in time and carry out a timely course of treatment, since it is easier to eliminate any disease in the initial stages of its development. And syphilis is no exception, since if it is detected early, it can be treated quite simply. But if the disease is neglected, serious and dangerous complications can develop. Indeed, under such circumstances, there is a risk that drug therapy will no longer give the expected effect, as a result, the treatment will be unsuccessful and useless.
Diagnostics
The rings of Venus on the neck mean that it is time for a woman to start taking more careful care of herself. To choose the right course of care, you need to see a cosmetologist and get advice from him.
You can diagnose a Venus necklace yourself by looking at your neck in the mirror. If the appearance of this area and the condition of the skin leave much to be desired, then you should not delay a visit to a specialist. The cost of an appointment with a cosmetologist depends on the level of the clinic where he is seen and on his professional qualities. On average, the first visit to a specialist costs from 600 rubles.
Stages of the disease
There are several stages through which patients infected with syphilis go:
- During the primary stage, about a month after infection, a characteristic rash appears on the patient’s body, which turns red in some places, forming small ulcers. After a few days, the spots may disappear, but then they will definitely appear again, since this disease does not go away on its own. Hard chancre also forms. Very often, a syphilitic rash that occurs on the face is confused with ordinary pimples or acne.
- At the next stage of syphilis, which is called secondary, the rashes become pale pink and convex mixed with bluish pustules. With secondary syphilis, the patient becomes dangerous to others, since he is already a carrier of the infection and can infect someone else.
- The third stage of the disease is an advanced course of the disease, in which pathogenic microorganisms penetrate into the body, affecting tissues and organs.
A competent and highly qualified specialist can easily distinguish a syphilitic rash from all other inflammatory elements on the skin of the body.
Features of the course of leukoderma
Unlike other types of rashes that disappear after a few months, the crown of Venus remains on the patient’s body for a very long time, sometimes for years. Often such a belt is the only manifestation of syphilis, even in stable remission.
In the fairer sex, this phenomenon is diagnosed several times more often than in men, and this sexual preference is also a mystery to scientists.
It is possible to eliminate the symptom with the help of qualified treatment, but after its disappearance, traces of its presence remain for a couple of months.
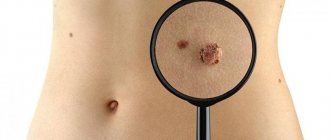
Signs of a syphilitic rash
in the photo the first signs of a syphilitic rash on the abdomen.
With the disease in question, the spots on the patient’s body differ in several characteristic features, among which the following can be distinguished:
- The rashes are usually not localized to a specific area of the body; they can appear anywhere.
- The affected areas do not itch, itch or hurt, and there is no peeling.
- The elements on the body are dense to the touch, round in shape, and can be single or merge with each other.
- A syphilitic rash may be pink or red with a blue tint.
- After the rash disappears, no marks or scars remain on the skin.
The attached photo clearly shows what a syphilitic rash looks like, which is difficult to confuse with any other.
Symptoms in men
In men, after infection with syphilis, a small ulcer appears on the genitals. It can occur on the penis itself, at the urethra, in the anal area. The ulcer is usually bright red with sharp edges.
Syphilis is a systemic disease that affects not only the reproductive system or epidermis, but also internal organs, the nervous system and even bones.
For men with this disease, it is characteristic that one stage successively replaces another, proceeding with all the symptoms inherent in each of them.
The location of chancre formation depends on how the syphilis infection was carried out. Since in men it is most often unprotected sexual intercourse with an infected partner, chancroid usually occurs on the genitals. But it can also form in the mouth when infected as a result of oral sex with a patient (with non-traditional male orientation), or when infected through contact and household contact.
The formation of a hard chancre is preceded by the formation of a small spot on the skin or mucous membranes, which gradually grows and ulcerates as the causative agent of the disease penetrates deep into the skin.
You can distinguish a syphilitic ulcer from another inflammatory element on the skin by some signs:
- regular round shape;
- has a red bottom;
- there is no inflammation or redness of the skin around the ulcer;
- there is no pain when pressed, as well as itching sensations.
After a few weeks, chancroid goes away on its own, which does not mean that the disease has receded. All this indicates the onset of the secondary stage of syphilis and its transition to the chronic stage.
The main symptom of secondary syphilis in men is syphilides or a skin rash that can be observed on any part of the body, even on the palms and soles of the feet.
Symptoms of secondary syphilis in men:
- general malaise, weakness;
- headaches and joint pain;
- slight increase in body temperature;
- enlarged lymph nodes.
The danger of this disease lies in the fact that when it becomes chronic or enters the tertiary stage, it affects internal organs and tissues, the nervous and skeletal systems, causing irreparable harm to human health. Moreover, it may not make itself felt for many years, and appear after a long period of time, when conventional treatment may simply be ineffective.
Consequences of infection
It is important to understand that syphilitic roseola is a rash that appears when the disease has already become serious. If treatment is not started at this stage, it will lead to irreparable consequences, irreversible damage to the brain and spinal cord, circulatory system and other internal organs. Syphilis will smoothly and imperceptibly pass into the third stage, which is absolutely not amenable to therapy. With tertiary syphilis, which develops in 40% of patients, it is only possible to maintain vital body functions and stabilize the condition. Like many sexually transmitted diseases, syphilis often results in disability or death.
Chancroid in men
In men, a phenomenon called chancroid often occurs. The soft chancre is located in the same place as the hard chancre, is distinguished by a bright red bloody color, and produces abundant pus. It differs from hard chancre in that it has softer edges and also causes discomfort and pain. Soft chancroid, another name for which is chancroid, provokes inflammation of the lymph nodes, nausea and vomiting, weakness and dizziness may appear.
Chancroid is also a symptom of syphilis, and because of its peculiar characteristics it is called a venereal ulcer.
Unlike hard chancroid, the causative agent of which is Treponema pallidum, the occurrence of chancroid is provoked by a microorganism such as streptobacillus or chancroid bacillus. The incubation period for this infection is approximately ten days, after which the chancroid stick begins its active reproduction and spread throughout the host’s body.
The ulcer, formed as a result of the activity of the bacterium, has uneven edges and, when pressed, releases a lot of purulent fluid. In the absence of timely and correct treatment, this lesion of the epidermis deepens and expands, as a result of which the infection penetrates into the deeper layers of the skin.
Differences between hard and soft chancre:
- The hard one does not cause pain and inflammation of the skin around it, does not ooze pus or blood, unlike the soft one, in which there may be small inflammatory elements, redness or rash around the ulcer.
- A chancre does not have a hard base; the skin around it may peel and become inflamed; ulcers often appear, which subsequently merge with the main source of inflammation.
Symptoms in women
in the photo, the manifestation of syphilis in women on the lips.
Women, like men, have three stages of syphilis: primary, secondary and tertiary. The disease progresses gradually; the incubation period in women is often prolonged due to various factors, for example, taking antibiotics.
Primary syphilis in women is characterized by the following symptoms:
- In the area through which the causative agent of the disease entered the body, at the end of the incubation period, a hard chancre is formed. This could be the genitals, anal area, or oral mucosa. After about fourteen or fifteen days, the lymph nodes located next to the ulcer become enlarged, which disappears on its own a month after it appears.
- An ulcer usually does not cause any discomfort or pain, but signs such as decreased performance, weakness, and a slight rash on the body may occur.
Signs of secondary syphilis:
- elevated temperature;
- headaches;
- pain and aches in the joints;
- a spotty rash on the body, the elements of which subsequently become convex and turn into ulcers;
- Many women experience hair loss on their heads.
In the absence of therapy, the tertiary stage develops, which is very dangerous due to the likelihood of complications and penetration of the pathogen into the body. The danger of tertiary syphilis is that syphilides affect internal organs, as a result of which the patient may face death. Damage to the nervous and skeletal systems also occurs.
What skin diseases can be confused with?
Syphilitic roseola is similar to other skin pathologies that are characterized by a pink rash:
- Toxic dermatitis as a reaction to medications, food, and household chemicals. The difference between allergic spots is that they tend to merge, itch, and merge with each other.
- Pityriasis rosea appears as symmetrical round spots. This is a harmless viral skin infection that goes away on its own without treatment. In this case, there is always a maternal plaque (up to 1 cm in diameter), which is detected first and has a larger size. The remaining elements appear gradually, their shape and size may be different and different from each other.
- Marbling of the skin can occur in response to hypothermia in absolutely healthy people. Dilated capillaries simply shine through the skin, giving it a marbled hue. Syphilitic roseola after vigorous rubbing of the integument becomes even brighter, and the marble pattern, on the contrary, disappears.
- Pityriasis versicolor (varicolored) patches are also pink in color, but sometimes take on a café-au-lait hue. They are located on the back, chest and more often on the upper half of the body. They originate from the mouths of the hair follicles and are very flaky, unlike the manifestations of syphilis.
- The presence of pubic lice is indicated by bite marks from lice. In the center of the gray-violet spots you can always notice a small dot. The marks do not disappear if you press on them.
- With rubella, the rash is found not only on the body, but also on the face. It rises slightly above the integument, affects the pharynx and disappears on the third day. Body temperature rises, conjunctivitis occurs, and lymph nodes enlarge.
- Measles is also characterized by a sharp increase in temperature, swelling of the eyelids, inflammation of the lining of the upper respiratory tract, difficulty breathing and conjunctivitis. The rash is large, tends to merge, and white dots are visible on the mucous membranes of the mouth and gums.
- Typhus and typhoid fever occur with severe general intoxication of the body, fever and weakness. If you lubricate the stains with an alcohol solution of iodine, they will acquire a darker shade.
Chancroid in women
Chancroid or chancroid is a sexually transmitted disease, which, unlike syphilis, is transmitted only through sexual contact. An ulcer that occurs on the genitals usually causes unpleasant painful sensations.
In women, the incubation period for this disease is longer than in men. The formation of chancre occurs on the labia, clitoris and vagina. Features of chancre:
- the ulcer is softer to the touch than with chancre;
- pus and blood are released;
- the area around the chancre becomes inflamed.
Very often, due to the contact of pus on healthy skin, a secondary chancre occurs. Women are characterized by the appearance of many bubonic ulcers located near the inflamed lymph nodes, which subsequently open and leave behind deep scars. Chancroid in women looks the same as in men.
Prevention measures
To avoid the possibility of secondary syphilis, you need to consult a doctor in time if, 10–90 days after unprotected sexual intercourse, an ulcer or erosion appears on the genitals, lips, corners of the mouth or throat.
In case of domestic syphilis, the site of introduction of treponema can be located anywhere.
But the main preventive measure remains avoidance of promiscuity. Even when using a condom, infection can occur through the serous discharge of ulcers on the patient's body. This is exactly how infection occurs with household varieties of the disease. In this case, a preventative measure can be personal hygiene: avoiding sharing bedding, underwear, towels, razors or utensils with a stranger or sick relative.
Syphilitic roseola
Spotted syphilides are external signs of syphilis, which are also called syphilitic roseola. The appearance of such spots, characteristic of the secondary stage of the disease, usually occurs along with the appearance of a syphilitic rash.
Syphilitic roseola symptoms:
- Spots of pink color, not distinguished by relief.
- Roseolas are not characterized by peeling.
- Do not cause discomfort, itching or burning.
- The shape of the spots is irregular.
- Before the formation of roseola on the skin, the patient has a fever and pain in the head and joints.
- Over time, the color of the rashes changes from pink to red, then they gradually turn yellow and disappear.
Syphilitic roseolas, as a rule, are located isolated from each other, and they can merge only if there are a lot of rashes.
Venus Necklace
Another manifestation of the sexually transmitted venereal disease in question is the so-called necklace of Venus. We are talking about white spots localized on the skin of the neck and shoulders. These spots usually appear months after syphilis infection occurs.
The beautiful and mysterious name of this phenomenon comes from mythology.
The round and white spots are usually preceded by hyperpigmentation of the skin in the area, which subsequently lightens, creating the appearance of lace on the neck. White spots are small in size, but they can merge with each other, and depending on this fact, syphilitic manifestations are divided into:
- Spotted, which are located isolated from each other.
- Reticulated, partially merging.
- Marble spots are called completely fused spots due to syphilis.
In addition to the neck, the necklace of Venus can appear on the skin of the chest or abdomen, as well as the lower back or back. The necklace of Venus, which occurs in an atypical location, is often confused with other skin diseases, such as vitiligo or lichen.
It is noteworthy that the causative agents of syphilis, microorganisms called Treponema pallidum, are never found in white syphilitic skin lesions. In medicine, there is an assumption related to the fact that Venus spots appear on the skin due to damage to the nervous system, which leads to pigmentation disorders.
But it has not yet been established why white spots appear only on the skin of the neck, and in very rare cases on other parts of the body, and also why it more often affects women infected with syphilis than men. The necklace of Venus occurs with secondary recurrent syphilis.
What it is?
This is a skin reaction to the presence of the Lewis pathogen in the body - Treponema pallidum. It is expressed in small-sized pigment spots covering the upper part of the body, and in rare cases – its central part.
This symptom appears several months after the infection enters the body and in medicine has a less romantic name: syphilitic leukoderma. This name was given to it by the German infectious disease specialist A. Neisser at the end of the nineteenth century, but the first descriptions of this symptom are more ancient, and its Latin name is more familiar to the ears of even modern doctors - venereologists.
Leucoderma has two more literary names: “Venus’s crown” or “Venus’s belt”.
In addition to spots covering the body of men and women in the décolleté and neck area, signs of syphilis also include similar symptoms spreading throughout the body, baldness (focal or diffuse), and syphilitic ulcers.
All these symptoms are part of the legend about the curse of the goddess Venus on the earthly youth, who decided to take revenge on him for his betrayal with gifts: a red shirt, a hat and a pearl necklace, which turned out to be the main signs of the disease.
Acne with syphilis
Peculiar rashes on the face or pimples often become one of the symptoms of damage to the body by Treponema pallidum. Very often, these symptoms of syphilis on the face are mistaken for an allergic rash, as a result of which proper treatment is not carried out. All this leads to the fact that syphilis takes a chronic form, and there is a risk of damage to the patient’s nervous system.
At the initial stage of the disease, acne looks like red formations, which after seven days turn into ulcers. After opening them, the rash may disappear, but after a certain amount of time it may reappear.
With secondary syphilis, pimples become purple with a bluish tint. During this period, the patient becomes very dangerous to others.
Tertiary syphilis is characterized by bumpy skin of the face, red with a blue tint, purulent elements merge with each other, forming extensive skin lesions. The result of such lesions is deep scars on the surface of the epidermis.
With syphilitic acne, the patient's body temperature often rises, and this condition requires mandatory drug treatment. In this situation, you cannot do without antibiotics to prevent the disease from reaching an advanced stage.
Possible complications
Such a multifaceted disease cannot pass without possible complications, especially when the time necessary for treatment is missed.
And by and large, even after recovery, it is difficult to say that the person is absolutely healthy and his body is no longer threatened by the consequences of the illness he suffered. Having penetrated the human body, Treponema pallidum primarily affects the central nervous system, especially the blood vessels and lining of the brain. As a result of such a lesion, a person risks experiencing symptoms of diseases such as neuritis, meningitis, hydrocephalus. At the initial stage of infection, a person is bothered by frequent headaches, nausea, vomiting, increased intracranial pressure, tinnitus, and dizziness.
Also, damage to the membrane and blood vessels of the brain can cause the patient to develop epileptic seizures. Quite serious speech impairments are often observed. The organs of vision and hearing can also be seriously damaged. Most often, disturbances in the normal functioning of these organs make themselves known in the form of pupillary abnormalities, hearing loss, neuritis, retinitis pigmentosa or optic nerve atrophy.
Further progression of the disease without proper treatment will contribute to the disruption of the normal functioning of these and other organs, and, therefore, more serious diseases will increasingly develop.
Over time, the entire musculoskeletal system is affected. First, the infection affects its membrane, causing such an unpleasant disease as osteoarthritis. Then the joints begin to swell (primarily the knees, legs, feet, collarbones, and chest), and movements of both the upper and lower extremities become increasingly limited.
Of the visually noticeable consequences, the first to cause trouble are various skin lesions. But if at the initial stage a spotted rash or roseola disappears independently and quite without a trace over time, then papular syphilides of subsequent stages turn into ulcers, which leave scars for life.
This terrible disease does not pass by the cardiovascular system. And so, first of all, it makes itself felt in the form of shortness of breath, heart murmur, low blood pressure, angina pectoris, disruption of the aortic valves and blood circulation, as well as general weakness. In turn, circulatory disorders cause the development of myocardial infarction.
The impact of treponema on the respiratory system occurs for quite a long time. However, the first symptoms of this exposure are shortness of breath, signs of bronchitis and a wet cough. Later, symptoms similar to those of tuberculous pneumonia make themselves felt.
The liver, which is one of the vital organs, also suffers greatly from the effects of Treponema pallidum. If the infection is not controlled for a long time, it can lead to the development of yellow acute liver atrophy. In this case, the mucous membranes, conjunctiva and skin become yellow, and the size of the liver is greatly reduced.
The patient experiences hepatic colic, convulsions, and even hallucinations. In such a situation, it is possible to save the liver only in very rare cases. But usually everything ends in a dangerous hepatic coma, which means the death of the patient. Even at the very early stages of the disease, the gastrointestinal tract is affected.
At first, the patient is concerned about symptoms that are characteristic of ordinary gastritis. But these symptoms are often confused with a stomach tumor, and this slows down the process of proper treatment. In some cases, this infection leads to female or male infertility.
Based on the foregoing, it is clear that the complications of infection are actually serious and can even lead to the death of a person. Therefore, quick and timely treatment is simply vital.
Source: tvoy-venerolog.ru
Syphilis on hands
Syphilitic rash, unfortunately, can appear on any part of the body, including the hands. In most cases, people do not pay attention to small spots because they do not cause concern or discomfort. Their occurrence is often associated with allergies or dermatitis.
Syphilitic rash on the hands appears in the second stage of the disease, and most often affects the palms and elbows in the form of the following formations:
- Roseola, which disappear after a certain amount of time, only to appear on the skin again. But their disappearance does not indicate the retreat of the disease.
- Small lumps on the skin that do not cause pain or discomfort.
- Abscesses, which are a sign of advanced syphilis.
Main places of manifestation
The favorite areas of the body for this phenomenon are the décolleté and neck area. Signs of the disease may also affect:
- upper back;
- breast;
- stomach;
- lumbosacral region.
In very rare cases, which are recorded in medical reference books, the patient’s cheeks and forehead, arms and legs, including palms and feet, were affected by the crown of Venus. Before classifying these lesions as signs of syphilis, they should be thoroughly analyzed, because similar phenomena are more typical for skin pathologies: various types of lichen, psoriasis, eczema, atrophic skin phenomena after scars, etc.
Syphilis in children
Syphilis is transmitted to children during intrauterine development from a sick mother. The fetus becomes infected around the fourth or fifth month of pregnancy, resulting in congenital syphilis. The disease, as a rule, makes itself felt within the first three months of the baby’s life. The following pathological changes occur in the child’s body:
- Damage to the central nervous system.
- Soft gummas are formed in the tubular bones.
- Syphilitic meningitis develops.
- Hydrocephalus.
- Paralysis.
For children from one year old it is typical:
- Development of cerebral ischemia.
- Convulsive attacks.
- Strabismus.
- ZPR.
Signs of childhood congenital syphilis, which appear from the age of four:
- Keratitis.
- Labyrinthitis.
- Skull in the shape of the buttocks and other severe pathologies.
If left untreated, the child's death occurs within a few months. In the attached picture below, you can see syphilitic pemphigus in newborns.
How to protect yourself from sexually transmitted diseases?
The content of the article
The main feature of sexual diseases is that they love to present surprises, so the infection hides for a long time, appearing when dangerous processes are running in the body.
Because early detection is difficult and delayed diagnosis can cause serious problems, the best way to combat sexually transmitted infections is to prevent them.
Transmission routes
Syphilis is one of the most common sexually transmitted diseases, ranking third in prevalence worldwide. In order to avoid contracting this infection, you need to know how it is transmitted and how it manifests itself.
The main routes of infection with syphilis:
- Sexual route - infection becomes the result of unprotected sexual intercourse, this can happen during traditional sexual intercourse, as well as during anal and oral sex. This is explained by the fact that Treponema pallidum, which is the causative agent of syphilis, is contained in male sperm and female secretions.
- The household route of infection is the rarest, since pathogenic microorganisms outside the human body die almost immediately. But if the patient has open chancres or ulcers, the infection can spread to household items. Then, in the absence of hygiene rules, for example, when using one towel, a healthy person becomes infected by getting microbes into microcracks or wounds on the skin, as well as on mucous membranes. Very often, infection occurs through a kiss.
- Transmission of the disease is also possible through blood, for example through transfusion. Or as a result of using one injection syringe among several people. Syphilis is a common disease among drug addicts.
- Infection of the fetus during intrauterine development from a sick mother. This is fraught with very serious complications for children, who in most cases are stillborn or die during the first months of life. If intrauterine infection of the baby can be avoided, then it remains possible through breast milk. Therefore, such children are recommended to be fed with artificial formula.
What is syphilis and what causes it
Even in ancient times, Hippocrates and Galen wrote about this disease. But a full historical account of the spread of the disease was not written until the late 15th century. It was then that the Italians called this disease “syphilis.” The disease was considered incurable until Fleming discovered the first antibiotic.
Syphilis has always been a common disease. For example, it is known for certain that many writers, poets, musicians, artists, kings and dictators suffered from syphilis, including Napoleon Bonaparte, Ivan the Terrible, Benito Mussolini, Abraham Lincoln, Vincent Van Gogh, Moggy, Paul Gauguin, Adolf Hitler, Oscar Wilde. But this is exactly the case when famous people should not be role models.
Currently, 12 million people fall ill with syphilis every year, mostly between the ages of 15 and 40. The peak of the disease lies between 20-30 years. In recent years, syphilis has become especially common.
Syphilis is caused by the bacterium Treponema palidum, which looks like a spiral when viewed under a microscope. The bacterium multiplies in the lymph nodes and spreads through the lymphatic system into the body. The infection is transmitted not only sexually, but also through blood, transplacentally (from mother to fetus), saliva, personal hygiene items (less commonly) and even breast milk. Medical personnel are at particular risk, as needles and surgical instruments can be the source of infection.
Source of syphilis infection
Without treatment, syphilis can last for years with alternating exacerbations and remissions. During the active period, signs of the disease appear on the skin, mucous membranes, and internal organs. Unfortunately, with a latent course, no symptoms are observed.
How to recognize
It is very important to know exactly how this terrible disease manifests itself, so that when the first symptoms appear, you can receive timely treatment.
The first signs of syphilis appear within two weeks after infection.
If you do not pay attention to them, you can lead the situation to irreversible consequences, when drug treatment becomes ineffective. And the result of untreated syphilis is death.
The main symptoms of syphilis:
- A painless ulcer located in the genital area.
- Enlarged lymph nodes.
- Rashes on different parts of the body.
- Increased body temperature.
- Deterioration in health.
- In later stages, paralysis, mental disorders and other severe abnormalities.
Treatment of syphilis
This disease can be treated only after consultation with a specialist dermatovenerologist, who will prescribe all the necessary diagnostic measures and adequate appropriate treatment.
It is unacceptable to make independent decisions about taking medications, as well as the use of traditional medicine. Treatment of syphilitic lesions in the human body is a rather lengthy process, in which it is necessary to take medications continuously for several months. And in later stages of the disease, therapy can last several years.
Treponema pallidum is very sensitive to penicillin antibiotics, which is why they are prescribed to all syphilitics. If these drugs are ineffective, they are replaced with tetracyclines, fluoroquinolones or macrolides.
Most often, treatment of syphilis occurs in a hospital setting, where the patient is administered penicillin every three hours for several weeks. The patient is also prescribed vitamin substances that help strengthen and restore immunity, which suffers during long-term treatment with antibiotics.
Among the medications prescribed to patients with syphilis are the following:
- Bicillin, Ampicillin, Retarpen, Azlocillin, Ticarcillin, Extensillin.
- Medicamycin, Clarithromycin, Ciprofloxacin, Ceftriaxone, Doxycycline.
- Miramistin, Doxilan, Biyoquinol, Bismoverol.
Treatment for syphilis can be considered successful only if the disease does not recur for five years. It is very important to follow all the doctor’s instructions, as well as completely avoid sexual intercourse during medication treatment. It is very important to follow preventive measures, avoid casual sex, and do not neglect personal hygiene and barrier method of contraception. A patient with syphilis must have his own separate dishes, towel, razor and other supplies.
Prevention of sexually transmitted diseases
You may be surprised, but the main recommendation for STI prevention from all medical organizations is to abstain from sexual relations. It turned out that the use of condoms is not 100% justified. If storage conditions are violated, the expiration date has expired or they are of poor quality, you can forget about protection against STDs. This is why condoms are called relatively safe rather than safe, this status emphasizes that the only thing completely safe is not having sex.
Preventive recommendations:
- Use a condom during sexual intercourse (pay attention to the expiration date, quality mark and storage conditions.
- Use a new condom every time.
- Stick with one partner for a long time.
- Avoid casual sex.
- Do not use other people's intimate items - underwear, towels, etc. Also, do not use a reusable syringe.
- Contact your gynecologist or urologist immediately after any suspicious contact or if you notice any symptoms.
Using a condom during sexual intercourse
Important points:
- Remember that good health cannot protect you from sexually transmitted diseases. Even if you are young and full of energy, this does not mean that you will not get sick. Moreover, since a young body is more sexually active, it is more likely to become infected.
- Birth control pills also do not protect against STIs. They protect against pregnancy - they do not prevent infection.
- Sexual relations outside of classical sexual intercourse also do not guarantee safety - for some pathogenic microorganisms, touching the external genitalia or oral mucosa is sufficient. The likelihood of infection is high even during oral and anal sex. The latter is considered the riskiest.
Remember also that a sexually transmitted disease is not measles or rubella, which leaves a strong immune system. No matter how many times you are treated, your chances of getting reinfected will be the same as before. Therefore, caution is always necessary.