- Acne treatment
- Rosacea Treatment
- Treatment of demodicosis
“ Subcutaneous mite ” sounds very unpleasant, and many may think that anyone can get this parasite, but “but not me.”
In fact, demodicosis - this is the name given to damage to hair and skin areas by a microscopic mite - is far from a rare phenomenon. And some cosmetic procedures can provoke an exacerbation.
Scientific fact: human skin can be parasitized by 2 types of Demodex , which feed on dead skin cells and live on the skin and hair follicles, including eyelashes and eyebrows:
- brevis;
- folliculorum.
As a result of their activity, a person feels itchy skin, redness, peeling appear, and the skin becomes rougher. If measures are not taken, all these unpleasant symptoms can develop into crusts and inflammatory elements.
Mite
The subcutaneous mite causes skin lesions in humans and animals - demodicosis. The mite settles in the hair follicles of the head, eyelashes and eyebrows, in the ducts and secretions of the sebaceous glands of the facial skin. A subcutaneous mite is a normal phenomenon, and for the time being it does not pose a danger, since it feeds on waste cells. But if the body’s defenses weaken, the mite begins to actively multiply, penetrates into the deeper layers of the skin and causes inflammation. According to the observations of researchers, women are more often affected by this disease.
FACT:
It is believed that more than 20% of people are carriers of demodicosis, but no clinical signs are detected.
Causes of the disease
The demodex iron mite has a strong protective shell, thanks to which it is very stable, making the treatment process quite complex and time-consuming. The main causes of demodicosis in humans are:
- weak immunity;
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract;
- metabolic disease;
- hormonal imbalances;
- long-term use of corticosteroid ointments;
- stress;
- problems with lipid metabolism;
- mental illnesses;
- lack of hygiene;
- ecology.
Studies have shown that this disease occurs more often in women with thyroid problems and in men with prostate adenoma.
Signs of illness
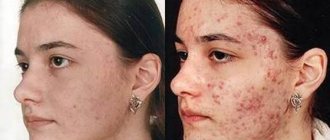
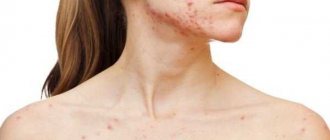
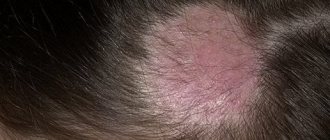
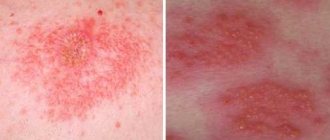
In its manifestations, damage to the subcutaneous mite is very similar to rosacea or acne. Peeling of the skin and its redness are noted, itching may occur, constant or worsening after using tonics or washing with cold water. Sometimes there is a combination of demodicosis caused by subcutaneous mites and the above-mentioned skin diseases. And this is not surprising, because the occurrence of demodicosis is influenced by negative changes in the skin. Thus, both acne vulgaris and rosacea weaken the skin’s natural defenses. When affected by skin mites, the following parts of the face are most often affected: eyelids, forehead, chin, nasolabial folds and brow ridges. Exacerbations of demodicosis occur in autumn and spring.
Causes of exacerbation of demodicosis
- various types of dermatitis;
- weakened immune system;
- acne;
- skin infections;
- HIV;
- gastrointestinal diseases.
To treat the disease, you must consult a doctor. Self-medication in this case is evil. The doctor will conduct an appropriate study and prescribe adequate therapy.
Risk factors
As mentioned above, what is unpleasant is not the presence of a subcutaneous mite as such - in itself it cannot harm a healthy person - but demodicosis, which is caused by a mite. If the body is weakened and there are additional risk factors, the tick can settle in the skin for a long time and cause considerable mental and physical damage to its “breadwinner”. Risk factors include:
- dysfunction of the sebaceous glands, changes in the composition of sebum, vascular changes;
- some skin diseases (rosacea, acne, seborrhea);
- long-term use of hormonal corticosteroid ointments;
- adolescence;
- pregnancy;
- stress.
Unfortunately, non-specialists react with unacceptable ease to the appearance of acne on the face and body. The appearance of such problems is attributed to age and ordinary acne, which sooner or later should disappear on their own. We have to disappoint you: demodicosis caused by subcutaneous mites will not go away on its own. The disease can travel from one area of the skin to another, existing for years and ruining the life of its “donor”.
IMPORTANT:
squeezing out acne when infected with a subcutaneous mite only leads to an exacerbation of the infection, since during this process the mites are pressed into healthy areas of the skin and infect them.
Make an appointment
What then is possible?
To begin with, we should say what is needed - a dietary regimen during and after treatment. What about cosmetic procedures? Some of them are a real salvation in the fight against demodicosis. They help restore infected areas of the skin:
- cryotherapy - cold exposure, causing a sharp spasm of blood vessels followed by persistent dilation; result - peripheral blood supply is enhanced, skin nutrition is improved, metabolic processes are accelerated, the immune system is activated, and the skin's resistance to stress increases;
- mesotherapy - carried out during the period of remission, this is an injection procedure, the essence of which is the delivery of restorative substances contained in the preparations / cocktails to the tissues;
- plasma therapy - carried out during the period of remission, this is the introduction of purified and platelet-rich blood plasma of the patient into the affected areas of the skin; As a result, skin immunity is stimulated, and regeneration processes are launched at the cellular level.
Each of the procedures described above is prescribed in a course; to achieve a sustainable effect, on average, 5–6 procedures are required, which are carried out every 7 days.
Treatment
Treatment of demodicosis caused by subcutaneous mites is a long and difficult process. Its complexity is that often this disease develops against the background of a decrease in the body’s defenses and has accompanying skin problems. Therapy tactics include suppressing the parasite, treating underlying diseases and increasing immunity.
The most commonly used local therapy is lotions and special ointments. In more severe cases, the doctor prescribes a course of antibiotics in combination with external therapy. Sometimes plasmapheresis procedures are recommended. In special cases, even surgical intervention is possible.
An important point in the course of treatment is diet. It is necessary to exclude hot, spicy and salty foods, foods rich in carbohydrates and fats from the diet. Those who are being treated for subcutaneous mite infestation are recommended to consume large amounts of fruits, vegetables, microelements, fiber, and dairy products. During treatment, you should not use face masks, especially those containing honey. You need to limit your exposure to the sun. You should also wait until better times to visit the bathhouse and sauna.
How the disease develops
Demodectic mange on the face can develop in several stages. Characteristic symptoms appear as follows:
- The skin on the face turns red. At the same time, the person feels irritation on the skin and heat. At first, the redness is temporary, intensifying in bright sun, after exercise, or drinking hot drinks.
- The redness becomes persistent and permanent. The face is red, especially on the cheeks, chin, nose, and in some cases on the forehead.
- Blood vessels dilate , spider veins appear on the face.
- Papules and pustules develop. These are painful ulcers, acne. They are painful, do not last long, and scars form in their place.
- Rhinophymas appear on the nose - these are compactions, small tumors on the skin. The blood vessels and sebaceous glands become inflamed, the nose enlarges and becomes shapeless. More often, this symptom is characteristic of men with demodicosis on the face.
All this is accompanied by increased sebum secretion or dryness. The skin becomes rough. The person feels burning and itching. There is a tingling sensation on the face and the skin hurts. The face becomes noticeably swollen and swollen due to impaired lymphatic drainage.
Demodicosis of the face is often, but not always, accompanied by demodicosis of the eyelids. Symptoms of eyelid damage include redness, irritation, dryness, and a feeling of a foreign object in the eyes. The eyelids become inflamed and blepharitis appears. Eyelashes stick together and fall out. The eyes are constantly inflamed and tired.
The nature of the course of demodicosis
According to the nature of the course of the disease, two forms are distinguished:
- secondary;
- primary.
Let's look at each form.
Primary demodicosis
Primary demodicosis occurs against the background of a general deterioration in health. This form of the disease occurs on healthy skin.
Secondary demodicosis
Secondary demodicosis is the most common type. In this case, demodicosis occurs against the background of other chronic diseases. With this form of the disease, laboratory technicians detect D. Brevis.
Characteristic features of the secondary form:
- possible total skin damage;
- the clinic corresponds to rosacea;
- Papulopustular elements appear on human skin.
The role of iron mites in the development of skin diseases
The parasitism of these mites on humans can often be asymptomatic. On average, up to 55% of people are carriers of iron mites. With age, tick infestation increases and, according to some authors, in older people it reaches 100%. Because of this, their role in the development of skin diseases is assessed ambiguously, but it has been proven that the number of D. folliculorum
more than 5 copies per sq. cm.
The number of iron mites significantly increases in patients with some forms of rosacea: mites of the genus Demodex
to be involved in the pathogenesis of these diseases.
1.4
Symptoms
Photo 2. Eye mites - symptoms of blepharitis.
In the initial stage of demodectic blepharitis, clinical manifestations are practically absent. Subsequently, with the increase in the reproduction of ticks, their waste products cause the appearance of the following symptoms:
- itching and burning of the eyes;
- redness, swelling, inflammation of the edges of the eyelids;
- sticky, thick discharge that accumulates in the corners of the eyes;
- sticking of eyelashes, appearance of scales and crusts on them;
- eyelash loss;
- dry eye syndrome.
Demodex analysis
If you suspect that you have this disease, then you need to seek qualified help from a medical institution.
You need to contact the following doctors:
- cosmetologist;
- dermatologist.
Scraping from the affected area is the material for analysis. A scalpel is used to remove material for analysis. And also the contents of a purulent follicle can be used as material for analysis.
The analysis will be completed within four hours . As a rule, test results are collected the next day. A special microscope is used to identify the parasite.
The diagnosis is made in the following cases:
- When signs of infection are detected.
- When ticks (adults) are detected.
- When eggs or larvae are found.
Preparing for the analysis:
- you cannot use medicinal cosmetics;
- It is forbidden to wash your face (for one day);
- ointments should not be used.
If these rules are not followed, the attending physician may prescribe a repeat study. Since the result may be negative, even if there are pronounced symptoms. If the result is positive, the laboratory technician determines the type of parasite.
The duration of therapy directly depends on the type of parasite:
- if a short type is detected, short-term therapy is prescribed;
- If a long type is detected, a long course of treatment is prescribed.
How to treat a person
In case of facial lesions in the recent past, a course of systemic therapy was indicated, which included:
- taking tablets Metronidazole (Trichopol), Suprastin, Tavegil
- At the same time, local therapy was carried out with ointments for demodicosis benzyl benzoate, yam ointment, sulfur ointment, aversectin ointment, permethrin ointment. Most of these drugs are veterinary; not a single ointment can cope with the disease on its own. The course of treatment consists of a combination of drugs. Due to similar semantics with other skin diseases, such as psoriasis, dermatitis, patients may be mistakenly prescribed medications containing hormones that are strictly prohibited for demodicosis. Be careful, if you are prescribed treatment with corticosteroid ointments, it must be discontinued.
| Damage caused by demodex mites. | |
| Destruction of hair follicles by subcutaneous demodex mites. A large number of subcutaneous mites parasitize the hair follicles, feed on the skin cells of the hair follicles and secrete toxins. | Hair follicles are destroyed, pathogenic bacteria invade them, metabolism is disrupted, skin health problems arise, acne appears, enlarged pores appear, skin oiliness increases, roughness and other skin problems appear. |
| Scheme of action of anti-demodex products of the Internet portal Demodex.Ru | ||
| Destruction of hair follicles by subcutaneous demodex mites. A large number of subcutaneous mites parasitize the hair follicles, feed on the skin cells of the hair follicles and secrete toxins. | Active herbal extracts return vitality to skin cells. | After eliminating subcutaneous mites and healing, the skin returns to a healthy state. |
Demodex (demodecosis) is a disease common in all countries and at all times of the year.
According to TsNIKVI: “Carriage of the Demodex parasite was found on the facial skin of 89% of people.” The average age of women suffering from the disease is 44.5±2, and men – 38.3±5.4 years. Among the patients, 90% are women.
Demodex disease is caused by the subcutaneous Demodex mite (mite), which is found in the hair follicles and sebaceous glands. The Demodex mite prefers places with increased sebum production.
“Long” demodex (Demodex folliculorum) and “short” Demodex (Demodex brevis)
An important concept in the treatment of demodicosis is “long” demodex (demodex folliculorum) and “short” demodex (demodex brevis).
“Long” demodex (demodex folliculorum longus) is a mite with a long, elongated worm-like body. The size varies from 0.272 to 0.480 mm. Lives inside hair follicles.
“Short” demodex (demodex folliculorum brevis) is a mite with a body length of 0.128 to 0.144 mm in males, 0.160–0.176 mm in females. Lives in the sebaceous glands.
Only a doctor can determine your type of demodex based on the results of a demodex test. When analyzing, be sure to ask your doctor what type of demodex was detected: “long” or “short”. This will determine the duration of your treatment:
- for “long” demodex, treatment with Demodex Complex products is 90 days;
- with “short” – up to 150 days.
Antiparasitic treatment quickly relieves the feeling of itching, which once again confirms the leading role of the Demodex mite in this disease, and also refutes the opinion of some dermatologists who deny its influence on the pathological process. Many doctors consider the iron mite only as a supporting factor for rosacea. Chinese dermatologists adhere to a different point of view, as do a number of scientists in our country (S.T. Pavlov, O.K. Shaposhnikov, V.I. Samtsov, I.I. Ilyin), expressing the opinion that demodex is an independent disease.
Infection occurs through direct contact. There are also known cases of infection in beauty salons during facial cleansing.
You will find more detailed information about demodex in the Questions and Answers section.
What are the most typical symptoms of demodicosis?
Where do inflammations caused by demodex mites occur (localization)?
The characteristic location of mites is the so-called “Demodex triangle”: wings of the nose, nasolabial fold, chin. The mite also affects eyelashes, ears, scalp, and neck. And with a long course of the disease, Demodex mites are detected on the skin of the chest, very rarely in the back area (0.5-0.7% of observations).
Demodex lives in the sebaceous glands and hair follicles and feeds on their contents. Prefers places with increased sebum secretion.
How is demodicosis diagnosed?
Demodectic mange on the face is often confused with rosacea and acne. In fact, tick infestation is very often combined with these diseases. When a person has both demodicosis and acne, the rashes are asymmetrical, there are more of them on the cheeks and closer to the temples. Demodectic mange worsens rosacea; due to mites, redness, itching and peeling become stronger.
To understand exactly what causes redness and discomfort, a diagnosis is necessary. If mites are found in the rashes, we can talk about demodicosis, and their number should be more than 5 individuals per square centimeter of facial skin. If there are fewer of them and there are no clinical symptoms, then in this case the person is considered not sick, but a carrier of the tick. It does not require treatment. To detect mites, the skin flakes and the contents of the sebaceous ducts are examined.
The main manifestations of demodicosis in humans
– the skin becomes constantly oily, greasiness increases, – pores expand, – redness in the central part of the facial skin, – the general condition of the skin is unhealthy, the complexion is earthy-gray, – skin inflammations appear: acne, acne, pustules, papules, pustules, blackheads , acne, sores, – itching, – facial skin becomes flabby, lumpy – facial expressions become difficult, – puffiness of the face and nose occurs, – hair and eyelashes fall out (if the hair is damaged).
The rapid progression of demodicosis is dangerous due to the appearance of difficult-to-remove cosmetic defects: scars, potholes, scars.
Untreated demodicosis can lead to an enlarged nose (rhinophyma), inflamed eyes (blepharitis), eyelashes to fall out, and early baldness.