- Signs of the disease
- Depriving forms
- Causes
- Initial stage of the disease
- Period of rash
- Crust formation
- Diagnostics
- How to treat an infection?
- What are antiviral drugs used for?
- Possible consequences
- Is shingles contagious?
- When is shingles transmitted?
- Disease prevention
- Which doctor should I consult with this disease?
Shingles has vivid and painful symptoms. Most often, the disease is detected in older people. An unfavorable environment contributes to the development of infection in young people with weak immunity. Shingles often develops against the background of cancer, especially in people with weakened immune systems (after chemotherapy, for example).
Depriving forms
The disease can be typical or atypical.
In the atypical form, symptoms may be mild:
- In the abortive form, the rash is absent or there is a single focus;
- Bullous form - multiple blisters with clear liquid;
- Hemorrhagic form - blisters with bloody fluid, in place of which scars remain.
- The gangrenous form leaves difficult-to-heal ulcers and rough scars.
Treatment
For local treatment, the doctor can use desiccant agents, disinfectants, zinc preparations, drugs acting on the DNA of the virus, and prophylactic drugs that protect against sunlight.
Treatment of herpes
Medicines - zoovirax cream up to 5 times a day, iodoxide, neomycin aerosol, vratizoline.
General treatment with acyclovir or famciclovir is indicated for patients with reduced cellular immunity, pregnant women, newborns, and in cases of recurrent infections, especially HSV2, but also HSV1. This treatment is more effective than topical treatment. This may reduce the relapse rate.
Drugs - Acyclovir (Zoovirax), Herpesin, Heviran, are prescribed in doses of 5 x 200 mg orally for 5 days. In case of complications, the drug is administered intravenously. Treatment should be started within the first 2 days of the first skin changes.
For recurrent herpes HSV1 or HSV2, acyclovir can be prophylactically prolonged at a dose of 200-400 mg per day in a chronic manner.
Period of rash
The type of rash depends on the severity of the disease. At the initial stage, the rashes look like small pink spots located on healthy skin.
If the process develops typically, then the next day they are replaced by bubbles with a clear liquid - grouped vesicles. After 3 days, their contents become cloudy. The rash occurs in spurts, with breaks of several days.
If a severe gangrenous form develops, the filling of the vesicles may be mixed with blood. It seems that the bubbles move to another place, located around the body.
If the form of inflammation is mild, the manifestation of the disease can only be neurological in nature, when the patient feels pain, but there is no rash. This is herpetic neuralgia.
HSV2 genital herpes
Primary infection occurs after sexual intercourse. In men, the infection most often affects the glans and penis. The most common symptom is erosion. The nearby lymph nodes may be enlarged. In homosexuals, lesions may occur in the anal area. In HIV-positive patients, a small ulcer is observed at the site of infection for a long time.
In women, similar changes occur in the labia, vagina, and cervix. Severe pain, dysuric symptoms, constipation, and back pain are possible. Repeated cervical infection may be a precancerous condition.
HSV2 genital herpes
HSV2 infections in pregnant women are an extremely important problem. Recurrent herpes carries less risk of harm to the fetus because the mother passes on antibodies against HSV to the baby. However, if HSV2 infection occurs for the first time during pregnancy, there is a very high risk of damage to the fetus, especially in the first 3 months of pregnancy.
What are antiviral drugs used for?
The goal is to exclude the development of complications. Antiherpetic treatment helps the ulcers heal quickly and improves the patient's condition.
The course of treatment and dosage of medications is determined by the doctor taking into account the general condition of the patient. On average, treatment time does not exceed 10 days.
If a gangrenous form with a bacterial infection develops, antibiotics, immunomodulators, physiotherapeutic procedures and vitamins are prescribed.
When it comes to treating rashes, there are different opinions regarding the use of drying agents. In any case, they should be used with caution so as not to worsen the condition of the skin by burning.
Hormonal medications should not be used as they suppress the immune system.
Treatment of the disease in elderly patients is not always successful, since antiviral drugs are not justified.
Herpes
The content of the article
Herpes, caused by herpes virus I or II, is one of the most common infectious diseases in humans.
There are two types of viruses:
- type I is most often associated with infection in the facial area;
- type II with localization of genital lesions.
After primary infection, both types of viruses remain latent in the ganglia. Due to a variety of factors that contribute to the development of infection, viruses can travel along nerves and multiply in the skin or mucous membranes, causing symptoms of the disease.
In carriers of active infection without symptoms, HSV viruses can be detected in saliva and vaginal discharge. This can lead to the spread of infections, especially HSV2. Infection occurs through personal contact or contamination with secretions.
Primary HSV1 infection occurs in young children and is often asymptomatic or in the form of stomatitis. It turned out that with high population density and poor housing conditions, 100% of children under five years old have antibodies to HSV1.
Primary HPV2 infection occurs after puberty, most often through sexual contact. Its consequence is always skin symptoms in the genital area. Rarely, HSV1 infection can occur in the genital area, most often due to infection during oral sex.
HSV1 or HSV2 infection in children in the genital area may result from sexual abuse.
Patients with a history of HSV infection have circulating serum antibodies that do not protect against recurrence of infection.
Which doctor should I consult with this disease?
You should first contact a therapist, then an infectious disease specialist or dermatologist. If the form of herpes is severe, the help of a neurologist is necessary; if the eyes are affected, the help of an ophthalmologist is necessary.
We recommend making an appointment at the neurological department of the RAS clinic (Moscow). The best doctors will examine you, study the signs of the disease, identify the causative agent of the infection, make a diagnosis, conduct a consultation, issue clinical recommendations and prescribe effective treatment.
Don't put off visiting a specialist! Specialists from the neurological department of the Central Clinical Hospital of the Russian Academy of Sciences in Moscow remind you: any symptoms that worry you are a reason to consult a neurologist. In this case, the doctor will be able to recognize and treat the disease at an early stage, before the situation worsens and becomes irreversible. You can make an appointment with a neurologist by calling the clinic or using the form on the website.
Clinical symptoms and course of herpes HSV1
Primary infection (herpetic gingivostomatitis) occurs most often in children under 5 years of age, in the form of painful blisters in the area of the tongue, throat, larynx, accompanied by fever and dilation of nearby lymph nodes. Symptoms disappear within 2 weeks. The disease is often not recognized.
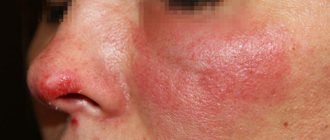
Skin symptoms in adults begin in the face, but can also be found on the fingers (for example, in people who bite their nails) and on the trunk. The result is follicular and papular lesions, sometimes painful, and swollen lymph nodes.
Skin symptoms of herpes HSV1
With recurrent herpes, general symptoms such as weakness or flu-like symptoms sometimes appear. Factors that initiate the occurrence of recurrent herpes can be UV rays, overheating or cooling of the body, fever, dehydration, menstruation, stress.
Patients with eczema or atopic dermatitis may experience diffuse herpes lesions due to damage to the epidermal barrier and local immune defenses. Herpes can also cause an exacerbation of pemphigus or the occurrence of erythema multiforme. Complications: keratitis, keratoconjunctivitis, pharyngitis, meningitis.
Complications
- Neuralgia, skin hyperalgesia - can persist for up to 8 months after the infection is cured;
- Transient paralysis of peripheral nerves - drooping eyelids, paresis of limbs, asymmetry of the corners of the mouth;
- With herpes zoster, severe complications can occur, leading to serious visual impairment (keratitis, scleritis, uveitis, optic neuritis);
- Balance problems, hearing problems, loss of taste, photophobia.
The most serious complications include ophthalmological changes and neuralgia. A rare, late complication of herpes zoster can be granulomatous vasculitis of the central nervous system, meningitis.
How is shingles transmitted?
You can get shingles from someone who has herpes or chickenpox. However, if the patient comes into contact with this virus for the first time, he will get chickenpox, and not shingles. The appearance of lichen is possible only in the case of a secondary lesion.
Most often, the pathogen is transmitted by airborne droplets; contact infection is also possible.
When the virus is inhaled, it remains in the respiratory tract and begins to spread throughout the body along with the flow of lymph and blood, as well as moving along nerve endings. Gradually, the pathogen penetrates most tissues of the body. This explains the recurrent nature of herpes zoster - it is impossible to suppress the virus with self-medication; complex therapy is required under the supervision of an experienced dermatologist.
How long is shingles contagious?
A person with shingles is contagious to others. The virus is in active form 1-2 days before the rash appears and until the vesicles have completely healed. To limit the spread of infections, during this period the patient is advised to avoid contact with other people,, if possible, limit communication with friends and relatives, and not use shared utensils or hygiene products.
After the rash goes away, shingles ceases to be dangerous for people around you - the immune system has suppressed the viral infection.
Treatment options for lichen depending on its type
Just like the causes and symptoms, treatment regimens differ depending on the type of fungus.
If shingles fungus is diagnosed at the very beginning of the disease, the doctor may prescribe the following medications: Acyclovir, Zovirax. According to individual indicators, drugs such as “Curantil” and “Furosemide” can be prescribed. If the immune system is particularly weakened, intravenous drips with immunoglobulin may be prescribed.
The treatment regimen for advanced shingles consists of taking the following medications:
- analgesics;
- antipyretic drugs in the presence of high fever;
- B vitamins, which help strengthen the body’s protective functions;
- sedatives for insomnia;
- prescribing diuresis when signs of intoxication appear;
- the skin at the site of the lesion can be treated with a solution of brilliant green, metacil ointment, "Solcoseryl".
Pityriasis in most cases goes away on its own and does not require treatment. The exception is severe itching, for which you can use antihistamines and hormonal creams.
During the course of the disease it is recommended:
- wear underwear made from natural fabrics;
- limit bathing and interaction of the affected area with water;
- exclude the use of cosmetics.
Treatment of versicolor versicolor is possible using the following medications: 5% salicylic ointment, Cycloperox, 5% sulfur ointment, Bifazol, Miconazole, Lamisil. If foci of the disease have spread throughout the body, then it is recommended to take Orungal or Itraconazole.
The flat red fungus causes significant discomfort to the patient due to severe itching and burning sensation. Suprastin, Tavegil and Zyrtec will help cope with itching. In addition, corticosteroids and antimalarial medications may be prescribed.
If lichen planus affects the mucous membrane, then treatment with Solcoseryl is necessary. If this type of disease recurs, antibiotics are prescribed.
If trichophytosis affects areas of the skin without the presence of hair, then the area can be treated with iodine and antifungal ointment (Exoderil, Microspor).
If there is hair in the area of the focus of trichophytosis, it is better to shave it off. In advanced cases, it is necessary to take antifungal drugs orally (for example, Irunin).
The course of the disease must be accompanied by taking a vitamin complex to maintain immunity.
Diet for fungal diseases
When the skin is affected by fungal diseases, it is important to maintain proper nutrition. In this case, it is useful to use the following products:
- breakfast with cereal porridge;
- dairy products;
- greens and green vegetables;
- honey;
- still mineral water;
- foods containing iron.
If you have pityriasis, you need to switch to dairy and plant foods. For other types of fungus, you should include in your menu:
- rose hips, viburnum and sea buckthorn;
- peanuts, hazelnuts and nuts;
- squid and salmon;
- seeds and vegetable oil;
- apples, apricots, cherries, blueberries, cherries;
- prunes and raisins;
- green bell peppers and carrots.
Along with the list of healthy foods, there is also a prohibited food group:
- dishes using spices and hot additives;
- alcoholic products;
- tangerines.
The following categories of drinks and food are subject to restrictions:
- coffee, tea and hot chocolate;
- cheeses that are too salty;
- broths cooked with meat and mushrooms;
- confectionery sweets with butter creams;
- canned food;
- fatty fish.
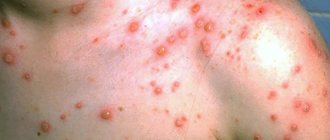
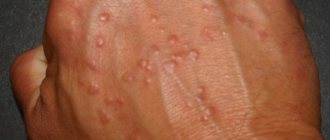
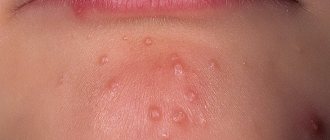
What does shingles look like?
One of the hallmarks of shingles is a specific pink rash that appears on the face and body. Vesicles appear on the 3rd-4th day of infection, they are preceded by:
- pain and burning of the skin;
- tissue redness;
- slight swelling of the skin.
Then one or more small pink-red bubbles with transparent contents appear. In most cases, the size of the rash does not exceed a pea; small bubbles can merge into larger formations.
After a few days, the contents of the bubbles become cloudy, they burst with the formation of a yellow-brown film. Vesicles do not appear all at once and continue to form over several days, occupying an increasing area of the body.
After recovery, patches of skin with disturbed pigmentation, scars and scar tissue often form at the site of the rash.
Symptoms
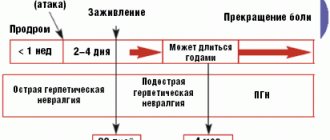
The appearance of skin lesions with herpes zoster may be preceded by prodromal symptoms in the form of pain - headache, pain in the ear, throat, shoulder, spine, abdomen, heart area. The pain may appear more than 5 days before the appearance of skin lesions similar to those seen with chickenpox.
Lesions are most often located unilaterally along the nerves of the face and trunk (the most common location also for chickenpox). After 2-3 days, erosions appear, covered with scabs, often with signs of a secondary bacterial infection.
The appearance of skin lesions may be accompanied by fever and dilation of nearby lymph nodes. In the case of herpes zoster around the face, the lesions also affect the mucous membranes of the mouth and may affect the eyeball.
According to the course and clinical picture, herpes zoster is distinguished:
- hemorrhagic;
- absent-minded
A common form may be a sign of a violation of the body’s immunity, the course of general diseases, such as lymphocytic hyperplasia, cancer, immunosuppression of various etiologies (autoimmune diseases, immunosuppressants, HIV-infected people). Therefore, in patients with severe or disseminated herpes zoster, general examinations should be performed to determine the cause of the exacerbation of the infection.
Causes of the disease
For most people, the herpes zoster virus first enters the body in childhood or adolescence. Chickenpox affects more than half of the population by adulthood. Healing and developing immunity to it does not mean that the pathogen has left the body. Like all types of herpes, this one persists in the nerve endings of the spinal cord and brain for life. Recurrence of chickenpox in these cases is prevented by the specific defense of the immune system. In rare cases: when the body is weakened or due to congenital genetic defects, the disease may return. In adults, activation of herpes provokes a more complex pathology that affects not only the skin, but also the nervous system.
Shingles, unlike chickenpox, occurs quite rarely: no more than 15 cases are recorded per 100 thousand population. The disease occurs mainly in the cold season. The virus tolerates frost well, but is not resistant to extreme heat. The majority of those affected are middle-aged and elderly people. Shingles is an infectious pathology, but it develops not as a result of the transmission of a pathogen from the outside, but due to the activation of what is already inside.
Main provoking factors:
- state of immunodeficiency in HIV carriers;
- severe stress;
- weakening of the body after transplantation of internal organs and other complex surgical operations;
- long-term use of suppressor drugs for rheumatoid arthritis and other autoimmune diseases;
- chemotherapy and radiation treatment for cancer tumors;
- diseases of the hematopoietic system;
- Hormone replacement therapy for endocrine disorders.
The mechanism of development of herpes zoster is not well understood. It is known that the Herpes zoster virus causes inflammatory reactions in the membranes and roots of spinal nerves, as well as the adjacent skin.