Pustular skin diseases
– a wide group of pathologies caused by streptococci and staphylococci as a result of weakening of the body’s protective functions, as well as adverse external influences – hypothermia, skin injuries, poor nutrition.
Symptoms of pustular diseases
can manifest themselves in the epidermis, hair follicles (folliculitis), sweat glands (hidradenitis, etc.) sebaceous glands (furunculosis). The rashes can be minor and not cause much discomfort, or they can occur in a severe form in the form of painful formations - boils, deep abscesses and other ailments.
Treatment in such cases can only be prescribed by a specialist!
The patient is recommended to observe the rules of personal hygiene, use antibiotic ointments and drugs and, if there are no contraindications, use physiotherapy methods, immunostimulating drugs, taking antibiotics orally, intravenously or intramuscularly, depending on the severity and extent of the disease, as well as antihistamines and desensitizing drugs.
What diseases do staphylococci cause?
The content of the article
The main causative agents of purulent-septic diseases are staphylococci (from the Greek "staphyli" - clusters, "kokkos" - kernels, balls, which corresponds to the appearance of these microbes under a microscope) and streptococci (from the Greek "streptos" - chain).
We owe to these microorganisms such diseases as boils, carbuncles, pyoderma, abscesses, phlegmons, panaritiums and other suppurations of the skin. When the mucous membranes are damaged, conjunctivitis, stomatitis, otitis, and enteritis develop.
Severe forms of the disease are pneumonia, osteomyelitis (bone tissue lesions) and septic - generalized inflammatory processes in internal organs when staphylococci and other microorganisms circulate in the blood (blood poisoning) are especially dangerous.
After purulent infections, various complications arise, including those that can lead to a chronic course of the disease and disability (myocarditis, heart defects, thrombophlebitis, peritonitis - inflammation of the peritoneum).
Losses associated with loss of ability to work only from staphylococcal diseases exceed those caused by all infectious diseases, with the exception of influenza. The number of newborns and adults who die from staph infections is more than twice the number who die from other contagious diseases.
Antibiotic resistance of staphylococci
The more we attack, for example, pathogens of purulent-septic infections with antibiotics, the more often antibiotic-resistant microorganisms appear.
Under the influence of antibiotics, the inhibitory effect on staphylococci of other microbes - common inhabitants of our body - is disrupted. Moreover, sometimes antibiotics simply stimulate the development of staphylococci and streptococci. Therefore, without medical prescription, the independent use of antibiotics (and other antibacterial agents) in the event of purulent skin lesions should be excluded.
Any treatment for staphylococcal skin pathologies should be prescribed by a dermatologist! Diseases of other organs are treated by appropriate specialists - gynecologists, urologists, therapists.
Where to sign up for treatment for pustular diseases in Moscow?
At a multidisciplinary medical center you can always sign up for treatment for pustular diseases
. Our medical center is located between the Konkovo and Belyaevo metro stations (South-Western Administrative District of Moscow in the area of the Belyaevo, Konkovo, Teply Stan, Chertanovo, Yasenevo, Sevastopolskaya, New Cheryomushki metro stations " and "Trade Union"). Here you will find highly qualified personnel and the most modern diagnostic equipment. Our clients will be pleasantly surprised by our quite affordable prices.
Why is staphylococcal infection dangerous?
Staphylococcus is especially dangerous in association with viruses and fungi, as well as with concomitant childhood droplet infections that reduce the overall reactivity of the body. It is not without reason that in many diseases local or general complications caused by staphylococci are observed.
Thus, during influenza epidemics, staphylococcal pneumonia is not uncommon, which most often turns out to be the cause of a child’s long-term illness and is the most common prerequisite for death.
Staphylococcal and streptococcal toxins have pronounced sensitizing properties, causing allergies and toxic damage to the heart muscle, kidneys and other important organs. Unlike a number of pathogens of childhood infections, the site of action of which is limited to certain areas of body tissue, staphylococcus and streptococcus are “omnivorous”.
They can cause inflammation of the gallbladder (cholecystitis), toxic dyspepsia and gastroenteritis, inflammation of the joints (arthritis), and genitourinary tract (urethritis and endometritis). In newborns, staphylococcal and other purulent inflammatory phenomena begin with the umbilical wound or other skin lesions that are invisible at first glance (scratches, abrasions).
It must be emphasized that up to 90% of cases of sepsis in young children are associated with staphylococcus.
Features of children's skin
At birth, babies have very thin skin. The skin of a newborn is almost half as thick as the skin of an adult. The outer layer thickens with age.
The skin of newborns is red or purple in color due to the close proximity to the upper layer of blood vessels and an insufficient layer of subcutaneous cellular tissue, as a result, the skin appears “transparent”. This phenomenon is especially pronounced if the baby is frozen - the appearance of a marbled vascular network on the body is observed.
Moisture evaporates faster from the skin of newborns. Children are more susceptible to bacteria, viruses, fungi and mechanical influences. Thickening of the skin begins at 2-3 years of age and ends by 7 years.
Staphylococcus in pregnant women is a threat to the life of newborns
The source of staphylococcal infection in maternity hospitals, children's hospitals and at home can be purulent lesions of the skin and mucous membranes of adults - the mother, others, and staff. Therefore, it is impossible to separate contagious skin diseases from other human infectious diseases.
Under normal conditions, the skin has protective properties in the fight against microbes, in particular, its secretions contain antibacterial substances. However, nutritional disorders, general diseases, and microtraumas of the skin can contribute to the development of pathogenic microflora on the child’s skin.
Active immunization of pregnant women with staphylococcal toxoid, as practice has shown, does not have a harmful effect on either the course of pregnancy or the development of the fetus, while at the same time reducing the incidence of purulent infections in mothers and newborns by 3-5 times.
At the same time, the mother develops active and the child develops passive immunity to pathogens of such infections as otitis media, pneumonia, skin suppuration, tonsillitis (tonsillitis), laryngotracheitis, sinusitis and other inflammatory diseases of the nasopharynx.
Staphylococcal diseases in young people and children
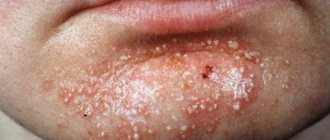
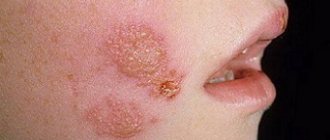
Pustular skin diseases are called pyodermatitis, which, depending on the cause of occurrence, are divided into strepto and staphyloderma. Their mixed form is often observed - streptostaphyloderma.
Streptoderma most often affects children and young men and is usually localized around natural openings - the nose, mouth, ears, that is, in areas subject to irritation by the discharge of these cavities (saliva, mucus). These lesions are very contagious and quickly spread to healthy areas of the skin. Streptoderma is transmitted through toys, diapers, clothes, and underwear.
A fairly common streptococcal skin lesion in newborns is impetigo (from the Latin “impetus” - sudden, attacking). With this disease, flat cavities with a flabby folded covering are formed, filled with serous-purulent contents - phlyctenas.
Merging, they form continuous foci with tortuous inflammatory outlines. Exposed parts of the body are predominantly affected, especially the skin of the face. Nearby lymph nodes often swell, and as the infection spreads, phenomena of general intoxication are observed.
Another form of purulent lesions is neonatal pemphigus. This type of pyoderma is characterized by the formation of large blisters that reach the pigeon egg and are filled with purulent contents. When they rupture, a bare bright red surface (erosion) is formed, which is easily subject to additional infection, resulting in a sharp deterioration in the child’s condition.
Streptococcal pemphigus is extremely contagious, contagious and, in the absence of proper preventive measures, can cause massive outbreaks of pyoderma in maternity hospitals and children's hospitals.
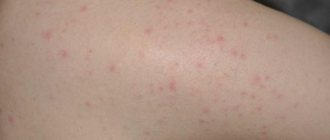
When a child moves home from the maternity hospital, a vesiculopustular form of pyoderma often occurs in places that are most often irritated by sweat (on the back of the head, neck, forehead, groin). Small bubbles with transparent contents (vesicles) the size of a pinhead appear. Then the contents of the vesicles become purulent (pustule) and are surrounded by a halo of hyperemia.
After two to three days, the pustules burst or undergo reverse development and superficial crusts form in their place. Despite the relative ease of this infection, its complications can be very insidious. They are expressed in widespread and severe phlegmon, occurring with significant swelling and subsequent necrosis (melting) of the subcutaneous tissue.
In infants with low nutrition, in improperly bottle-fed children, as well as in older children with weak protective reactions (due to tuberculosis or other types of intoxication), streptococcal infection is not limited to superficial skin lesions, but invades deeper tissues, forming deep ulcers - ecthyma .
They occur on the most frequently injured parts of the body (lower back, lower legs) and are characterized by a sluggish, long-lasting course. After they are healed, scars remain.
Speaking about streptococcal pyoderma in children, we cannot ignore erysipelas, which especially often affects the face (hence the name “erysipelas”). The skin of the face becomes red and swollen. The disease is accompanied by an increase in temperature and sometimes a severe general condition requiring emergency treatment measures.
The so-called “zaeda” is also known - streptococcal phlyctena (a type of impetigo) in the corners of the mouth, which opens and forms a long-term non-healing wound, constantly renewed in connection with facial movements of the facial muscles and food intake. With insufficient sanitary control, seizures can cause real outbreaks in children's groups.
Pemphigus of newborns can also be caused by staphylococci. In the most severe form of this disease, serous fluid accumulates in large areas under the stratum corneum of the skin and detachment of the skin occurs to such an extent that the child gives the impression of being “scalded.”
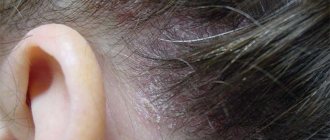
With staphyloderma, hair follicles are often affected, for example on the head, which leads to a small pustular rash, which disappears without a trace after treatment.
Staphylococci cause not only local, limited skin lesions, but also sore throat, severe pneumonia, inflammatory foci in various organs and tissues (liver, spleen, kidneys), resulting from the spread of microbes through the blood and lymphatic tracts. A generalized staphyloccal infection - sepsis - poses a mortal threat.
Staphylococci can cause real epidemic outbreaks in maternity hospitals and children's hospitals. Due to them, the vast majority of skin and septic lesions in newborns and purulent diseases in mothers occur. Postpartum sepsis, mastitis, pneumonia, meningitis, inflammation of the birth canal, conjunctivitis are a real disaster. Of course, they are especially dangerous for women in labor and newborns.
The most common pustular skin diseases
Furuncle
– acute purulent inflammation of the follicle, sebaceous gland and surrounding tissues. The cause of its occurrence is a staphylococcal infection, which begins to become more active when the immune system is disrupted. Cuts, scratches, and scratching of the skin during diseases with itching also contribute to the entry of staphylococci into the body. Most often, boils appear on the face, neck, armpits, thighs and buttocks, chest and lower back. In its development, the formation goes through three stages - infiltration, suppuration, healing. As a result of improper treatment, a boil can cause serious complications such as an abscess or sepsis. Under no circumstances should you squeeze it out yourself! Only a specialist can prescribe the correct treatment regimen. Prevention of complications includes preventing mechanical damage to a mature boil and the spread of infection.
Furunculosis
– necrotic disease of the hair follicle and surrounding tissues with the formation of pus and severe inflammation. The main cause of furunculosis is a staphylococcal infection. Symptoms - at the first stage, the appearance of a small infiltrate and bright red color around the hair follicle, which after a few days affects the adjacent sebaceous gland and surrounding tissues. The purulent core increases in size, and the formation begins to resemble a cone, very painful on palpation. The patient may have a fever and weakness. Acute furunculosis can last up to several months and be accompanied by numerous boils. Complications - rough scars on the skin, possible abscess or phlegmon, sepsis, lymphadenitis. The patient must urgently seek help from a dermatologist, who will prescribe systemic antimicrobial therapy, recommend ointments and diet, and also refer the patient for surgical opening of the abscess.
Erysipelas
– an infectious-inflammatory disease of the skin and subcutaneous tissue, characterized by constant relapses. The main symptoms of erysipelas are the formation of a red swollen area on the body, separated from the healthy area by a raised ridge, fever, weakness, and enlarged local lymph nodes. The disease affects all age groups. The reasons for its occurrence are decreased immunity due to stress or chronic diseases. The basis for the treatment of erysipelas is the use of antibiotics and antibacterial drugs, as well as antihistamines, vitamin-mineral complexes and dietary nutrition. Self-medication is strictly prohibited, as this can lead to death for the patient!
Streptoderma
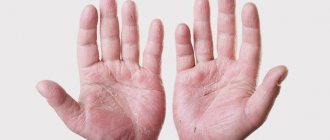
– an infectious skin lesion caused by streptococcal microorganisms, which is accompanied by the appearance of flaky purulent elements with a diameter of several millimeters to several centimeters. The diagnosis is made by a specialist based on the results of scraping from the affected area and bacteriological culture data. Infection most often occurs through household contact from the patient himself or objects shared with him. Treatment of streptoderma consists of isolating the patient in quarantine for up to 10 days, taking general strengthening and vitamin preparations, antibiotics, treating surfaces with antimicrobial agents, and applying aseptic dressings. It is recommended to follow a hypoallergenic diet and avoid contact with water.
Staphyloderma
– formation of foci of purulent-inflammatory skin lesions caused by staphylococcal infection. The disease can be transmitted through touch or objects used. Symptoms of staphyloderma are increased body temperature, general weakness and lethargy, abscesses. The superficial form of the disease is characterized by the appearance of individual folliculitis - conical pustules with purulent contents in the area of the hair follicle. The deep form is characterized by multiple pustules with significant damage to the skin and a general deterioration in the patient’s condition. Treatment of most forms of superficial staphyloderma consists of the use of antibacterial and antiseptic ointments. In more serious cases, intravenous and intramuscular antibiotics are prescribed, as well as ultraviolet irradiation and other physiotherapeutic techniques.
Sign up for treatment for pustular diseases
Make an appointment