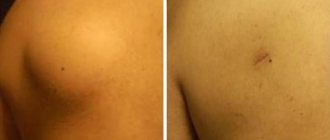
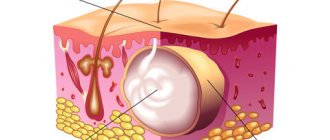
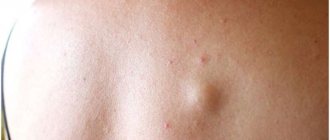
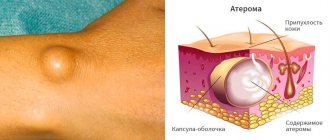
Atheroma is a tumor-like skin formation that appears as a result of disruption of the sebaceous glands. It looks like a small round or oval-shaped compaction that rises above the skin and is a cavity with mushy contents.
Atheroma can appear in any area of the body where hair grows and, accordingly, sebaceous glands are present (most often on the scalp, neck, genitals, mammary glands). Despite the fact that this is a benign neoplasm that does not pose a threat to life and rarely becomes malignant, without treatment it can cause significant inconvenience and aesthetic discomfort. Atheroma is not prone to self-healing, so it can periodically become inflamed and lead to the development of infectious complications.
General information
Atheroma is also called a sebaceous cyst. Its appearance is typical for young people 20–30 years old. According to statistics, the problem is more often found in women.
The location is the zones that most actively produce sebaceous secretions and are prone to clogging pores. Cysts can be either single or multiple. They slowly increase in size over several years. Large atheromas can compress nearby tissues and blood vessels.
As a rule, cysts do not hurt, itch or fester. The formation itself does not pose a health hazard, but with prolonged existence, atheromas often become inflamed and suppurate, and can also become a chronic source of infection. This often occurs due to mechanical pressure or irritation, which facilitates the penetration of a bacterial infection. Timely qualified assistance will help avoid such complications.
Attempts to independently open the atheroma in the hope of squeezing out its contents do not lead to the expected effect. Self-medication can lead to infection and other unpredictable consequences. Even in the case of a favorable outcome, after an independent autopsy, in one hundred percent of cases there will be a scar. In addition, what you think is a cyst may turn out to be a formation of a completely different nature and even malignant.
A surgeon can correctly diagnose and safely remove a sebaceous gland tumor. Don't be afraid of going to the doctor. The procedure for removing atheroma is completely safe and painless. [3.5]
Prices
Price (rub.)In installments* (rub.) Removal of benign formations of the skin, subcutaneous tissue, soft tissues, category I. complexity 9100—Removal of benign formations of skin, subcutaneous tissue, soft tissues, category II. complexity 16600—Removal of benign formations of skin, subcutaneous tissue, soft tissues, category III. difficulty27300—* You can read more about the conditions here - Treatment on credit or in installments
The cost is preliminary. The exact cost of the operation can only be determined by a surgeon during a free consultation.
Pathogenesis
The mechanism of development of the pathology is associated with disruption of metabolic processes, leading to a change in the nature of the secretion and blockage of the ducts of the sebaceous glands. At the same time, sebum production does not stop. If there is a difficulty along the way, sebum begins to actively accumulate under the tissue. Because of this blockage, tumor formation occurs.
The accumulation of contents leads to compression and gradual stretching of the walls of the cavity. Blood vessels and nerves are not affected, which explains the absence of pain.
Punctures of the cyst do not give the desired effect, since the cavity fills with fluid again and again. Only complete removal of the formation along with the capsule will prevent relapse.
Prevention
There are no effective methods of prevention. If there is increased secretion of the sebaceous glands, atheromas may appear in places near removed bumps or in new locations. As a preventative measure, you can eat less fatty and high-carbohydrate foods so as not to stimulate the glandular apparatus. Use antiperspirants as little as possible; your skin is oily. Use the right skincare products for your skin type to ensure that your pores are free of sebum.
Causes and symptoms of atheroma
Reasons for appearance
The main reason for the appearance of a soft-elastic cavity is the blockage of the lumen of the sebaceous gland, which develops against the background of the continuous production of sebum. A number of reasons can serve as a trigger for the development of atheroma, namely:
- structural features of the ducts of the sebaceous glands (tortuosity, deformation or complete absence of excretory ducts);
- genetic disorders;
- psychogenic changes, against the background of which there is a change in the amount and consistency of sebum;
- abuse of decorative cosmetics, perfumes, as well as antiperspirants, which narrow the ducts of the sebaceous glands;
- hormonal imbalances, endocrine disorders (hypothyroidism, hyperandrogenism);
- non-compliance with hygiene rules, incorrect skin care;
- acne;
- increased sweating;
- wounds, abrasions, cuts;
- external influence. [4,5,6]
Symptoms
Atheroma is not an infectious disease and cannot be transmitted from one person to another. For many years, the formation can remain small and not cause any inconvenience. It grows slowly and asymptomatically.
The formation can be detected during a visual inspection. The tumor has clear boundaries, but when pressed they can move. The cyst can be the size of a pea or reach the size of a chicken egg or even larger.
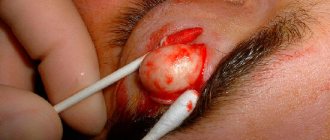
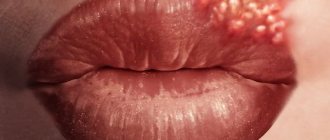
Typically, atheroma is not accompanied by the appearance of severe symptoms. Patients complain of a cosmetic defect, especially if the tumor is located in a visible place (for example, on the lip, lower eyelid or cheek).
There is also usually no pain. Exceptions may be cases where the atheroma is permanently damaged. When the cyst reaches a large size, unpleasant sensations may also appear in the form of discomfort and a feeling of pressure).
Patient complaints may vary depending on the location of the skin lesion. So, with atheroma on the scrotum, discomfort appears during urination or sexual intercourse.
Quite often, atheromas are found in the area behind the ear, since there are countless sebaceous glands here. Formations can also be found in the ear canal itself. Most often, it is discovered completely by accident while washing or washing your hair.
The location of the cyst in places of close contact with clothing (for example, on the arm or leg) can cause inflammation, manifested by pain and redness of the skin. The appearance of atheroma in the scalp area is accompanied by baldness. The skin in this area becomes dense and bluish, painful to the touch, and also covered with small ulcers. Regular traumatization of atheroma can lead to minor bleeding and necrosis (death). [1,2]
Degeneration of a sebaceous cyst is a rather rare occurrence, but this possibility should not be excluded. The following signs may indicate malignancy:
- severe pain, aggravated by touch;
- discharge of pus with an unpleasant odor;
- edema;
- local increase in temperature;
- hyperemia (redness);
- bleeding;
- relapse after removal.
If the above symptoms appear, you should consult a specialist as soon as possible. To exclude a malignant tumor, a puncture biopsy is performed.
Separately, it is worth mentioning the peculiarities of the development of pathology in children. Their sebaceous glands work less intensively, so the formation of atheroma is extremely rare. If this happens, then most often cysts appear on the head. Hormonal disorders, excess weight, and hereditary predisposition can provoke the development of pathology in a child.
Causes
The development of atheromas is noted in every tenth adult, mainly at a young age (up to 35 years), equally often in both sexes. Epithelial cysts develop when difficulties form for the release of secretions - narrowing or blockage of the excretory duct of the gland. Their reasons are as follows:
- congenital structural features of the glands, in which case the formations are detected immediately after birth;
- violation of the desquamation of keratinized skin cells, with the mouth of the gland being blocked completely or partially;
- excessive sebum production due to hormonal imbalances or psychosomatic disorders;
- mechanical damage to the skin: it has been noticed that atheromas often form in areas of scars after burns or frostbite;
- insufficient hygiene.
Classification of atheroma
According to the type of origin, sebaceous gland cysts are classified as follows:
- True. Their development is based on a genetic disorder. The formation of the formation occurs at the stage of intrauterine development of the fetus. As a rule, cysts are multiple in nature.
- False. The reason for the formation is associated with blockage of the sebaceous ducts. False atheromas, as a rule, are rare.
Atheromas in adults appear in areas with a large number of sebaceous glands:
- On the head, neck. Most often they occur in people with seborrhea and hyperhidrosis.
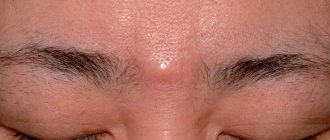
- On the face (on the nose, on the eyelid, on the forehead). The cause is usually metabolic disorders.
- Behind the ear. The problem may be due to poor hygiene.
- On the back. The appearance of a cyst in this area is usually associated with excessive sweating. [7]
Clinical picture
The cyst is a soft lump with rounded contours, located subcutaneously. Even small atheromas are clearly visible if you part your hair and carefully examine the changed skin.
Non-inflammatory atheromas are painless and do not cause discomfort, but if an infection occurs (which almost always happens with an accidental injury), the symptoms become more obvious. Suppuration of the cyst leads to its increase in size, intense pain, redness of the skin, and local swelling. The skin in the area of the inflamed atheroma is hot, and pus may be released from the outlet of the sebaceous duct.
Complications of atheroma
For a long time, atheroma may not cause concern. However, if pathogenic microflora attaches, the infected formation can cause significant harm. Delay in treatment is fraught with suppuration of the tumor, when its capsule increases in size, swells, turns red, the skin over it becomes tense and causes pain.
Independent attempts to squeeze out the contents of the cyst often end in the transition of the disease to a new stage - abscessing atheroma, characterized by spontaneous opening of the lesion and the subsequent spread of purulent contents to nearby tissues. The condition is accompanied by severe pain and general intoxication of the body. If the cyst bursts, purulent contents with a foul odor begin to be released from it. The most unfavorable outcome in this situation may be the penetration of infection from the purulent sac into the patient’s circulatory system, which can cause the development of sepsis (blood poisoning). [4,5]
The most dangerous complication is the degeneration of atheroma into a malignant formation. This happens extremely rarely, but this risk should not be neglected. That is why, in controversial situations, the contents of the cyst are sent for histological examination.
After surgery to remove a cyst, there is also a risk of complications. Fluid with blood clots may accumulate in the resulting cavity. The danger is that this secretion represents a favorable environment for the development of infection. Drains and pressure bandages are used to prevent fluid accumulation. Low-grade body temperature on the first day after opening the atheroma is a variant of the norm. The appearance of fever, swelling, and pain may indicate infection.
To avoid relapses and complications, do not wet the wound for several days after surgery. Visits to the bathhouse, sauna, and solarium are prohibited for at least two weeks.
We not only know how to remove atheroma correctly. We do it WITHOUT SCARS!
It is not enough to remove atheroma. We need to make sure that nothing reminds us of its existence.
. Especially when it comes to removing atheroma on the face or head.
Exclusive multi-stage seam processing
in “Platinental”, allows you to achieve the formation of a thin and invisible scar after surgery:
- The minimum necessary incisions in the natural folds hide the very fact of the surgeon’s intervention.
- special adhesive strips
match the edges of the wound without suturing
- application of special medical glue protects the wound from germs, eliminates the need for daily dressings and creates a favorable microclimate for fast and beautiful healing.
- When removing large atheromas, special multi-layered
self-absorbing sutures are applied.
This technique allows you to raise the seam level with healthy tissue
and form
an invisible scar
.
- sutures placed in Platinental heal very quickly and are extremely comfortable to wear: you can shower the very next day after the operation.
By following the recommendations for care after removal of atheroma, you can be sure that no one will suspect the fact of surgical intervention.
Scar after removal of atheroma on the head. Performed by surgeon: Maxim Vasiliev.
Diagnosis of atheroma
Diagnosis of atheroma is carried out by a dermatologist or oncologist surgeon. Mostly, the doctor identifies sebaceous gland cysts already at the stage of visual examination and palpation (palpation) of the tumor. The location, mobility, size of the tumor, as well as the rate of formation are of important diagnostic importance.
Additional information can be obtained using ultrasound. The study allows you to visualize the capsule and its contents. This method is effective for differential (comparative) diagnosis with diseases that can give a similar clinical picture (for example, lipoma, fibroma, hygroma).
The study is also carried out after removal of the tumor. The biological material is sent for histological examination, which makes it possible to determine the cellular composition of the tumor, exclude a malignant nature and, if necessary, adjust the treatment. In rare cases, an MRI or CT scan may be required to determine the extent of soft tissue invasion and differential analysis. [2,6,9]
Preparation for surgery includes the following studies:
- general blood analysis;
- biochemical research;
- tests for syphilis, hepatitis and HIV;
- coagulogram.
What kind of doctor is needed to remove atheroma correctly?
This should not be a dermatologist (cosmetologist).
Why? Simply because a large atheroma is a subcutaneous formation. And everything that is under the skin is beyond their competence.
Why is a surgeon needed?
Because the atheroma needs to be removed, and completely removed, 100%. Only surgery is a guarantee against relapse.
Why do you need a plastic surgeon?
Because after removing the atheroma using the classical technique, an unsightly recess and scar remains under the skin.
At Platinental, plastic elements are used in the process of removing atheroma. The subcutaneous tissue is moved so that the area where the atheroma was previously located is 100% aligned with the healthy surface of the skin.
Treatment methods for atheroma
Treatment for a cyst involves removing it. Without surgical intervention, atheroma often recurs. Moreover, such treatment is accompanied by the formation of a skin scar.
There is an opinion that atheroma can be cured at home using external ointments. However, this is a misconception. Atheroma has a specific structure that is not susceptible to the influence of either drugs or folk remedies.
Indeed, external treatment can temporarily relieve the inflammatory reaction. However, there may also be danger here, since medicinal components, after penetrating into the opening of the cyst, can lead to the spread of the inflammatory process even deeper and cause a subcutaneous abscess. The only effective treatment is to remove the formation along with its own capsule to prevent relapse. [5,8]
Conservative therapy is prescribed only at the stage of preparation for surgery to relieve inflammation. For this purpose, antibacterial and disinfectants are prescribed, as well as drugs that stop the active production of sebaceous secretions.
In advanced cases, when complications develop (inflammation, infection), emergency surgical intervention is required. In this case, the formation is not removed, but only cleaned. Complete excision is carried out after healing (approximately three months later). [10,11]
Surgical excision
The classic method of removing atheroma involves excision of the formation through an incision in the skin. Typically used to remove large formations. The main advantage of surgical excision is the almost zero chance of recurrence. The disadvantages include the formation of a small scar and scar.
Low-traumatic methods
A sebaceous cyst can also be removed using low-traumatic methods. The most common methods are:
- radio wave method;
- laser removal;
- electrocoagulation;
- cryodestruction (using liquid nitrogen).
The use of such techniques is possible only in the case of small tumors. Their main advantage is the absence of a postoperative scar and a good cosmetic result. Although a small scar is left immediately in the area of the incision, it disappears over time. That is why experts give preference to low-traumatic manipulations, especially when localizing the formation in open areas of the body, for example, on the face.
Another distinctive feature is simple rehabilitation. The recovery period does not require strict restrictions and boils down to regular antiseptic wound treatments and dressings. Sutures are removed approximately one week after surgery. On average, after two weeks the wound is completely healed.
Laser removal
The technique is used when the tumor is located close to the surface of the skin. The essence of the procedure is the impact of an intense, narrowly directed laser beam, which destroys the tumor along with its contents. The beam has a targeted effect without affecting nearby tissues.
The procedure is performed under local anesthesia and is not accompanied by pain. During the manipulation, blood vessels are cauterized, so the risk of bleeding, infection and scar formation is virtually eliminated.
Disadvantages include limitations in the use of manipulation. Laser excision is not possible in the case of cysts of large size. Hyperpigmentation at the site of laser beam exposure is also a contraindication.
Radio wave removal
The procedure is carried out using a radio wave knife. The specialist uses a scalpel to push the tissue apart and remove the cyst without significant damage to nearby structures. Tumor removal is performed in one session. There are no scars left on the skin.
In some cases, radio wave removal is most convenient. For example, this applies to cases where a lump appears on the scalp, since there is no need to shave off the hair.
Cryodestruction
The essence of the manipulation is that low-temperature nitrogen freezes the blood vessels that feed the tumor. As a result, the pathological cells die.
The duration of exposure and the need for repeated procedures depends on the size of the tumor formation. Like the other above-mentioned techniques, cryodestruction does not leave scars, but has a longer recovery period.
Is it necessary to remove atheroma if it is harmless?
- All atheromas are continuously growing
. And in some cases - extremely quickly. If the atheroma is not removed on time (that is, as early as possible), it becomes larger and larger, sometimes reaching gigantic proportions! Medicine knows of atheromas the size of a child’s head.
- As the atheroma grows, it becomes visible to the naked eye. And if atheroma on the body can be hidden for a long time under clothing, ugly bumps on the face and head arouse the morbid curiosity of others.
- The contents of atheroma often leak out, ruin clothes and have an extremely unpleasant odor that cannot be masked.
- Atheroma is a chronic inflammatory lesion that has negative health consequences. Do you often get colds, get tired, want to sleep, and find it difficult to stand 8 hours at work? All these symptoms are her work.
- The larger the atheroma reaches, the wider the incision is required to remove it. The more difficult it is to hide the scar and skin sagging.
- The contents of atheroma are sebum. This is a delicious delicacy for bacteria. Accumulating sebum, atheroma grows and gradually turns into a time bomb. Infection in the atheroma guarantees the development of purulent inflammation
.
Removing pus from the atheroma will require a large incision, which will leave behind a scar. But greater operational access to atheroma is not the only consequence of suppuration. Such an area rarely heals beautifully, and a painful keloid scar often forms in place of the inflamed atheroma.
The Platinental Clinic offers all the most modern methods for removing atheromas:
- without pain,
- without seams,
- replenishment of tissue volume after removal of atheroma,
- numerous techniques for forming invisible scars.
You can make an appointment with a surgeon online or by phone.
Postoperative period
Depending on the size of the formation, whether it was suppurating, you can predict whether a scar will remain at the site of the atheroma or not.
The wound is dressed twice during the day:
- In the morning, sanitation is performed with hydrogen peroxide, the wound is covered with a plaster;
- In the evening, after treatment with peroxide, Levomekol ointment is applied.
After the wound healing process has begun and its edges have been glued together, you can stop using the patch by using BF-6 medical glue. The use of plaster and medical glue at the site of surgical sutures is not carried out until they are removed. The above technique is the standard for postoperative wound management. In situations with various deviations from the norm, the surgeon establishes an individual procedure for treatment.
In 3% of cases, relapse of atheroma is diagnosed due to incomplete enucleation of the cyst membrane. Most often this occurs when removing a festering formation.
Cost of the operation
Destruction of atheroma in the usual way using a scalpel will cost the patient about 1,500 rubles. More complex procedures using a laser or radio wave knife will cost 5 thousand rubles and more.
Author of the article:
Volkov Dmitry Sergeevich |
Ph.D. surgeon, phlebologist Education: Moscow State Medical and Dental University (1996). In 2003, he received a diploma from the educational and scientific medical center for the administration of the President of the Russian Federation. Our authors