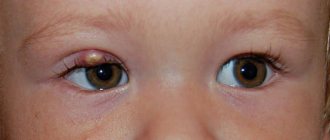
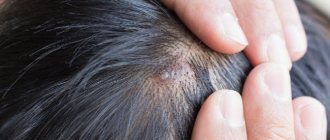
A furuncle is a purulent inflammation of the hair follicle (follicle) involving the sebaceous gland and surrounding tissues in the inflammatory process. If inflammation affects several follicles at once, a carbuncle
– extensive and rapidly developing inflammation, a disease more dangerous than a boil.
If several boils occur simultaneously (in different parts of the body), they speak of furunculosis
.
The popular name for a boil is also widely known - boil .
Symptoms of the disease
The formation of a boil manifests itself as follows:
- a small raised cone-shaped nodule above the skin;
- change in skin tone over the tubercle to red-violet;
- increased pain in the inflamed area;
- swelling of surrounding tissues;
- the formation of a white dot in the center of the painful area;
- opening of an abscess;
- discharge of necrotic hair follicle and purulent masses.
To establish a diagnosis and treatment, you should contact a surgeon.
Important Tips
When treating boils, several important rules should be followed to help speed up recovery and prevent complications:
- It is prohibited to squeeze out boils yourself - this is a huge risk of spreading infection and dangerous consequences;
- Water procedures should be excluded until complete recovery; going to the bathhouse can be forgotten until better times; even a shower is not recommended.
It is impossible to get boils wet so as not to complicate the treatment process. The only acceptable hygienic procedure is wiping healthy skin with antiseptics and baths with potassium permanganate; - to strengthen the immune system, immunomodulators are used - Interferon, Polyoxidonium, Galavit;
- The spots on the skin or bumps remaining after the boil has healed do not require special treatment; they heal over time without leaving marks.
Scars can be removed surgically or through therapy with special ointments and creams - Contractubex, Kelofibrase, Dermatix.
Complications of a boil
The disease may seem quite safe, but this is not so - a boil can cause complications that pose a serious threat to human health:
- furunculosis;
- phlegmon;
- erysipelas;
- carbuncle;
- lymphadenitis;
- inflammation of the veins;
- cutaneous lymphatic nocardiosis;
- inflammation of the vagina and uterus - formed in women from boils on the genitals;
- meningitis;
- accumulation of pus in the brain matter;
- abscesses in various tissues and internal organs;
- sepsis.
ICD-10 code
WHO (World Health Organization) has developed a generally accepted international classification of diseases, according to which medical diagnoses are coded in a certain way. Today the classification of the 10th revision is in effect.
The boil has its own ICD-10 code - L02, which also includes skin abscess and carbuncle.
Furunculosis, abscess and carbuncle of the face are listed under code L02.0, neck - L02.1, torso - L02.2, buttocks - L02.3, limbs - L02.4, other locations (including the head, except the face) – L02.8.
Boils of unspecified localization are designated with code L02.9.
General characteristics of the disease
Furuncle is a common disease - about 17% of dermatological patients are observed with it. Currently, an intensive increase in patients with the presence of boils in the nose and nasal cavity has been recorded. This significantly increases the likelihood of developing a chronic pathology – idiopathic non-allergic rhinitis.
The disease is common among adults, but boils can also appear in children. Men are susceptible to this disease more often than women. An increase in the incidence of furunculosis is observed during periods of vitamin deficiency - in autumn and spring.
Psychosomatics
Psychosomatics explains the occurrence of many diseases by mental causes, that is, the characteristics of each person’s psyche, his emotions, ideas about the world around him and about himself. Every disease has its own cause.
According to the psychosomatics of furunculosis, favorable emotions for its occurrence are fear, anxiety, anger and irritation.
Psychologist Louise Hay, author of popular books, has compiled a table showing the probable psychological causes of illness. According to her, boils arise due to negative emotions - confusion and anger.
To heal, you need to get rid of mental problems and the burden of negative experiences.
The causative agent of the boil
The formation of a boil is mainly due to the penetration of Staphylococcus aureus into the hair follicle. These bacteria can normally be found on the skin and are not dangerous. However, when introduced into the hair follicle, an inflammatory process begins.
The disease begins to develop with reduced immune activity. When the immune system is unable to fully prevent the spread and growth of pathogenic microorganisms, they begin to rapidly multiply and penetrate the pores. This leads to deterioration of the skin microflora and the formation of abscesses.
Diagnostics
It is easy to detect a tumor in the head area. The specialist carries out an external examination and, when it is necessary to make a diagnosis, other diagnostic measures of the damaged area.
To determine the provoking factors in the formation of such a pathological process, a specialist carries out urine and blood tests, and diagnostics to detect failures of organs and systems.
Sometimes the examination requires consultation with a specialist.
If there are difficulties with the maturation of the rod, a specialist may prescribe a blood culture test. Such research is required to prevent plasma contamination in time.
Prerequisites for development
It has been found that in the presence of certain skin characteristics or in the absence of proper care for it, the risk of the formation of boils increases significantly. People with these characteristics should monitor their health more closely and improve their immunity. The main factors that contribute to the formation of boils include the following:
- Increased sweating. Sweat contains aggressive salts that negatively affect microflora. The protective qualities of the skin are reduced, thereby creating an optimal environment for the causative agent of the disease.
- Presence of skin diseases or damage to the skin. Various cracks and rashes are excellent starting points for infection, thanks to which the pathogen is able to bypass several levels of defense in the body.
- Irritated skin due to regular discharge from the ears or nose due to chronic illnesses. The constant presence of pathogens on the skin leads to a decrease in its protective properties.
- Constant scratches, cuts and abrasions. Bacteria from the genus Staphylococcus can easily penetrate the hair follicles through various damage to the skin, which leads to the development of the disease.
- Use of low quality skin cosmetics.
- Lack of personal hygiene. On uncleaned skin, frequent friction causes irritation, which is an excellent conductor for the causative agent of the boil.
- Disruption of the natural microflora of the skin due to regular exposure to irritants due to certain activities. Dust and lubricants are particularly hazardous.
If these features are present, it is necessary to carefully monitor the condition of the skin. It is very important to properly care for the skin, and in case of damage, immediately treat it with antiseptic agents and protect it with a bandage or plaster. If a boil has formed, it is recommended to consult a doctor.
Prevention
A boil in the head area appears as a result of neglect of hygiene rules. Their observance is required in order to maintain health. These include:
- Strengthening the immune system : consuming plenty of vitamins. Implementation of hardening in the shower, giving up bad habits (alcohol and smoking).
- Adjusting your own diet . Healthy food products: vegetables, fruits. Flour and smoked foods are limited.
- Purchasing cosmetic and hygiene products of proper quality.
Compliance with the above instructions helps prevent a large number of diseases.
A boil on the head is an unpleasant pathological process that causes significant discomfort to the patient. If the disease is treated promptly and correctly, the problem will be quickly resolved. With constant observance of preventive measures, suppuration appears much less frequently.
Reasons for the formation of boils
The main reasons for the formation of boils include decreased immunity or hormonal imbalance in the body. In accordance with the specific cause, a treatment plan is prescribed - with or without hormonal agents.
In a healthy body, the immune system serves as an insurmountable obstacle to the causative agent of abscesses and is able to resist dangerous bacteria, preventing them from entering the tissues and hair follicles from the surface of the skin. After a decrease in the body’s protective functions, the immune system ceases to intensively fight pathogens, and often completely stops perceiving them as a threat and makes no attempt to destroy Staphylococcus aureus. This behavior of the body is observed after a recent viral infection, which seriously affected the immune system. Long-term use of psychotropic drugs, local hypothermia or hypothermia also cause a decrease in immunity.
If the appearance of a boil is associated with hormones, then it is often related to complications of diabetes. When blood circulation is impaired, tissues do not receive sufficient nutrition, which leads to a decrease in the protective activity of the skin. As a result, the causative agent of the disease can easily enter the hair follicle and start the inflammatory process.
Under the professional supervision of a doctor, a boil can be completely cured.
Furunculosis
Furunculosis is an infectious disease characterized by the appearance of several boils at the same time (acute furunculosis) or the appearance of one boil after another (chronic furunculosis). With chronic furunculosis, the presence of boils at different stages of development is noted. Furunculosis can be limited or widespread. The disease lasts a long time - months and even years. Furunculosis often affects people with reduced immunity and those suffering from diabetes. During treatment, tolerance to the therapy with antibacterial drugs is noted.
Furunculosis complicates the course of many skin diseases.
Causes of furunculosis
The main cause of furunculosis is Staphylococcus aureus. It causes disease in 60 - 97% of patients. In other cases, the cause of the disease is epidermal staphylococci, group A and B streptococci and other types of bacteria.
Recently, more and more staphylococci resistant to a number of antibiotics have been sown from lesions, about 90% of which are staphylococci resistant to penicillin and ampicillin, about 19% to erythromycin.
Risk factors for the development of furunculosis:
- The presence of foci of chronic infection in patients with furunculosis is recorded in 75 - 90% of cases. The most common pathologies are the ENT organs (tonsillitis, sinusitis and pharyngitis) and the gastrointestinal tract (chronic gastroduodenitis and cholecystitis). Dysbacteriosis contributes to the development of furunculosis.
- In 40% of cases, diseases of the thyroid gland, gonads and diabetes mellitus are registered in patients with furunculosis.
- Consumption of large amounts of carbohydrates and diabetes mellitus contribute to the development of furunculosis. An increased amount of sugar in the blood is a good breeding ground for staphylococci.
- In 39% of cases, the patient’s body is sensitized to different types of allergens.
- The development of furunculosis is caused by disturbances in carbohydrate, fat and protein metabolism, as well as by hypo- and avitaminosis. Furunculosis often occurs in weakened, exhausted patients suffering from severe somatic pathology. Anemia, chronic diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, immunodeficiency conditions (HIV infection and oncology) are the main ones.
- Constant physical activity and mental stress contribute to the development of furunculosis.
The presence of Staphylococcus aureus on the skin and weakened immunity are the main factors in the development of furunculosis.
Immune status disorders in furunculosis
The human immune system is designed to protect the body when in contact with infectious agents. The causative agents of furunculosis cause a whole “cascade” of protective reactions, most of which are disrupted during the disease.
- Up to 70% of patients with chronic furunculosis have impaired phagocytosis (capture, absorption and destruction of pathogenic microorganisms).
- A low level of iron in the blood serum causes a decrease in the processes of killing (destruction) of pathogenic microorganisms.
- In the blood of 43% of patients with chronic furunculosis, a decrease in the level of T and B lymphocytes is recorded.
- In the blood of 60% of patients with chronic furunculosis, there is a decrease in the level of immunoglobulins (IgG and IgM).
Severity of furunculosis
Mild severity of furunculosis is characterized by the presence of single boils. The inflammatory reaction is moderate. Relapses occur 1-2 times a year. There are no signs of intoxication. Peripheral lymph nodes enlarge during exacerbations. Indicators of immune status in this category of patients in 70% of cases remain within normal limits.
The average severity of furunculosis is characterized by the presence of single large boils or multiple boils. The inflammatory reaction proceeds rapidly. Relapses occur up to 3 times a year. During exacerbations, inflammation of the lymphatic vessels and lymph nodes is noted. Often the disease occurs with symptoms of intoxication. Violations of the cellular and humoral immunity are noted.
Severe severity of the disease is characterized by the presence of multiple boils with a continuously relapsing course. Furunculosis is accompanied by severe intoxication. Patients experience weakness, malaise, headache, elevated body temperature and sweating. Violations of the cellular and humoral immunity are significant.
Rice. 32 and 32.1. The photo shows furunculosis.
Complications of furunculosis
The penetration of bacteria into the blood causes bacteremia, which is a serious complication of furunculosis. Bacteria settle in the internal organs, causing endocarditis, osteomyelitis, pneumonia, meningitis, kidney inflammation, etc. Septic shock often ends in the death of the patient.
Differential diagnosis of furunculosis
To prescribe adequate treatment for furunculosis, the method of differential diagnosis should be used with diseases such as pseudofurunculosis, hidradenitis, anthrax and carbuncle.
Rice. 33 and 34. The photo shows furunculosis. On the skin of the abdomen and buttocks there are boils at different stages of development.
Stages of boil development
This disease has three stages of development. Please note: you should consult a doctor at the initial stage of boil formation.
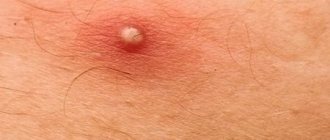
- Infiltration stage, i.e. accumulation of fluid in tissues. At this stage, the abscess is just beginning to form. The infiltrate is concentrated near the hair follicle, where the staphylococcus has entered. Swelling and hardening of tissues occurs. The size of the reddened area of inflammation is 1-3 cm in diameter. Often the patient complains of a tingling sensation at the site of inflammation, which becomes stronger when touched. At first the pain is not strong, but gradually becomes more pronounced.
- Stage of purulent-necrotic process. It begins on the third or fourth day from the moment of inflammation. In the middle of the boil, a core is formed, consisting of dead cells and thick purulent masses. From above, the rod appears above the skin and looks like a white abscess. When the tension of the skin over the rod becomes too intense, it diverges and purulent accumulations come out, then the furuncle cavity is completely cleared.
- Healing stage. After the wound heals, there will be no scar left from a small boil. After a large boil, there is a slight even scar, which should disappear over time.
Complications of the disease often develop at the second stage, when problems arise with the release of purulent-necrotic fluid. An attempt to remove a boil by squeezing can also have serious consequences.
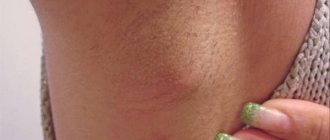
What it looks like: photos from the back and front
A furuncle differs from a regular pimple in the large area of the affected area, severe redness of the skin around the pus, and is accompanied by painful sensations. The suppuration can grow to a lump the size of a walnut - a purulent core is located inside the formation.
Most often it appears on the back and where clothes come into most contact with the skin - at the back of the neck, mainly in the lower hair growth zone (it is in this place that clothes come into most contact with the skin, which also sweats a lot). Sometimes boils also appear on the front of the neck.
Pay attention to the photo of purulent inflammation at the initial stage:
Also, the occurrence of a boil can be accompanied by a general malaise - it is important to identify dangerous suppuration in time and begin its treatment in time.
Methods for treating boils
There are two treatment methods: drug therapy and surgery. Specific tactics depend on the stage and severity of the disease.
Drug therapy
Treatment with various medications is suitable if you seek help in a timely manner. Local therapy is generally required; broad-spectrum antibiotics are used in rare cases.
At the first stage of the disease, the inflamed area is cauterized with a pharmaceutical solution of iodine several times a day and dry heat is applied to it. The use of compresses is strictly prohibited, as this can lead to a severe deterioration in the patient's condition.
When the formation of the boil core begins, to speed up the process, bandages with ichthyol ointment should be applied to the abscess. This medicine helps to draw out purulent masses and reduce the duration of tissue restoration in the future. It is necessary to treat a boil with medication after mandatory consultation with a doctor.
During the healing stage, bandages with ointments containing an antibiotic are applied to the inflamed area, as well as drugs that significantly accelerate the tissue healing process. In case of severe suppuration of the boil, immediately after the rod comes out, a special drainage can be placed and the recesses can be washed with antiseptic agents.
It is impossible to cure the disease entirely and for a long period with the help of folk remedies.
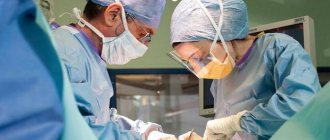
Surgery
Removal of a boil by surgical intervention is permissible only in advanced cases: when there is already an abscess or there is a high probability of developing complications of the disease. The method helps to immediately improve the patient's condition. In such a situation, it is important to remove the purulent-necrotic core of the boil as soon as possible and carry out antiseptic treatment of the tissue. All actions are carried out under local anesthesia, often on an outpatient basis. Hospitalization is only necessary for a large abscess or serious subcutaneous abscess that requires regular medical monitoring.
Which doctor should I contact if nothing helps or the boil cannot be treated?
Sometimes self-treatment can be dangerous to a person’s life and health.
If the inflamed boil does not decrease after several days of treatment or causes severe discomfort, the body temperature is elevated, and the lymph nodes are inflamed, you should urgently seek help from a doctor. A qualified surgeon or dermatologist (at least a therapist, if there are no other specialists in the clinic) will tell you how to treat suppuration and determine whether surgical intervention (cleaning the abscess) with antibiotic therapy is required.
Sources
- Shallcross, Laura J et al. “Incidence and recurrence of boils and abscesses within the first year: a cohort study in UK primary care.” The British journal of general practice: the journal of the Royal College of General Practitioners vol. 65.639 (2015).
- Clinical protocol for diagnosis and treatment of “skin abscess, boil and carbuncle of other localizations” Expert Council of the Republican State Enterprise at the Republican Center for Healthcare Development of the Ministry of Health and Social Development of the Republic of Kazakhstan dated December 12, 2014 protocol No. 9.
- Boils and carbuncles. Mayo Clinic.
- Federal clinical guidelines for the management of patients with pyoderma. Russian Society of Dermatovenereologists and Cosmetologists, 2015.