Surgeon
Bohyan
Tigran Surenovich
Experience 37 years
Surgeon of the highest category, Doctor of Medical Sciences, member of the International Association of Surgeons, Gastroenterologists and Oncologists
Make an appointment
An abscess is an accumulation of purulent contents in various tissues. Purulent inflammation is usually caused by a bacterial infection. In this case, in the process of melting the tissue, a cavity is formed. The occurrence of an abscess is caused by bacteria entering the tissue from the outside - through abrasions and injuries or from other infected tissues and organs. This disease differs from other similar diseases in the formation of a capsule that prevents the spread of inflammation.
Based on the location of the pus, there are superficial accumulations in the subcutaneous fatty area and deep ones inside organs and deep tissues. Depending on the method of penetration of pathogenic microorganisms, there are exogenous accumulations (from the external environment) and endogenous (migration within the body of one person).
Symptoms and signs
Regardless of the location of the purulent accumulation, the symptoms of an abscess are the same:
- intoxication – fever, chills, weakness, malaise, nausea, vomiting, poor appetite, muscle and joint pain, headaches;
- superficial location - redness and swelling of the skin directly above the site of accumulation, pain on palpation or during movement;
- disruption of the functioning of the damaged organ or related tissues.
A chronic abscess does not have symptoms of an acute inflammatory process. Deeply located accumulations have only general signs of intoxication and are detected by instrumental diagnostics. The most common locations of an abscess are:
- inside the bones - the main symptom is pain from physical activity or when the weather changes;
- Lung abscess is manifested by shortness of breath and weak breathing. A lung abscess is often confused with pneumonia;
- in the abdominal cavity and liver is accompanied by signs of any disease of this organ;
- in the brain causes seizures and loss of coordination;
- prostate abscess causes pain when urinating;
- a throat abscess causes cough spasms and pain;
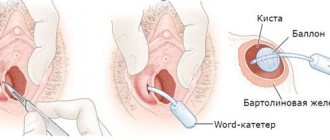
- Bartholin gland abscess and others.
Cold occurs without signs of intoxication and appears in immunodeficiencies. Natechny eliminates the presence of an inflammatory process in tissues. Acute abscess has more pronounced symptoms compared to other forms.
Are you experiencing symptoms of an abscess?
Only a doctor can accurately diagnose the disease. Don't delay your consultation - call
How is an abscess treated?
You should carefully remove all hair from the inflamed area and treat it with an antiseptic.
To accelerate the removal of the rod, Ichthyol and Fukortsin ointments are used. However, they are effective only in the initial stages of inflammation.
Ichthyol ointment for accelerated removal of pus core
An abscess should not be treated on your own; this should be done by a specialist.
An advanced disease will lead to very serious consequences, including fatal blood poisoning.
In a hospital setting, the patient is given antibiotics and painkillers, and a bandage with sodium salicylic is applied. This treatment stimulates the rejection of pus and accelerates the regeneration process.
After a wound appears at the site of the abscess, it is necessary to treat it with an antiseptic and apply a bandage with Levosin. During treatment, it is forbidden to engage in sports or physical work, as this increases sweating.
Causes of occurrence and development
The main cause of an abscess is a bacterial infection that has entered the tissue from the outside world. Bacteria enter the body due to microtraumas that violate the integrity of the skin. Such injuries include cuts and minor abrasions/scratches/damage received during shaving or hair cutting, manicure or pedicure, and others. At the same time, if dirt or small particles in the form of a splinter get in, the likelihood of a purulent accumulation increases.
The occurrence of an accumulation of pus can occur for other reasons for an abscess:
- migration of infection from the primary source of infection;
- festering hematomas and cysts;
- surgical manipulations – violation of sanitary rules in the form of unsterile instruments;
- disturbances during the administration of drugs and preparations, for example, disturbances in concentration during vaccinations.
The abscess develops further under the influence of reduced immunity or poor circulation in the area of the abscess.
Publications in the media
Furuncle - acute purulent-necrotic inflammation of the hair follicle and surrounding soft tissues •
Furunculosis is multiple lesions with boils that appear simultaneously or sequentially one after another in different parts of the body. Most often, boils are localized in areas of the skin exposed to contamination (forearms, back of the hand) and friction (back of the neck, lower back, gluteal region, thighs).
Etiology . Golden, less often white staphylococcus.
Risk factors • Skin contamination and microtraumas • General exhaustion • Chronic diseases • Vitamin deficiencies • Diabetes.
Pathomorphology • Stage of serous infiltrate - cone-shaped infiltrate with regional hyperemia up to 1-1.5 cm in diameter • Purulent-necrotic stage - appearance of a purulent pustule at the apex • Stage of rejection of the necrotic core and healing.
Clinical picture
• During the formation of a pustule in the form of a nodule - slight itching and tingling • On days 1–2, an inflammatory infiltrate appears, protruding cone-shaped above the level of the skin, which turns red and becomes painful when touched • At the top of the infiltrate, a small accumulation of pus with a black dot appears (necrosis) in the center • The pustule usually breaks through and dries up, and on days 3–7 the infiltrate purulently melts and the necrotic tissue in the form of a rod, together with the remains of the hair, is excreted with pus • The resulting wound is cleaned, filled with granulation tissue and heals. The swelling around it gradually decreases, the pain disappears. A small, whitish, somewhat retracted scar remains at the site of inflammation.
• When the boil is localized in the external auditory canal, severe pain occurs in the nose • In the facial area (lips, forehead), as well as on the scrotum, boils are accompanied by significant swelling of the surrounding tissues
• A severe clinical course is typical for boils of the upper lip, nasolabial fold, nose, and periorbital region. Thrombophlebitis of the veins with a facial boil can spread through anastomoses to the venous sinuses of the dura mater, which leads to their thrombosis, creating a threat of the development of purulent basal meningitis. Facial swelling quickly increases, dense, painful veins are palpated, the patient’s general condition sharply worsens, body temperature reaches high values (40–41 °C), neck rigidity and blurred vision may be expressed.
Laboratory research . Leukocytosis with a shift in the leukocyte formula to the left, an increase in ESR.
TREATMENT
Management tactics • Patients with severe systemic inflammatory response syndrome, when boils are localized in the nasolabial triangle, and in the presence of severe concomitant diseases (DM, tumors) are subject to hospitalization.
Conservative treatment • Thorough cleansing of the skin around the source of inflammation •• 70% ethyl alcohol •• 2% salicylic alcohol •• 0.5–1% alcohol solution of brilliant green •• In the formative stage - 5% alcohol solution of iodine • Antibacterial therapy, first empirical, and then taking into account the data of bacteriological research •• oxacillin •• cefazolin • NSAIDs • Physiotherapeutic treatment: UHF, ultraviolet radiation • Detoxification therapy, immunomodulators (if necessary).
Surgery . _ Opening the boil with removal of the necrotic core.
Complications • Lymphangiitis • Regional lymphadenitis • Carbuncle • Acute thrombophlebitis • Sepsis, often develops with facial boils, due to attempts to squeeze out the contents, cutting it off while shaving.
Prevention • Compliance with personal hygiene requirements • Preventing clothing from rubbing areas of the skin where a boil may form.
Course and prognosis • With timely and correct treatment, the prognosis is favorable • In exhausted, weakened patients, if complications occur, the prognosis is serious.
ICD-10 • L02 Skin abscess, boil and carbuncle
Forms of the disease and routes of infection
An abscess can be an independent disease, but in the vast majority of cases it appears as a complication of an underlying disease, for example, purulent tonsillitis causes a peritonsillar abscess. Pathogenic microorganisms have a lot of ways to get inside - through damage to the skin as a result of injuries and cuts, from other organs and tissues that were previously infected, through non-sterile equipment during surgical procedures, and others.
Forms of the disease are classified according to the location of purulent accumulation:
- retropharyngeal abscess;
- peripharyngeal;
- peritonsillar abscess;
- subdiaphragmatic;
- soft tissues;
- periodontal;
- appendicular and others.
What causes ulcers on a child’s bottom?
Abscesses in children occur due to the penetration of Staphylococcus aureus through injured skin into the body. Babies often get injured, damaged areas need to be treated with antiseptics. Against the background of decreased immunity, opportunistic microflora is activated, and as a result of the vital activity of microorganisms, an infiltrate of the gluteal region is formed.
The cause of an abscess is untreated infectious diseases that undermine the child’s immunity. Violation of the technique of drug administration can lead to the formation of an abscess.
Children have a high risk of pathology developing into phlegmon. Examination of the attribute, therapy at an early stage acts as a prevention of dangerous complications.
Complications
In the absence of timely and adequate treatment, complications of abscesses are very dangerous for the life and health of the patient:
- phlegmon;
- neuritis;
- osteomelitis;
- internal bleeding of the walls of blood vessels;
- peritonitis,
- sepsis as a result of purulent abscess of the appendicular region;
- purulent meningitis and others.
Contacting the clinic
A purulent accumulation is fraught with dangerous consequences, therefore, if the slightest sign of the presence of an accumulation of pus in tissues or organs appears, you should immediately consult a doctor. The ideal solution would be to call an ambulance.
At (academician Roitberg’s clinic) you will receive the necessary assistance in treatment. In addition, JSC “Medicine” (academician Roitberg’s clinic) has the ability to accommodate patients in a 24-hour hospital and has the function of calling a doctor at home around the clock.
Ways of spread of purulent processes in the gluteal region
Ways of distribution of the substance in the interfascial spaces if the abscess breaks through with the formation of phlegmon:
- The surface of the thigh suffers when the tissue surrounding the sciatic nerve is involved in the pathological process.
- Purulent contents can flow into the pelvis and anus.
- As phlegmon develops, the underlying layers of tissue melt.
Need advice from an experienced doctor?
Get a doctor's consultation online. Ask your question right now.
Ask a free question
Good blood supply to the soft tissues and numerous ways of spreading pus into the internal organs cause the development of sepsis.
Diagnostics
Purulent accumulations located near the surface of the skin are easily diagnosed during an external examination based on characteristic signs. A throat abscess is detected during examination by an otolaryngologist.
Diagnosis of an abscess located deep inside requires special laboratory and instrumental studies:
- a biochemical blood test will show the inflammatory process in the body with an increased content of leukocytes and ESR, as well as shifts in protein fractions;
- radiography is used to detect subdiaphragmatic, intraosseous and pulmonary collections;
- Ultrasound is aimed at identifying accumulations in the abdominal cavity and liver;
- computed tomography, as an auxiliary method, detects purulent accumulations in the brain, lungs and liver, subdiaphragmatic region and inside bones and joints;
- encephalography of various forms (echo-, electro-, pneumo-) is aimed at studying the brain;
- laparoscopy and angihepatography are used as an auxiliary method for examining the liver;
- puncture of the abscess and culture of its contents are performed to determine the specific type of pathogen and its sensitivity to certain antibacterial drugs.
Most often, purulent accumulations are caused by streptococci, staphylococci in combination with various kinds of bacilli, but now other aerobic and anaerobic bacteria are also becoming widespread.
Causes of abscess
The causative agents of the inflammatory process can live on the skin for years without causing any problems until they find conditions favorable for active reproduction.
Provoking factors include:
- failure to comply with personal hygiene rules;
- skin damage (scratches, cuts, cracks);
- weak immunity;
- unbalanced diet;
- avitaminosis;
- diabetes;
- hormonal imbalances;
- hypothermia.
Treatment
The key to successful treatment of an abscess lies in its timely detection. This is why it is so important to immediately consult a doctor if you have any symptoms.
Treatment principles:
- Only superficial purulent accumulations can be treated at home under the supervision of a doctor. All other cases require hospitalization;
- opening and drainage of the area of purulent accumulation is carried out by a surgeon; it is necessary to remove the abscess;
- drug therapy is based on taking the following drugs: antibacterial agents, antipyretics, painkillers, drugs to reduce intoxication, vitamin complexes, immunomodulators and others;
- balanced nutrition, gentle bed or semi-bed rest, and rest;
- physical therapy, physiotherapy and sanatorium-resort treatment are possible as rehabilitation measures during the recovery stage.
Special ointments are used as adjuncts in the treatment of subcutaneous fatty suppuration.
Purulent accumulations in the lungs are initially treated with broad-spectrum antibiotics, and after receiving the results of culture culture studies, adjustments are made to the medications taken. In severe cases, bronchoalveolar lavage may be performed. If there is no positive effect of classical therapy, an abscess operation is forced to remove the affected part of the organ.
Treatment of purulent accumulations in the brain is carried out using surgical methods. Contraindications for removal of accumulations, namely the location in the deep parts of the brain, necessitates washing out the purulent contents by puncture. Treatment of purulent accumulations at home using traditional medicine is unacceptable.