The article was prepared by a specialist for informational purposes only. We urge you not to self-medicate. When the first symptoms appear, consult a doctor.
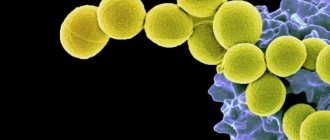
Staphylococcus is a bacterium that can be either opportunistic for the human body or pathogenic. That is, in the first case, the bacterium simply exists on the skin or mucous membranes without causing disease, and in the second it leads to the development of an inflammatory process. The most dangerous type of bacteria is Staphylococcus aureus.
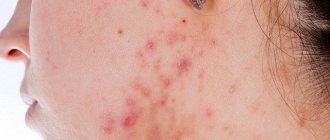
The disease can affect the skin, causing purulent inflammatory processes, which are the body's response to the introduction of a foreign agent. Such facial skin diseases are called pyoderma. The sebaceous and sweat glands of the face, as well as the hair follicles located on it, can be affected.
According to statistics, almost a third of all pyoderma are primary, that is, they develop as a result of infection with staphylococcus, and not against the background of pre-existing diseases.
What it is
Staphylococcus aureus (lat. Staphylococcus aureus) is a bacterium that looks like a small ball. Approximately 2 out of 10 people are carriers of this infection. It can be in the nose, throat, genitals, or skin.
Enters the body by contact and airborne droplets. You can become infected in places where large numbers of people gather.
The main problem is that the bacterium produces a special toxin that poisons skin cells.
A completely healthy person has a powerful immune system that protects him from pathogenic bacteria. But when it weakens due to certain factors, a person can easily become infected with it.
Who is at risk for staph and acne?
- Nurses, doctors, patients with diabetes, and hemodialysis patients are particularly at risk;
- Newborns;
- Women who are breastfeeding;
- Obese people;
- People living in crowded communities or hot climates;
- Gymnasts sharing exercise equipment, people going to the gym;
- Persons with skin injuries, surgical wounds, piercings and fresh tattoos;
- People with atopic dermatitis or seborrhea, a compromised immune system, cancer, diabetes, blood or lung diseases, including those treated with steroids or chemotherapy
- People prone to the appearance and rapid development of acne, which can develop into a more severe form of acne under the influence of staphylococcus, are especially at risk.
How to quickly remove and relieve acne inflammation overnight on the face and body?
Causes
The main reasons for how it is transmitted:
- deterioration of the body's protective properties due to frequent stressful situations, vitamin deficiency, use of antibiotics, side effects from certain medications;
- incorrect compliance with sanitary standards in the presence of open wounds on the body;
- eating vegetables and fruits that have been poorly processed;
- presence of chronic diseases.
The main problem with contracting this infection is that it is very difficult to treat.
Where can you get infected with Staphylococcus aureus?
Very often, this infection can be contracted from person to person in a hospital. Staphylococcus aureus enters the body both by eating food and by airborne droplets.
Infection occurs primarily through the skin, digestive tract, and respiratory tract. Bacteria spread throughout the body along with the bloodstream and affect other vital organs, such as the lungs, bones, heart, and brain.
Factors that provoke the disease
Unfortunately, not a single person has a chance to avoid the occurrence of Staphylococcus aureus. The problem also lies in the fact that microorganisms are capable of producing a special enzyme called coagulase. It is he who helps protect staphylococcus from the body's natural defenses.
There are several factors that significantly increase the chance of becoming infected with Staphylococcus aureus:
- drug use by injection;
- the presence of chronic diseases, including diabetes mellitus, circulatory disorders;
- weakened immunity in young children and older adults;
- use of medications that must be used intravenously;
- visiting places with large crowds of people (for example, a beauty salon, hospital, subway).
Causes of staphylococcal infection
The main reason for the development of the disease is a decrease in immunity due to stress, illness, poor diet, vitamin deficiency or taking medications. A decrease in immunity, including seasonal ones, can provoke the proliferation of bacteria and subsequent infection.
There are other reasons:
- failure to follow doctor's recommendations when caring for wounds, abrasions and injuries;
- close interaction with a carrier of the infection, for example, with a family member suffering from a sore throat;
- eating poorly processed food - bacteria can be transmitted through food.
Infants become infected due to pathologies during pregnancy and childbirth, for example, a long anhydrous period, prematurity, and poor hygiene.
Due to the nature of its modes of transmission, staphylococcal bacteremia is relatively easy to prevent by observing basic hygiene requirements, not interacting with other people's personal belongings, following doctor's recommendations and, if possible, avoiding close contact with infected people.
Staphylococcus aureus infection routes
The bacterium in question lives on the surface of the epidermis, mucous membranes, household items, medical equipment and even food. At the same time, Staphylococcus aureus is not always dangerous; the reasons for its active reproduction and toxic effect on the skin are a decrease in the activity of the immune system. A healthy person will not become infected with anything upon contact with a microbe.
Routes of transmission of the bacterium:
- airborne;
- direct contact with the carrier;
- consuming contaminated food or drinks;
- wounds, cuts, scratches;
- medical manipulations.
Staphylococcus aureus and acne
Staphylococcus aureus, which can accompany acne, is the most dangerous of all the common staph bacteria.
These bacteria are spread by direct contact with an infected person, using a contaminated object, or by inhaling infected droplets dispersed by a sneeze or cough.
Skin infections are common, and bacteria can spread through the blood and infect distant organs.
In addition to acne, a Staphylococcus aureus infection on the skin can cause blisters, abscesses, redness and swelling in the infected area.
Diagnosis is based on the appearance of skin or identification of bacteria in a sample of contaminated material.
Thorough hand washing can help prevent the spread of infection.
Antibiotics to treat the problem are chosen based on whether they can be effective against this type of Staphylococcus aureus, which causes an infection on the skin accompanied by persistent severe acne.
Staphylococcus aureus infection is more present in the nose, usually around 30%, and on the skin, around 20%. Percentages are higher for people who are hospitalized or work there, and for people prone to acne on the face and body. .
People who have the bacteria but do not have any symptoms caused by Staphylococcus aureus are called carriers. People who are most likely to be carriers include those whose skin has been repeatedly exposed to skin infections, such as:
- People with diabetes who must take insulin regularly;
- People who use drugs;
- People prescribed hemodialysis or chronic ambulatory peritoneal dialysis;
- People with skin infections, AIDS, or previous staph blood infections.
People can move bacteria from the nose to other parts of the body with their hands, sometimes triggering a more severe and active phase of the infection.
Staphylococcus aureus bacteria can spread from person to person through direct contact through contaminated objects (such as gym equipment, telephones, door handles, TV remote controls, or elevator buttons) or, less commonly, by inhaling contaminated droplets dispersed by sneezing or coughing.
Staphylococcus acne on the face photo
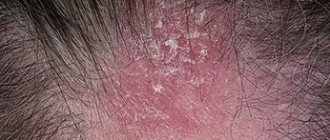
How does staphylococcus appear on the skin?
Infection with the described pathogenic microorganism has several similar manifestations. What staphylococcus looks like on the skin depends on the location of the bacterial inflammation, its intensity and the state of the person’s immune system. The introduction of microbes into the epidermal integument is always accompanied by:
- suppuration;
- swelling of nearby tissues;
- pain syndrome;
- hyperemia.
The main symptom that provokes staphylococcus is a rash on the skin. They can take several forms:
- blisters (vesicles with exudate);
- acne;
- boils;
- extensive red spots (erysipelas);
- carbuncles;
- felon;
- phlegmon;
- pustules;
- abscesses and others.
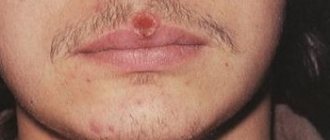
Staphylococcus aureus on the face
Infection with this microbe in the specified area is accompanied by a rapidly spreading rash. Staphylococcus aureus on the skin of the face causes a large number of acne. First, deep, painful inflammations form, which look like bright red bumps with severe swelling of the surrounding tissues. Signs of staphylococcus progress rapidly, and a white, purulent head appears in the center of such pimples. Over time, it turns yellow and opens, leaving a pit-shaped scar at the site of inflammation.
Staphylococcus on the skin of the hands
The main symptom of bacterial infection in this area is felon. Inflammation affects the fingers and periungual ridges and is often a consequence of a carelessly performed manicure. Staphylococcus aureus on the skin of the hands is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- accumulation of pus in the dermal layer;
- pronounced redness of the inflamed tissue;
- strong pain;
- twitching sensation in the affected area;
- swelling and swelling of the skin;
- change in nail color.
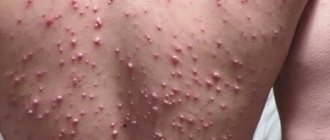
Staphylococcus on the body
The most common form of infection is a purulent rash. It can form on any part of the body, but is more common in the upper half of the body (chest, back, abdomen). Staphylococcus on the skin in this case looks like a cluster of deep red pimples with white heads in the center. When pressing on such elements, intense pain is felt.
Cutaneous staphylococcus on the body can have other forms. A more severe type of inflammatory process is a boil (boil). It represents severe suppuration of the sebaceous gland or hair follicle. In the center of the abscess there is a deep purulent core. If it is not completely removed, bacteria will penetrate and damage the surrounding tissue.
Another type of staphylococcal infection is erysipelas. It is characterized by the following symptoms:
- the appearance of a large red spot on the skin;
- swelling of inflamed tissues;
- local increase in body temperature;
- painful sensations;
- small pinpoint hemorrhages at the site of the lesion;
- sometimes the presence of translucent blisters with a purulent mass on the epidermis.
Symptoms of infection
Symptoms vary widely depending on the affected organ, the patient’s immunity, and his age. There are cases of asymptomatic bacteremia, when microorganisms are found in the blood, but do not cause concern and do not affect the functioning of organs.
However, the most common symptoms may include:
- formation of pustules and carbuncles on the skin;
- stomatitis, conjunctivitis and other local inflammations;
- the appearance of skin rashes accompanied by itching;
- increased body temperature, fever;
- loss of appetite, general weakness and apathy;
- problems with the gastrointestinal tract: nausea, vomiting, flatulence, diarrhea;
- Redness of the throat and enlarged tonsils are symptoms of tonsillitis.
Since staphylococci can affect any organ, symptoms may also vary.
What is the disease
Staphylococcal infection is the infection of the body with Staphylococcus microbes. These can be both mild and complex forms of pathological processes.
During their life, microorganisms produce large amounts of enzymes that are toxic to the body. More often this affects the condition of the skin, less often the functioning of the nervous system.
These microbes are highly resistant to environmental influences and antibiotics.
Symptoms
The symptoms of cutaneous staphylococcus depend on its location and the state of the immune system. In some cases, symptoms may vary, and it is extremely difficult to determine their nature.
| Symptom | Characteristic |
| Pyoderma | It is more common in newborns due to lack of normal care. Manifests itself in the form of small purulent blisters. When they burst, pus flows out and affects adjacent, healthy tissue. This condition is accompanied by deterioration of health and increased body temperature. |
| Furunculosis | The most common symptom. It develops due to damage to the skin by a microorganism that provokes inflammation and tissue necrosis. The most dangerous boils are in the neck and face. |
| Felon | Inflammation of the periungual fold, affecting the nail plate and nearby tissues. Due to the inflammatory process, it is characterized by redness, fever, and pain. When the inflamed area is opened, pus will begin to flow out of it. It can spread to other fingers and penetrate deep into the skin. |
| Phlegmon | Accompanied by severe swelling and redness of the inflamed area. Body temperature rises and health worsens. In advanced stages it causes necrosis. |
| Erysipelas | The most serious symptom. Accompanied by high body temperature, nausea, and vomiting. Typically, inflammatory processes occur on the legs, are red, hot to the touch, and have miniature rashes. |
Is a staph infection on the skin contagious?
This type of microorganism is always present on human skin. In case of any violation of the integrity of the skin, it penetrates into the blood and becomes the cause of the development of inflammatory processes.
You can become infected:
- using non-sterile medical instruments;
- eating dirty, unprocessed food;
- by airborne droplets;
- by household means in case of non-compliance with personal hygiene rules;
- sexually.
A weakened immune system is the main cause of infection.
Is staph acne an infectious disease?
Staph infections are contagious until the infection resolves. Direct contact with an infected sore or wound or with personal care items such as razors, bandages, etc. are common ways of transmitting the infection. Casual contact such as kissing or hugging. pose little risk of transmission unless there is direct contact with the infected area.
Some types of staph infections (see below) include staph, which causes food poisoning or toxic shock syndrome. These specific staph bacteria cause illness by producing a toxin. The toxin is not contagious, but food poisoning can affect groups of people who eat the same contaminated food. .
Staphylococcal infection on the face and head
The danger of this infection lies in its resistance to antiseptic and antimicrobial drugs. The infection can affect both children and adults. Staphylococci can affect any organs, causing inflammatory processes.
Purulent lesions form on the skin; due to lack of treatment, they spread to nearby areas and infect them.
The bacterium can cause blood poisoning, which leads to the development of serious pathologies. People with weakened immune systems are most susceptible to infection; the body is unable to independently resist the microorganism.
Treatment of Staphylococcus aureus and facial acne
Antibiotics
Staphylococcus aureus infections are treated and treated with antibiotics. First, doctors try to determine whether the bacteria are resistant to antibiotics and, if so, which antibiotics.
The infection, which is acquired as a result of the development of pimples and acne, is treated with antibiotics that are effective against Staphylococcus aureus, such as: vancomycin, linezolid, tedizolid, Quinupristin plus dalfopristin, ceftaroline, telavancin, or daptomycin.
If testing results later indicate that the skin is sensitive to methicillin and the person is not allergic to penicillin, a methicillin-related drug such as nafcillin is used. Depending on how severe the infection is, a course of antibiotic treatment may be prescribed. which can last from several weeks.
Prevention of staphylococcal infections
Effective prevention of staph infections includes:
- Regular daily shower;
- Wearing comfortable, non-tight clothing made from natural fabrics without using synthetics;
- Don't share towels and razors with another person;
- Cleaning sports equipment before use;
- Avoid contact with infected people with pronounced purulent discharge and pimples;
- Avoid scratching the skin or squeezing pimples;
- Avoid wearing slippers in public showers and swimming pools;
- Wearing gloves when in contact with infected people.
Staphylococcal skin infection in children and newborns
After infection, the child develops:
- at an early stage, vomiting, bowel movements and fever;
- later there are purulent formations throughout the body.
This serious infection can provoke the development of purulent formations, infection of internal organs, infection of the mucous membranes, and the development of sepsis.
Sometimes recognizing the signs of staphylococcus is extremely difficult. Usually they are similar to the development of diathesis, ARVI, dysbacteriosis. To determine the pathology, it is necessary to undergo a laboratory examination, after which the doctor will be able to select adequate treatment methods.
Treatment is not aimed at eliminating symptoms, it must neutralize the infection that caused them.
Why does a staph infection appear on the skin?
The following factors can provoke the appearance of the disease:
- decreased immunity;
- bad ecology;
- infection with pathogenic microflora;
- stress;
- hypothermia;
- endocrine and autoimmune diseases.
In addition, the cause of staphylococcal pathology is increased sweating and improper skin care. To reduce the likelihood of developing the disease, it is necessary to lead a healthy lifestyle. If inflammation is detected, you must contact a dermatologist and conduct a diagnostic examination.
Pathogenic flora for skin disease can be Staphylococcus epidermidis and Staphylococcus aureus. The presence of excessive bacteria is determined during a diagnostic examination.
Who is at risk
{banner_banstat9}
If a person has a weak immune system, is in contact with someone who is sick, or does not take care of their hygiene, then the risk of developing a staphylococcal infection increases significantly. Resistant strains of staphylococcus are found in hospitals and clinics. To prevent the occurrence of the disease, it is enough to monitor your immunity.
What are the symptoms of infection?
When infected with a staphylococcal infection, the manifestations depend on the type of disease and its location. Staphylococcus can lead to the following pathologies:
- furunculosis;
- vesiculopustulosis;
- sycosis;
- phlegmon;
- erysipelas;
- felon.
Each disease has its own symptoms and characteristic features during development. After the examination, it becomes known what exactly the staphylococcus led to.
Vesiculopustulosis
{banner_banstat10}
Vesiculopustulosis is a disease that is diagnosed in newborns. Staphylococcus causes inflammation in the area of the eccrine sweat glands. In this case, the following manifestations appear:
- purulent inflammation in the form of a small rash;
- malaise;
- itching;
- temperature.
The causes of vesiculopustulosis are considered to be imperfect immunity and improper hygiene of the newborn. The pediatrician should select a treatment regimen, taking into account the individual characteristics of the baby.
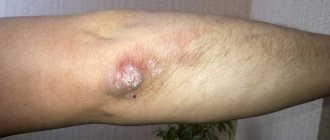
Furunculosis
Furunculosis is a purulent inflammation of follicular and perifollicular tissue. It is characterized by the appearance of a boil, which develops in several stages. As it forms, symptoms of the inflammatory process appear, among which are:
- pain;
- swelling;
- suppuration.
Body temperature may increase. A few days after the appearance of the boil, the boil opens. A large amount of pus comes out of it, and an ulcer forms. From this moment on, the disease declines.
Even one boil can bring a lot of inconvenience to a person. With severe immunodeficiency, severe furunculosis occurs, which is characterized by the appearance of several inflammatory elements. The disease is most dangerous when localized on the neck or face. In this case, serious complications (purulent meningitis or sepsis) may occur. If you find a boil on your face or neck, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Phlegmon
Under some circumstances, staphylococcus can cause cellulitis. Cellulitis is inflammation of cellular spaces and adipose tissue without clear boundaries. The inflammatory process can spread to muscles and tendons. Cellulitis poses a great threat to human health. When it appears, the following symptoms occur:
- severe swelling;
- subcutaneous compaction;
- heat;
- general malaise.
If phlegmon penetrates into the deep layers, it can lead to necrosis. Treatment of inflammation is carried out in a hospital setting. It is necessary to open the phlegmon and remove the purulent contents. The sooner a person seeks help, the less likely it is to develop dangerous complications.
Erysipelas
Erysipelas is an acute infectious disease that causes damage to the skin or mucous membranes. The main distinguishing feature of erysipelas is the intense redness of the affected area.
In addition, the disease is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- temperature 38-39 degrees;
- headache;
- malaise and nausea;
- enlarged lymph nodes.
In most cases, the cause of erysipelas is a streptococcal infection. When staphylococcus is added, the course of the disease becomes more complicated. In the absence of proper treatment, abscesses, ulcers and phlegmon begin to form in the area of redness. This can eventually lead to sepsis. Timely treatment is required, otherwise erysipelas will cause serious harm to health or even cause death.
Felon
Panaritium is an acute purulent-inflammatory process that is localized in the tissues of the fingers and toes. With felon the following manifestations occur:
- pain;
- edema;
- redness.
The cause of the disease is Staphylococcus aureus. In the initial stages, panaritium is characterized by inflammation. If adequate treatment is not undertaken, suppuration occurs. If an abscess occurs, it will need to be opened. This can only be done in stationary conditions.
A simple cut or crack on a finger can trigger the development of felon. After the addition of staphylococcus, inflammation begins. At an early stage, it is enough to use antibacterial agents to stop the damage.
Sycosis
Sycosis is an inflammatory disease that is more often observed in men. The reason for the appearance of Staphylococcus aureus is endocrine disruption and reduced immunity. Characteristic manifestations of sycosis are:
- inflammation of the follicles;
- redness;
- swelling.
Sycosis begins with the formation of single inflammations, which quickly disappear. They are localized on the face (in men in the beard area, in women on the eyebrows and the inner surface of the wings of the nose). In the presence of a constant infectious agent and a malfunction of the body, the disease becomes chronic. Redness becomes constant, pustules fester and form ulcers. Severe sycosis leaves scars on a person's face and therefore requires immediate treatment. Men due to sycosis cannot shave, as the inflamed area of the skin is injured.
How is diagnostics carried out?
Laboratory tests are used to detect staphylococcus on the skin. First of all, the doctor conducts a visual examination, determining the extent of the damage. Based on the initial examination, a preliminary diagnosis is made and additional examinations are prescribed. The following tests are used to diagnose staphylococcal infection:
- bacteriological culture;
- blood test for staphylococcus proteins;
- General and biochemical blood test.
Visual manifestations of staphylococcal infection are:
- purulent inflammation;
- redness;
- swelling.
It is worth noting that there are many other bacteria that cause diseases with such manifestations. It is laboratory tests that make it possible to determine the type of pathogenic flora and methods of treating it. During bacteriological culture, the sensitivity of the infection to various medications is determined.
Based on the results of the diagnostic examination, a treatment regimen for the disease is determined.
Visual inspection
The initial examination is carried out by a dermatologist or therapist. The degree of damage is determined. If the doctor detects phlegmon, he may recommend treatment in a hospital. When a person comes in with a boil in the neck or face, the most optimal treatment method is selected. In some cases, the doctor can immediately open the abscess.
Through visual examination, it is possible to determine the location of inflammation and associated diseases. An accurate diagnosis will be made after laboratory tests.
Laboratory research methods
For laboratory research it is necessary to obtain material. To do this, a scraping or fluid released from the lesion is taken. The degree of damage and the condition of the human body will be determined by a general and biochemical blood test. Acute infectious inflammation affects the number of leukocytes and erythrocyte sedimentation rate.
Blood tests are taken on an empty stomach in the morning. To obtain material for laboratory tests, it is necessary to stop using local medications the day before scraping or taking purulent fluid. The doctor will tell you in detail what needs to be done to make a correct diagnosis.
Methods for diagnosing staphylococcal acne
Blood tests are needed to diagnose staph when there is doubt or more serious infections occur.
In cases of minor skin infections and pimples, your healthcare provider can usually diagnose staph infections by their appearance without the need for laboratory testing. More serious staph infections, such as bloodstream infections, pneumonia, and endocarditis, require culturing samples of blood or infected body fluids or tissues.
The laboratory makes a diagnosis and performs special tests to determine which antibiotics are effective against such bacteria.
How is staphylococcus treated?
Regardless of the location of the disease and its severity, antibiotics and antiseptics are used. After a diagnostic examination, the most effective medicine is determined. In case of serious damage, systemic antibacterial agents are used. For minor inflammation, apply antibacterial ointments topically. When treating staphylococcal infections, the following principles must be adhered to:
- always complete treatment;
- stimulate the immune system;
- avoid provoking factors.
Many types of staphylococcus are resistant to antibacterial agents. It is necessary to accurately determine a drug that will be effective against the bacterium. The treatment regimen should include not only antibiotics, but also drugs that stimulate the immune system.
A person must adjust his lifestyle in order to achieve results in the treatment of chronic infection.
Tablets and injections
Antibiotics in tablets or injections are used for severe staphylococcal inflammation. They are used in cases of erysipelas and severe furunculosis. The most commonly prescribed medications are:
- Clarithromycin;
- Azithromycin;
- Amoxicillin;
- Tetracycline.
To treat resistant strains, the latest generation antibacterial agents (Levofloxacin, Roxithromycin) are used. It is worth remembering that antibiotics are toxic and have a lot of side effects, so their use is limited.
Ointments and antiseptic solutions
For local treatment of the inflammatory process, ointments and antiseptics are used. The following medications have proven themselves well in the treatment of staphylococcal diseases:
- Gentamicin ointment;
- Chlorhexidine bigluconate;
- Levomekol.
For purulent-inflammatory lesions, it is recommended to use Levomekol. It suppresses infection and promotes speedy healing.
Local agents are used throughout therapy. It is necessary to choose the right ointment in order to achieve a good effect in the treatment of skin staphylococcal infections. The treatment regimen should be drawn up by an experienced dermatologist or therapist. It is necessary to take into account the individual characteristics of a person.
Surgery
If the disease is advanced and poses a threat to human health, surgical treatment is performed. During the operation, the abscesses are opened and the internal cavity is cleaned. After surgery, antibiotics are taken and the wound is cleaned daily.
To treat chronic skin lesions, it is necessary to use a complex effect. Therapy can take time and take a lot of energy. A person must change his lifestyle and follow all doctor’s recommendations.
Immune stimulation
To help the body's defenses, a person can use vitamin complexes and dietary supplements. In some cases, the doctor may prescribe immunomodulators or immunostimulants.
To improve immunity, a person should:
- Healthy food;
- give the body a small load;
- use supplements.
If the disease is acute, then you need to adhere to bed rest and drink plenty of fluids. Despite the lack of appetite, you must adhere to your normal diet.
What is the treatment for staph infections and acne?
Poll: When did your acne appear? (Number of votes: 4295)
I've been suffering all my life
It's been a couple of years now
About a few months
Recently
To vote, click on the desired answer. results
Minor staph infections and skin pimples are usually treated with antibiotic ointment, such as Triple Antibiotic Blend, which is available over the counter. In some cases, oral antibiotics may be prescribed for skin infections. Additionally, if abscesses are present, they are surgically removed. More serious and life-threatening infections are treated intravenous antibiotics and supportive medical care in the hospital.
Doctors use several different types of antibiotics that have been used to treat staph infections. The choice of antibiotic depends on the type and severity of the infection, as well as the drug resistance patterns of the particular bacterial type. Some of the antibiotics that have been used to treat staph infections are cefazolin, cefuroxime, cephalexin, nafcillin ( nalpen), oxacillin (Bactocill), dicloxacillin, vancomycin, clindamycin (Cleocin), rifampin and telovacin (Vibativ) Combinations of antibiotics with other antibiotics can also be used. Some types of staphylococcus, such as MRSA, still remain resistant to many antibiotics.
Staphylococcus acne under a microscope photo
First aid
It is necessary to have local first aid products in your first aid kit in case of infection. Any staphylococcal lesion is characterized by the appearance of suppuration. If a person discovers a boil, the first aid in getting rid of it will be to apply an antibacterial ointment. If the situation does not improve within 4 days, you need to make an appointment with a doctor.
Self-medication can be done only with minor inflammation of the skin and complete confidence in the diagnosis.
Prevention of staphylococcal infection
To prevent the appearance of staphylococcus on the mucous membranes and skin, it is necessary to carry out prevention. You will need to do the following:
- support immunity;
- maintain hygiene;
- lead a healthy lifestyle;
- Avoid contact with things of sick people.
Prevention is aimed at preventing infection and stimulating the immune system. In order not to encounter staphylococcal disease, you will need to avoid stress, hypothermia, excessive physical activity and other factors that provoke a decrease in the body’s protective function.
If you suspect a staph infection, it is advisable to make an appointment with a dermatologist. He will conduct a visual examination and prescribe tests. At an early stage, getting rid of inflammation of the skin is extremely simple.
Staphylococcus is present on the skin and mucous membranes of all people. A healthy body controls its amount, so the bacterium does not cause any harm. If there are malfunctions or decreased immunity, the risk of developing the disease increases. If a person constantly suffers from furunculosis or sycosis, this is a reason to conduct a full examination of the body.
Staphylococcus aureus symptoms, causes and treatment:
Staphylococcus: what to expect and what to do?
Staphylococci are widespread in nature.
They are everywhere.
In water, soil, on the skin and mucous membranes of people and animals. But pathogenic, i.e. Staphylococcus aureus (Staphylococcus aureus) and, to a lesser extent, staphylococcus epidermidis (Staphylococcus epidermidis) may be potentially dangerous. These microbes are classified as opportunistic microorganisms, i.e. they can cause disease only under certain conditions, and generally live quietly on human mucous membranes and skin without causing harm.
In humans, Staphylococcus aureus lives in the intestines, vestibule of the nose, perineum, armpits, and navel. They are found in the vestibule of the nose in 40-50% of healthy adults, in the intestines in 60-70% of healthy people.
Staphylococcus epidermidis is considered non-pathogenic, but in patients with immunodeficiency, prosthetic heart valves, and vascular catheters, they can cause nosocomial infections.
The pathogen can be transmitted from a patient or carrier by airborne droplets, contact, and fecal-oral routes.
The list of diseases caused by staphylococci is very long.
These are infections of the skin and subcutaneous tissue (styes, boils, carbuncles, skin abscesses, imetigo, phlegmon).
Staphylococci are involved in a variety of infections of the ENT organs (sinusitis, tonsillitis, adenoiditis, otitis), and also cause bronchitis and pneumonia.
It is dangerous if infection occurs in a hospital, because nosocomial staphylococci are resistant to many antibiotics and treating such an infection becomes very problematic.
Sometimes, especially in young children, staphylococcal intestinal infections and enterocolitis occur. In adults, foodborne toxic infections more often occur, when the disease is caused not by staphylococcus itself, but by its toxins accumulated in a poor-quality product that has been infected with staphylococci.
If a virulent (highly contagious) strain of staphylococcus appears in a maternity hospital or maternity ward, the infection can spread quickly. More often, the infection in newborns is mild, manifesting mainly as pustules around the nail folds, and occasionally deeper tissues are affected.
In newborns, some strains of staph can cause a severe skin infection called scalded skin syndrome (Ritter's disease). Women who feed a sick child may develop staphylococcal purulent mastitis.
Staphylococcus is also involved in such a serious disease as osteomyelitis (inflammation of the bones and bone marrow). Staphylococci most often enter the bone from foci in the skin or nasopharynx, but sometimes the entrance gates of the infection remain undetected.
If staphylococci penetrate the so-called blood-brain barrier, a terrible disease develops - meningoencephalitis.
Also, with severe immunodeficiency, staphylococcal sepsis can develop. In this case, staphylococcus penetrates into the bloodstream from any source of infection on the skin or subcutaneous tissue.
However, the above severe diseases rarely occur, because in most cases the protective barriers are triggered, and the infection is either limited to local forms and easily treated, or does not develop at all. But it can remain as a carrier, which does not prevent a person from feeling absolutely healthy.
If tests reveal staphylococcus, this does not mean that it needs to be treated.
We should treat only the disease, not tests. And if a person has no complaints, then there is no need to worry in vain.
Workers of certain professions, enterprises and organizations (food industry, maternity hospitals, surgical departments, etc.) are subject to periodic examination and testing for staphylococci. And so, if pathogens are identified, they undergo preventive sanitation of possible foci of infection so that their carriage of staphylococcus does not become a risk factor for others.
Be healthy!
about the author
- Dobrelya Ekaterina Alexandrovna
- Pediatrician, infectious disease specialist of the highest category. Head of outpatient department No. 2
- All publications by the author
Characteristics of rashes on the face
Types of rashes:
- spot (skin color changes, degree of pigmentation, fuzzy edges, no irritation),
- tubercle (a compaction without a cavity in the deep layers of the dermis, tissue destruction, possible scars),
- blister (a cavityless element, the result of inflammatory edema of the upper layer of the dermis, disappears during the day, leaves no traces),
- node (red spots, provoke inflammation),
- pustule (a rash resulting from inflammation, filled with pus, appears in the face and back, forms scars and creates uneven pigmentation),
- papule (a pink nodule on the surface of the skin up to 3 cm in size).
General strengthening agents
A strong immune system helps resist microorganisms and bacteria. Taking multivitamin complexes, herbal preparations of adaptogens (ginseng, eleutherococcus), intramuscular transfusion of purified own venous blood (autohemotherapy) will help maintain the body’s defense at the proper level. Complex combinations of synthetic immunomodulators are also used when ready-made immune preparations (staphylococcal immunoglobulin) are administered.
About pathology
Colonies grow on a medium - blood agar. The bacterium got its name because of its golden color. In fact, approximately one-quarter of the world's population is carriers of this bacterium.
Staphylococcus aureus
Its favorite locations are the armpits, nasal cavity and groin area. But, despite its normal presence on the skin, it does not cause any diseases in humans. It is classified as normal skin flora.
It is worth noting that it does not cause any pathologies as long as it is in moderate quantities. As soon as its quantity exceeds the permissible norm, the development of the pathological process begins. As a rule, staphylococcus begins to penetrate into the deeper layers of the skin through the presence of scars, cracks and other damage. As a result, a skin infection or even an abscess develops.
Basically, all body systems are damaged. First of all, the liver and spleen are affected. Then the musculoskeletal system. But that’s not all, because often the consequences are much more serious. Therefore, you should not neglect the first symptoms of the disease and immediately go to a specialist.
Ways to prevent diseases
Preventive measures and a number of precautions will help reduce the risk of developing staphylococcal infections:
- strengthen the immune system (diet and regular exercise),
- personal hygiene (wash hands thoroughly), personal care products and personal wardrobe (do not use other people’s toothbrushes, clothes, sports equipment),
- treat skin lesions, use sterile bandages and plasters for bandaging, the bandage will prevent the spread of microorganisms beyond the wound, will prevent the entry of new infections,
- wash clothes, children's toys, bedding in hot water,
- heat treatment of products and compliance with sanitary and hygienic standards during the cooking process.
Treatment of staphylococcus on the face
Staphylococcal inflammation on the face is treated by a dermatologist. The patient is prohibited from water procedures. It is necessary to exclude contact with water during the acute phase of the disease.
As is known, Staphylococcus aureus reacts poorly to some antibiotics, especially penicillin. Therefore, it is advisable to conduct an antibiogram before starting treatment.
The skin will need to be wiped with antiseptic agents.
It is possible to treat staphylococcus on the face by taking bacteriophages. These viruses absorb the multiplied bacteria and promote recovery.
Prevention
In addition, there are preventive measures aimed at preventing infection of the facial skin with pathological bacteria. First of all, it is compliance with the rules of personal hygiene. It is important to observe sanitary and hygienic standards not only at home, but also at work.
In the presence of concomitant diseases, it is necessary to more carefully care for the dermis of the face in order to increase its protective properties. This is especially true in the presence of diabetes, when even a minor scratch on the face can lead to the development of deep skin lesions.
Particular attention should also be paid to the condition of the skin of children and if even minor inflammation occurs, consult a doctor. Protecting the dermis from the sun and frost, following a diet, avoiding traumatic situations - all these measures can prevent infection with bacteria.
Author of the article:
Kuzmina Vera Valerievna |
Endocrinologist, nutritionist Education: Diploma of the Russian State Medical University named after. N.I. Pirogov, specialty “General Medicine” (2004). Residency at the Moscow State Medical and Dental University, diploma in Endocrinology (2006). Our authors