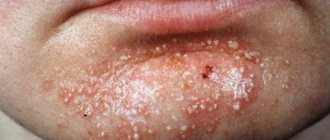
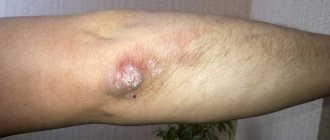
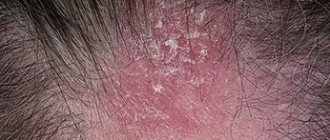
Syphilis is one of the most common sexually transmitted diseases. And at the same time one of the most dangerous. Due to the not very clear symptoms in most patients, syphilis is detected in late stages, so it takes a long time to treat. All the time from the moment of infection, a person remains infectious to others - he can transmit the disease to a sexual partner, and to others, even to children.
Cost of services in our clinic
| Appointment with a dermatologist, candidate of medical sciences | 1500 rub. |
| Consultation with a dermatologist (KMS) when removing 2 tumors | 0 rub. |
| Removal of a neoplasm (wart, mole) using the radio wave method | 500 rub. |
| Make an appointment by phone: 8-800-707-15-60 (toll-free) |
| *The clinic is licensed to remove tumors |
How is it transmitted?
The most common and typical route of transmission of the causative agent of syphilis is sexual. Infection can occur through vaginal, oral or anal sex. As already mentioned, infection is most likely with skin manifestations of syphilis; the most contagious are hard chancre - painless ulcers that form during primary syphilis. Erosive papules that appear with secondary syphilis also pose a great danger, but with nonspecific rashes it is possible to become infected. The sexual route of transmission of syphilis is the most common, since during intimate intimacy microtraumas are formed on the mucous membranes and skin, through which the pathogen actually penetrates.
Another route of transmission of infection is transplacental (from mother to fetus). It is known that in the first three years after the mother is infected, the likelihood of developing congenital syphilis increases. The pathogen penetrates the placenta at 4–5 months of pregnancy, but there are cases of infection as early as 10 weeks of gestation.
Blood transfusion is another way of contracting syphilis. The transfusion route is possible at any stage of infection, including the incubation period. Currently, all donor blood is thoroughly checked, so this route of transmission of infection is practically excluded.
It is almost impossible to become infected through household contact, but in medical practice this has still happened. The infection is not transmitted through shared utensils and household items, but in close contact with a patient this is still considered possible.
There is another way of infection - professional. We are talking about laboratory employees, as well as sex workers. There are known cases of syphilis infection among surgeons, dentists and obstetricians-gynecologists.
At risk for the disease:
- prostitutes;
- homosexuals;
- persons who are promiscuous;
- persons practicing group sex;
- asocial elements of society;
- drug addicts;
- patients with gonorrhea;
- patients with hemophilia.
Syphilitic rupee
One type of syphilitic ecthyma is syphilitic rupee.
It occurs in weak patients.
Characterized by the severe general condition of the patient.
Often combined with inflammatory lesions of the eyes, nasal mucosa, bones, etc.
Rupa occurs in the same way as ecthyma.
The difference is that underneath the crust, rapid tissue breakdown continues.
As a result, it is constantly increasing.
Over time, it can reach sizes up to 8 cm in diameter and up to 3 cm in depth.
When you press on the crust, pus is released.
There is an ulcer underneath.
After it heals, a large scar remains.
It may be pigmented at first and then colorless.
Rupees are usually single.
They develop slowly and last a long time.
Rupees can occur not only in the secondary period of syphilis, but also in the tertiary stage.
Classification of the disease
Syphilis is divided into forms and types, due to different timing, routes of spread and varied symptoms.
According to the degree of damage, syphilis is divided into:
- primary;
- secondary;
- tertiary.
In addition, it can be:
- hidden,
- congenital,
- late,
- chronic.
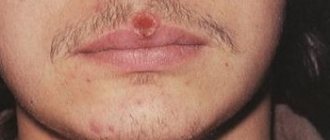
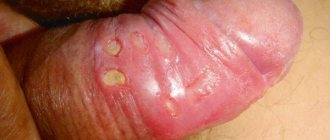
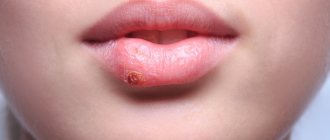
Primary syphilis - stage 1 of infection, a distinctive feature is the appearance of chancre. Chancres often appear on the genitals, since the sexual tract is the most common route of transmission of infection. Chancres can also appear on the face, mouth, mammary glands, and legs. Primary syphilis has no other manifestations.
Secondary syphilis - stage 2 of infection. It is characterized by the appearance of a papular rash. At this time, the patient experiences inflammation of the lymph nodes, damage to the nervous and musculoskeletal systems.
Tertiary syphilis develops in people who have not received treatment or have not completed treatment for the disease. Syphilitic granulomas appear on the mucous membrane, skin, bones, and internal organs, which destroy these structures. Currently, this stage is rare, since at stages 1 and 2 the disease can be successfully treated.
Latent syphilis is considered the most dangerous because the patient has no symptoms, but it poses a danger to others. Syphilis is classified as late if more than 2 years have passed since infection and symptoms have just appeared. Syphilis, which has developed over decades, is called chronic; it slowly destroys the body, and is not always accompanied by symptoms.
Provoking factors
With the use of modern treatment methods, the tertiary stage of syphilis develops extremely rarely. The factors that provoke primary syphilis most often are old age or infancy (secondary and tertiary are the most dangerous).
Lack of treatment, or incorrectly calculated doses of medications, if secondary syphilis was treated:
- Failure to maintain personal hygiene, living in unacceptable social and living conditions;
- Injuries, chronic diseases;
- Immune system dysfunction, accompanied by immunodeficiency;
- Physical, mental and mental stress accompanying secondary syphilis;
- Poor nutrition, lack of the required amount of proteins, vitamins and microelements in food.
If secondary syphilis was not identified and treated in a timely manner, then it becomes the most common cause of the disease transitioning to the tertiary stage, the symptoms of which are described below. Predisposing factors to this are also alcohol addiction, smoking and promiscuity. However, patients in whom syphilis has reached the tertiary stage of development may not be infectious. Treponema pallidums are located inside the granuloma and die when they disintegrate.
Symptoms of syphilis
Since the disease goes through 3 stages, replacing each other, the symptoms at different stages will vary:
- The appearance of chancre. This is a round ulcer with smooth edges and a dark red bottom. When rubbed, a liquid may be released from the formation, which contains live and active pale spirochetes. A couple of weeks after the appearance of chancre, inflammation begins in the lymph nodes. At this time, the pathogen has already spread throughout the body and multiplies in the internal organs. At the end of the first stage, a general intoxication syndrome occurs.
- The appearance of a rash on the body. The rash most often appears after the ulcer has healed. Red-brown spots appear on the neck, chest and upper back. They are called the necklace of Venus, they do not hurt, do not itch and, apart from aesthetic discomfort, do not cause any inconvenience. At this stage, fever, sore throat, swollen lymph nodes, headache and muscle pain, patchy hair loss, fatigue, and weight loss appear. In every 10 patient, pathologies of the joints, bones, and nervous system are detected in stage 2.
- Pallor of the rash. There are more of them in places of friction. Serious pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract, heart, respiratory tract, and brain occur. Since the pathology affects internal organs, it can be fatal.
Important! Without treatment, syphilis affects the eyes (ocular syphilis) and the brain and nervous system (neurosyphilis).
Tertiary roseola
A rare type of tertiary syphilis, the photo of which is posted below. It is a pale pink spot with a diameter of 15 centimeters or more. Groups of spots are localized in the arms, legs and sacrum. Their appearance is associated with vascular disorders. The spots may merge, forming different patterns on the skin.
Patients have no subjective feelings about the appearance of spots (nothing bothers them). Roseola remains viable for 1 year, after which it disappears or recurs. A soft scar forms in their place.
Diagnosis of syphilis
It is very important to identify syphilis at its first stage, at which time it is easier to treat and does not leave complications. Diagnostic measures begin with a visual examination of the skin and mucous membranes. During the examination, the doctor discovers dense purulent foci. You can differentiate chancre from other formations using palpation - it is painless.
For accurate diagnosis, a number of laboratory tests are required:
- RSKk;
- RMP;
- RPR;
- RSKt;
- RPGA;
- ELISA.
For research take:
- discharge from erosions, ulcers and papules;
- lymph;
- blood serum;
- cerebrospinal fluid;
- umbilical cord and placenta tissue.
A venereologist diagnoses and treats syphilis.
Gunma
Gumma: deep nodular syphilide, appearing in half of people with the tertiary stage of syphilis. Gum is formed under the skin in the fiber and deep layer of the dermis. A gumma nodule is formed in the subcutaneous fatty tissue; it is mobile, changes in size and merges with the skin. In turn, the skin at the confluence becomes thinner and tighter, acquiring a red-violet hue. The diameter of the gumma often reaches 10 centimeters.
Having reached the largest possible volume, the nodule begins to disintegrate, which is accompanied by the opening of the granuloma and the formation of an oozing ulcer in its place. The liquid released from the wound is stretchy, has no specific color, and smells unpleasant. The depth of the ulcer reaches 1 centimeter, it has the shape of a circle with clear boundaries and steep edges. The bottom of the ulcer is dense, gray granulations are present.
Healing of the gummous nodule is slow, sometimes taking several months. After the process is completed, an unsightly pink star-shaped scar remains on the skin. Over time, the scar acquires a normal color, but does not disappear completely.
In some cases, the opening of the gumma does not occur, but an atrophic-looking scar still forms. Gummas can degenerate fibrously or become petrified. Several gummas can merge and form gummous infiltration, spreading to healthy areas of the skin and destroying tissue and bones.
Treatment of syphilis
Treatment of syphilis is based on the impact on the cause of the disease, that is, on the pathogen. This treatment is called etiotropic therapy.
Drug treatment consists of taking antibiotics:
- penicillins;
- tetracyclines;
- cephalosporins;
- macrolides.
Local treatment consists of using ointments, creams or gels, the action of which is aimed at mitigating the skin manifestations of the disease.
To generally strengthen the body and combat neurological symptoms, physiotherapy is prescribed, but it, of course, cannot be the main thing in the fight against infection.
Adjuvant treatment may also be used. The patient is prescribed:
- vitamin complexes;
- dietary supplements;
- immunomodulators.
Treatment tactics for pregnant women will depend on the duration of pregnancy and the severity of the disease. In some cases, when the disease threatens the child with dangerous pathologies, it is recommended to terminate the pregnancy. But most often, pregnant women are prescribed antibiotics.
There are no traditional methods for treating syphilis. Self-medication will not lead to a positive effect; therapy should only be selected by a doctor.
Consequences and prognosis
Regardless of whether syphilis manifests itself or not, in any case it has a negative effect on internal organs. The list of complications of syphilis includes the following:
- damage to the cardiovascular system;
- damage to the central nervous system;
- neurological deficits;
- impairment of intellectual abilities and memory;
- blindness;
- hearing loss;
- meningitis.
Development is possible:
- IHD;
- gastritis;
- hepatitis, up to coma and death;
- osteoarthritis;
- syphilitic pneumonia.
In the primary form of syphilis in men, the following may appear:
- phimosis;
- balanoposthitis;
- gangrene of the genital organ;
- balanitis
As for the prognosis of the disease, it depends on the stage of the disease and the effectiveness of treatment. With primary and secondary syphilis, the treatment prognosis is favorable; the third stage can lead to disability of the patient.
With congenital syphilis, the prognosis for treatment is positive, but only if adequate treatment is started immediately.
Prevention
It is enough to see at least once what syphilis looks like to forever decide to give up promiscuous sexual intercourse. This is the most effective way to prevent this disease.
If a person has to live with a sick person, strict hygiene rules must be observed. Despite the fact that the risk of household transmission of infection is minimal, it still exists. Also, a person living with an infected person must periodically visit a doctor and undergo diagnostics to make sure that infection has not occurred.
If you have sexual contact with an infected person, it is recommended to immediately urinate, wash your genitals with laundry soap, and wipe your private parts with a disinfectant solution. This treatment is effective only in the first 48 hours after possible infection, since during this period of time the pathogen is still on the skin and mucous membrane. After more than 3 hours, such treatment is useless.
Syphilis is a dangerous disease that in the vast majority of cases is transmitted sexually. The disease is insidious in that even in the absence of symptoms, it can affect any organ of the human body and provoke various ailments. It is important to understand that cure for syphilis does not guarantee protection against re-infection. Immunity to Treponema pallidum is not developed. Therefore, you should always adhere to preventive measures, and at the first suspicion of a disease, immediately consult a doctor. With timely treatment, syphilis can be successfully treated. But untreated syphilis will destroy the body for years and can be fatal.