Before starting treatment for onychomycosis, the patient must be tested for nail fungus. Thanks to it, it is possible to identify the type of infection, its resistance to drugs and the stage of damage to the plate. How is the test done, and what do you need to know before performing it?
What is nail fungus?
Fungal infection of the nail plate is called onychomycosis. This is an extremely common disease that is diagnosed in people of any age, including children. The pathological process is caused by the active proliferation of infections on the feet and hands, which leads to yellowing, delamination, changes in the structure of the nail, as well as damage to the skin tissue around it.
The disease is classified depending on its pronounced manifestations:
- onycholytic – characterized by damage to the nail plate and its rejection from the nail bed;
- hypertrophic, in which the plate loses its glossy shine, turns pale, turns yellow, darkens, and also changes its structure: it thickens, becomes deformed, and collapses at the edges;
- normotrophic, when a seemingly healthy nail plate becomes covered with small spots;
- total, in which the entire nail is affected;
- distal, when the lesion is located only at the edge.
It is very easy to become infected with onychomycosis. Pathogens are transmitted from a sick person, as well as through the things he uses.
Increase the likelihood of infection:
- weak immunity;
- violation of the integrity of the skin and nails;
- vascular diseases;
- wearing low-quality, tight shoes;
- failure to comply with personal hygiene rules;
- severe stress.
If signs of illness occur, you should consult a dermatologist or mycologist. The sooner therapy is carried out, the faster it will be possible to cope with mycosis.
Microscopic examination for micromycete fungi
general information
A disease caused by fungal infection of the skin and its appendages (nails, hair (eyelashes)) is called superficial mycosis. When infected, fungi invade and form colonies in the outer layer of skin (epidermis), hair and hair follicles (“bulbs”), and nail apparatus.
Diagnosis of superficial mycoses is carried out by a dermatologist. The research algorithm is as follows:
- a general examination of the patient is carried out;
- the affected area is examined using a Wood's ultraviolet lamp;
- A scraping is taken from the skin, the affected hair is removed with tweezers along with the bulbs and examined under a microscope for the presence of fungi.
The most common cause of the development of superficial mycoses is fungi of the genus Dermatophytes, the infection of which is called dermatophytosis. In addition, the pathology can be caused by:
- fungi of the genus Candida (candida) - an opportunistic fungus that is part of the normal microflora of the body, and in large quantities is the causative agent of candidiasis;
- pathogenic fungi of the genus Trichosporon (trichosporon - in the scalp causes the disease white piedra (the formation of soft nodules of yeast cells around the hair shafts), and in people with weakened immunity it can cause the development of trichosporonosis (systemic damage to the body by fungi of this type));
- parasitic fungi Microsporum, which is the causative agent of microsporia - a disease of the hair and head
- pathogenic fungi Epidermophyton, which cause dermatomycosis and should not normally be found on human skin and mucous membranes;
- Hortaea mushrooms - their representative Hortaea werneckii is the causative agent of shingles in humans;
- Malassezia (Malassezia) is an opportunistic fungus that is part of the normal microflora, but with an increase in the number it causes malassezia of the skin: dandruff, seborrhea (an inflammatory skin disease that occurs due to an increase in the amount of sebum) and atopic dermatitis (an inflammatory skin lesion of an allergic nature); Malassezia furfur is the causative agent of pityriasis versicolor, etc.
Transmission of superficial mycoses from one person to another in several ways:
- in personal close contact with a person affected by the infection;
- when wearing someone else's shoes, using a comb, hats, scissors, hygiene and household items;
- when visiting public places, for example, baths, swimming pools, showers, hairdressers, etc., as well as children's and educational institutions.
The infection enters the body through wounds, cracks, diaper rash, and ulcers. A superficial examination of the affected areas allows us to make only an assumption about the presence of a disease, since fungal damage is visually similar to other diseases that affect the skin and its appendages (for example, psoriasis). The presence of fungi is determined by microscopic examination of samples of skin, hair, and nails taken from the affected areas. This test does not indicate the type of mushrooms detected, but only states the fact of their presence. For a more in-depth study to determine the type of fungi that caused mycosis, the biomaterial under study is inoculated on nutrient media.
Skin mycoses
Depending on the symptoms of the disease, the type of fungus, and the degree of its penetration into the skin, mycoses are divided into two categories:
- superficial mycoses - those that affect
- deep mycoses - affecting the dermis (the connective tissue part of human skin lying under the outer layer of skin, the epidermis) and deeper soft tissues lying under the skin, and with a significant deepening - bone tissue.
In addition, mycoses are divided according to the area affected, in particular:
- mycoses of smooth skin, in which fungi are localized in the face, torso, and limbs);
- keratomycosis - the formation of fungal colonies on the surface parts of the skin (stratum corneum of the epidermis) and fungal follicles;
- mycoses of the scalp;
- Onychomycosis is fungal infection of the nail apparatus.
The most common mycoses of the skin and its derivatives are:
1. Superficial mycoses
a) dermatophytosis:
- Rubrophytia is the most common fungal disease of the feet, affecting the skin and nails, as well as any areas of smooth skin and vellus hair, including skin folds, nails and skin of the hands;
- trichophytosis is a highly contagious fungal disease of the skin, hair, and nails caused by fungi of the genus Trichophyton (in common parlance lichen);
- microsporia is a fungal infection of the skin involving long or vellus hair, caused by fungi of the genus Microsporum (in common parlance - “ringworm”);
- favus - mycosis, which is caused by the parasitic fungus Trichophyton schonleinii, which affects mainly smooth skin (in very rare cases, the effect of the fungus can spread to hair, nails, and internal organs);
- epidermatophytosis inguinalis is a fungal infection accompanied by itching and rash, localized in the folds of the skin of the groin area, and sometimes in other large folds of the body;
- Athlete's foot is a common fungal infection that affects the skin and nails of the feet.
b) candidiasis – damage to the mucous membranes and skin by opportunistic candida yeast fungi;
c) keratomycosis – infection of the stratum corneum of the epidermis by a fungus, one of the representatives of which is lichen versicolor.
2. Deep mycoses:
- chromomycosis is a deep mycosis, more often found in the subtropics and tropics, which affects the skin, subcutaneous tissue, and in some cases, internal organs;
- keloid sporotrichosis is an infectious disease caused by the dimorphic fungus Sporotrix, shencki, and less commonly, s. Shenki var. luriei;
- North American blastomycosis is a fungal infection of animals and humans, most often affecting the lungs, common in North America, the causative agent of which is the dimorphic fungus Blastomyces dermatitidis.
The causative agents of skin mycoses are quite often the yeast fungi Candida and Malassezia, as well as dermatophyte fungi - Trichophyton, Epidermophyton, Microsporum.
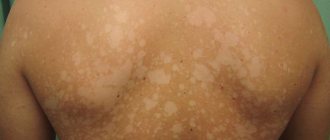
Representatives of yeast fungi are part of the normal microflora, being, in fact, conditionally pathogenic fungi. Exposure to provoking factors on the body (high temperatures, humidity, decreased defense response, failure to comply with personal hygiene rules, etc.) can cause their excessive growth. Signs of skin candidiasis are red or pink rashes in the folds of the skin. Tinea versicolor, caused by Malassezia furfur, is manifested by multiple foci of peeling on the skin. The resulting spots can be of different colors - pink, white, brown, which is why the disease received such a “bright” name.
Dermatophyte fungi - Trichophyton, Microsporum, Epidermophyton, are pathogenic. Normally, they should not be found on human mucous membranes and skin. The nutrient medium for these fungi is the protein keratin. It is contained in the upper layers of skin and hair, as a result of which the location of parasite colonies can be observed in different parts of the body. Hair affected by fungi breaks and falls out, the skin itches and peels, and ring-shaped rashes typical of infection appear on it.
Infection with agents of superficial mycoses occurs through personal contact with an infected person, when sharing personal items (combs, scissors, hats, etc.), when visiting public places (baths, saunas, swimming pools). Mushroom particles are resistant to external influences. They can remain on surfaces for a long time.
Infection can also occur through animals, among which the most common carriers of infection are dogs and cats. Factors that increase the risk of contracting mycosis are decreased immune defense, the presence of damaged skin areas, and diaper rash.
Microscopic examination of skin scrapings is a preliminary test and is carried out to confirm/refute the presence of lesions by opportunistic or pathogenic fungi without specifying the specific causative agent of the infection.
Hair mycoses
Fungal infections of the scalp are characterized by certain characteristics. The most common causative agents of infection include the dermatophyte fungi Trichophyton, Epidermophyton and Microsporum. The infection is caused by fungal spores landing on the head. This occurs when there is contact with a carrier of the infection, which can be a person or animal, or violation of personal hygiene rules. Fungal spores are resistant to environmental factors and remain viable for a long time on contaminated surfaces.
After entering the scalp, fungi cause the formation of one/several lesions, characterized by fragility and hair loss, itching and redness of the skin.
One type of mycosis of the skin and hair is called microsporia. Its causative agents are the fungus Microsporum ferrugineum, which is pathogenic for humans (anthropophilic), and the fungus microsporum lanosum, which is zoophilic (a threat to humans and animals). When affected by fungi, the hair becomes whitish and breaks off, leaving stubs up to 6 millimeters.
Another hair disease, trichophytosis, develops when infected with the fungi Trichophyton tonsurans (more often) and Trichophyton violaceum (less often). The cause of infection is contact with a person suffering from mycosis, the use of his personal belongings - scissors, comb, hats. The most common places of infection are hairdressers, preschools and educational institutions.
Before conducting a microscopic examination of the hair, it is removed from the affected area with tweezers. Examining the affected hair under a microscope allows you to determine the structure of the hair and detect fungal particles in it.
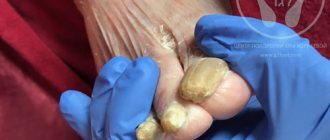
Mycoses of the nail apparatus
Fungal infection of the nail plate is called onychomycosis. This disease is observed only in humans. Infection can occur through personal contact or through objects used by the patient, at home or in public places. There are a number of factors, both external and internal, that create favorable conditions for the development of fungus. Thus, the likelihood of infection increases:
- when receiving minor injuries;
- when wearing rubber shoes;
- with increased sweating;
- when the body's resistance decreases;
- in case of dysfunction of the thyroid gland;
- in the presence of chronic and somatic diseases;
- with immune deficiency.
Nails may be affected:
- dermatophyte fungi (E.floccosum, T.rubrum, T.violaceum, T.tonsurans, M.gypseum, T.schonleinii, T.mentagrophytes v.interdigitale);
- yeast-like fungi Candida;
- mold fungi (Penicillium. spp., Scopulariopsis brevicaulis, etc.).
Every second patient with onychomycosis is affected by several types of the listed fungi, and the disease spreads to the nails of both the upper and lower extremities.
The most informative methods for confirming infection are microscopy of fragments of the nail and scrapings taken under it, as well as culture of the material and isolation of the culture.
To conduct a bacteriological study, material is taken from the visible affected area (optimally at the border between the affected and healthy area). The types and clinical form of fungal nail infection differ, which influences the choice of sampling site. The fungus can be located:
- under and inside the nail (distal and proximal forms);
- in the outer layers (surface form);
- in the posterior nail fold (paronychia) - the area located behind the cuticle.
Material for research is taken from the affected area of the fingernails or toenails. Depending on the clinical form of nail damage, the sampling technique changes, which is reflected in the table:
| Clinical form onychomycosis | Sampling area | Methodology used |
| superficial | nail plate | surface scraping |
| distal-lateral subungual | nail bed | section of the nail plate |
| nail plate | scraping of the nail bed, closer to the proximal edge | |
| proximal subungual | nail bed | section of the nail plate |
| periungual fold | nail dust obtained using a drill | |
| nail plate | biopsy (removal) of the nail | |
| scraping from under the removed part of the nail |
When should you get tested?
A fungal infection manifests itself differently in everyone. In more sensitive people, itching and burning immediately begins in the affected area, and redness of the skin appears. If you continue to ignore the unpleasant symptoms and do not test the nail for fungus before therapy, the plates become deformed, thicken, become covered with longitudinal or transverse grooves and stripes, take on an unpleasant hue, and emit a putrid odor.
Further:
- folds in the interdigital area crack;
- thickenings appear on the skin;
- severe, painful itching and burning appears;
- the nail becomes very fragile and brittle.
When the first signs of pathology appear, you will need to conduct an analysis for the presence of fungus on the nails.
Testing is also necessary when:
- the dermatologist doubts the diagnosis;
- the treatment, which may take a long time, does not give positive results, and the disease progresses;
- the course of treatment has ended, but there are doubts about the complete destruction of the infection;
- clinical manifestations of the fungus are still observed, although in a blurred form;
- the infection became chronic.
Diagnosis is required after therapy is completed.
Important! Clinical testing of biological material is prescribed to identify infections in the body. If fungal flora is present, systemic treatment is prescribed, since the use of external agents alone will be ineffective.
Types of tests for fungus
The following types of biomaterial are used to diagnose fungal diseases:
- Discharge of the genitourinary organs (analysis of semen and prostate secretions, smears from the urethra, uterine walls and cervical canal);
- Nail plate;
- Hair;
- Skin;
- Blood;
- Urine;
- Feces;
- Upper respiratory tract discharge (nasal and throat swab);
- Lower respiratory tract discharge (sputum);
- Discharge from wounds, ears and eyes;
- Bile;
- Puncture fluids (cerebrospinal fluid, articular fluid, pleural and abdominal effusion, etc.).
Preparing for analysis
Having decided on the problem, where the necessary tests can be taken and knowing the price of services, the patient needs to find out how the procedure goes and how to properly prepare for it.
Often the examination takes place in stages:
- the scraping is examined under a microscope;
- bacterial culture is carried out;
- do a PCR test;
- hemotest.
The biomaterial for study is particles of the affected nail and venous blood.
A scraping for nail fungus will be as informative as possible if you follow these recommendations before going to the laboratory:
- do not wash the affected areas with soap or other cosmetic detergents for three days before the test;
- do not use antifungal drugs during the same time;
- do not drink strong tea or coffee drinks 6 hours before testing;
- 10 days before the examination, do not cut your nails;
- remove decorative and medicinal varnish from the nail surface;
- Do not wet your hands/feet 4 hours before the test.
When taking a blood test for fungus, you need to consider that:
- 8 hours before testing you should not eat;
- do not drink alcohol for 48 hours;
- do not overwork and avoid severe stress;
- do not smoke before taking blood.
You also need to tell the laboratory assistant what medications the person is taking. You may have to stop taking some medications the day before.
Research methods
The fungus is detected using microscopy.
Research methods include:
- scraping for demodex;
- analysis for fungus detection.
In order to identify the pathogen, it is necessary to find out which of the four groups of pathogenic fungal infections it belongs to:
- Keratomycosis. Caused by pathogenic microorganisms that affect the upper layers of skin and hair, while the surrounding tissues are not involved in the inflammatory process.
- Epidermomycosis. It manifests itself as inflammation of the skin with deeper tissue damage.
- Trichomycosis. With insufficient attention to one's health and untimely treatment, the disease progresses and turns into purulent inflammation with the development of local changes.
- Dermatomycosis. It is observed in patients with a weakened immune system and metabolic disorders. Fungal microflora penetrates into the deep layers of the dermis, the disease most often affects children and elderly people with chronic pathologies.
Medical offers to sign up for diagnostics and tests. In our laboratory it is possible to take all types of tests in Tula. Tel. for recording.
The doctor visually assesses the patient’s condition in order to then prescribe the necessary diagnostic tests:
- General analysis of urine and blood.
- Scrapings from affected areas to determine mycotic infection.
- Collection and inoculation of biomaterial samples.
The collection of biomaterial is carried out by a laboratory assistant by grinding the nails in order to subsequently conduct a study to detect dermatophyte spores or pseudohyphae of mycelium. The basis of the study is microbiological analysis. Before treatment and during antifungal therapy, a dermatologist may prescribe a biochemical blood test to determine the development of a fungal infection.
For a comprehensive diagnosis of nail mycoses and making the correct diagnosis, a number of tests are carried out to determine:
- stage of the disease;
- how far the fungus has spread in the patient’s body;
- patient's sensitivity to drugs;
- degree of risks and complications.
Types of blood tests
Having discovered changes on the nail plates, you should find out their origin, which helps to analyze the nail for fungus.
Diagnostics includes several types of tests:
- PCR test (polymerase chain reaction);
- clinical and biochemical test of venous blood or urine.
Venous blood is collected in the manipulation room. The laboratory technician puts on sterile gloves and uses a vacuum tube with patient information labeled on it. Tubes with collected blood are sent to the laboratory for careful examination and evaluation of indicators.
Important! Diagnostic procedures should not be postponed for a long time, since fungal infection is extremely contagious and is characterized by rapid progression. It is transmitted through household contact and has a high index of contagiousness.
Bacteriological culture
By taking a bacteriological test to determine nail fungus using the culture method, you can determine the causative agent of onychomycosis. The laboratory assistant collects the necessary biomaterial and places it in a nutrient medium in which microbes begin to multiply intensively. The growth of pathogenic flora is maintained by a thermostat at a comfortable temperature for it. Fungal colonies grow within 3-14 days.
There are negative factors that affect the reliability of the survey:
- type of collected biomaterial. Fungi are rarely detected in the blood. They are mainly localized in scrapings from the affected plate;
- use of fungicidal oral medications on the eve of the examination. In this case, the analysis will give a false result.
Polymerase chain reaction
This is the most reliable nail fungus test, allowing you to identify the pathogens that cause the development of onychomycosis:
- Any biomaterial is suitable for the test;
- using this reaction, you can determine the DNA of the pathogen and identify its type;
- get reliable results within five hours after taking the test;
- the ability to detect even single pathogenic particles.
Despite its many advantages, the PCR method can give false results. This mainly happens when particles of an already destroyed pathogen are detected.
Hemotest
This is an assessment of blood parameters for the compatibility of foods with the body. Allowed foods should be included in a person’s menu, and junk food should be avoided or its consumption reduced to a minimum.
Testing is carried out after taking antifungal medications, when the mycosis has been completely overcome. This diagnostic procedure is considered an excellent prevention of both fungal and other diseases.
Urine examination
The urine of a healthy person should not contain fungal infections. Their identification means that a malfunction has occurred in the body, and the patient requires systemic treatment.
Laboratory methods can detect the following types of fungus in urine:
- moldy;
- yeast;
- radiant;
- candida.
To conduct tests for fungus, you must bring morning urine to the laboratory in a sterile container designed for this purpose.
Profile “Beauty of hair, nails, skin”
Hair
- Do not use medicated hair products 2 weeks before the test. Dyed, bleached, permed hair is not suitable for research.
- Hair should be clean and dry. Using scissors, cut one tuft of hair (the thickness of a match) from the occipital, temporal, parietal and frontal parts of the head.
- After this, place all the bundles in one envelope and seal it. Write your full name on the envelope. and research code.
Nail analysis
In case of external damage to the nail plate at any stage of the disease, analyzed for fungus:
- microscopy of scrapings (approximate price 600 rubles);
- sowing the fungus for nutritious flora (approximate cost 1550 rubles).
Test for mycosis
When learning how to get tested for nail fungus, you need to find out what material is used. Its careful examination will help determine the infection that affects the plates.
The test for mycosis is carried out as follows:
- Before figuring out how to get tested for nail fungus, the patient should see a dermatologist. The doctor examines the damaged nails and decides whether further diagnostics are needed. Sometimes an initial examination is enough to understand how advanced the pathology is and what drugs are needed to combat it;
- First, the plate is scraped to determine the etymology of the pathogen;
- then bacteriological culture is used to determine the degree of sensitivity of pathogens to antimycotics;
- Based on the results of the research, the specialist determines treatment tactics, which may include taking tablets, using creams, ointments, fungicidal varnishes, and folk remedies.
What is tank seeding?
Nail particles affected by the fungus are placed in a nutrient medium, where colonies of the pathogen begin to actively grow. At the same time, the resistance of the crop to fungicidal substances included in all antimicrobial preparations is determined. The resulting infections are treated with a certain type of drug and see how they react.
It is not advisable to prescribe fungicidal agents without this test, since other dermatological ailments affecting the skin of the hands and feet have similar clinical symptoms: eczema, vitamin deficiency, intoxication, etc. Also, the nail could be severely injured, and an infection could penetrate into the wound, causing severe swelling, redness and suppuration. In this case, antimycotics will not provide a therapeutic effect, but will only worsen the situation.
How is scraping performed?
The sample is taken with a medical spatula, with which the top layer is removed along the furrows or under the nail folds. Biomaterial is also collected under the nail itself. If a small part of the plate is affected, toenail and fingernail fungus is identified by scraping. If the lesion is large, cut off a piece of the nail.
Does scraping hurt?
Patients who are scheduled to have their nails tested for fungus by scraping are interested in whether the procedure is painful. Taking biomaterial this way does not hurt. The test is quick and painless. The resulting material is sent for bacteriological culture, which determines the presence of pathogenic flora.
What does the analysis show?
If a nail fungus test is carried out with blood donation, this is done so that the specialist can understand:
- whether inflammation occurs in the body;
- what stage is the pathological process at?
A biochemical examination shows the condition of the internal organs: liver, pancreas, kidneys. After all, fungi can affect not only the skin and nails, but also important systems of the body, gradually destroying and poisoning them. The pathological process negatively affects the mucous membranes, joints, ligaments, and bone tissue. In addition, this way you can determine which drug should be prescribed: local or oral.
Fungicidal drugs are processed by the liver, excreted by the kidneys and put a strain on the pancreas. To prevent drug therapy from aggravating their effects, it is necessary to conduct a blood test for the fungus. Microbiological examinations of the nail plate itself help to identify the pathogen and determine its sensitivity to drugs.
It is also recommended that the patient donate blood for culture. Normally, it should be sterile, without the presence of fungal flora. If a generalized fungal infection develops, elements of the pathogen are found in the bloodstream, and on the legs and arms the fungus will only be a symptom of the general pathological process. A clinical blood test is required both at the beginning and at the end of the therapeutic course, which helps to monitor treatment measures and determine the degree of their effectiveness.
A dermatologist explains how to get tested for nail fungus. He tells the patient how long the test takes and what specific tests will need to be performed. If a person does not remember what the test for fungal pathogens is called, they will be helped in the laboratory. There you can find out how much the procedure costs and when the results will be ready.
Can I do the test at home?
If it is not possible to carry out diagnostics in the laboratory, you can do an analysis for the presence of fungus at home:
- prepare a pink solution of potassium permanganate;
- put your feet or hands in it for three minutes;
- wipe the limb thoroughly;
- examine the nail plates: if they are yellowed, then there is no fungal infection. If the color of the nails has not changed, then this is a sign of developing onychomycosis.
With such a test it is impossible to determine the type of pathogen, but it is quite possible to suggest a diagnosis. Therefore, visiting a dermatologist and conducting a laboratory examination should not be postponed.
Some patients don't like going to hospitals. The reason for this is the lack of free time and long waits outside the offices. Also, few people want to voice their problem, because it is still believed that only unscrupulous people can get fungus on their nails. To make the examination as comfortable as possible, some private medical centers offer testing at home. A person will not need to waste time traveling and will not have to wait for his turn. Specialists come to your home, collect material, and send the result by mail.
If changes appear on the nail plate, it has lost its healthy shine, is covered with cracks, spots, or has changed color, then this may be a sign of a fungal infection or onychomycosis. When contacting a specialist, the patient is referred for an examination, which should not be refused. Using the results obtained, you can make an accurate diagnosis and determine what medications you need to use.
The procedure for taking material for nail fungus
In the laboratory, skin particles and material from under the nail plates are carefully removed by scraping. The procedure is painless, does not take much time, and sometimes requires repeated manipulations. The specialist assesses the condition of the nails, after which:
- Performs scraping - if there is initial detachment and brittleness of the nail.
- Uses material from the transverse hollow of the nail - if there are all signs of distal onychomycosis.
- Take a scraping from the inflamed area near the nail - if there is a visible lesion.
- Performs a biopsy of the material using a milling tool - in case of rejection of the nail plate.
After the procedure, the site where the material is taken should not be treated with anything unless the doctor himself recommends anything.