Psoriasis and modern methods of its treatment
Psoriasis (scaly lichen) is a chronic, very common skin disease, known for a long time. Its prevalence in different countries ranges from 0.1 to 3%. However, these figures reflect only the proportion of psoriasis in patients with other dermatoses or the frequency of its occurrence in patients with internal diseases. Since the disease is often localized and inactive, patients usually do not seek help from medical institutions and, therefore, are not registered anywhere.
The cause of the disease remains unclear. Despite the huge number of proposed hypotheses, none is generally accepted. Only the role of genetic factors has been clearly established - the family rate of patients is several times higher than the population one. There are indications of a connection between psoriasis and HLA system antigens - B13, B15, B16, B17, B27, B39, Dw11, DRW6, DR7, A1. There is evidence of the possible pathogenetic significance of the genetic markers Lewis, MN, Ss, Duffy, Hp.
The main pathogenetic link that causes the appearance of skin rashes is increased mitotic activity and accelerated proliferation of epidermal cells, leading to the fact that the cells of the lower layers “push out” the overlying cells, preventing them from becoming keratinized. This process is called parakeratosis and is accompanied by abundant peeling. Of great importance in the development of psoriatic lesions in the skin are local immunopathological processes associated with the interaction of various cytokines - tumor necrosis factor, interferons, interleukins, as well as lymphocytes of various subpopulations.
The trigger point for the onset of the disease is often severe stress - this factor is present in the anamnesis of most patients. Other trigger factors include skin trauma, medication use, alcohol abuse, and infections.
Numerous disorders in the epidermis, dermis and all body systems are closely related and cannot separately explain the mechanism of disease development.
There is no generally accepted classification of psoriasis. Traditionally, along with ordinary (vulgar) psoriasis, erythrodermic, arthropathic, pustular, exudative, guttate, palmoplantar forms are distinguished.
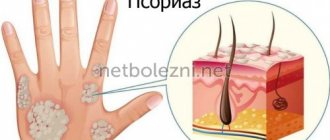
Normal psoriasis is clinically manifested by the formation of flat papules, clearly demarcated from healthy skin. The papules are pinkish-red in color and covered with loose silvery-white scales. From a diagnostic point of view, an interesting group of signs occurs when papules are scraped and is called the psoriatic triad. First, the “stearin spot” phenomenon appears, characterized by increased peeling when scraped, which makes the surface of the papules resemble a drop of stearin. After removing the scales, the phenomenon of “terminal film” is observed, which manifests itself in the form of a wet shiny surface of the elements. Following this, with further scraping, the phenomenon of “blood dew” is observed - in the form of pinpoint, non-merging droplets of blood.
The rash can be located on any part of the skin, but is mainly localized on the skin of the knee and elbow joints and the scalp, where the disease very often begins. Psoriatic papules are characterized by a tendency to grow peripherally and merge into plaques of various sizes and shapes. Plaques can be isolated, small or large, occupying large areas of the skin.
With exudative psoriasis, the nature of peeling changes - the scales become yellowish-grayish, stick together to form crusts that fit tightly to the skin. The rashes themselves are brighter and more swollen than with regular psoriasis.
Psoriasis of the palms and soles can be observed as an isolated lesion or combined with lesions in other locations. It manifests itself in the form of typical papulo-plaque elements, as well as hyperkeratotic, callus-like lesions with painful cracks or pustular rashes.
Psoriasis almost always affects the nail plates. The most pathognomonic is the appearance of pinpoint impressions on the nail plates, giving the nail plate a resemblance to a thimble. Loosening of the nails, brittle edges, discoloration, transverse and longitudinal grooves, deformations, thickening, and subungual hyperkeratosis may also be observed.
Psoriatic erythroderma is one of the most severe forms of psoriasis. It can develop due to the gradual progression of the psoriatic process and the fusion of plaques, but more often it occurs under the influence of irrational treatment. With erythroderma, the entire skin acquires a bright red color, becomes swollen, infiltrated, and there is abundant peeling. Patients are bothered by severe itching and their general condition worsens.
Radiologically, various changes in the osteoarticular apparatus are observed in most patients without clinical signs of joint damage. Such changes include periarticular osteoporosis, narrowing of joint spaces, osteophytes, and cystic clearing of bone tissue. The range of clinical manifestations can vary from minor arthralgia to the development of disabling ankylosing arthrosis. Clinically, swelling of the joints, redness of the skin in the area of the affected joints, pain, limited mobility, joint deformities, ankylosis, and mutilation are detected.
Pustular psoriasis manifests itself in the form of generalized or limited rashes, localized mainly on the skin of the palms and soles. Although the leading symptom of this form of psoriasis is the appearance of pustules on the skin, which in dermatology are considered a manifestation of a pustular infection, the contents of these blisters are usually sterile.
Guttate psoriasis most often develops in children and is accompanied by a sudden rash of small papular elements scattered throughout the skin.
Psoriasis occurs with approximately equal frequency in men and women. In most patients, the disease begins to develop before age 30. In many patients, there is a connection between exacerbations and the time of year: more often the disease worsens in the cold season (winter form), much less often in the summer (summer form). In the future, this dependence may change.
During psoriasis, there are 3 stages: progressive, stationary and regressive. The progressive stage is characterized by growth along the periphery and the appearance of new lesions, especially at the sites of previous lesions (isomorphic Koebner reaction). In the regressing stage, there is a decrease or disappearance of infiltration around the circumference or in the center of the plaques.
Vulgar psoriasis is differentiated from parapsoriasis, secondary syphilis, lichen planus, discoid lupus erythematosus, and seborrheic eczema. Difficulties arise in the differential diagnosis of palmoplantar and arthropathic psoriasis.
With vulgar psoriasis, the prognosis for life is favorable. With erythroderma, arthropathic and generalized pustular psoriasis, disability and even death are possible due to exhaustion and the development of severe infections.
The prognosis remains uncertain regarding the duration of the disease, duration of remission and exacerbations. Rashes can exist for a long time, for many years, but more often exacerbations alternate with periods of improvement and clinical recovery. In a significant proportion of patients, especially those not subjected to intensive systemic treatment, long-term, spontaneous periods of clinical recovery are possible.
Irrational treatment, self-medication, and turning to “healers” worsen the course of the disease and lead to exacerbation and spread of skin rashes. That is why the main purpose of this article is to give a brief description of modern methods of treating this disease.
Today, there are a huge number of methods for treating psoriasis; thousands of different drugs are used in the treatment of this disease. But this only means that none of the methods gives a guaranteed effect and does not cure the disease completely. Moreover, the question of cure is not raised - modern therapy is only able to minimize skin manifestations, without affecting many currently unknown pathogenetic factors.
Treatment of psoriasis is carried out taking into account the form, stage, degree of prevalence of the rash, and the general condition of the body. As a rule, treatment is complex, involving a combination of external and systemic drugs.
The patient’s motivation, family circumstances, social status, lifestyle, and alcohol abuse are of great importance in treatment.
Treatment methods can be divided into the following areas: external therapy, systemic therapy, physiotherapy, climatotherapy, alternative and folk methods.
External therapy
Therapy with external drugs is of utmost importance for psoriasis. In mild cases, treatment begins with local measures and is limited to them. As a rule, drugs for topical use are less likely to have any side effects, but are inferior in effectiveness to systemic therapy.
In the advanced stage, external treatment is carried out with great care so as not to cause deterioration of the skin condition. The more intense the inflammation, the lower the concentration of ointments should be. Usually at this stage, the treatment of psoriasis is limited to Unna cream, 0.5–2% salicylic ointment, and herbal baths.
At the stationary and regressing stage, more active drugs are indicated - 5-10% naphthalan ointment, 2-10% ASD ointment, 2-5% salicylic ointment, 2-5% sulfur-tar ointment, as well as many other methods of therapy.
In modern conditions, when choosing a method of therapy or a specific drug, the doctor must be guided by official protocols and formularies developed by the governing health authorities. The Federal Guide to the Use of Medicines (Issue IV) suggests steroid medications, salicylic ointment, tar preparations, and calcipotriol for topical treatment of patients with psoriasis.
Based on the “Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of the most common sexually transmitted infections and skin diseases” developed by the Central Scientific Research Institute of Medical Sciences in 2001, 1–2% salicylic ointment, ointments containing 5–10% tar, are used as external therapy. naphthalan 5–10%, vitamin D3, as well as corticosteroid ointments (betamethasone with salicylic acid, mometasone) and zinc pyrithioneate aerosol. The “Patient Management Protocols” developed by TsNIKVI scientists in 2003 recommend the same drugs.
We will focus mainly on the drugs indicated in the manuals.
Hydrating agents. Soften the flaky surface of psoriatic elements, reduce skin tightness, improve elasticity. They use creams based on lanolin with vitamins, Unna cream. According to the literature, even after such mild exposure, clinical effects (reduction of itching, erythema and peeling) are achieved in a third of patients.
Salicylic acid preparations . Typically, ointments with a concentration of 0.5 to 5% salicylic acid are used. It has antiseptic, anti-inflammatory, keratoplastic and keratolytic effects and can be used in combination with tar and corticosteroids. Salicylic ointment softens the flaky layers of psoriatic elements, and also enhances the effect of local steroids by enhancing their absorption, therefore it is often used in combination with them. Salicylic acid itself easily penetrates the skin and then into the blood. Therefore, it is not used on large surfaces and in concentrations greater than 2%, and in children even 2% ointment is applied only to limited areas of the skin. Intolerance is rare, but salicylic acid may cause increased skin inflammation as a side effect.
Tar preparations . They have been used for a long time in the form of 5–15% ointments and pastes, often in combination with other local drugs. In Russia, ointments with wood tar (usually birch) are used, in some foreign countries - with coal tar. The latter is more active, but, according to our scientists, it has carcinogenic properties, although numerous publications and foreign experience do not confirm this. Tar is superior to salicylic acid in activity and has anti-inflammatory, keratoplastic and anti-exfoliative properties. Its use in psoriasis is also due to its effect on cell proliferation. The use of tar preparations is limited due to the unpleasant odor; they cannot be applied to the face. Combinations of tar with zinc or salicylic acid do not have significant advantages over monocomponent tar preparations. Tar's ability to increase photosensitivity is used for combination therapy in combination with ultraviolet irradiation. Tar preparations should not be used for a long time and in high concentrations, as this can lead to absorption and systemic effects (kidney damage, general intoxication, paralysis). When prescribing tar preparations, one should take into account its photosensitizing effect and the risk of deterioration of kidney function in people with nephrological diseases.
To wash your hair, use shampoos with tar (Friderm-tar, T/gel).
Naftalan oil . A mixture of hydrocarbons and resins, contains sulfur, phenol, magnesium and many other substances. Naftalan oil preparations have anti-inflammatory, absorbable, antipruritic, antiseptic, exfoliating and reparative properties. To treat psoriasis, 10–30% naphthalan ointments and pastes are used. Naftalan oil is often used in combination with sulfur, ichthyol, boric acid, and zinc paste.
Local retinoid therapy . The first effective topical retinoid approved for use in the treatment of psoriasis is tazarotene. This drug has not yet been registered in Russia. It is a water-based jelly and is available in concentrations of 0.05 and 0.1%. In terms of effectiveness, it is comparable to potent corticosteroids. Side effects include itching and skin irritation. One of the advantages of this drug is its longer remission compared to GCS. Thus, according to J. Koo, 3 months after treatment, relapse was observed only in 185 patients (after fluocinonide - in 55%). The work of A. Marchetti shows the pharmacoeconomic advantages of tazarotene in the form of a 0.1% gel in comparison with fluocinonide ointment (local corticosteroids) and calcipotriene (a type of vitamin D3 for topical use).
Hydrantrons . In the first half of the 20th century. ointments were used with a mixture of natural anthracene derivatives - chrysarobin, which was obtained from the trunks of the Brazilian tree Vonacopua araroba of the legume family.
Currently, synthetic hydroxyanthrones are used in Europe and the USA - dithranol, anthralin, cignolin, anthrarobine.
Dithranol is an analogue of natural chrysarobin, has a cytotoxic and cytostatic effect, leads to a decrease in the activity of oxidative and glycolytic processes in the epidermis. As a result, the number of mitoses in the epidermis, as well as hyperkeratosis and parakeratosis, decreases. Unfortunately, dithranol has a pronounced local irritant effect, and if it comes into contact with healthy skin, burns can occur. On the other hand, dithranol is very effective and does not cause systemic side effects. Several years ago, drugs appeared in Europe that release dithranol only at human skin temperature (micanol). As a result, the coloration of the skin is weakened. Today, dithranol is used in fairly high concentrations (>1%), applied for 5–30 minutes. This method is not inferior in effectiveness to using the drug in low concentrations at night. According to the literature, the average remission during treatment with dithranol is 4–6 months.
Russian specialists rarely use drugs from this group; they are not produced in Russia and are not purchased abroad. Previously, several drugs in this group were offered - cygnoderm, ditrastik, psorax. They come in the form of a stick, like lipstick. The addition of paraffin allows drugs to be applied precisely to the affected area, which is especially convenient when treating limited, old lesions.
Drugs in this group include anthralin, which is used in European and American treatment centers. The drug inhibits the synthesis of nuclear and mitochondrial DNA, inhibits metabolism in tissues, which leads to a decrease in proliferation. When used, it strongly stains contacted surfaces and can cause irritation and burns.
Derivatives of mustard gas.
These include psoriasin and antipsoriaticum. They contain blister agents - mustard gas and trichlorethylamine. Treatment with these drugs is carried out with great caution, first using ointments with a small concentration on small lesions once a day. Then, if well tolerated, the concentration, area and frequency of use are increased. Treatment is carried out under close medical supervision, with weekly blood and urine tests. Now these drugs are practically not used, but they are very effective in the stationary stage of the disease.
Zinc pyrithioneate . An active substance produced in the form of aerosols, creams and shampoos under the trade name “Skin-cap”. It has antimicrobial, antifungal, and antiproliferative effects - it suppresses the pathological growth of epidermal cells in a state of hyperproliferation. The latter property determines the effectiveness of the drug for psoriasis. The drug relieves inflammation, reduces infiltration and peeling of psoriatic elements. Treatment is carried out on average for a month. For the treatment of patients with lesions of the scalp, aerosol and shampoo are used, for skin lesions - aerosol and cream. The drug is applied 2 times a day, shampoo is used 3 times a week. In Russia, since 1995, the clinical effectiveness and tolerability of all dosage forms of zinc pyrithioneate have been studied. According to the conclusion of the leading dermatological centers - TsNIKVI, RGMU, MMA, VMA - the effectiveness of the drug in the treatment of patients with psoriasis reaches 85–90%. Based on data published in periodicals by leading specialists from these and other centers, clinical cure can be achieved by the end of 3–4 weeks of treatment. The effect develops gradually, but it is very important that the results of treatment are obvious by the end of the first week from the moment of starting to use the drug - itching is sharply reduced, peeling is eliminated, and erythema turns pale. Such a rapid achievement of clinical effect leads, accordingly, to a rapid improvement in the quality of life of patients. The drug is well tolerated. Approved for use from 3 years of age.
Ointments with vitamin D3 . Since 1987, a synthetic preparation of vitamin D3, calcipotriol, has been used for local treatment. Numerous experimental studies have shown that calcipotriol inhibits the proliferation of keratinocytes, accelerates their morphological differentiation, affects the factors of the skin immune system that regulate cell proliferation, and has anti-inflammatory properties. There are 3 drugs of this group from different manufacturers on the Russian market. The drugs are applied to the affected areas of the skin 1-2 times a day. The effectiveness of ointments with D3 approximately corresponds to the effect of corticosteroid ointments of classes I, II, and according to J. Koo - even class III. When using these ointments, a pronounced clinical effect occurs in the majority of patients (up to 95%). However, to achieve a good effect it may take quite a long time (from 1 month to 1 year), and the affected area should not exceed 40%. I. V. Khamaganova reports positive experience with the use of calcipotriol in children. The drug was applied 2 times a day, a pronounced effect was observed by the end of the fourth week of treatment. No side effects were identified. V. A. Samsonov reports the same treatment results when using calcipotriol in adults.
Sometimes when using calcipotriol, skin irritation, dermatitis, photosensitivity, exacerbation of the psoriatic process, and hypercalcemia may occur. However, calcipotriol does not cause side effects characteristic of steroids, and sometimes provides a more lasting effect than ointments with corticosteroids. Although, according to the same J. Koo, relapses occur in more than 50% of patients, while the average duration of remission does not exceed 1.5 months.
More pronounced effects are achieved with the combined use of calcipotriol with any form of phototherapy, as well as with systemic therapy.
Corticosteroid drugs . They have been used in medical practice as external agents since 1952, when Sulzberger first demonstrated the effectiveness of external use of steroids. To date, about 50 glucocorticosteroid agents for external use are registered on the Russian pharmaceutical market. This undoubtedly makes it difficult to choose a doctor, who must have information about all drugs. A special survey conducted by N. G. Kochergin among dermatologists showed that when choosing products for external therapy, doctors proceed from the following data: the activity of the skin process, the localization of rashes, the age of the patient, the effectiveness of advertising and the cost of the drug in the pharmacy. The most commonly prescribed corticosteroids for psoriasis, according to the same survey, include combination drugs (flumethasone pivalate with salicylic acid), mometasone furoate or betamethasone dipropionate.
The therapeutic effect of external corticosteroids is due to a number of potentially beneficial effects:
- anti-inflammatory effect (vasoconstriction, resolution of inflammatory infiltrate);
- epidermostatic (antihyperplastic effect on epidermal cells);
- antiallergic;
- local analgesic effect (elimination of itching, burning, soreness, feeling of tightness).
Changes in the structure of GCS affected their properties and activity. This is how a fairly large group of drugs appeared, differing in their chemical structure and activity. Hydrocortisone acetate is practically not used today for psoriasis; it is used in clinical studies for comparison with newly produced drugs. For example, it is believed that if the activity of hydrocortisone is taken as one, then the activity of triamcinolone acetonide will be 21 units, and betamethasone - 24 units. Of the second class drugs for psoriasis, flumethasone pivalate in combination with salicylic acid is most often used, and the most modern are non-fluorinated corticosteroids. Due to the minimal risk of side effects, ointments and creams with aclomethasone are approved for use on sensitive areas (face, skin folds), treatment of children and the elderly, when applied to large areas of skin.
Among the drugs of the third class, one can distinguish a group of fluorinated corticosteroids - fluocinolone acetonide, triamcinolone acetonide, betamethasone valerate and dipropionate. A pharmacoeconomic analysis of the use of these drugs (though not for psoriasis), which consists of studying the price/safety/efficacy ratio, according to V. A. Akovbyan, revealed favorable indicators for betamethasone valerate - rapid development of the therapeutic effect, lower cost of treatment .
When treating psoriasis, you should start with milder drugs - hydrocortisone, prednisolone, aclomethasone, and in case of repeated exacerbations and ineffectiveness of the drugs used, give stronger ones. However, the following tactics are popular among American dermatologists: first, a strong GCS is used to achieve a quick effect, and then the patient is transferred to a moderate or weak drug for maintenance therapy. In any case, strong drugs are used in short courses and only on limited areas, since side effects are more likely to develop when they are prescribed.
In addition to this classification, drugs are divided into fluorinated, difluorinated and non-fluorinated drugs of different generations. Non-fluorinated first-generation corticosteroids (hydrocortisone acetate) compared to fluorinated ones are usually less effective, but safer in terms of adverse reactions. Now the problem of low effectiveness of non-fluorinated corticosteroids has already been solved - non-fluorinated drugs of the fourth generation have been created, comparable in strength to fluorinated ones, and in safety - to hydrocortisone acetate. These are, in particular, hydrocortisone butyrate, mometasone furoate, methylprednisolone aceponate. The problem of enhancing the effect of the drug is solved not by halogenation, but by esterification. In addition to enhancing the effect, this allows you to use esterified drugs once a day. For example, hydrocortisone butyrate has the following pharmacodynamic properties: inhibition of the migration of leukocytes and lymphocytes to the area of inflammation, inhibition of the proteolytic activity of tissue kinins, inhibition of fibroblast growth, prevention of the development of connective tissue in the area of inflammation. It is the fourth generation non-fluorinated corticosteroids that are currently preferred for topical use in psoriasis.
Standard side effects when using local steroids are the development of skin atrophy, hypertrichosis, telangiectasia, pustular infections, systemic action with an effect on the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal system. With the modern non-fluoridated medications mentioned above, these side effects are kept to a minimum.
Pharmaceutical companies are trying to diversify the range of dosage forms and produce GCS in the form of ointments, creams, and lotions. Fatty ointment, creating a film on the surface of the lesion, causes more effective resorption of infiltration than other dosage forms. The cream better relieves acute inflammation, moisturizes, and cools the skin. The fat-free base of the lotion ensures its easy distribution over the surface of the scalp without sticking the hair.
According to literature data, when using, for example, mometasone for 3 weeks, a positive therapeutic effect (reduction in the number of rashes by 60–80%) can be achieved in almost 80% of patients. According to V. Yu. Udzhukhu, the most favorable “efficacy/safety” ratio can be achieved when using hydrocortisone butyrate. The pronounced clinical effect when using this drug is combined with good tolerability - the authors did not observe any adverse reactions in any of the patients who underwent treatment, even when applied to the face. With long-term use of other corticosteroids, it was necessary to stop treatment due to the development of side effects. According to B. Bianchi and N. G. Kochergin, a comparison of the results of the clinical use of mometasone fuorate and methylprednisolone aceponate showed the same effectiveness of these drugs when used externally. A number of authors (E. R. Arabian, E. V. Sokolovsky) propose staged corticosteroid therapy for psoriasis. It is recommended to start external therapy with combination drugs containing corticosteroids (for example, betamethasone and salicylic acid). The average duration of such treatment is about 3 weeks. Subsequently, there is a transition to pure GCS, preferably of the third class (for example, hydrocortisone butyrate or mometasone furoate).
Patients are attracted by the ease of use of steroid drugs, the ability to quickly relieve the clinical symptoms of the disease, accessibility, and lack of odor. In addition, these medicines do not leave greasy stains on clothes. However, their use should be short-term to avoid worsening the course of the disease. With prolonged use of steroid ointments, addiction develops. Abrupt withdrawal of corticosteroids can cause an exacerbation of the skin process. The literature indicates different durations of remission after topical treatment with corticosteroids. Most studies indicate short-term remission - from 1 to 6 months. Research by R. Seville has established that GCS in combination with other methods (in particular, dithranol) increases the effectiveness of treatment, but reduces the duration of remission. Patients should be advised to avoid the use of corticosteroid ointments for as long as possible. In many foreign sources, ointments containing glucocorticosteroid hormones are recommended to be used preferably on limited open areas of the skin surface - face, hands. However, one should remember the danger of developing steroid perioral dermatitis or rosacea on the face, especially when using fluorinated corticosteroids.
For psoriasis, combinations of steroid hormones (most often betamethasone) with salicylic acid are most effective. Salicylic acid, due to its keratolytic and antimicrobial effects, complements the dermatotropic activity of steroids.
It is convenient to apply combination lotions with corticosteroids and salicylic acid to the scalp. According to domestic authors (G.I. Sukolin, V.A. Molochkov, N.S. Potekaev), the effectiveness of combined preparations reaches 80 - 100%, while skin cleansing occurs very quickly - within 3 weeks.
To summarize, it should be said that in practice, the doctor always needs to decide whether to use only external methods of treatment or prescribe them in combination with any systemic therapy in order to increase the effectiveness of treatment and prolong remission.
Yu. N. Perlamutrov , Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor A. M. Solovyov , Candidate of Medical Sciences MGMSU, Moscow
Pharmacological group of vitamin Milgamma
Agents that affect tissue metabolic processes. B vitamins (Milgamma) do not contain mineral complexes.
The active ingredients of the drug are B vitamins: B1 (thiamine), vitamin B6 (pyridoxine) and vitamin B12 (cyanocobalamin).
The choice of the form of administration of this medication into the body depends on the individual characteristics of the patient, whether ampoules with a solution or tablets
The active ingredients of Milgamma injections are B vitamins: B1 (thiamine), vitamin B6 (pyridoxine) and vitamin B12 (cyanocobalamin), as well as lidocaine, which has local anesthetic properties.
Milgamma tablets are intended for oral administration. Their composition is identical to the injection solution (B vitamins - active substances benfotiamine 100 mg, pyridoxine hydrochloride 1) and differs in the absence of lidocaine hydrochloride and the presence of excipients.
Side effects
Milgamma has a beneficial effect on the body, saturating it with essential elements and vitamins. But we must not forget that this is a medical drug and should be taken only as prescribed by a doctor. Before taking a course of taking the drug (whether it be tablets or injections), the doctor must make sure that the patient does not have an individual intolerance to one of the components of the drug
Side effects from taking Milgamma can be in the form of allergic reactions - rash, itching, as well as increased sweating, dizziness, arrhythmia or convulsions. All these phenomena can occur with sudden administration of the drug or if the dosage is not observed.
Reviews from patients and doctors about Milgamma
By analyzing the totality of the complex of vitamins that make up Milgamma, you can understand the benefits this drug brings to the human body. It is the B vitamins that have a positive effect on the overall strengthening of the immune system and have a powerful therapeutic effect in the treatment of diseases of the central nervous system and musculoskeletal system. Thanks to the use of Milgamma, specialists achieve quick relief from acute pain; the treatment brings a long-term positive effect. In addition, experts recommend taking Milgamma vitamins for various diseases of internal organs, since this replenishes the elements and nutrients that a weakened body lacks.
What is it prescribed for?
Milgamma contains B vitamins.
B vitamins are fat-soluble substances that play a major role in the cellular metabolism of the body and are involved in all vital processes. The group of vitamins B includes the main components of the drug Milgamma - vitamin B1 (thiamine), B6 (pyridoxine) and B12 (cyanocobalamin). Each of the components of the Milgamma vitamin complex plays its own important role.
Vitamin B1 (thiamine)
Thiamine (B1) is responsible for normalizing carbohydrate metabolism in internal organs (liver, brain and living tissues). In addition, it is involved in the production of fatty acids and optimizes amino acid metabolism. An important function of thiamine is that it effectively reduces inflammation of the skin and improves the condition of the mucous membranes. Thiamine is involved in hematopoiesis and in the process of cell division, preventing the aging process of the body.
Thiamine is prescribed by specialists in the following cases:
- with liver disease;
- if the endocrine system is disrupted (consequences of obesity, diabetes);
- for eczema, psoriasis, pyoderma;
- in case of malfunction of the kidneys, brain and central nervous system;
- for gastritis, ulcers, pancreatitis and other gastrointestinal diseases.
Vitamin B6 (pyridoxine)
Pyridoxine (B6) is a water-soluble element that regulates metabolic processes and normalizes blood circulation. Pyridoxine is involved in the synthesis of molecules and the breakdown of carbohydrates. In addition, vitamin B6 reduces the risk of obesity, diabetes and the development of cardiovascular diseases. The level of cholesterol in the human body depends on the amount of vitamin B6. The role of vitamin B6 is indispensable in the synthesis of new red blood cells, i.e. this component is actively involved in the restoration of hematopoietic function. Like the other vitamins of the Milgamma complex, vitamin B6 affects the strengthening of the human immune system. In addition, a sufficient amount of pyridoxine protects against depression, relieves anxiety, and ensures calm.
Vitamin B6 is prescribed:
- patients with atherosclerosis, anemia and diabetes;
- pregnant women with toxicosis;
- teenagers with problems with improper functioning of the sebaceous glands.
Vitamin B12 (cyanocobalamin)
Cyanocobalamin (B12) helps accelerate the breakdown of proteins, fats and carbohydrates. Responsible for the synthesis of leukocytes, which are involved in protecting living tissues from foreign elements. Reduces cholesterol levels in the human body. Vitamin B12 helps normalize sleep and optimize the production of melatonin, the sufficient amount of which determines the sleep-wake cycle.
Indications for the use of cyanocobalamin are as follows:
- radiculitis;
- cirrhosis of the liver;
- polyneuritis;
- skin diseases (dermatitis, psoriasis);
- radiation sickness;
- bone injuries;
- acute and chronic hepatitis;
- bone injuries;
- radiculitis and others.