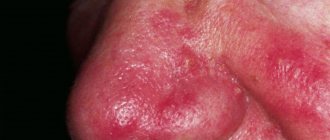
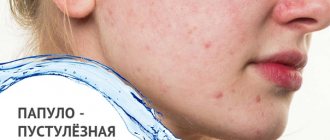
Spregal is prescribed for demodicosis to achieve maximum effect during therapy. This parasitic skin disease is caused by Demodex mites. It is largely asymptomatic, but if the necessary conditions are created for the reproduction of mites, then demodicosis appears on the face in the form of skin inflammation, rash, itching and peeling. It is worth considering that Spregal should be taken by all family members who are in close contact with a carrier of parasites.
Description of the disease
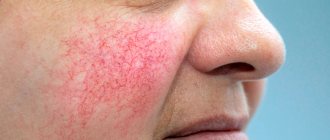
Damage to the smooth surface of the skin and hair by the demodex mite is medically called demodicosis. The first manifestations of the disease appear in the form of skin rashes, ulcers, acne on the back, chest and dermis of the face. As the disease progresses, the skin loses its natural pink tint and acquires a grayish color. At risk of developing demodicosis are people who are exposed to constant stress, nervous strain, as well as those who have weak immunity and a tendency to skin diseases.
Provoking factors include frequent visits to the steam room, eating spicy foods in large quantities, prolonged exposure to sunlight and the use of hormonal-based cosmetics. Those with sensitive and loose skin that is prone to redness are more susceptible to mite infection. A distinctive feature of the described disease is the inflammatory processes of the skin of the face, which, if observed, should immediately begin treatment measures. To do this, the patient needs to consult with a specialized doctor and, if necessary, undergo a diagnostic examination.
General information about the medicine
Spregal aerosol can also be used for the treatment of demodicosis.
The combined drug "Spregal", intended to eliminate scabies, can be used to treat demodicosis - a disease characterized by damage to the skin or hair of the body by a mite-like parasite. Due to its composition, this medication is considered highly effective, it is well tolerated by patients and can be used even by newborns. The dosage form of “Spregal” makes the antiparasitic medicine convenient to use and economical, so one bottle can be used by 3 people at once.
The pharmaceutical product "Spregal" contains 2 active components: esdepalletrin and piperonyl butoxide. Additional substances are:
- macroglycerides;
- ethanol;
- propellant HFA 134a;
- monoethyl ether;
- oleyl macrogol glycerides.
After the drug penetrates the body, its maximum concentration in the blood plasma is observed after an hour. After a day of presence of the components of “Spregal” in the blood fluid, its indicators in the blood are minimal or not determined at all. After another 2 days, no traces of its presence in the patient’s blood plasma are detected at all.
Keep the medication “Spregal” in a dry room at a temperature that should not exceed 25 degrees Celsius. The medicine should be stored away from direct sunlight and small children. If all conservation conditions are met, the shelf life of the antiparasitic drug in question is 2 years.
Analogues of the drug
Ointment "Benzyl benzoate" is a medication similar in action to the treatment of demodicosis.
If treatment of demodicosis with the antiparasitic drug “Spregal” is impossible for some reason, then a specialized physician can prescribe a medication with a similar effect. However, it is worth considering that due to the unique composition, which includes 2 active components at once, the described medication has no structural analogues for the active substance. According to the pharmacological group, the following synonyms are presented:
- "Yurax";
- "Belogent";
- "Sodium thiosulfate";
- "Benzyl benzoate".
Treatment of patients with rosacea complicated by demodicosis
The article discusses diseases caused by the Demodex mite and the principles of their therapy. The results of treatment of patients with rosacea complicated by demodicosis are presented, demonstrating the effectiveness of including Demoten gel in complex therapy.
Rice. 1. Patient S. before treatment (A) and five days after treatment (B)
Rice. 2. Dynamics of clinical manifestations of diseases during treatment
The causative agent of demodicosis is the iron mite. Currently, out of 65 species and several subspecies of this mite, only two have been found in humans: Demodex folli culorum
and
Demodex brevis
.
D. folliculorum
was first identified in 1841,
D. brevis
- in 1963. The first species is most often identified.
The tick's habitat is considered to be hair follicles, sebaceous glands, and meibomian glands. D. brevis
has a wider distribution on the skin of the body.
Mite D. folliculorum
, as a rule, is found in the upper part of the pilosebaceous canal in numbers ≤ 5 organisms/cm2.
D. brevis -
in the sebaceous glands and ducts.
Mites use sebum as a food source.
According to various authors, 55–100% of the population are carriers of the iron worm, although clinical manifestations of such carriage may be absent. So, N.I. Syuch (2004) established carriage of the parasite in 89% of patients. At the age of 30–44 years, the disease is detected in 42.6% of subjects; the average age of women is 44.5 ± 2 years, men – 38.3 ± 5.4 years [1].
Tick carriage in healthy individuals at different ages is 19.3–61.2% [2].
In infants and children, due to low sebum production, Demodex
insufficient. Adolescents and young adults also have a low prevalence of mites. It increases in the population from 20 to 60 years of age and remains stable after reaching 80 years of age [3].
The prevalence of ticks is higher among men than among women (23 versus 13%). In addition, D. brevis
(23 vs. 9%, respectively).
Because the Demodex
found on healthy skin, it can be considered an opportunistic parasite. Under normal conditions, it is located within the basement membrane of the epidermis [4].
The fertilized female lays diamond-shaped eggs at the mouth of the follicle. Demodex development cycle
lasts 15 days in the skin. The optimal temperature for tick development is 30–40 °C. At 14 °C, torpor occurs, at 52 °C, death occurs. A tick can live in water for up to 25 days, in dry air only a day and a half. The most favorable nutrient media for it are vegetable oil, fat, and petroleum jelly [5].
Outside the host, tick reproduction stops [6]. However, even then it can remain viable for up to nine days in the presence of darkness, constant humidity and room temperature.
Infection occurs directly from a person (carrier or patient) or indirectly - through underwear or bed linen. Some authors do not exclude the possibility of infection from domestic animals.
Under the influence of certain factors, ticks can become pathogenic organisms. We are talking, in particular, about dysfunction of the sebaceous glands and changes in the composition of sebum, diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, liver, nervous system, dysfunction of the endocrine glands, long-term use of topical glucocorticosteroids [7]. A change in the ratio of opportunistic skin flora can also serve as a trigger for the development of demodicosis [8]. It is known that D. folliculorum
may participate in the development of the disease if its number exceeds 5 organisms/cm2 [9].
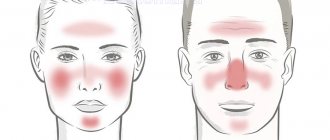
Currently, two forms of demodicosis are distinguished. Primary demodicosis develops on externally unchanged skin. Secondary demodicosis is a complication of the underlying disease (rosacea, perioral dermatitis, etc.) [4]. As a rule, a combined course of the disease is observed.
Objective signs of demodicosis are accompanied by itching, burning, slight pain in the area of the rash, a feeling of skin tightness, and a decrease in its elasticity and softness [10].
The diagnosis is made on the basis of the clinical picture and the detection of mites in the contents of pustules, the secretion of the sebaceous glands, in scrapings and scales from lesions [7]. It is important not only to establish the presence of mites, but also to determine their number [4].
Question about the role of Demodex
in the development of various diseases of the skin and mucous membranes, including rosacea, remains controversial [11, 12]. Previous studies have demonstrated a higher number of mites per 1 cm2 in patients with rosacea [13] than in patients with seborrheic dermatitis and acne.
On the surface of Demodex
Bacillus oleronius
bacteria have been identified that can stimulate the inflammatory response and growth of
Streptococcus
and
Staphylococcus
. As a result, conditions are created for their reproduction [14]. In the presence of various favorable factors, mites begin to actively reproduce, destroying the epithelium of the follicles and penetrating into the dermis. As a consequence, an inflammatory reaction is triggered and the course of dermatoses is aggravated [15, 16].
Treatment of demodicosis
Therapy for demodicosis should be gradual. One of the first stages is carrying out sanitary and hygienic measures [17].
When choosing drug therapy, it is necessary to take into account the clinical picture of the disease, the type of mites, their number, as well as the presence of concomitant pathology: rosacea, perioral dermatitis, acne, etc.
For use against Demodex
acaricidal agents are used, which include derivatives of the nitroimidazole group.
The structural features of tick integument necessitate long-term courses of antiparasitic therapy and the selection of drugs with a minimum molecular size.
The treatment regimen also needs to include symptomatic, anti-inflammatory, antibacterial, and desensitizing drugs.
Gel Demoten
Demodicosis rarely occurs as an independent disease, so the creation of products for the treatment of skin pathologies complicated by demodicosis and the care of such skin remains relevant.
More recently, a new product has appeared on the pharmaceutical market - Demoten gel. It contains sulfur, hyaluronic acid, aloe vera juice, polyvinylpyrrolidone.
Sulfur has antiseptic, antiparasitic, anti-inflammatory effects and helps normalize the proliferation of epidermal cells.
Hyaluronic acid moisturizes the skin, increases its elasticity, and stimulates epidermal renewal.
Aloe vera juice contains a large number of biologically active substances: simple sugars, polysaccharides, amino acids, enzymes, minerals, organic acids, a complex of vitamins A, C, E. Its inclusion in the gel improves the condition of the skin, promotes cell regeneration, and provides an antiseptic effect.
Polyvinylpyrrolidone has a sorbing and detoxifying effect. As a result, the skin is well cleansed.
Application experience
We observed 23 patients: 14 patients diagnosed with “papulopustular form of rosacea”, 9 patients with “erythematous form of rosacea”. The age of patients is from 39 to 67 years. Of these, 11 are men and 12 are women.
The patients were divided into four groups. The first group consisted of four patients with erythematous rosacea who received only basic therapy, the second - five patients with the same diagnosis who received accompanying therapy in addition to basic therapy, the third - five patients with papulopustular rosacea on basic therapy, the fourth - nine patients with a similar diagnosis on basic and accompanying therapy.
All patients underwent laboratory testing for the presence of D.
folliculorum
. From six to ten individuals were found in the preparation.
Complex therapy for erythematous rosacea involved the use of azelaic acid in the form of a gel or metronidazole in the form of a gel once or twice a day, depending on the severity of clinical symptoms. Demoten gel was used as accompanying therapy twice a day (morning and evening).
Treatment of papulopustular rosacea at the first stage included the use of systemic and topical medications. The first includes the antibiotic doxycycline (at a dose of 100 mg twice a day for ten days), the second includes the antiparasitic drug metronidazole gel (once or twice a day) and Demoten gel. Demoten gel was applied 15–20 minutes after metronidazole.
Three to five days after the start of therapy, the severity of skin manifestations decreased significantly in patients of the second and fourth groups. In particular, hyperemia, swelling, and itching decreased (Fig. 1). The dynamics of clinical manifestations of hyperemia and swelling during therapy in four groups are presented in Fig. 2.
At the second stage of treatment for papulopustular rosacea, patients of the fourth group continued to use Demoten gel.
Repeated laboratory testing for the presence of Demodex mites,
carried out ten days from the start of treatment, showed a decrease in the number of individuals in the preparation to one to three.
During two months of observation, no exacerbations of the disease were recorded.
Considering that strong antiparasitic agents were not used in therapy and the number of mites in the preparations was reduced, we can conclude that Demoten gel has a persistent antiparasitic effect.
Conclusion
The use of Demoten gel in the complex therapy of rosacea complicated by demodectic mange allows you to quickly achieve positive dynamics. This drug can be prescribed long-term for various forms of rosacea, which ensures an increase in the period between relapses.
How to use Spregal for demodicosis
“Spregal” is used for demodicosis of the face in order to quickly achieve the maximum effect from the therapeutic course. For a medicine to be truly effective, it is important to use it correctly. The product is applied to the face, previously cleaned of dust and dirt. The entire surface of the skin is treated, and not selectively affected areas. It is important to carry out antiparasitic measures for all family members living with the carrier of the infection.
The aerosol, due to the risk of contact with the eyes, should be sprayed onto a cotton pad and wiped over the skin of the face.
It should be borne in mind that “Spregal in the form of a facial spray is not used due to the risk of contact with the eyes; it is sprayed onto a cotton pad and wiped over the skin. All other parts of the body are treated with the medicine according to the instructions. It is recommended to treat demodicosis in the evening, preferably after 18:00. Like all sprays, when using Spregal, you need to be careful, namely:
- stay away from fire;
- ensure unimpeded flow of air into the room;
- Before spraying the bottle, remove clothes and place a cloth or towel under your feet;
- Apply the spray from a distance of at least 20 cm, avoiding the eye area and hair.
After treatment of demodicosis has been carried out, you cannot take bathing procedures for 12 hours. After the time has passed, you should wash with soap and rinse thoroughly under running water. If you used Spregal on your face, you also need to wash your face with soap and thoroughly rinse your face with water.
Security measures
Before using Spregal in the form of a spray, you should familiarize yourself with its safety rules:
- Do not point the bottle with the medicinal solution towards the mouth, eyes and nose.
- If the medicine gets into your mouth, eyes or nasal cavity, you should rinse them with plenty of water.
- Do not swallow or inhale sprayed medication.
- Do not smoke when using the medicine.
Treatment of demodicosis of the eyes
It should be kept in mind that demodicosis of the eyes is caused by parasites, and the disease will not go away on its own. It must be treated over a long period. If you do not follow all the doctor’s instructions, demodicosis quickly becomes chronic, which is more difficult to treat. The insidiousness of the disease is that after some time the external signs of the disease disappear, but repeated self-infection may occur.
Therefore, treatment of demodicosis is quite long and includes a number of measures, including the following:
- compliance with personal hygiene rules, disinfection of bed linen;
- treating the eyelids with special products, cleaning the skin from crusts and plaque;
- treating the base of the eyelashes with drops or bactericidal gel;
- regular application of medicinal ointment prescribed by a doctor to the eyelids;
- regular massage of the eyelids and removal of discharge along with mites;
- the use of physiotherapeutic methods - magnetic therapy, electrophoresis, etc.;
- following a diet excluding sweets, spicy and salty foods;
- increasing immunity, eliminating foci of chronic infection.
Contraindications
Pregnancy is one of the contraindications for the treatment of demodicosis with the drug "Spregal".
It is not recommended to use the described medicine for the treatment of a disease caused by demodex mites in patients with obstructive bronchitis and bronchial asthma. Antiparasitic medicine is contraindicated during pregnancy and during breastfeeding, as well as in case of individual intolerance to its components. If contraindications are neglected, then taking the medication will negatively affect the patient’s condition, aggravate the disease and provoke side effects.