Author of the article:
Soldatova Lyudmila Nikolaevna
Candidate of Medical Sciences, Professor of the Department of Clinical Dentistry of the St. Petersburg Medical and Social Institute, Chief Physician of the Alfa-Dent Dental Clinic, St. Petersburg
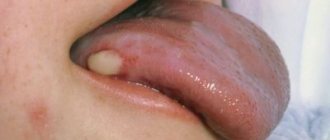
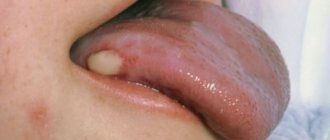
The appearance of purulent formations on the gums is one of the most common complications of various diseases and pathological conditions of the oral cavity, in particular caries and tartar. In dentistry, an abscess on the gum is called an “abscess,” but in everyday life such formations are often called “abscesses.”
Often the patient is not even aware of the appearance of an abscess - in the initial stages of development, the formation can make itself known only by slight redness and soreness of the gums, bleeding when brushing teeth or chewing solid food. However, ulcers, like many other infectious diseases, are characterized by a long course and development, which often leads to more serious complications. One of the most dangerous consequences of this disease is sepsis - blood poisoning. If the course of the disease is unfavorable, sepsis can even lead to death, so you should not delay solving the problem. You will learn about what to do if an abscess appears on your gum from our material.
Why did an abscess appear on the gum?
The main, main cause of abscesses is the penetration of infection into the gum tissue. In this case, a reaction of the body’s defenses occurs: leukocytes that destroy hostile cells die, and a large amount of pus accumulates at the site of infection. As a result, a pus-filled sac forms in the gum tissue, which can gradually increase in size and eventually rupture. Infection can enter the gum tissue in a variety of ways. In addition, the formation is promoted by the presence of diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, immune system, permanent plaque on the teeth and tongue, and smoking.
There are many factors that increase the risk of developing abscesses inside the oral cavity, but ultimately all the reasons come down to two main ones:
- Periodontitis
Periodontitis is a disease in which a focus of infection forms at the very root of the tooth (usually at the apex). The development of periodontitis is caused by untreated caries and advanced pulpitis (inflammation of the soft tissues of the tooth). Often, the infection penetrates into the tissue surrounding the tooth root during dental procedures and manipulations - for example, when the dental canals are not completely cleaned during the treatment of pulpitis or when the filling is not dense enough. The development of periodontitis is also facilitated by the presence of chronic infectious diseases that cause a steady decrease in the activity of the body's defenses, stress and overwork, and the presence of bad habits. Infectious foci often arise under crowns when they are installed poorly.
Sometimes periodontitis can affect two teeth at the same time. Most often, when this disease occurs, patients complain of severe pressing, aching, acute pain and swelling, but in some cases these symptoms may be absent. Over time, pus accumulates inside the gums, and the cavity containing it expands to the boundaries of the outer mucous membrane of the gums. As a result, an “abscess” or fistula (a small hole through which pus comes out) may form on its surface.
A common result of periodontitis is the appearance of cysts or granulomas - benign formations associated with changes in the structure of the tissues of the oral cavity. To diagnose such conditions, X-ray examination is used, which often makes it possible to detect the disease in the early stages of development and prevent the formation of an abscess. However, due to the latent course of the disease in the initial stages, diagnosis is sometimes difficult: often the presence of infection in the root apex is discovered by chance, when examining other teeth.
The release of pus to the surface of the gum and the formation of an abscess on the gum in the mouth is most often accompanied by acute pain. However, if inflammation on the gums does not hurt, this does not mean that the disease is progressing favorably and you can postpone a visit to the dentist. The absence of pain is usually due to the fact that when a fistula or abscess forms, the pressure of pus on the root and nerve of the tooth decreases. But the main cause of the disease, the focus of chronic infection, still persists. In addition, ulcers without pain often turn out to be formations of other types - for example, wen or benign tumors.
If a white abscess forms on the gum, this usually indicates the presence of a focus of inflammation deep in the gum, at the root of the tooth. Due to the deep location of the infectious focus, characteristic signs of inflammation are often absent.
- Periodontitis
Periodontitis is a disease in which “pockets”, areas of sagging gum tissue, form between the lower edge of the teeth and the gums. As a result, cavities are formed in which food debris and bacterial mass accumulate. All this creates the most favorable conditions for the emergence of a focus of infection, which subsequently leads to inflammation.
As a result of the constant presence of pathogenic microorganisms, the part of the gum adjacent to the tooth becomes inflamed, becomes red and swollen, and may bleed when brushing or applying pressure. The deepening of the gum pocket against the background of the constant presence of a source of infection leads to the accumulation of pus in it, as a result of which an abscess is formed.
Unlike periodontitis, with periodontitis the source of inflammation is not deep in the gums, but on the surface. Therefore, even with a simple examination, you can detect characteristic signs of inflammation: swelling and redness. Since periodontitis pockets often form on several or even all teeth of the jaw, the abscesses caused by this disease can also be multiple.
Diagnostics
Before proceeding with dental flux treatment, the doctor must conduct an appropriate diagnostic examination. The exact diagnosis is determined based on data obtained during a clinical examination and x-ray diagnosis. Laboratory tests allow you to accurately determine the stage of the inflammatory process. Only after making an accurate diagnosis will a specialist be able to decide what to do with gumboil and which method of treatment in this particular case will be optimal.
Complications
In the absence of timely and high-quality treatment, the disease can cause serious complications. A frequent consequence of suppuration during periodontitis is periodontal disease, a disease characterized by the formation of very deep gum pockets and the spread of foci of infection and suppuration throughout the gums. Over a long period of time, periodontal disease usually leads to loosening of teeth and their loss. In addition, inflammation can lead to the formation of gumboil, a large abscess that causes the gums and cheek to swell and lose their natural shape. Treatment for flux usually requires surgery.
The presence of a constant source of infection in the body negatively affects the functioning of all organs and systems, in particular the functioning of the immune system. Abscesses and other chronic infectious diseases lead to a steady decrease in immune status, which creates favorable conditions for the development of a whole range of diseases.
We should not forget that the muscles and nerves of the face are located in close proximity to the gums. For example, the formation of a large abscess on the gingival part of the upper jaw can lead to damage to the trigeminal nerve, which innervates the nasolabial triangle. Sharp pain of a neurogenic nature, paresis and paralysis of the facial muscles are rare, but still probable consequences of gingival abscesses.
What to do after removal or opening?
After opening the flux, you should not wait for the swelling to disappear immediately. Many patients feel that the flux does not go away after tooth extraction, although this is not the case at all. In some cases, the swelling may increase slightly after the procedure. Approximately on the third day after surgery, the patient should make a dramatic recovery, but the infiltration may remain for quite a long time. Within a few hours after the operation, the toothache in the area of the lesion should disappear and the body temperature should decrease.
Usually the swelling goes away only a few days after opening the purulent focus. Do not be alarmed if the swelling increases slightly after surgery.
The specialist installs a special rubber drainage in the incision, which you should never try to fix yourself. Otherwise, the recommendations are the same as for regular tooth extraction. You should not eat for several hours after the procedure. During the day, try to avoid hard and rough foods, as well as hot drinks. Regarding the use of medications in each individual case, the specialist gives individual recommendations.
How to cure an abscess on the gum?
Treatment for this disease should include not only the elimination of inflammation, but also the causes that caused it: periodontitis, periodontitis, tartar or plaque, and somatic diseases. The treatment regimen largely depends on the reasons for the formation of an abscess on the gum and the presence of concomitant diseases.
The first stage of treatment consists of sanitation of the oral cavity. The dentist conducts a thorough examination of the abscess and opens it surgically to ensure the drainage of pus (if the abscess on the gum has ruptured, this procedure is not required). The operation is usually performed under local anesthesia. The cavity is cleaned and treated with disinfectants. If possible, other sanitation procedures are also carried out at this stage: caries is treated and carious cavities are filled, plaque and tartar are removed, and sometimes professional teeth cleaning is performed. This is necessary in order to eliminate all sources of infection inside the oral cavity, which may cause re-infection and the formation of new abscesses.
If the source of infection is a focus of inflammation in the root apex, additional surgical treatment may be required: removal of the granuloma or cyst, refilling of the canals, or resection (removal) of the root apex. In the most severe cases, the tooth that served as the source of infection is removed. If there are signs of periodontitis or periodontal disease, the patient is referred for consultation and treatment to a specialist - a periodontist.
After opening and disinfection, the patient is most often prescribed antibiotics and disinfectant rinses to prevent secondary infection and allow the cavity to heal. Drugs that accelerate tissue regeneration can be added to the treatment regimen.
The best way to avoid lengthy and costly treatment is to take preventive measures. You can significantly reduce the risk of ulcers forming on your gums by regularly brushing your teeth with a brush and floss, and using disinfectant rinses. It is necessary to conduct regular preventive examinations at the dentist, as well as independently monitor the condition of the gums.
ASEPTA Active mouth rinse will be a reliable assistant in the treatment of gum inflammation. This unique product contains:
- Benzydamine, which has anti-inflammatory and local anesthetic effects, which may be accompanied by a feeling of numbness. Benzydamine is absorbed through mucous membranes and penetrates into inflamed tissue. Reduces pain sensitivity at the site of inflammation.
- Chlorhexidine, active against vegetative forms of gram-negative and gram-positive microorganisms, yeast, dermatophytes and lipophilic viruses.
Treatment
Depending on whether a permanent or baby tooth caused a lump on the child’s gum , the doctor carries out appropriate treatment. If a permanent tooth is damaged, seek help immediately while there is a chance to save the child’s tooth. The doctor will have to remove the nerve and fill the canals. In this case, adult dental treatment is a necessity, because if high-quality treatment and appropriate treatment are not carried out, the child may lose a tooth.
Milk teeth are removed immediately - their root system has not yet had time to form, and it is impossible to properly fill the canals. In addition, if a diseased tooth is left, the molar may grow back with defects (stains, damage.
At the Family Dentistry Center, you can remove a child’s tooth without pain or fear. All procedures in the clinic are performed under medical sedation. While the baby is sleeping peacefully and does not feel pain or discomfort, the doctor can carry out all the necessary procedures. Being able to treat your teeth while you sleep is a great way to cope with dental phobia.
Clinical trials
According to the results of clinical trials of the ASEPTA rinse after 3 weeks of use of the rinse, gum bleeding is reduced by 28.3%, inflammation is reduced by 32.3% and the hygienic condition of the oral cavity is improved by 33.5%.
Sources:
- Clinical experience in using the Asepta series of products Elena Ivanovna Fuchs, assistant at the department of therapeutic and pediatric dentistry. State budgetary educational institution of higher professional education Ryazan State Medical University named after Academician I.P. Pavlova of the Ministry of Health and Social Development of the Russian Federation (GBOU VPO RyazSMU Ministry of Health and Social Development of Russia)
- The use of adhesive balm "Asepta®" in the treatment of inflammatory periodontal diseases L.Yu. OREKHOVA, Dr. med. Sciences, Professor, Head of Department V.V. Thermal Power Plant, Dr. med. Sciences, Professor, Head of Department S.B. ULITOVSKY, Dr. med. Sciences, Professor A.A. LEONTIEV, dentist A.A. DOMORAD, O.M. YAKOVLEV SPbSMU named after. acad. I.P. Pavlova, St. Petersburg - *Department of Therapeutic Dentistry, Department of Microbiology
- The use of new anti-inflammatory drugs in the complex of therapeutic and preventive measures for periodontal diseases (E.D. Kuchumova, A.A. Leontyev, O.V. Kalinina, L.Yu. Orekhova, S.B. Ulitovsky) E.D. Kuchumova, Ph.D., Associate Professor, A.A. Leontyev, dentist, O.V. Kalinina, dentist, L.Yu. Orekhova, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor, Head of Department, S.B. Ulitovsky, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Prof. Department of Therapeutic Dentistry of St. Petersburg State Medical University named after. acad. I.P. Pavlova
- Evaluation of the effectiveness of treatment of chronic generalized periodontitis of mild and moderate severity using Asepta antibacterial agents (S.I. Gazhva, A.I. Voronina) S.I. Gazhva, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Prof., Head of Department A.I. Voronina, PhD, dentist. Department of Dentistry FKPV GOU VPO "Nizhny Novgorod State Medical Academy"