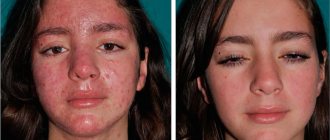
Skin diseases are accompanied not only by pain and severe discomfort, but also by the risk of unaesthetic scars or scars appearing on the skin. Therefore, it is extremely important to promptly contact a dermatologist who can diagnose the disease at an early stage and prescribe effective therapy. Our medical center provides the opportunity to receive qualified medical care, as a result of which it is possible to accurately diagnose and eliminate signs of skin damage. One of the most common problems with which patients come in this direction is demodicosis. This is a rather dangerous and problematic pathology, which is almost impossible to cope with on your own.
What is this?
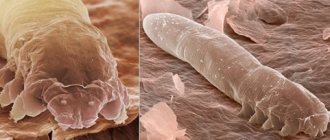
Demodicosis in humans develops as a result of reproduction in the hair follicles, sebaceous glands of the skin and meibomian glands of the iron mite (Demodex). The breeding ground for the development of this parasite is sebum, so its main habitat is the skin of the face and external ears. But with a complicated course and lack of timely treatment, the skin of the chest and back is involved in the pathological process.
It is important to understand that healthy people can also be carriers of such a tick, since it is a representative of normal microflora. According to official statistics, about 60% of people are infected with Demodex, but not everyone develops this parasitic disease. Demodicosis of the body develops with the slightest disturbance of the biocenosis and a drop in immune defense.
Epidemiology of demodicosis
Source of infection
The main source of demodex mites are sick people or carriers.
Distribution routes
- Iron mites can be transmitted through bedding, underwear, and personal items. The parasites were found in house dust, the source of which was bedding.
- Some researchers suggest that ticks can get on a child during breastfeeding from a sick mother.
Sustainability
Constant humidity, darkness and air temperature within 30-40°C are optimal conditions for iron mites. Outside the host, at room temperature, constant humidity and in the dark, ticks live up to 9 days.
According to the observation of some researchers, parasites remain viable in water for 7 days, and up to 2 weeks in immersion oil.
Rice. 6. Demodex mite under a microscope.
Causes of demodicosis
As mentioned above, the main reason for the development of this disease is the active reproduction of the iron mite. There are several possible reasons that can lead to increased activity of these opportunistic microorganisms. These are internal and external factors. The first category includes:
- A significant drop in immune defense and exhaustion of the body caused by poor nutrition, autoimmune pathologies, previous diseases, constant stress, etc.;
- Viral and microbial diseases that occur in chronic forms (hepatitis, tuberculosis, etc.);
- Helminthiases. The vital activity of helminths contributes to the weakening of the immune system;
- Malignant neoplasms. With many types of oncology, the body becomes exhausted, making it more difficult for it to cope with infections;
- Damage to the gastrointestinal tract. There is a proven relationship between the bacterium Helicobacter pylori and demodicosis;
- Other skin diseases. These are seborrheic dermatitis, rosacea, acne, etc. In the presence of inflammatory processes or integrity disorders on the skin, the risk of pathogenic activation of opportunistic flora increases significantly;
- Hormonal imbalance associated with illness or natural condition (for example, pregnancy or breastfeeding).
Skin demodicosis can also develop as a result of exposure to unfavorable external factors. As a rule, they are combined with internal ones, but in some cases (for example, choosing the wrong skincare products) they can be the main etiology. Among them:
- Temperature effect. This parasite multiplies especially actively in warm conditions;
- Unhealthy Lifestyle. This includes poor nutrition, frequent stress and bad habits;
- Use of low-quality cosmetics for care. This is especially true for cosmetics that do not have quality certificates and do not meet legal requirements;
- Poor environmental conditions. High levels of environmental pollution lead to a weakening of the barrier function of the skin.
Medical certificate
Human skin is a favorable place for the life of various fungi, parasites, and bacteria. One of these is the subcutaneous mite. In small quantities, these parasites live on the skin of healthy people, performing the function of normalizing the acidity level of the epidermis. However, under the influence of unfavorable factors, they begin to multiply intensively. The disease enters the acute stage. Its treatment is complex and usually consists of the use of ointments and tablets, changes in habitual lifestyle, and diet.
Demodectic mange symptoms
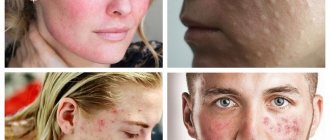
Due to the fact that this disease can affect different areas of the skin, the clinical picture differs. In the cutaneous form, the following signs of demodicosis appear:
- Acne of varying severity: from small nodules and ulcers to rosacea;
- A strong tooth that causes discomfort. In most cases, it intensifies in the evening and night;
- Excessive sebum production. It is the greasy environment that is most nutritious for ticks of this genus;
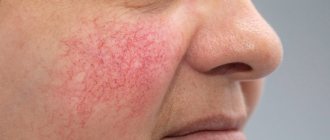
- Red spots that are a symptom of high blood pressure in the blood vessels. This indicates the presence of an inflammatory process in the body;
- Nose enlargement. If you contact a dermatologist late or in the absence of adequate treatment, it is possible to replace the functioning tissue with connective tissue.
Demodicosis of the eyelids and eyes, in turn, manifests itself as follows:
- Clumping of eyelashes. Along their growth line, a thin layer of film is formed that has adhesive properties;
- Redness of the eyelids as a result of the inflammatory process;
- Tired eyes. This symptom occurs due to inflammation and due to the fact that the patient is forced to strain his vision;
- Eyelash loss caused by damage to hair follicles.
Products for eyelashes and eyelids
The favorite location of the subcutaneous mite is the area of the eyelids and eyelashes. To destroy parasites, agents are used that inhibit their active reproduction and increase skin reactivity. The standard treatment regimen involves the use of the following drugs:
- Blepharogel-2
. Available in the form of drops. The medication has an antiparasitic and wound healing effect. Used to moisturize the mucous membranes of the eyes, eliminate symptoms of fatigue and treat demodicosis. - Prenatsid
. The hormonal drug is available in the form of drops. It is characterized by vasoconstrictor, antiallergic and wound healing effects. In the case of demodicosis, drops are prescribed to reduce the symptoms of the disease and prevent purulent lesions of the eyelids. - Demazol
. The ointment accelerates the process of removing subcutaneous mites from tissues. It relieves swelling well and eliminates flaking. The drug also stimulates recovery processes.
Before using these products, the skin around the eyes and eyelids should be cleaned of dirt with a cotton pad soaked in any antiseptic solution. After this, a thin layer of the drug should be applied to the affected area. The procedure is repeated twice a day.
Diagnostics
Demodicosis on the face and skin is diagnosed by a dermatologist. If the disease is secondary and has developed against the background of the underlying disease, then doctors of other specialties (gastroenterologist, gynecologist, trichologist, endocrinologist, etc.) may be involved for diagnostic and therapeutic purposes. For diagnosis, first of all, visual inspection is used. The doctor evaluates the condition of the skin, eyes and affected areas of the body. In addition, eye biomicroscopy and laboratory examination methods are practiced. The most informative of them are:
- Slit lamp biomicroscopy of the eye is a non-invasive examination aimed at looking for active inflammation. This is an absolutely painless manipulation that does not require special preparation;
- Eyelash test - involves taking freshly removed eyelashes (4 from each eyelid) for further examination under a microscope. Using this method, it is possible to determine the number of parasites (the presence of more than 1 mite on 2-4 eyelashes is pathogenic). This is also a painless procedure, but before it is carried out it is necessary to abandon decorative and skincare cosmetics for several days;
- Biopsy. This is the most informative diagnostic method, but the most traumatic. Diagnosis is carried out under local anesthesia using a tubular knife or scalpel. The taken biomaterial is fixed in a formaldehyde solution for a day and treated with dyes. This makes it possible to fully visualize the gland and adjacent tissues with the pathogenic mite.
Methods for diagnosing demodicosis
The symptoms of demodicosis coincide with the symptoms of some other diseases (dermatitis, allergies). Acne with demodicosis is similar to the manifestations of rosacea (rosacea disease). Therefore, laboratory diagnostics are necessary to confirm the diagnosis.
Demodex analysis
The material for analysis is a scraping from the skin. If the eyelids are affected, eyelashes are taken for analysis. Next, a microscopic examination is carried out, which is designed to detect tick individuals or eggs.
More information about the diagnostic method
Sign up for diagnostics To accurately diagnose the disease, make an appointment with specialists from the Family Doctor network.
Classification
Demodicosis (photo can be found below) is classified into 2 main clinical forms - primary and secondary. The first diagnosis is made in the event of a sharp surge in parasitic reproduction and effective treatment with the use of antiparasitic drugs. In most cases, it occurs in people over 40 years of age. The secondary form is diagnosed by identifying concomitant skin lesions and systemic diseases (usually associated with immunodeficiency). In some cases, this diagnosis is found in people taking epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitors and in those who have been exposed to ultraviolet radiation.
Based on the symptoms manifested on the skin, the following types of demodicosis are distinguished:
- Acneiform - the presence of papules and pustules similar to acne;
- Rosacea-like - papules appear due to diffuse erythema;
- Seborrheic - skin rash combined with peeling;
- Ophthalmic - inflammation of the eyelids, accompanied by discomfort in the affected eye.
Demodectic mange against the background of rosacea
Demodicosis complicates the course of rosacea in 88.7%. The disease is more common in women over 30 years of age. The phymatous form of the disease is more common in men. The pathological process is characterized by redness of the skin of the face, associated with the expansion of small superficial vessels, the appearance of papules and pustules. Papules increase in size over time and merge, forming dense infiltrates. The sebaceous glands become hyperplastic. Fibrosis develops. Persistent redness and fibrous lumps on the nose are called rhinophyma.
There are many reasons for the development of diseases. Factors contributing to the development of the disease can be divided into endogenous and exogenous.
Rice. 20. Erythematotelangiectatic form of rosacea. Multiple telangiectasias (dilated subcutaneous arterioles) are visible on the skin.
Rice. 21. The photo shows the papulopustular form of rosacea. Against the background of erythema (redness), multiple rashes are visible, which are papules with thin scales on the surface. The affected areas are infiltrated and swollen.
Rice. 22. Demodex brevis (short mite) causes the appearance of inflammatory infiltrates and granulomas in the deep layers of the dermis, which are similar to the granulomatous (phymatous) form of rosacea. The photo shows the phymatous (papular-nodular) form of rosacea.
Rice. 23. Severe form of rosacea.
Rice. 24. The ocular form of rosacea is registered in 50% of patients. Inflammation of the eyelids, redness of the conjunctiva, iritis and keratitis are the main manifestations of the disease.
Complications of the disease
Treatment of demodicosis on the face should be carried out exclusively with the assistance of a doctor. Self-medication or ignoring this problem may not only not bring the desired result, but also worsen the course of the pathology. Skin scratching and regular trauma to the skin (due to severe itching and the patient’s desire to remove the rash mechanically) lead to disruption of the barrier function. As a result, the risk of developing a pustular infection significantly increases, which can be diffuse and affect large areas of the body.
In addition, this disease (especially demodicosis on the face in women) leads to psychological problems. As a result of the appearance of visible defects, the patient becomes withdrawn, begins to feel embarrassed about his appearance and stops leading a full-fledged lifestyle (closes himself off from the outside world, stops communicating with people, prefers to be alone). As this problem worsens, the developed complexes can develop into psychoses, neuroses and prolonged depression.
A large number of people with this diagnosis have concomitant pathologies (gastrointestinal tract, endocrine glands, etc.) and chronic infectious foci. Demodicosis damage to the body contributes to the aggravation of these conditions and, accordingly, deterioration of well-being.
Diagnosis of the disease
Like any other disease, demodicosis is characterized by the manifestation of external signs that can be associated with the appearance of a subcutaneous mite in humans:
All of the above symptoms indicate the appearance of a subcutaneous mite. This is a signal to begin treatment immediately.
Illness confirmation
If the first signs of demodicosis appear, you should immediately consult a doctor to confirm your concerns. To decide on a treatment regimen, you need to undergo tests. This is the only way to count on a quick recovery.
In no case should you self-medicate, since getting rid of this parasite is not so easy.
Before taking tests, you must not perform any manipulations to treat problem areas for 24 hours and do not use antibacterial drugs. To do the analysis, scrapings are taken from the affected areas, after which the material is examined under a microscope.
If the concentration of these arthropods exceeds more than 5 individuals per 1 cm square of skin, then the diagnosis of demodicosis is confirmed. Confirmation of the diagnosis is the basis for starting a full course of treatment to get rid of parasites.
Skin demodicosis
The transmission route is contact or contact-household. Can be transmitted through contaminated clothing, bedding, contaminated hands and more. Demodex is distinguished by its survivability under comfortable conditions that correspond to the daily life of most people. The parasite remains viable at a temperature of 17-20°C for 10 days or more, and in an aquatic environment at a temperature of 12-18°C for 3 days. When water is heated to 50° C, the microorganism dies within one minute, and at low temperatures it dies immediately.
To date, there is no single theory explaining the etiology of the development of the inflammatory process and the active reproduction of mites. But there are several predisposing factors that can provoke these processes:
- Excessive sebum production;
- Improper skin care, abuse of cosmetics (especially low quality);
- Long-term use of external corticosteroids;
- Poor nutrition (abuse of sugar, soda, spicy foods, coffee, alcoholic drinks);
- Concomitant gastrointestinal diseases;
- Reduced immunity;
- Hormonal imbalance, excess weight;
- Psychological problems, frequent stress.
Use of other drugs
For patients with long-term demodicosis, it is important to strengthen the immune system. The waste products of subcutaneous mites can cause allergic reactions that look like swelling and redness. To improve the general condition of the body, the following groups of drugs are additionally used in medical practice:
- Antihistamines (Tavegil, Clemastine). Used for symptomatic treatment. They relieve itching and swelling well.
- Vascular strengthening. Prevents damage to blood vessels by parasites.
- Immunostimulating (Likopid, Atlant-Iva). Increases the body's protective functions.
- Vitamins and antioxidants (Elkar, Actovegin). Strengthen the immune system, remove free radicals from the body, speed up the healing process.
- Sorbents and prebiotics (Hilak forte, Bifiform). The activity of subcutaneous mites is most often caused by decreased immunity and problems with the gastrointestinal tract. Normalization of microflora plays an important role in the treatment of demodicosis.
Specialized cosmetics for the treatment of subcutaneous mites Demodex Complex are also popular.
Products from this line normalize the process of sebum secretion and inhibit the growth of bacteria.
Cosmetics can be used both at the treatment stage and for preventive purposes.
Demodectic mange of the eyelids
Treatment of demodicosis of the eyelids requires a comprehensive approach and qualified medical intervention. Demodectic blepharitis is a chronic disease that occurs with periodic exacerbation and remission. It has the following clinical picture:
- Severe eye fatigue associated with the need to strain to better focus on an object or letters;
- Intense itching in the eyelashes and eyebrows. Often this symptom intensifies with external exposure to heat, in the evening and at night;
- Foreign body sensation, burning and tingling that does not go away after washing or scratching;
- Sticky discharge from the eyes after waking up;
- Accumulation of foamy contents in the eye corners;
- Hyperemia, swelling and thickening of the eyelids (especially at the edges).
- The chronic form of demodectic blepharitis can be complicated by keratoconjunctivitis, keratitis and dry eye syndrome. Therefore, it is strongly recommended to consult with an ophthalmologist at our clinic, who will be able to prescribe preventative and therapeutic therapy aimed at maintaining eye health.
Expanding the boundaries
Over the past decades, the range of ixodid ticks has changed and expanded. Thus, if previously it was believed that in Russia the problem of tick-borne infections was relevant only for Siberia and the Far East, now it is well known to residents of the western regions of the country. Ticks are increasingly spreading in other regions of the planet: in the USA and Canada, China and the countries of Southeast Asia, South America.
Scientists believe that one of the reasons for this phenomenon is climate warming. It has been repeatedly shown that migratory birds can carry ticks over long distances (Sparagano et al., 2015). But if earlier ticks could not take root in the northern territories, now the situation has changed. In many regions of the planet, winters have become shorter and milder, and ticks are able to survive the winter more easily.
One star mite Amblyomma americanum
widespread in the southeastern United States.
This tick is known as a carrier of several species of Ehrlichia, the causative agent of tularemia and the recently discovered Heartland
and
Bourbon
. Thus, in Sweden and Norway for the period 1994–2008. The limit of occurrence of ticks has moved more than 200 km north along the Baltic coast (Jaenson et al., 2012). On the North American continent, ticks began to be found almost 1000 km further north compared to the period 1943–1983. And in the mountains in the north of the Czech Republic, where temperatures have risen by 1.4° over four decades, ticks appeared at altitudes of up to 1,300 m above sea level. In Russia in the 1960s. The taiga tick was found only in the southern regions of the Komi Republic, but now it is also found in the central ones: over the past forty years, the northern border of its range has moved 150–200 km (Loktev, 2015).
Extensive range of the meadow mite Dermacentor reticulatus
includes the territory of Europe, the European part of Russia and Western Siberia.
Often found in forested areas and on the outskirts of cities (in wastelands). It has two peaks of activity - spring and autumn. It poses the greatest danger to dogs, since it is a carrier of pathogens that cause a serious, life-threatening disease in them - canine piroplasmosis. In Eastern Siberia and the Far East, where D. reticulatus
is absent, cases of canine piroplasmosis have not been described. This photo was taken in the Moscow region. © CC BY-SA 4.0, photo by A. Yakovlev
The second possible reason for the change in the range of ticks is a change in the ecological situation caused by human activity. For example, naturalists who traveled to the USA in the mid-18th century noted a large number of ticks there. But a century later, due to the development of agriculture, the number of white-tailed deer, the main feeders of black-legged ticks,
, which led to a decrease in the number of these parasites. However, in the second half of the last century, the number of both host animals and ticks themselves increased manifold. Accordingly, the number of tick attacks on humans has increased as city dwellers began to spend more and more time in nature.
Western black-legged tick Ixodes pacificus
distributed on the western (Pacific) coast of the United States, where it serves as the main carrier of tick-borne borreliosis (Lyme disease).
The photo
shows a view from the dorsal and ventral sides. © CC BY 2.0, photo by Don Loarie
Recently, in Western Siberia, the range of the Pavlovsky mite
, and the cause of this event remains unclear.
At the end of the last century, its habitat was only in the territory of Altai and other mountainous regions (Salair Ridge, Kuznetsk Alatau). Now it is found in most of the studied lowland areas of the Novosibirsk and Tomsk regions, while in some areas, mainly with high anthropogenic load, the Pavlovsky tick has almost completely replaced the taiga tick
(Livanova et al., 2011; Romanenko, 2011).
Perhaps this change in range is associated with long-term anti-tick treatments of the area around large cities, which were carried out in the 1960–1980s. When these places began to be repopulated by ticks, I. pavlovskyi
received an advantage, since its life cycle is shorter, and it can feed on birds, the number of which in anthropogenic foci is higher compared to the number of large mammals, the main feeders of the taiga tick.
Tick Ixodes trianguliceps
parasitizes only on small mammals; it does not attach itself to people and large mammals.
At the same time, its range overlaps with the range of other ticks of the genus Ixodes, which attack people, and their feeders are the same species of animals. Therefore, I. trianguliceps
can infect people indirectly, through ticks of other species (Filippova, 1977; Yakimenko, 2013).
The photo
shows a well-fed female and nymph
of I. trianguliceps
on a vole. Photo by V. Yakimenko (Omsk Research Institute of Natural Focal Infections)
In some cases, the habitat of ticks is expanding southward. Thus, in Western Siberia in the 1960–1970s. range of the meadow tick
moved south, from the forest to the forest-steppe zone. The reason could be a combination of several factors: acaricidal treatment of forests and a change in the structure of rodent populations, the main hosts of the tick (Yakimenko, 2013).
Based on modeling of changes in climate and biotopes as a result of human activity, it was shown that in the 21st century. One can expect a reduction in the range of the taiga tick on the territory of states bordering Russia from the west, and by the end of the century this process will also take place in the European part of Russia (Yasyukevich, 2019). Presumably, in the Moscow region and the regions bordering it in the west and north-west, the taiga tick will disappear. A similar process will take place in areas to the south, where, due to climate warming, the forest will retreat, giving way to drier habitats.
At the same time, there are prerequisites for a significant expansion of the range of the taiga tick in the Kamchatka Territory and its appearance in the Magadan Region, and these forecasts are already beginning to come true. Thus, taiga ticks were recently discovered in the vicinity of Magadan (Dokuchaev, 2015). These ticks have been found on the Kamchatka Peninsula for quite a long time. At the same time, no larvae or nymphs were found there, which would be indirect evidence that the taiga tick can go through a full life cycle in this territory (according to the Federal Budgetary Institution of Health “Center for Hygiene and Epidemiology in the Kamchatka Territory” for 2022). Probably, the ticks are brought there by migratory birds.
Stages of the life cycle of ixodid ticks using the example of a widespread species - the European forest or dog tick Ixodes ricinus
. © CC BY-SA 3.0, photo by Alan R. Walker
Interspecies alliances
Pavlovsky's mite Ixodes pavlovskyi
was first discovered in the Russian Far East in the middle of the last century. The range consists of two separated parts - eastern and western, located in the Far East and Western Siberia. In morphology, genetic characteristics and activity it is similar to the taiga tick. It serves as a carrier of the same infectious agents as the taiga tick, although their occurrence in these two types of ticks differs significantly (Rar et al., 2017).The movement of the Pavlovsky tick population to the north coincided with another phenomenon—the discovery of its hybrids with the taiga tick. Interspecific hybridization is a fairly common phenomenon among closely related species of ixodid ticks. However, in the vast majority of cases, these interspecific hybrids are not capable of reproduction.
Thus, in Russia and Estonia, in places where the ranges of taiga and European forest ticks overlap, ticks with morphological and genetic characteristics of hybrids were found (Bugmyrin et al., 2015). However, the offspring obtained by laboratory crossing of these two species turned out to be infertile.
The entire range of the Pavlovsky tick is located within the distribution area of the taiga tick, and molecular genetic analysis revealed ticks with a hybrid genotype in all habitats of the Pavlovsky tick in the Tomsk and Novosibirsk regions and the Altai Republic. In some places, the relative abundance of hybrids exceeded 30%, and among them there were hybrids of both the first and second generations (Kovalev et al., 2015; Rar et al., 2019). All this suggests that these two types of ticks are capable of not only interbreeding, but also producing fertile offspring.
Demodicosis of the ear
This pathology does not always stop at the face. In advanced cases or in the absence of timely treatment, it spreads to neighboring areas of the body, including the ears. In such a situation, it will not be possible to quickly get rid of demodicosis, especially without medical help. Damage to the auricle is accompanied by the following clinical symptoms:
- Intense itching and irritation of the skin. As a result of constant scratching, bruises and microtraumas appear;
- Hyperemia and swelling of the ear, indicating an inflammatory process;
- The presence of red rashes of varying sizes and quantities;
- Pain upon contact with the skin (often a consequence of a violation of the barrier function of the tissue).
Stages of development of demodicosis
There are several stages in the course of the disease; we will consider each of them in detail.
Prodromal period
At the first stage, the disease manifests itself still implicitly, it does not cause severe discomfort, and therefore often goes unnoticed. But it is the first stage that is the most important for identifying the disease. At this stage, it is still possible to prevent the further development of demodectic mange if you start treatment of the facial skin in time.
At the initial stage of demodicosis, redness appears on the skin, and they have clear boundaries and differ from normal redness of the skin.
During the prodromal period, it is easy to trace the reasons that provoke the formation of redness.
Most often this is:
- Drinking alcohol;
- Salty or spicy foods;
If you identify the cause of redness, that is, the proliferation of demodex on the face, and limit the impact of the harmful factor, the disease will bypass you. If this cause is not identified and eliminated, the disease will develop further. Remember that treatment of demodicosis at the initial stage significantly increases the chances of a complete and rapid recovery.
Erythematous period
At this stage, redness becomes more and more pronounced and occurs for no apparent reason. At this stage, you can still successfully fight the disease using medical or folk remedies. We’ll talk about how to get rid of ticks on your face at home a little later.
Papulopustular stage
Nodules begin to form on the skin, which then develop into pimples and ulcers. This is already a serious stage of demodicosis, at which it is not recommended to treat subcutaneous mites at home. You need to see a doctor urgently.
Hypertrophic stage
This is the last stage of the disease, which is accompanied by the appearance of pineal growths on the face, thickening of the skin and the appearance of large ulcers. It is very difficult to treat the disease in this condition even with the most modern medications and procedures. Never delay treatment of demodicosis!
Demodicosis of the head
Ticks of the genus Demodex are representatives of opportunistic microflora of the skin on the body, including the head. They are present in almost all people on the planet. In everyday life, their activities do not cause visible discomfort; they exist in a mutually beneficial relationship with humans, fighting harmful microorganisms. But when the immune defense drops and unfavorable conditions set in, the parasites begin to multiply uncontrollably, as a result of which their numbers increase greatly, and the vital activity of these parasites becomes noticeable. This situation can result from:
- Hormonal imbalance;
- Long-term use of antibacterial and hormonal medications;
- Poor nutrition;
- Abuse of saunas, steam baths and solariums;
- Using low-quality cosmetics to care for skin and hair (since demodicosis needs to be treated comprehensively, our clinic specialists help patients choose the right and safe care products);
- Failure to comply with simple hygiene rules.
Meet the Ixodid tick
Many ixodid ticks have only light-sensitive cells instead of eyes, so they use other senses to “hunt.”
Almost all ticks, with the exception of those belonging to the genera Ixodes and Haemaphysalis, have a pair of eyes. The legs consist of 6 movably connected segments. At the end of the paw there are two claws, and the pad located between them acts as a suction cup. On the paws of the first pair of legs are the main sensory organs of ticks - Haller's organs. The tick is fixed on the host's body with the help of teeth on the legs and outgrowths at the base of the head, between which the animal's hair is clamped. The elongated oral parts on the head form a proboscis, from the base of which palps with chemoreceptor and mechanoreceptor hairs extend. On the underside of the proboscis there are parallel rows of teeth directed backwards. The “jaws” (chelicerae) consist of a long “trunk”, from which, like a case, movable “fingers” extend, with which the mites cut through the host’s skin. Up
— “head” of the taiga tick (ventral view) and outgrowths at its base. Scanning electron microscope. Photo by E. Mitrofanova (IVEP SB RAS, Barnaul)
At long distances the main role is played by the multifunctional Haller organ
, with the help of which ticks are able to perceive changes in the concentration of carbon dioxide, specific components of the smell of a potential host (hydrogen sulfide, ammonia) and its thermal radiation at a distance of up to 10 m. Having reached the “victim”, ticks determine the most suitable place for suction using sensitive sensilla, consisting of cuticular hair and receptor cells, which are especially numerous on the paws and mouthparts.
The body of the ixodid tick consists of two sections: an unsegmented body, bearing legs (6 in larvae, 8 in nymphs and adult males and females), and a head. On the dorsal side there is a hard shield, which in females, nymphs and larvae covers only the anterior third or half of the body. The remaining part is covered with an extensible cuticle, which in hungry individuals forms a system of parallel microfolds that straighten during feeding.
The paired salivary glands of the tick secrete a secret containing many biologically active components that act as an analgesic, prevent blood clotting, suppress the host's immune responses, stimulate the release of histamine by the host's cells, etc. They can also secrete components of the cement sheath involved in fixing the tick on the body owner.
Well-fed and hungry female forest tick Ixodes ricinus
. © CC BY-SA 2.5, photo by Richard Bartz; © CC BY-SA 3.0, photo NOBBI
Another unique function of the salivary glands is osmoregulation. When there is a threat of drying out, hygroscopic saliva is secreted into the pre-oral cavity of the tick, which adsorbs water molecules from the air, which allows the tick to retain the necessary moisture in the body and remain viable for many months between blood meals. And, on the contrary, when feeding on blood, the tick is able to return about 70% of the “excess” absorbed water and salts by salivating at the bite site. As a result, the volume of saliva secreted by the tick during the entire feeding period significantly exceeds the body weight of the engorged tick (Biology of Ticks, 2014).
An Ixodid tick that has fed on the blood of its host animal. © CC BY 2.0 Michael Coghlan
Most ixodid ticks are characterized by the grazing-lurking type.
parasitism: hungry individuals climb onto vegetation, where they lie in wait for potential hosts passing by. Having received the necessary signals, the tick goes into a state of “active lurking,” making oscillatory movements with the first pair of legs extended forward until direct contact with the host animal.
For many ticks of the genus Ixodes
The nest-burrow type
is characteristic , when hungry individuals at all stages of development attack potential hosts in burrows and nests;
some have a mixed type of parasitism. There are also ticks adapted to living in houses, for example, the dog tick Rhipicephalus sanguineus
(Balashov, 1998; Yakimenko, 2013; Biology of Ticks, 2014).
About 60 species of ticks from the family Ixodidae have been found on the territory of Russia, but the most dangerous are ticks of the genus Ixodes
, the main carriers of the tick-borne encephalitis virus, the causative agents of ixodid tick-borne borreliosis (Lyme disease) and borrelia from the group of relapsing fevers.
Ticks of the genera Dermacentor
,
Haemaphysalis
and
Rhipicephalus
are the main carriers of pathogenic species of rickettsia, and
Hyalomma
- the Congo-Crimean hemorrhagic fever virus (Filippova, 1977, 1997).Ticks of the genus Hyalomma belong to the desert species. H. marginatum
(
left
) lives in the south of European Russia.
Larvae and nymphs feed on birds and rodents, while adults feed on ungulates. H. marginatum
is the main carrier of the Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever virus, a dangerous disease with a mortality rate of 16%.
The steppe tick Dermacentor marginatus
(
right
) lives in steppe and forest-steppe biotopes in southern Europe, European Russia and Western Siberia to the Krasnoyarsk Territory in the east. Serves as a carrier of pathogens of Siberian tick-borne typhus and Q fever. Photo by V. Yakimenko (Omsk Research Institute of Natural Focal Infections)
Demodicosis treatment
The treatment regimen for demodicosis is a set of measures aimed at eliminating external symptoms and the cause that provoked them. The final stage of therapy is the use of preventive measures that help consolidate the therapeutic result and prevent relapse of the disease. It is important to understand that it is almost impossible to cope with this problem on your own. This problem requires qualified help and long-term drug treatment, since an infected person is dangerous to others. It is a source of infection and can therefore infect other people.
Standard therapy aimed at eliminating demodicosis infection consists of several parts:
- Diet for demodicosis. The patient will need to give up fatty, spicy and smoked foods. It is also recommended to reduce your consumption of sugar and sweets. The diet should consist of low-fat fish, vegetables and fruits;
- Local treatment. For this purpose, sulfur ointment is used for demodicosis, creams and sprays that have antibacterial and antiparasitic properties;
- Systemic treatment. It is aimed at normalizing sebum production and eliminating existing imbalances (hormonal or metabolic). To do this, it is possible to involve specialized specialists, prescribe antibiotics in tablet or injection form;
- Symptomatic treatment. It is aimed at improving the patient’s well-being, eliminating active symptoms (inflammation, itching, soreness and redness). For this purpose, a special anti-demodetic mange may be prescribed;
- Physiotherapy. To improve the condition of the skin, electrophoresis, laser therapy and ozone therapy are prescribed.
Since it is practically impossible to cure demodicosis quickly but effectively, the average duration of the treatment course ranges from one to several months. The duration depends on the severity of the pathology and the individual characteristics of the body (in some cases, treatment may take a year or more). The main criterion for cure is a repeat tape test with a negative result.
Treatment
Treatment of demodicosis caused by subcutaneous mites is a long and difficult process. Its complexity is that often this disease develops against the background of a decrease in the body’s defenses and has accompanying skin problems. Therapy tactics include suppressing the parasite, treating underlying diseases and increasing immunity.
The most commonly used local therapy is lotions and special ointments. In more severe cases, the doctor prescribes a course of antibiotics in combination with external therapy. Sometimes plasmapheresis procedures are recommended. In special cases, even surgical intervention is possible.
An important point in the course of treatment is diet. It is necessary to exclude hot, spicy and salty foods, foods rich in carbohydrates and fats from the diet. Those who are being treated for subcutaneous mite infestation are recommended to consume large amounts of fruits, vegetables, microelements, fiber, and dairy products. During treatment, you should not use face masks, especially those containing honey. You need to limit your exposure to the sun. You should also wait until better times to visit the bathhouse and sauna.
Demodicosis - drugs for treatment
Today, finding effective remedies for demodicosis will not be a problem. The specialists of our medical center select medications in the optimal form on an individual basis, thereby speeding up the healing process. The most popular and effective remedies are described below.
Soap
- Demolan Forte and Stop Demodex demodex.by are especially popular among patients. For demodicosis of the eyelids, the treatment regimen often includes these drugs, as they show excellent results due to the presence in the composition:
- Glycerin - absorbs moisture, holding it on the skin. This helps prevent drying, promotes hydration and improves elasticity;
- Octopirox is an antimicrobial component that inhibits the activity of ticks. It gently exfoliates the top layer of the epidermis, normalizing the process of formation of new cells;
- Propylene glycol - helps normalize microflora, moisturizes the stratum corneum;
- Diazolidinyl urea - provides an antimicrobial effect.
Lotion
Demolan Forte and Stop Demodex lotions are prescribed for constant facial skin care and for cleansing damaged skin areas (even demodicosis on the back) before using the gel. They are often used for eyelid hygiene (for blepharitis), as they deeply cleanse the pores and facilitate the penetration of the active substances of subsequent medications. With their help, it is possible to soften the epidermis and normalize fat metabolism without resorting to tapping the skin. As a result of their regular use, mites are deprived of their nutrient medium, and the tissue is regenerated at an accelerated rate without the formation of scars.
Balm
Therapeutic and prophylactic balm Stop Demodex significantly increases the effectiveness of the main therapy. With its regular use, a visible therapeutic effect is observed after 2-3 days. It has the following properties:
- Anti-inflammatory and bactericidal;
- Moisturizing the skin;
- Promotes rapid tissue regeneration and healing;
- Improves local metabolism;
- Penetrates the cell membrane of the epidermis, replenishes the lack of microelements.
Eye gel
When diagnosing eye demodex, it is strongly recommended to use Demolan Forte and Stop Demodex gels. The presence of peppermint extract in the composition guarantees local anesthesia and inhibition of inflammation. They have a calming and refreshing effect, due to which the patient’s well-being noticeably improves. The presence of metronidazole provides effective antiprotozoal and antibacterial effects, while hyaluronic acid helps improve skin elasticity and firmness. These demodicosis preparations are perfectly absorbed, do not clog pores and do not disrupt cellular metabolism. They accelerate tissue regeneration and prevent the formation of scars.
Cream
An effective cream for demodicosis, Stop Demodex, with constant use, makes it possible to stabilize the normal secretion of the sebaceous glands, restore the skin microflora, eliminate the uncontrolled proliferation of parasites of the Demodex genus and noticeably cleanse the skin from foci of inflammation. It does not contain antibiotics, perfectly nourishes, increases tissue firmness and elasticity, and does not have a comedogenic effect.
Mask
For demodicosis infection, it is strongly recommended to buy a Stop Demodex treatment mask. It contains the active Cutipure complex and white clay, which promotes deep cleansing of pores and reduces the proliferation of pathogenic mites. It has anti-inflammatory, antibacterial and keratolytic effects. Its use allows you to normalize sebum production, tone the skin, improve metabolic processes in cells and accelerate tissue regeneration. Moreover, with its help it is possible to remove toxic molecules.
Shampoo
Using Stop Demodex shampoo for demodicosis of the head, you can significantly reduce itching, eliminate dandruff and stop the active reproduction of parasites. It has a strong anti-inflammatory and regenerating effect, fights mites and helps eliminate the consequences of the disease. Its effect is aimed at preventing ticks from sucking nutrients, disrupting their DNA replication and protein synthesis in the cell. The drug inhibits tissue respiration, which is vital for parasitic life.
Antiparasitic tablets
Treatment of demodicosis is not limited to the use of local drugs. Patients with this diagnosis must be prescribed medications for oral use. Antiparasitic drugs are usually used for a long period of time, since the likelihood of relapse is quite high.
- Trichopolum
. This is a broad-spectrum antimicrobial drug. Prescribed during the pastular-pupular stage of the disease. The duration of the course of therapy may be delayed, but does not exceed 10 days. - Metronidazole
. The antimicrobial drug is active against subcutaneous mites. Taking it daily significantly reduces the number of parasites. For medicinal purposes, the medication is taken one tablet every 8 hours. - Efloran
. The active ingredient is metronidazole. The medicine is used for pustular rashes or in case of bacterial infection.
It is recommended to supplement the course of treatment with antiparasitic drugs with Detox. It has an anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effect, helps cleanse the body of decay products of subcutaneous mites. The medication effectively soothes the skin and helps restore the secretory activity of the glands.
Prevention
Demodicosis of eyelashes and other parts of the body can be prevented. To do this, it is enough to follow simple preventive rules. This:
- Maintaining personal hygiene (regular showering, thoroughly washing your face, washing your hair and hair);
- Eat a varied, rational and healthy diet (include fish, vegetables and fruits in your diet);
- Increased immune defense;
- Correct selection of decorative and skincare cosmetics;
- Do not use other people's cosmetics and personal hygiene products.
Demodicosis in children
- In childhood, this pathology rarely develops (due to the low activity of the sebaceous glands), but its course is much more complicated than in adults. As a rule, in children this disease is chronic, and relapses occur in the off-season. The main signs of the problem are:
- Swelling of the eyelids;
- Loss of eyelashes and hair;
- Severe eye fatigue;
- The appearance of spots on the skin;
- Itching, worse at night and on contact with water;
- Decreased appetite, moody behavior, decreased physical activity;
- Pain in the eyes.
The treatment regimen for democosis of the face and other parts of the body in children is practically the same as therapy for adults. It also includes diet, medication and rehabilitation aimed at healing the tissue and preventing scarring. The fundamental difference in the treatment method is only the dosage of medications, which will be lower in childhood.
Traditional methods of treatment
Traditional methods of treatment are also used for demodicosis. However, they should be used as a supplement to the main course and after consultation with a doctor. Below are several recipes on how to deal with subcutaneous mites:
- To prepare an infusion of celandine, you will need to mix 250 g of crushed plant roots and 200 ml of vegetable oil. It is better to place the container with the product in a warm place for 2 weeks. Then the mixture should be strained and refrigerated. Before treating affected surfaces, it is recommended to add a small amount of sour cream. The product can be instilled into the nose and eyes.
- To remove subcutaneous mites, some use a 6% solution of apple cider vinegar. You can soak cotton swabs in it and treat your legs, arms or chin.
- If the entire head is affected by demodicosis, a decoction of calendula and chamomile should be used to cleanse the affected areas and rinse the hair.
It is difficult to completely cure demodicosis using only folk recipes. However, their regular use helps eliminate unpleasant symptoms. Also, some traditional methods can be used for preventive purposes.
Chatterbox recipe
Twice a day you can lubricate the mite-affected areas with mash. This is a decades-tested remedy. It is prepared at home according to the following recipes:
- 4 tablets of Levomycetin and Trichopolum must be crushed to a powder state. Then add 100 ml of salicylic alcohol to the mixture and pour into a glass bottle. This product can be used as a tonic by rubbing the affected areas morning and evening.
- Mix a tablespoon of castor oil with two crushed Trichopolum tablets. It is recommended to use the product before bedtime. After applying to mite-affected areas, do not rinse off and leave until morning.
To avoid drying out the skin after treating it with mash, it is necessary to apply any nourishing cream. Preference should be given to products that are simple in composition. You can even use regular baby cream.
Boltushka is a potent remedy and is not suitable for all patients.
For example, it is not recommended for use if there are open wounds on the skin. It is also important to avoid getting the composition on the mucous membranes. It is not suitable for oral use and is rarely prescribed to children. To know all the restrictions on use, you should consult a dermatologist.
Demodicosis in men
Demodectic mange infection occurs in both women and men, regardless of age or race. It has no distinctive features in its course, prognosis, symptoms and causes of development. Therapy is prescribed on an individual basis, but is usually the same for all genders. Differences may only relate to the dosage of medications.
According to statistics, women suffer from demodicosis 4 times more often than men. There is no scientific explanation for this information, but many are inclined to the hormonal theory. It is based on the fact that due to a regular surge of hormones (menstrual cycle, pregnancy), female representatives are more prone to stress and immunodeficiency states. The clinical picture of the disease is standard and includes:
- Skin rash of varying severity;
- Itching, pain and discomfort in the damaged area;
- Increased sebum production;
- Pain in the eyes, sensation of a foreign body.
The treatment regimen for demodicosis for women is standard. It consists of a diet, long-term medication and the use of special care products (oils, lotions, creams, etc.) to prevent relapse and consolidate the therapeutic result.
What are subcutaneous mites - characteristics of the disease
Demodicosis is a dangerous disease that everyone should know about. It is caused by a subcutaneous mite and causes significant deterioration of the skin condition. It is important to recognize this disease as early as possible, since in the early stages it is much easier to cure.
In this publication we will talk about why the subcutaneous mite on the face becomes active, how to identify it, how the disease progresses, we will consider methods of home and drug treatment, as well as preventive measures.
The subcutaneous mite on the face is called demodex or iron acne.
This is a small arthropod that lives in the sebaceous glands and hair follicles of humans. Its size varies from 0.1 to 0.4 mm. Normally, it is present in every person - no more than 2-3 individuals per square centimeter.
In small quantities, the mite does not cause any harm to the body; on the contrary, it serves to maintain the normal acid-base balance of the skin. But when exposed to certain factors, the mite begins to actively multiply, and this leads to pronounced negative changes in the skin of the face.
Types of subcutaneous mites in humans and their characteristics
As a rule, 2 types of mites take root in humans, depending on the part of the body where they parasitize. For example:
- Demodex folliculorum, which prefers to live in hair, eyebrows and eyelashes. This type of mite reaches sizes from 0.2 to 0.4 mm.
- Demodex brevis. This type of mite parasitizes the sebaceous glands of humans. The size of the parasite is from 0.15 to 0.48 mm.
- As a result of direct person-to-person contact. This can be an ordinary handshake, touching a person’s skin, or as a result of a kiss, maybe even the most harmless, friendly one.
- As a result of indirect contact, through everyday objects.
Such items can be: bedding, personal hygiene products, a cover for an armchair or sofa, interior items, etc.
- Poor functioning of the immune system.
- Disturbances in the normal functioning of the endocrine system.
- Leading an unhealthy lifestyle.
- Problems with the normal functioning of the gastrointestinal tract.
- Neuropsychic imbalance.
- Prolonged exposure to direct sunlight.
- Hormonal imbalance in the body.
- Violation of metabolic processes.
- Pregnancy period.
- Environmental problems.
- Passion for cosmetics, solarium and baths.
- Acne;
- Oily sheen;
- Redness of the skin;
- Itching;
- Nose enlargement.
- the skin around the nose and cheeks has become very oily, the pores on the face have expanded;
- the face became lumpy;
- the skin is red, itchy, and it feels like something is crawling on it;
- hair falls out a lot;
- There is itching at the roots of the eyelashes, itching of the ears.
During the active phase, which is observed in autumn and spring, mites release toxic substances that affect the glands of the eyelids, hair follicles, and sebaceous glands. The parasite's diet consists of fat compartments and dead cells. The life cycle of demodex is 13–19 days. Adult Brevis mites penetrate the sebaceous glands and feed on their contents. At the same time, their back part remains at the entrance to the gland.
Thanks to this, eggs are released, which, together with sebum, are carried to the surface of the skin.
Subsequently, larvae hatch from them, which, being under particles of the epidermis, undergo metamorphosis, turning into adults. It is noteworthy that the tick in the skin is nocturnal. With its movements, it causes itching in a patient with demodicosis.
Routes of infection
This serious disease can occur in any person, regardless of gender and other characteristics. As far as is known, there are two routes of infection with demodicosis. Namely:
The subcutaneous mite thrives in conditions where a person’s immunity is weakened and he is unable to cope with the vital activity of such parasites. These arthropods, from the class of arachnids, begin to actively reproduce under certain conditions, which will be discussed further.
Reasons for development
A subcutaneous mite is a parasite that can stay in the human body for a long time and wait for optimal conditions in order to appear “in all its glory,” causing maximum discomfort to a person. When such favorable conditions appear and the mite begins to actively develop, demodicosis develops.
Further actions are treatment of the disease.
The appearance of such a disease is associated with certain factors that, one way or another, influence the development of the disease. For example:
Such a disease can be treated if a person approaches the problems of treatment with all seriousness. In order to correctly determine the treatment, it is necessary to thoroughly study the symptoms of this disease.
Symptoms of the disease
How can you tell if there is a subcutaneous mite on your face? Characteristic signs (symptoms) of demodicosis include:
Since demodicosis interferes with the normal functioning of the skin, its characteristic feature is a constant oily sheen on the skin. The face always seems to be in a greasy shell, and no amount of washing removes these sensations.
Increased oiliness of the skin without a reason is often the first manifestation of subcutaneous mites.
A malfunction of the skin causes the formation of numerous pimples (they are also called “tick pimples”), acne, and later ulcers. The skin looks lumpy. Redness, which is one of the first symptoms of a tick-borne infection, worsens as the disease progresses.
Itching becomes a constant companion for patients with demodicosis. The fact is that the waste products of “facial” mites cause an allergic reaction, causing the face to itch and itch. Some people feel as if they can actually feel the mites moving around in the top layer of their skin.
Symptoms worsen at night. During the day, the activity of subcutaneous mites is much lower, this is due to the fact that Demodex is afraid of light. If a tick settles in the nose area, the organ tissue is replaced with connective tissue, causing the nose to become larger and fleshier. Part of the skin thickens and becomes crusty.
The unpleasant presence of “sand” is constantly felt in the eyes; they turn red and watery. At first glance, demodicosis is very similar to acne.
So, girls and boys, women and men may experience pimples, rosacea and even pustules, small ulcers. At first, all this “decorates” only the face, but if treatment is delayed, the source of the disease can spread to the skin of the back and chest.
With demodicosis, pimples are most often localized in a specific place, for example, on the left or right cheek, on the chin, etc. Pimples can also line up in a row - this groove shows the path of movement of the mite.
You can suspect demodicosis based on the following signs:
With demodicosis, eye fatigue and swelling of the eyelids may occur. Plaque may also form along the edges of the eyelids. Remember: regular pimples don't itch. If you notice that you want to scratch your face more and more often, do not delay visiting a dermatologist.
All the symptoms described sound scary, but they do not appear immediately.
By identifying the disease at an early stage and managing to cure it, you can prevent the most unpleasant manifestations of demodicosis. To do this, you need to understand what stages of disease development there are.
Questions and answers on the disease
Can a sick person infect others?
Yes, you can become infected with demodicosis through contact and household contact. Kissing, hugging, contact with contaminated things of a patient (towel, bed linen, clothes and much more) can be dangerous for a healthy person. But this does not guarantee the manifestation of symptoms of the disease. Ticks of the genus Demodex are representatives of the opportunistic microflora of the skin. They are found in almost all people, but most of them are simply carriers. For the development of a pathological process, the presence of certain factors is necessary (for example, reduced immune defense against the background of an active or past disease).
Can you get infected from animals?
Animals, like humans, suffer from the activity of Demodex mites. But pathogens come in different types - and each of them survives exclusively in the body of its host. When exposed to other conditions, the parasite immediately dies. Therefore, it is impossible to become infected with demodicosis from a pet or wild animal.
How the disease develops
Demodicosis in humans can develop for the first time and occur as an independent disease, or develop against the background of existing skin diseases (acne, perioral dermatitis, rosacea, seborrheic dermatitis, etc.). From 55 to 100% of the population are carriers of iron ticks and do not have any manifestations of the disease, which proves that the parasites belong to the opportunistic flora. Damage to follicles by parasites increases with age.
Factors in the development of the disease
Acne iron mites are an opportunistic infection. They can parasitize a person for many years without causing him any harm. Their activation and active reproduction depends on a number of factors.
- Changes in microbiocenosis, the function of the sebaceous glands and the composition of sebum are the trigger mechanism of the disease. Changes in the composition of surface lipids lead to the development of dysbiosis.
- Demodex mites are carriers of viruses and microbes into the sebaceous glands and hair follicles. When pathogenic pyococci and fungi Pityrosporum spp are introduced, purulent-necrotic inflammation develops.
- The bacillus Bacilluss oleronius found on the surface of the parasite increases the activity of ticks and stimulates staphylococci, streptococci, acne propionobacteria, and fungi of the genus Malassezia to produce anti-inflammatory proteins, which triggers a cascade of immune reactions.
- The presence of foci of chronic infection, disturbances in the functioning of the liver and gastrointestinal tract, endocrine glands, nervous system, and corticosteroid therapy contribute to the activation of ticks.
- The rise in incidence in the spring-summer period is associated with increased insolation. An increase in the production of vitamin D under the influence of ultraviolet radiation leads to an increase in the synthesis of cathelicidins, which support the inflammatory process.
- The likelihood of infestation by Demodex mites increases in individuals with a sharply reduced functioning of the immune system, which occurs with primary and secondary immunodeficiencies, long-term use of corticosteroids and cytotoxic therapy, HIV infection, leukemia, T-cell lymphoma and other malignant neoplasms.
- The mite infestation maintains the activity of the existing inflammatory process. An imbalance in the cytokine cascade develops when the immune response is too strong.
Mechanisms of action of iron mites on humans
The impact of Demodex mites on humans is multifaceted:
- When feeding, the parasites secrete aggressive saliva and mechanically destroy the cell walls of the sebaceous glands and follicles, inflammatory infiltrates and granulomas form in the dermis, and the processes of keratinization and pigmentation develop.
- Substances formed after the death of ticks have antigenic properties, which leads to allergization and increased immune response.
- When the immune system is suppressed, opportunistic flora is activated, which successfully colonizes the host.
Acne iron mites act as carriers of bacteria and viruses, which complicates the course of demodicosis and complicates treatment.
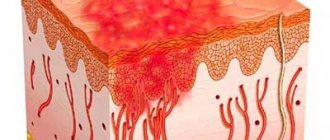
Rice. 7. Histological preparation of a skin section. Arrows indicate the location of demodex mites.