Home / Articles / Why does the skin around a mole itch?
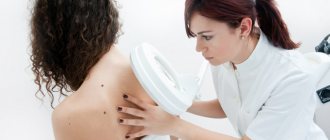
Moles and age spots should not cause discomfort or discomfort to a person. If at least one nevus begins to hurt or itch, becomes red or swollen, you need to make an appointment with a dermatologist. Sometimes it is enough for a specialist to examine the patient to determine why the skin around the mole and the mole itself are itching. In some cases, only examination of the tumor tissue helps to find the cause of the discomfort. Find out what causes itching nevi exist and why this symptom is dangerous.
Causeless itching
Probably each of us periodically feels the desire to scratch one or another area of the skin. This can happen up to several times a day, for no apparent reason. For example, a person simply scratched his nose, but after that, no thoughts about possible diseases of the nasal cavity (sinusitis, rhinitis) arise. By the way, according to research, a person’s nose itches more often when he knows that he is not telling the truth.
The same can happen with a mole - it is not the mole itself that itches, but the area of skin around or next to it.
Why does a mole itch?
If a mole itches, this is not a reason to panic, but a reason to pay close attention to it. The occurrence of itching and the desire to scratch a convex brown tubercle does not mean that any processes are taking place in the neoplasm. The reasons that the nevus itches may include:
- mechanical in nature - friction or constraint by elements of clothing;
- allergic in nature - irritation caused by the use of cosmetics, sweat, synthetic fabric or a product, such as washing powder;
- hormonal in nature - during adolescence, pregnancy or the onset of menopause.
The mole and the area around it itches
When not only the mole itself itches, but also the area adjacent to it, carefully observe this area of skin for several days. Identification of the following symptoms is a reason to visit a doctor:
- occasional itching or burning sensation occurs;
- the skin around the mole has reddened or darkened and become cracked;
- the mole changes color and itches;
- the tumor has increased or decreased;
- hair loss;
- blood or fluid is released from the mole.
Itches and flakes
Peeling processes from the surface of a mole may indicate that its cells are dividing. However, this is not the only reason why the nevus itches and flakes. This effect can result from:
- seasonal vitamin deficiency;
- increased dryness of the skin in the area where the mole is located;
- the beginning of the degeneration of education.
The last point is a reason to immediately contact a specialist. If the nevus itches, rejects dead skin, has greatly increased in size, hurts, bothers you, or its appearance has changed greatly - size or color, go to a dermatologist for an examination. If necessary, the doctor will refer you for the necessary tests that will help clarify the picture of the processes occurring in the skin formation.
It grows and itches
Why do moles on the body itch? There are many reasons for this phenomenon, and often it is not about the onset of the disease, but about a reaction to external irritation. Sometimes the fact that dark bumps on the skin itch is also caused by internal changes occurring in the body, such as hormonal imbalances. However, when the nevus greatly increases in size, this is a reason to visit the doctor. The growth of the neoplasm indicates that cell division processes have begun in it, and this can give rise to the degeneration of the nevus.
Itchy and red
If a mole not only itches, but also turns red, or has darkened, lightened, or lost color, this is a sign of changes occurring with the neoplasm. In all cases, only an oncologist can determine whether a patient is developing the process of malignancy (transformation of benign cells into malignant ones). A change in the color of the nevus is one of the main signs of this phenomenon. Malignancy of a mole is also accompanied by:
- changes in size (growth) and structure;
- blurring of the edges of the formation - the tubercle becomes asymmetrical;
- discharge of blood or other fluids.
- Pasta sauce - recipes with photos. How to prepare pasta sauce with or without minced meat
- Lose 10 kg in 2 months
- Homemade face mask with lifting effect
Itches around the mole
Is the mole and the area of skin adjacent to it itchy? Remember that the reasons why this phenomenon may occur vary widely. The influence of factors such as tanning cannot be ruled out. Prolonged exposure to the sun or frequent visits to the solarium is a condition that can cause itching and pain in the nevi and the areas around them. To prevent the unpleasant consequences of sunbathing, you must use sunscreen.
Psychological itch
Repeatedly I listened to the following story from the lips of different patients:
“A mole itched. I went online with the request “mole itches.” I’ve read horror stories from unknown authors, who all write that this is a sign of degeneration into melanoma. The mole began to itch 2 times more intensely and 3 times more often, until the skin around it turned red. I didn’t sleep at night, I didn’t eat for a day, I barely made it to you for a consultation, tell me, am I going to die?”
If you smiled now and recognized yourself in this story, try not reading the Internet on the topic of melanoma and skin cancer for 3 days and perhaps the mole will itch less.
Surgical treatment
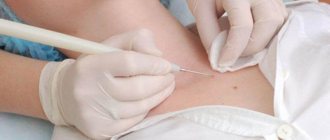
In some cases, the doctor may prescribe surgical removal of the mole. The procedure is safe and is performed under local anesthesia, but the decision about surgery is up to you. If the tumor does not bother you in any way, experienced dermatologists do not recommend resorting to its excision. After the operation, cosmetic stitches are applied to prevent the wound from becoming inflamed. As it heals, a small scar will remain at the site of the mole.
Sometimes a nevus may itch after removal. This phenomenon indicates that the healing processes are in full swing; the use of special drugs in this case is not required. If itching continues several weeks after surgery, it is worth visiting a dermatologist to ensure the effectiveness of the treatment method used.
Briefly about the main thing:
Itching alone is EXTREMELY rarely a sign that a mole has turned into melanoma. Most often it is caused by other reasons. In addition, the malignancy of the mole should be accompanied by symptoms other than the feeling that the mole itches
.
If you still have questions, the following will help you:
- In-person appointment with an oncologist
(St. Petersburg) - Mole removal
with histology (St. Petersburg) - My online consultation (from anywhere in the world)
What is a mole
Why do moles appear and what are they? A mole (the medical term for this skin growth is a nevus) appears on the human body due to the accumulation of melanin pigment in the skin cells, which gives these bumps on the surface of the skin a dark color. There are more than ten types of nevi, the most common are:
- angiomas - red moles, which are a plexus of microscopic blood vessels;
- lentigo - pigment spots on the surface of the skin of a uniform dark color;
- intradermal nevi are dark formations of medium and large sizes protruding above the surface of the dermis, with hair growing from their center.
In newborns, the skin is practically free of moles and birthmarks. Most of these formations occur in childhood, sometimes new ones can appear in an adult. Seemingly harmless dark spots, areas or bumps on the skin are not only an unpleasant aesthetic problem. Over time, they can change:
- increase in size;
- change color;
- inflame.
If you notice that a mole has begun to grow, or itching or pain appears, do not delay and make an appointment with a dermatologist. Nevi capable of degeneration can cause the formation of benign and malignant skin formations, in some cases leading to the development of a serious disease - melanoma, one of the most dangerous types of skin cancer.
Only a doctor can determine what processes are occurring in a mole if it begins to bother you. The doctor is able to recommend protective measures to prevent the development of a dangerous disease and improve the general condition of the skin. General prevention of diseases caused by the activity of pigmentation processes includes:
- avoiding exposure of the skin to ultraviolet rays and radiation waves;
- preventing skin damage;
- control of general hormonal levels.
Features of hanging moles
All moles can be divided into congenital and acquired, with the vast majority of pendulous structures belonging to the second type. The color characteristics of such a formation can vary widely - from light beige to dark brown. Moreover, regardless of the color and shape of the nevus, its formation is based on the mechanism of intracellular accumulation of the melanin pigment, which in the human body is responsible for the color of the skin, eyes and hair. If, due to any reason, there is an excessive accumulation of pigment in a certain epidermal zone, a mole is likely to appear in this place.
The appearance of a hanging mole in itself does not necessarily indicate the presence of any pathology in the patient’s body, since many people live with such benign formations without experiencing discomfort. However, most patients faced with hanging pigmented growths identify the following problems:
- Aesthetic unattractiveness. If a hanging mole forms on an open area of the body, most often it becomes a serious cosmetic problem for its owner, since the appearance of such structures is not distinguished by beauty and attractiveness;
- Possibility of malignant transformation. The probability of a hanging mole degenerating into an oncological formation, such as melanoma, is indeed somewhat higher than the same indicator for a flat pigmented structure, however, if the mole does not cause discomfort and does not increase, there is no need to sound the alarm.
- Physical discomfort. Moles that protrude above the general level of the epidermis can easily rub against clothing, linen and accessories, which in turn can lead to itching, pain and discomfort.
- Risk of injury to the structure. Mechanical damage or tearing off any mole carries the risk of developing cancerous manifestations, bleeding, inflammation and infection. Hanging moles are especially dangerous in this regard, since it is much easier to injure protruding tissue than a flat pigmented spot.
It should be understood that hanging moles do not mean epidermal neoplasms that have a long stalk. This type of nevi includes only protruding skin structures that have a relatively short base. However, sometimes hanging moles can consist of several lobes, which form some kind of “cauliflower”.
Why are hanging moles dangerous?
The main risk of any mole, including hanging ones, is the possibility of its transformation into skin cancer. If a hanging nevus does not cause discomfort and does not change its visual characteristics, most likely it is a benign structure, the degeneration of which into melanoma is unlikely. At the same time, the following manifestations are considered the first signs of malignant transformation:
- Itching, pain, burning in the mole area;
- A noticeable increase in size and change in the shape of the nevus;
- Change in density and surface of the formation to the touch;
- Color transformations of a hanging mole;
- Bleeding and the appearance of ulcerations on its surface.
Having noticed any signs of transformation, it is necessary to contact a dermatologist or oncologist as soon as possible, who, based on a visual examination and diagnostic measures, will determine the level of danger and method of therapy.
Types of moles
Science identifies several types of moles:
- Dark spots
. Usually chocolate color, sometimes black. The color depends on the presence of melanin in the blood. - Vascular moles
. Usually red, sometimes bluish. Refers mainly to cosmetic defects. - Teratomas
. Such spots appear due to surges in hormone levels in the body.
Moles are usually small in size, but can be large. There are convex, flat, and smooth ones, less often covered with hairs.
Moles can be located in different parts of the body. Sometimes a mole forms on the mucous membrane. The appearance of such neoplasms on the tongue, choroid of the eyes, and genitals is becoming more common. This mainly happens to women.
Moles are not transmitted by airborne droplets.
Inflammation of a mole
Most often, neoplasms do not attract much attention until they begin to cause discomfort and change in size. That’s when the patient goes to a dermatologist for help.
Experts recommend not waiting for pain and removing formations in a timely manner. Timely help will help avoid bad consequences. Often, in the presence of painful sensations, there is already a rapid growth of atypical cells that degenerate into cancer.
But if inflammation has already begun, you should visit a dermatologist immediately. A change in skin color will help determine inflammation in the area of the mole. It usually turns red and may become swollen. This is how the body begins to fight inflammation.
Care after laser mole removal
If the laser ablation procedure was performed by a qualified specialist, the risk of side effects is minimal, but the patient will also have to follow certain post-procedure rules, listed below.
- It is necessary to provide rest to the wound surface, without injuring it by friction of clothing or shoes, and also by taking care of the protective crust;
- Contact of the wound with water should be avoided for two weeks after manipulation;
- It is recommended to protect the skin surface from direct sunlight, and also use creams with a high UV protection factor. To the question of when you can sunbathe after removing a mole, the answer will be at least three weeks;
- You cannot use ointments, creams and gels for healing on your own without a doctor’s prescription;
- The procedure area should be protected from any mechanical damage, carefully protecting the integrity of the protective scab.
Laser removal is one of the simplest and least traumatic methods of mole destruction. Compliance with simple rules of rehabilitation will allow you to avoid scars, cicatrices and other unpleasant consequences and obtain an ideal physiological and aesthetic result.