A lipoma of the spermatic cord is a benign tumor consisting of adipose tissue cells. The tumor does not hurt, so in men it is detected more often during examinations associated with other pathologies - infertility, prostatitis, etc. Lipoma causes complications and can degenerate into cancer.
What are spermatic cord lipomas and why are they dangerous?
The content of the article
The spermatic cord is a complex organ, 15-20 cm long, located in the groin - inside the scrotum in men. The cord stretches from the inguinal ring to the top of the testicle and consists of several structures: the vas deferens, arteries and veins of the testicle and vas deferens, lymphatic vessels and nerve plexuses. The organ performs a reproductive function by connecting the testicles, which produce sperm, and the penis.
Statistics indicate that neoplasms in the spermatic cord are registered less frequently than others. Moreover, in 70% of cases the tumor turns out to be benign. Doctors consider lipoma to be one of the most popular and at the same time most predictable types of tumor affecting the spermatic cord.
Lipomas, called wen, can develop on any part of the human body, including in the area of the spermatic cord, which contains loose connective tissue. Neoplasms are benign tumors, but without proper control or treatment they can cause a lot of problems for their carrier.
From a tumor of the spermatic cord the following can develop: myoma and fibromyoma, sarcoma (cancer), myxoma, dermoid, lymphangioma. There is no point in describing these pathologies - they all have unpleasant consequences and require surgical treatment, therefore, having discovered a neoplasm, you should not allow complications to develop.
Hydrocele (hydroxycele) - symptoms and treatment
First of all, when treating hydrocele, it is necessary to make an accurate diagnosis in a timely manner. In children in the first two years of life in the presence of hydrocele, conservative therapy and expectant management are recommended [1][2][3][9]. Drug therapy is not required at this time. Hydrocele usually disappears during the first year of a child’s life, so surgical treatment in most cases is not indicated; only dynamic observation by a pediatric surgeon or urologist is required [1][2][3]. Taking into account modern clinical recommendations, early surgical treatment is indicated only if a concomitant inguinal hernia or testicular pathology is suspected.
However, if the hydrocele does not go away within two years of the baby's birth, surgery will be required. If the hydrocele is not surgically removed at an older age, it can continue to grow. Surgery is recommended for all children with hydrocele over the age of 2 years as a planned procedure.
Drug therapy may be required for isolated hydrocele in children against the background of acute epididymitis and orchitis, and for allergic edema of the scrotum. In such cases, rest, wearing a bandage to immobilize the scrotal organs, antimicrobial and desensitizing drug therapy are required [6].
The most radical and effective method of treating hydrocele is surgical treatment. First of all, these are open surgical interventions :
- Bergman operations;
- Winkelmann operation;
- plication (reduction in size) of the testicular membranes;
- Lord's operation;
- plasma coagulation of the tunica vaginalis of the testicle [4].
These are minimally invasive operations with video assistance for excision of testicular membranes. The main objective of most of the listed methods is aimed at eliminating the serous cavity between the plates of the tunica vaginalis of the testicle. The operation performed must meet certain requirements:
- do not relapse;
- be minimally invasive;
- do not cause complications;
- do not cause testicular dysfunction;
- the subsequent period of hospitalization should be short.
For hydrocele of the testicular membranes, in most clinics in Russia, preference is given to three types of open surgical interventions:
Winkelmann operation. During this surgical intervention, one of the layers of the testicular membrane is cut along the anterior surface, turned inside out and sutured behind the testicle. In this case, fluid accumulation no longer occurs. This operation consists of making a 4–5 cm long incision on the anterior
the surface of the scrotum on the side of the presence of hydrocele. All membranes are dissected up to the vaginal membrane. The testicle is removed into the wound. Next, puncture of the vaginal membrane and evacuation of fluid is carried out. Then this membrane is also cut and the testicle is exposed. The testicle and its epididymis are examined.
Next, plastic surgery of the testicular membranes is performed according to Winkelmann: the membranes are everted and stitched. The fluid produced by the epithelium of the tunica vaginalis of the testicle will be absorbed by the surrounding tissues. Next, the testicle is immersed in the wound, a layer-by-layer suture of the wound is made, leaving a drainage half-tube, which is removed the next day after the operation, and a tight bandage is applied. Sutures are removed on the 10th day after surgery.
Bergman's operation. A skin incision is made above the dropsy. The hydrocele is cleared of fascia and pierced with a trocar; the serous fluid is collected in a prepared container. The testicular membranes are excised, careful hemostasis is performed, and the testicle is again placed in its bed. A drainage is installed under the testicle. The skin is sutured with antibacterial, self-absorbing, cosmetic material that does not leave scars. An aseptic dressing is applied. A correctly performed Bergman operation eliminates the possibility of complications. Damage to the spermatic cord during Bergmann's operation is also excluded. In the postoperative period, antibacterial drugs are prescribed. It is necessary to wear a suspensor for some time.
Lord's Operation . During this operation, the testicular membranes are dissected, the hydrocele is released, and the vaginal membrane around the testicle is corrugated. In this case, the testicle itself is not freed from the surrounding tissues and does not dislocate into the wound. This allows you to reduce trauma to adjacent tissues and feeding vessels of the testicle.
In 2005, a method of plasma coagulation of the tunica vaginalis of the testicle [11]. This method is based on the effect of a plasma flow (ionized inert gas argon) on the vaginal membrane of the testicle. However, the method has not received widespread use [4].
Laparoscopic closure of the opening of the tunica vaginalis of the testicle is one of the surgical treatment options, however, the use of laparoscopy in the treatment of hydrocele in children remains controversial, as there is a risk of relapses and complications associated with the duration of anesthesia [12].
Sclerotherapy occupies a special place among surgical minimally invasive methods of treating hydrocele [4]. Serous fluid is sucked out with various instruments (primarily a syringe), for this purpose a puncture of the hydrocele is performed. After removing the fluid, sclerosing drugs are injected into the cavity. The basis of their mechanism of action is the stimulation of an inflammatory cellular response to the introduction of a chemical substance. In the future, this leads to sticking of the layers of the vaginal membrane. For sclerotherapy for hydrocele, various substances are used, such as:
- tetracycline;
- betadine (polyvidone-iodine);
- polidocanol;
- sodium tetradecyl sulfate;
- ethanolamine;
- phenol;
- 96% ethyl alcohol [4].
Sclerotherapy is somewhat less effective than open surgery. It can be used to a limited extent in elderly people, as well as with large hydroceles. Elimination of dropsy by puncture without the administration of sclerosing drugs is temporary. The hydrocele puncture method is currently not used due to the high risk of infection of the hydrocele [1][2][3][6].
Complications are possible after surgical treatment - any surgical intervention carries this risk. After surgical treatment of hydrocele, bleeding may occur, hematomas, swelling and suppuration may form [9][10].
Causes of lipoma formation in men
The cause of lipoma development has not yet been precisely established. Doctors are confident that there is a genetic predisposition to the pathology, since wen in this area is often found in most men from the same family.
It is believed that the tendency to form lipomas is established in men during embryonic development, so the pathology is congenital. In the embryo, cells are formed in the scrotum area that can accumulate fat in the future. When the process starts, these cells quickly divide, turning into a wen.
Contributing factors:
- metabolic disease;
- injuries to the scrotum and groin;
- diseases of the liver and pancreas associated with the processing of fats;
- disruption of the thyroid gland and pituitary gland - organs that produce hormones involved in metabolism;
- diabetes mellitus, which inhibits all metabolic functions in the body;
- alcohol abuse;
- excessive physical activity leading to the formation of an inguinal hernia.
Despite the fact that the wen grows from fat cells, obesity does not put a person at risk. Lipomas can also occur in thin people.
Often this type of tumor is registered in people with Cowden's syndrome (hereditary genetic autoimmune disease).
Symptoms of lipoma in the spermatic cord
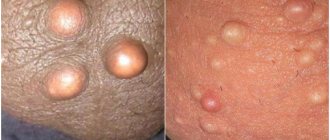
Benign and malignant tumors at the first stage reveal themselves by the appearance of a small compaction. Externally, a lipoma looks like a small ball filled with fat. At the initial stages, it is difficult to identify pathology, which is due to the peculiarities of its localization and development.
Features of the development of lipoma and other tumors in this area:
- Benign tumors grow slowly. Some of them take several years to reach a size of 3 cm in diameter. Others (fibroids and lipomas) can grow to enormous sizes. Due to the expansion of tissues, a man may be bothered by the feeling of the presence of a foreign body.
- Over time, the wen grows, so the scrotum changes size, increasing on one side. Unpleasant sensations arise when touching underwear.
- At first, nothing hurts; pain in the inguinal-scrotal area occurs a little later. The resulting pain is not constant, tending to intensify with pressure and movement. The growth of the tumor leads to a constantly pursuing feeling of heaviness and constant pain. It can radiate to the sacrum, lower back and lower abdomen.
- A large wen compresses the testicle and pinches the veins of the spermatic cord, they expand and become deformed. Due to heat exchange disturbances, spermatogenesis is disrupted, so lipoma is often accompanied by male infertility. Problems with blood flow make themselves felt by a burning sensation in the groin and scrotum.
- Malignant tumors are very insidious. They prefer to grow in the groin area, gradually infiltrating surrounding tissues and organs and forming metastases in the pelvic lymph node. Sarcoma grows slowly until a certain time, which can mislead a man. A sharp increase in tumor with the formation of multiple metastases begins suddenly.
The appearance of pain in the groin area and increased temperature require immediate contact with a urologist to receive a referral for examination. There is a small chance that the tumor will degenerate into cancer.
How to examine the testicles?
Examine the testicles while showering because the warm water will soften the scrotum, making it easier to feel the inside of the testicles.
During a self-exam, first look for a tumor on the testicle. Edema or swelling may be an important symptom. It is important to note that one testicle can (and very often) be larger than the other. Look for a hard lump or swelling of the skin.
Examine each testicle separately and then compare them. With both hands, gently grasp the testicles with your thumb and forefinger. Both testicles should be smooth.
The hard lump should not be confused with the epididymis, located on top and behind each testicle. If you notice a hard lump anywhere else on your testicle, you should see a doctor as soon as possible.
An additional sign to look out for is severe pain. It may indicate torsion, injury, or infection (inflammation). Also during self-examination, you may notice a varicocele - an enlargement of the veins in the upper part of the testicles. It appears as nodules or growths under the surface of the skin.
Diagnostics
The symptoms of spermatic cord lipoma are similar to other urological diseases: lymphadenitis, varicocele, cancer, so the diagnosis can only be clarified by undergoing diagnostics.
- Palpation.
Decent-sized tumors can be palpated. To the touch, the tumor is defined as a heterogeneous tissue formation. Men discover large lumps on their own before seeking medical help. But with palpation it is impossible to determine the type of tumor, so additional studies must be carried out. - Ultrasound of the scrotum
. This is the primary examination method - it is inexpensive, accurate and painless. Ultrasound is necessary to determine the size of the tumor and its exact location. - Dopplerography
. Ultrasound with a Doppler sensor showing the quality of blood flow. On an ultrasound, the wen is visible as a knot-shaped formation. - X-ray of the scrotum
. Inexpensive, but hazardous to health method. During the examination, soft x-rays are used, but repeated diagnosis in this way in the next few months is contraindicated. On an X-ray, a lipoma appears as a bright spot of regular shape, since fat does not absorb X-rays well. - Diaphanoscopy.
Transillumination helps to exclude hydrocele of the spermatic cord, which is much more common than lipoma; - CT, MRI
. If there are any doubts about the diagnosis, the urologist will send you for an MRI or CT scan - such an examination involves radiation and costs several times more than an ultrasound. - Biopsy.
If cancer is suspected and the diagnosis cannot be made using other means, tumor tissue is removed with a thin needle for careful examination under a microscope. If the lipoma degenerates into cancer or is initially an oncological tumor, atypical (modified) cells are found in tissue samples taken for biopsy.
In addition to instrumental methods, you need to undergo tests. Laboratory tests include: general blood and urine tests, blood biochemistry tests. These tests allow us to screen out other diagnoses associated with inflammatory processes and infections.
Symptoms of a lump on the testicles
In addition to the nodules themselves, it is especially important to note that there are certain accompanying symptoms. They can help in diagnosis:
- upon palpation, you can feel the consistency of the formation (liquid or hard);
- possible blood in the urine;
- erythema (redness of the skin);
- pain and tingling in the testicles;
- heat;
- nausea.
When visiting a doctor, it is important to list all the symptoms you observe. The doctor may not notice on his own.
Treatment of lipomas in men
Attempts to treat spermatic cord lipoma with folk remedies are unsuccessful. Herbal medicine is not able to affect adipose tissue, therefore it is useless in the treatment of this pathology. There are no medications that give a significant effect.
The only way to deal with spermatic cord lipoma is surgery. A small lipoma does not require removal provided it is painless, lacks growth and has stable consistency. Violation of any of these conditions is considered an indication for surgery. The intervention is carried out in one of three ways.
- The surgical method
is traumatic, but cheap. The tissue that has undergone the change is excised, and then the wound is sutured. The operation is performed under local anesthesia. Recommended only for large lipomas. - Liposuction
. In this case, a needle is inserted into the lipoma and all its contents are pumped out. The method is unreliable because it does not guarantee ideal removal of fat cells and, therefore, does not protect against subsequent relapses. - Laser exposure
. This method is the most gentle, but is used only for tumors not exceeding 3 cm in diameter. - Radio wave technique is the newest method of treatment that does not cause complications. It is also carried out if the wen is still small.
In some cases, the spermatic cord lipoma reaches very large sizes, which makes its isolated removal impossible. Doctors recommend that such patients agree to radical removal of the tumor along with the testicle and cord.
Treatment of testicular nodules
Treatment primarily depends on the cause.
Inflammation caused by sexually transmitted diseases is treated with medications (corticosteroids), and an accurate diagnosis is important.
Hydroceles, varicoceles and cysts are treated symptomatically or with antibiotics, and in some cases with surgery.
Hernia can also be treated surgically.
Testicular cancer is the most serious medical problem. Its treatment requires surgery and post-operative treatments such as chemotherapy and radiation therapy. If detected early, the prognosis is very good.