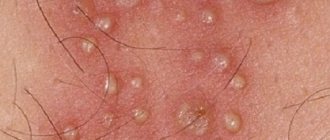
Herpes in the intimate area in women or genital herpes in women is one of the most common clinical types of sexually transmitted herpes infection. Genital herpes in women is characterized by the appearance of characteristic rashes on the skin and mucous membranes in the urogenital and/or anal area, characterized by variability in the clinical picture and a tendency towards a persistent recurrent course.
The causative agent of genital herpes is the herpes simplex virus (HSV, Herpes Simplex virus).
Fact Infection with genital herpes in 76% of cases is caused by HSV-2 and in 24% by HSV-1.
In most patients, the causative agent of genital herpes is herpes simplex virus type 2 (HSV-2). There are cases of genital herpes caused by HSV type 1, which reflects the increased prevalence of oral-genital contact in various population groups. In some patients, the disease can be caused simultaneously by two types of herpes simplex virus (HSV-2 and HSV-1).
What is genital herpes
The content of the article
Genital herpes is one of the most commonly diagnosed sexually transmitted diseases in both men and women. The causative agent is the herpes simplex virus type HSV-1 and HSV-2. In many people, the disease is completely asymptomatic, so the likelihood of infection through sexual contact is very high.
Symptoms of genital herpes are easy to recognize by visual examination. Mild pain and changes appear on the skin of the genitals and perineum, resembling blisters. The first wave of the disease can last from 2 to 3 weeks, sometimes less. When the disease relapses, the symptoms of GG are usually less disturbing than the first time.
Special antiviral drugs alleviate the condition. Patients whose symptoms of genital herpes appear regularly are forced to take medications every day.
Treatment with immunomodulators, prevention of herpes –
If you have a high frequency of relapses of herpes, or even rare, but severe outbreaks, it is very important for you to take up the prevention of outbreaks of herpes. And the point here is not only that the severe course of a herpetic infection and/or its frequent relapses themselves indicate problems with your immunity. The fact is that the herpes virus has an immunosuppressive effect on the entire immune system - both cellular and humoral immunity.
This means that the immune system under the influence of the herpes virus will continue to weaken, leading to a further increase in the frequency of relapses and the severity of outbreaks. At the moment, there are the following directions for preventing outbreaks of the herpes simplex virus (HSV-1, HSV-2), but you should choose one or another method only after consulting a doctor. All patients with a frequency of outbreaks of more than 6 during the year must be tested for the number of specific IgG and IgM antibodies to the herpes simplex virus, as well as consult an immunologist and have an immunogram (which evaluates the subpopulation composition of cells, NK activity, and also the levels of α- and γ-interferons).
Prevention methods:
- Prolonged use of antiviral drugs - in this case, Acyclovir tablets are prescribed 400 mg 2 times a day (but we do not recommend this option, since the use of acyclovir in patients with weakened immune systems very often leads to the development of resistance of the herpes virus to acyclovir ).
A preventive course of drugs from the list below should last about 9-12 months, and only on the recommendation of a doctor. The drug "Valacyclovir" - 500 mg 1 time per day (but for patients with a relapse rate of more than 9 times a year - 500 mg 2 times a day). The drug "Famciclovir" - 250 mg 2 times a day. Studies show that the preventive effect is more pronounced with Valacyclovir, but cross-resistance must also be taken into account (since if the herpes virus is resistant to acyclovir, it will also be resistant to valacyclovir). - Immunocorrective therapy – the immune system can be improved with special drugs “immunomodulators”. There are several drugs that have proven effective in preventing relapses of herpes, and for which this indication for use is directly stated in the instructions. The use of immunostimulating drugs allows - 1) to reduce the frequency of relapses by about 40-50%, 2) to reduce the duration of each outbreak, for example, complete healing will occur faster by about 2-3 days than usual.
Good drugs, the instructions for which specifically indicate “as part of the complex therapy of herpetic infection” are over-the-counter tablet drugs “Cycloferon”, “Polyoxidonium”, “Licopid” (you can look at the official instructions for treatment regimens). The first two drugs also have a release form as an injection solution, but this is only by prescription. By the way, Cycloferon, in addition to stimulating the immune system, also has its own antiviral activity against the herpes simplex virus (24stoma).Accordingly, if the patient has active manifestations of herpes, and the immunomodulator is used as part of complex therapy for herpes infection (together with antiviral drugs), Cycloferon will be the optimal choice. And, by the way, it can be used from 4 years old. If you use an immunomodulator between herpes outbreaks, i.e. in the absence of clinical manifestations, it is better to choose “Likopid” or “Polyoxidonium” (they can be used from 3 years of age).
Likopid" can be in tablets of 1 and 10 mg (tablets of 10 mg can only be taken as prescribed by a doctor, and tablets of 1 mg are available over the counter). Recommended use of Likopid 1 mg for adults – 2 tablets 3 times a day (orally or sublingually), course of treatment is 10 days. Scheme of use of Likopid 10 mg tablet for adults - 1 tablet 1 time per day, course of treatment for 6 days. For children over 3 years old, Likopid 1 mg tablets can be prescribed, and the regimen is as follows - 1 tablet 3 times a day (orally or sublingually), for a total of 10 days.
Important: taking immunomodulators is indicated not only for the prevention of relapses of herpes infection - in patients who are often and/or seriously ill with herpes. Immunomodulators should be used as part of the basic therapy of herpes infections (in addition to therapy with antiviral drugs) in patients with weakened immune systems.
Moreover, if the immunomodulator is used during an exacerbation of herpes, then it is best to use Cycloferon, because it also has a direct antiviral effect on the herpes simplex virus. If we are talking about taking immunomodulators in the period between outbreaks, then you can use Lykopid or Polyoxidonium. In the next section we will talk about the Vitagerpavac vaccine, which is nothing more than a real herpes vaccine.
The causative agent of the disease
Herpes (from the Greek ἕρπης - creeping, spreading skin disease). Genital herpes is a viral infection that affects the penis in men (penile herpes) and the external genitalia and vagina in women (herpes vaginalis, labia), as well as the area around the genitals, usually the perineum. Infection is manifested by the appearance of blisters on the skin. Sometimes they can occur on the buttocks and anus.
The causative agent of the disease is the human herpes virus. There are two types of AI virus: herpes virus type 1 and herpes simplex virus type 2.
- AI virus type 1 most often leads to the appearance of herpes on the lips. Causes half of the cases of genital herpes.
- AI virus type 2 is responsible almost exclusively for the development of genital herpes. Very rarely it can also cause herpes on the lips.
Herpes on the lips
Clinical forms
- Typical;
- Atypical;
- with macrosymptoms;
- with microsymptoms;
- Asymptomatic form;
It is very difficult to establish the real incidence of damage to the internal genital organs in both women and men, since in 25-40%, and according to some data, in 60% of patients, the disease occurs without subjective sensations. It can be assumed that this pathology occurs much more often than it is diagnosed.
With herpes of the internal genitalia there may be no complaints. Sometimes they note periodically appearing light mucous discharge from the urethra and vagina. During laboratory examination of smears of the cervical canal, vagina and urethra, an increased number of leukocytes is periodically noted (30-40 in the field of view of the urethral discharge, 200-250 or more in the field of view when examining smears from the vagina), indicating the presence of an inflammatory process.
The asymptomatic form of genital herpes of the internal genitalia (asymptomatic shedding of the virus) is characterized by the absence in patients of any complaints about the genital area, objective clinical data confirming inflammation. During a laboratory examination of the discharge of the urogenital tract, HSV is isolated, while in smears there are no signs of inflammation (leukocytosis). In 25-30% of men with idiopathic (when the cause of infertility is not clear) infertility, HSV is isolated from semen.
It is known that genital herpes, in 70-80% of cases, occurs in the form of a microbial association, in combination with chlamydia, urea-, mycoplasma, strepto-, staphylococci, fungal flora. It is possible that the genitals may be affected by HSV, gonococcus, treponema pallidum, and viral diseases transmitted through sexual contact, which indicates the need for a thorough examination of patients to exclude STIs and HIV infection.
Ways of infection with genital herpes
Genital herpes is transmitted primarily through sexual contact with a person who is already a carrier of the virus. The thin, delicate mucous membranes of the mouth, genitals and anus are very vulnerable to viruses and infections. This allows the virus to pass from one person to another during sexual intercourse, including oral and anal sex.
Transmission of the virus from the lips to the genitals occurs during oral sex, when one of the partners has signs of herpes on the lips. The herpes simplex virus can also enter the body of another person through wounds or cracks in the skin on other parts of the body: fingers, palms, knees, etc., provided that the surface comes into contact with the infected area of the skin. Re-infection with your own virus through accidental touch is unlikely.
Local immunomodulators for HPV and HSV
Among the “universal” drugs that can be prescribed for various viral infections - from common respiratory infections to herpes and human papillomavirus - are interferons. In particular, preparations of human recombinant interferon alpha-2b.
Interferon alpha-2b has antiviral, immunomodulatory and antiproliferative properties. It suppresses the replication of RNA and DNA viruses, enhances the activity of macrophages, and increases the cytotoxicity of lymphocytes to target cells. The use of drugs containing interferon alpha-2b is accompanied by an increase in the level of immunoglobulins type A and normalization of IgE [5]. However, these therapeutic effects are fully manifested when the drug is administered systemically.
when its high concentration in the blood is reached. It should be noted that quite powerful side effects can develop, including fever, loss of appetite, headaches, muscle pain, joint pain and many other adverse reactions.
Due to the specific safety profile, injectable interferon preparations are prescribed only in very serious cases, when the risk of side effects is justified - for example, in the treatment of hepatitis, a number of oncological diseases, etc. HSV and HPV infections do not apply to such situations and are not indications for systemic interferon administration. At the same time, the Russian Federation has registered a very impressive list of local forms of interferon alpha-2b, including ointments/creams for treating mucous membranes with genital herpes.
Theoretically, local interferon preparations should have all the advantages of injectable ones and not have their side effects, since local forms are either very slightly absorbed into the systemic circulation or do not penetrate into the blood at all. However, today there is no sufficiently reliable evidence of the effectiveness of interferons when applied topically. However, in domestic practice they are quite often prescribed as part of the complex treatment of recurrent genital herpetic infections.
Along with local forms containing only interferon alpha-2b, several combination drugs are also registered in the Russian Federation:
- Interferon alpha-2b + acyclovir + lidocaine, ointment. Indications: HSV.
- Interferon alpha-2b + taurine + benzocaine, vaginal and rectal suppositories, prescription. Indications: HSV, HPV. Taurine, according to the instructions, acts in combination as a reparative, antioxidant and anti-inflammatory component.
+
High safety profile.
!
The feasibility of using local forms of acyclovir for genital herpes is subject to serious doubts due to insufficient activity, which is confirmed in Western recommendations [3]. Interferon alpha-2b preparations, both mono- and combined, are available with or without a prescription, depending on the indications of the dispensing rules in the instructions for a particular drug. It is important to draw the visitor’s attention to the fact that the first-line treatment for HPV - oral forms of acyclovir and valacyclovir - must be prescribed by a doctor, so you should be advised to immediately consult a doctor.
Asymptomatic course of the disease
The first infection with the herpes simplex virus is often called the primary infection. Such an infection can cause symptoms of the disease, but this does not occur in all cases. After the primary infection, the virus is not eliminated from the body; it lives in it in the form of an inactive form (in sleep mode).
In some people, the virus “wakes up” from time to time and enters the surface of the skin. This, in turn, causes a relapse of the viral disease on both the genitals and lips.
For most people, infection with the herpes virus in intimate areas is not a cause for concern. At least 8 out of 10 people with genital herpes don't even know they have it. Sometimes only very mild symptoms may appear that are difficult to associate with genital herpes. Such symptoms may include a slight burning sensation or slight redness that quickly disappears.
In such people, the virus remains dormant and never causes a wave of symptoms to return. However, even those who develop the disease asymptomatically are dangerous to their sexual partners. It is in such cases that infection with the herpes virus occurs.
What happens after infection?
One of the characteristics that distinguishes viruses from the herpes virus family from other types of viruses is latency. HSV and other herpes viruses have the ability to create small but permanent colonies of viral particles inside the body. These colonies are often completely inactive (or dormant), but they remain in the body for life.
As soon as HSV gains a foothold in the body, it begins to create copies of itself and spread. This can lead to a clinical picture of the infection ranging from mild and unnoticed symptoms to severe illness. In response to this, the immune system mobilizes its forces and limits the spread of HSV. Regardless of the severity of symptoms, the virus remains in the body. To avoid the immune system, HSV “retreats” along the nerve fibers and hides in the nerve ganglia. In the case of genital herpes, the virus is located in the sacral plexus of ganglia, located at the base of the spine. In the ganglia, the virus remains inactive (latent) for an indefinite period of time.
The phenomenon of latency is similar to the sleep cycle. Basically, the virus remains dormant in a safe place, sometimes for a very long time. Unfortunately, various biological events can activate HSV, after which the virus spreads along nerve fibers back to the skin. This may cause the symptoms and signs of genital herpes to reappear.
It is difficult to answer the question of how often the virus can be activated. Previously, it was believed that all cases of HSV activation lead to the development of a clinical picture of the disease. Research then revealed that the virus can become active without causing noticeable symptoms or signs—no itching, no pain, no rash. This phenomenon is called "asymptomatic reactivation."
Asymptomatic reactivation refers to the following situations:
- Some herpetic eruptions may appear in places that are difficult or impossible to see.
- Some herpetic lesions can be mistaken for something else, such as an ingrown hair.
- Some manifestations of herpes cannot be seen with the naked eye.
The fact is that when the herpes virus is activated and moves to the surface of the skin or mucous membranes, it is difficult for even a doctor to notice. In addition, even for a person with symptoms and signs of genital herpes, several days pass before the full clinical picture develops, during which he will not be aware of the reactivation of the virus.
Signs of genital herpes
At the initial stage of the disease, a person is worried about a slight increase in body temperature, general malaise and poor health. Small groups of blisters, often painful, appear around the genitals and/or anus. There may be visible changes on the skin of the labia, as well as the clitoris, in the area of the vaginal opening, on the thighs around the anus.
Herpes blisters
The blisters grow for one to two weeks before bursting and turning into small, painful sores. Lymphatic inguinal nodes are enlarged and identified, palpated as compactions, lumps in the upper thighs. Painful urination is often a concern.
Women may experience unusual vaginal discharge. The herpes virus in women affects the cervix, first blisters appear on it, then ulcers appear. Typically, blisters and ulcerative lesions develop within 10-20 days, after which they gradually disappear without leaving scars.
The first symptoms of genital herpes may appear months or even years after infection. Therefore, the first wave of symptoms may occur while a person is married or in a long-term relationship with a reliable partner.
It is not entirely known why some people experience symptoms of infection and others do not. It is also not fully understood why the first wave of symptoms occurs months or years after the actual infection. This may have to do with how the immune system responds to the virus in individuals.
Herpes test
You should get tested for herpes if you have typical symptoms.
When diagnosing, the doctor takes into account complaints, medical history and external examination. Identifying typical cases of genital herpes is usually not difficult and is based on clinical manifestations. No special preparation is required to take blood tests for the herpes virus. You can get tested for the herpes virus in Moscow at our clinic. Collection of biological material (separated from the genital tract, saliva, etc.) for a PCR smear for women, children and virgin girls is carried out on any day of the cycle, except for menstruation itself. It is possible to take material for diagnosis from the following places: “U” - urethra “C” - cervix (except virgins) “V” - vagina “R” - rectum “O” - oropharynx
Recommendations for patients on how best to get tested for the herpes virus
It is not recommended to take biomaterial earlier than 24-48 hours after sexual intercourse.
Scraping for PCR analysis of herpes types 1 and 2 from the urogenital tract (in men): it is recommended to take it no earlier than 2 hours after the last urination.
Scraping from the urogenital tract (in women): smears for genital herpes should not be taken: • during menstruation (1, 2, 3, 4 days); • earlier than 5 days after using vaginal suppositories, tampons or spermicides; • after a vaginal examination (pelvic ultrasound, colposcopy), douching.
Diagnostics
What tests for herpes are performed and their cost, ₽
| List of tests | Prices |
| Analysis for herpes types 1 and 2 | 550 |
| Test for herpes type 6 (mouth/nose/throat swab) | 550 |
| Blood test for herpes | |
| PCR blood for herpes type 1 and 2 | 750 |
| Antibodies to herpes type 1 IgG | 850 |
| Antibodies to herpes type 2 IgG | 850 |
| Antibodies 1 and 2 IgG | 950 |
| Antibodies 1 and 2 types IgM | 850 |
| Antibodies type 1 and 2 IgG (avidity) | 950 |
| Test for herpes type 6 IgG | 850 |
| Herpes virus type 6 (colic) | 750 |
Development of disease relapses
Some people sometimes experience recurrences of genital herpes. Scientists are unable to explain why, after the latent stage, the virus is activated from time to time, that is, the reasons for the relapse have not been established. Factors that contribute to the development of the virus and relapse of the disease are known:
- influenza, ARVI, other diseases with high body temperature;
- local damage to the external genitalia, as well as the mouth and lips;
- decreased defense mechanisms, immunodeficiency;
- ultraviolet radiation, a side effect of radiation therapy;
- changes in a woman’s immune system during menstruation;
- hypothermia;
- stress;
- excessive alcohol consumption.
ARVI
Stress
Relapses are often milder and last shorter than the first wave of the disease. In case of relapses, symptoms usually occur within 7 to 10 days. Most people do not complain of either elevated body temperature or poor health. A relapse of the disease may be indicated by a slight tingling sensation or itching of the genitals for 12-24 hours.
Over time, relapses of genital herpes appear less frequently. The frequency of their occurrence may vary. For some people they occur six or more times during the year, for others much less often. As a rule, during the first 2 years from the first wave of symptoms, relapses occur 4 to 5 times. Some people do not relapse at all.
Herpes symptoms –
A striking hallmark of herpes is the appearance of a group of blisters filled with liquid. However, before they erupt, there is always a period (lasting from several hours to 1 day) when there are no clinical manifestations yet, but the virus has already been activated. As a rule, during this period you may feel itching, burning or swelling of the tissue in the area where herpetic blisters should appear in the future (24stoma.ru). Further symptoms depend on the location of the rash...
- Herpes on the lips (Fig. 7-9) - the red border of the lips and the skin around the mouth are the most common localization of herpes. Herpes of this localization is called “labial”. The blisters that appear on the skin and red border of the lips burst and dry out after 2-3 days, and the affected surface becomes covered with crusts that persist for a period of 7 to 10 days. Under no circumstances should the crusts be peeled off, because... Removing the crusts can also lead to a new outbreak of herpes.
Labial herpes: photoFor detailed information about the most effective treatment regimens for herpes of this localization, read the article: “How to quickly get rid of herpes on the lip”
- Herpes on the skin of the face – foci of herpes can appear on any part of the facial skin, which is usually associated with a violation of the integrity of the skin (scratches, cuts, abrasions). Typical localization is herpes on the cheeks and nose, earlobes, chin, and forehead. The skin around the eyes can also be affected, but we have identified this type of lesion in a separate column.
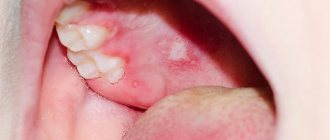
Depending on the extent of skin damage and the severity of clinical manifestations, either a skin cream with an antiviral effect or a cream in combination with tableted antiviral drugs may be prescribed. You can see a detailed review of treatment drugs at the end of the article. - Herpes in the mouth (Fig. 10-11) - herpes of the tongue, gums and other areas of the oral mucosa most often occurs in children, rarely in adults. This disease is called herpetic stomatitis. After the bubbles on the mucous membrane burst, bright red erosions form in their place, which are quickly covered with a whitish-yellow fibrinous coating. Along the perimeter of the lesions there is always a bright red rim of inflamed mucous membrane.
In children, herpetic stomatitis is often accompanied by gingivitis. In this case (in addition to multiple blisters and erosions in some area of the oral mucosa), you can see bright red inflamed gums.
- Ophthalmoherpes
(Fig. 12-13) – the herpes simplex virus can spread to one or both eyes. Most often, this happens when you introduce the virus with unwashed hands that have recently touched areas of the skin affected by herpes. You can spread the virus simply by using a regular face towel. Most often, the virus infects the upper layer of the cornea, causing herpetic keratitis. If rashes may appear on the skin of the eyelids, this option is called “herpetic blepharitis.”Symptoms: pain, blurred vision, sensitivity to light in one eye (if one eye is affected), feeling of “sand in the eyes.” Eye herpes is very dangerous, and untimely or improper treatment can lead not only to dryness of the cornea and the appearance of scars on it, but also to deterioration of vision, constant pain, and even blindness and loss of the eye.
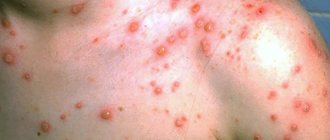
General symptoms of herpes - primary herpes infection can occur with symptoms similar to influenza or ARVI (fever, muscle pain and even enlarged submandibular lymph nodes). But such acute symptoms are observed in only 10% of all patients. With repeated outbreaks, the general condition of the body is usually not disturbed.
How to diagnose genital herpes
To diagnose the disease, a visual examination is generally sufficient. The type of changes, their location and other symptoms are sufficiently characteristic to make a diagnosis of genital herpes.
In case of doubt and for invasive infections, carry out:
- Isolation of the virus from a cell culture, examining the smear or the content of the bubbles, however, the absence of the virus in dilution (negative result) does not exclude infection;
- The polymerase chain reaction (PCR) method is a more sensitive method of testing a smear or fluid from the rash, but a negative result also does not rule out infection.
- Serological study. Allows the detection of antibodies to the HSV virus, which appear after a few weeks, as well as differentiation of the type of virus that caused the infection.
If antibodies against HSV-2 are detected, genital herpes is diagnosed, which poses a higher risk of relapse of the disease. Antibodies against HSV-1 indicate herpes simplex virus, so there is less chance of recurrence of lesions in the genital area.
Recurrent herpes
Recurrences of genital herpes are observed in 50-70% of women and men after the disappearance of the primary signs of the disease.
The frequency of relapses and the duration of remissions are very variable - from once every 2-3 years to monthly exacerbations. The frequency of relapses and the severity of the clinical picture can be criteria for the severity of the process. With a mild form of chronic herpetic infection, exacerbations occur no more than 1-3 times a year, with a moderate form - 4-6 times a year. Severe course is characterized by monthly exacerbation of the disease.
Treatment of genital herpes
The use of antiviral drugs does not remove the virus from the body. Their goal is to suppress the reproduction process of the pathogen. The most effective use of medications is during the first manifestation of signs of the disease. Moreover, it is necessary to start therapy within the first five days from the moment the first symptoms appear. This allows not only to stop the spread of lesions, but also to reduce the duration of the disease.
The course of treatment for genital herpes is most often five days; if the rash persists, it is extended. To shorten the duration and relieve symptoms, you should start taking the drug as quickly as possible. The earlier treatment is started, the greater the chances of a rapid cure, effective reduction of symptoms and prevention of relapse of the disease.
In the treatment of relapses of the disease, antiviral drugs are not always used. Therapy is indicated and brings good results in cases of frequent severe symptoms. In case of frequent relapses, it is possible to take an antiviral drug every day. In people who use this form of treatment, relapses will either be completely absent or their frequency will be significantly reduced.
How to treat herpes in adults (medicines) –
Very often, patients ask questions about how to cure herpes forever. Unfortunately, at the moment medicine does not have the ability to achieve complete removal of the herpes virus from the body. However, modern antiviral agents (ointments and tablets) can effectively block the replication of the virus, especially when it comes to the herpes simplex virus (types HSV-1 and HSV-2). It can be much more difficult to cure herpes on the body, which is referred to as “shingles” or “herpes zoster”.
Modern antiviral tablets and ointments for herpes can significantly reduce the severity of herpes infection, speed up healing, and also reduce the frequency of relapses. There is also a domestic vaccine against the herpes simplex virus (types HSV-1 and HSV-2) called “Vitagerpavak”, which can reduce the frequency of repeated outbreaks of herpes infection by several times. Below we will tell you about the best remedy for herpes - both among means for external use and among tablet preparations.
But in order for herpes treatment to be as effective as possible, you must strictly follow the following rules:
- Herpes therapy will show good effectiveness if it is started no later than 12 hours from the moment the first herpetic rash appears. Keep in mind that the later treatment is started, the less effective even the best herpes medications will be.
- The maximum effectiveness will be shown by therapy that is started in the prodromal period (i.e., when the actual herpetic blisters have not yet appeared, but the patient already feels itching, burning or swelling of the tissue in this area). If treatment begins during this period, then the number and size of herpetic blisters formed in the future will be significantly smaller, and in this case, complete healing can be achieved in just 4-5 days.
- Remember that if you start treatment later than 48 hours , or after the herpetic blisters have opened, such therapy will not noticeably affect the speed of recovery (healing of lesions). However, in patients with severe and frequent relapses, such therapy can avoid complications.
Drugs for the treatment of genital herpes
Zovirax ®
(Zovirax)
. Original drug. The medicine is manufactured by Glaxo Wellcome, SA. The active ingredient is acyclovir 200 mg. Clinico-pharm. group: antiviral drug. Pharmaceutical therapeutic group: antiviral agent. Pharm. action: a synthetic analogue of purine nucleoside that inhibits the replication of Herpes simplex AI viruses types 1 and 2.
There are known generics of the drug Zovirax - Acyclovir (manufactured by Belupo, Croatia), Acyclovir (manufactured by Akrikhin, JSC Vertex, JSC Sintez, Russian Federation).
Drug for the treatment of genital herpes
Valtrex®. Original drug. The drug is manufactured by Glaxo Smith Kline, SA. Contains the active ingredient valacyclovir hydrochloride 556 mg (= valacyclovir 500 mg). Clinical and pharmacological group: antiviral drug. Pharmacotherapeutic group: antiviral agent. It is an L-valine ester of acyclovir. Valaciclovir is quickly and completely converted into acyclovir and valine in the body.
Choosing tablets for herpes -
Herpes treatment in adults: drugs in tablets
- Acyclovir,
- Valaciclovir,
- Famciclovir.
Below we will compare the effectiveness of these antiviral tablets against the herpes simplex virus. It should be noted that Acyclovir tablets are approved for use from 0 years of age, and the drugs “Valacyclovir” and “Famciclovir” - only from 12 years of age. All these drugs are available only with a doctor's prescription.
Acyclovir in tablets of 200 and 400 mg –
Tablet acyclovir has the same disadvantages as creams: low tropism for the virus (i.e., acyclovir molecules do not find viral particles well); in patients with poor immunity + frequent courses of acyclovir use in the past - in 10-27% of cases the herpes virus may be resistant to acyclovir; plus low oral bioavailability. Pros: no age-related contraindications, affordable price, fairly few side effects.
We recommend choosing the original drug with acyclovir - Zovirax 200 mg tablets (instructions for use, see PDF). Moreover, its cost is not much higher than that of Russian generics.
Examples of drugs with acyclovir -
Acyclovir tablets certainly work, especially when it comes to patients with good immunity and rare relapses of herpes. If you have a weakened immune system, if you have taken acyclovir too often in the past, if you decide to start taking the drug more than 24-48 hours after the onset of herpetic rashes, acyclovir will not be particularly effective. In this case, it is better for you to immediately start taking the drug Famciclovir, which works better even at later dates of initiation of therapy, as well as in patients with immunodeficiency conditions.
The regimen of use - if you look at the official instructions, the standard regimen for adults and children over 2 years old - is to take acyclovir 200 mg 5 times a day (for 5 days). A single dosage of 400 mg is recommended in the official instructions - either only for severe herpes infection, or in patients with weakened immune systems. However, most clinical studies (source) show that a dosage of 200 mg has virtually no effect on either the duration of symptoms or the healing time of herpes.
Studies have shown that only 400 mg (respectively, 5 times a day, for 5 days) is an effective single dose. In children under 2 years of age, the dosage is reduced by exactly 2 times - from the adult dosage. In case of severe herpes infection, taking the drug can be extended to 7-10 days. By the way, abroad, at the moment, acyclovir is practically not used for chronic recurrent herpes, giving preference to valacyclovir and famciclovir.
Valacyclovir (Valtrex) tablets –
We have already said above that tableted acyclovir has poor bioavailability, i.e. only about 10-20% of its amount is absorbed in the intestine, which makes it difficult to achieve high concentrations of acyclovir in tissues. This problem is solved by Valacyclovir, which has a bioavailability of 50%. Valaciclovir is a precursor to acyclovir (i.e., it is converted to acyclovir once it enters the bloodstream). Taking tablets with valacyclovir allows you to create a concentration of acyclovir in tissues that can be achieved with traditional acyclovir - only through intravenous infusions of the latter.
The drug Valtrex is the original drug of Valaciclovir (we recommend this drug), but there are also a large number of cheaper generics. The cost of the original drug “Valtrex” (UK) is from 1350 rubles for 10 tablets. 500 mg each. There is a good Bulgarian generic “Valvir” - it costs from 750 rubles for a package of 10 tablets. 500 mg each. The cost of the Russian “Valacyclovir-Akos” will be from 450 rubles (for a package of 10 tablets of 500 mg).
Regimen: There is a short 1-day treatment regimen. Clinical studies have shown that taking high dosages of the drug for 1 day was the most effective for the treatment of herpes on the lips and facial skin, as well as herpetic stomatitis. In this case, the dosage regimen is 2000 mg 2 times a day, with an interval of 12 hours (1 day in total). But it should be noted that such a short regimen will be effective only if treatment begins no later than 12 hours from the moment the herpetic eruptions appear, and also in patients with satisfactory or good immunity.
If more than 12 hours have passed since the appearance of the rash, and also if you have a weakened immune system, it is optimal to use the standard treatment regimen of 500 mg 2 times a day for 3-5 days (for severe herpes infection - up to 10 days). When choosing a drug, keep in mind that if your herpes virus is resistant to acyclovir, taking valacyclovir will also be ineffective.
Famciclovir tablets (Favirox, Famvir) –
Famciclovir products are the most modern and effective tablets for herpes. Above we told you about the cream “Fenistil-pencivir” (based on penciclovir), which is used on the skin of the face and the red border of the lips. So, drugs with famciclovir are tablet analogues of penciclovir. Most often in pharmacies you can find drugs with famciclovir - under the trade names “Favirox” or “Famvir”.
The advantage of famciclovir drugs like Favirox is their rapid antiviral effect due to maximum bioavailability (for famciclovir it is about 74%, for example, for valacyclovir it is only 54%, and for acyclovir only 10-20%). Therefore, a package of three 500 mg tablets is enough for a short 1-day course of therapy to relieve the manifestations of herpes on the lip. Read more about this application scheme below.
→ Favirox instructions for use (view PDF)
Regimen for using famciclovir - there is a short 1-day treatment regimen: either take 1500 mg once, or 750 mg 2 times a day (with a 12-hour interval between doses) - our experience suggests that the second option is still better. This 1-day regimen is effective only if you start taking the drug before 12 hours from the moment the herpetic rash appears, and also if the patient’s immunity is normal. In case of weakened immunity, and/or if treatment is started later than 12 hours from the moment of the appearance of herpetic eruptions, the standard dosage regimen should be used.
The standard regimen according to the instructions is 250 mg 2 times a day for 5 days (however, in severe cases of herpes infection, dosage can be extended to 7-10 days). Here I would like to add that numerous clinical studies show the weak effectiveness of this standard regimen - especially in patients with poor immune system conditions. Studies have shown that the effectiveness of therapy increases significantly when famciclovir is prescribed in higher dosages. In patients with good immunity, a more effective regimen will be 500 mg 2 times a day (for 5 days). In immunocompromised patients - 500 mg 3 times a day (for 7 days).
Important: once again we draw your attention to the fact that short 1-day treatment regimens for herpes in adults (herpes on the lips and skin around the mouth, on the face) work well only if the following conditions are met. Firstly, only if you start taking medications no later than 12 hours from the moment the herpetic rash appears. Secondly, if you have a satisfactory or good immune system. If treatment is started later than 12 hours from the onset of the rash, as well as in patients with weakened immune systems, short 1-day courses of therapy are usually ineffective. Here we already need a standard regimen of administration.
Important : if more than 12 hours have passed since the first rash appeared (and even more so if more than 24 or 48 hours), it is better to opt for famciclovir, because the latter works better at later dates of initiation of therapy for herpetic infection.
Genital Herpes – Symptom Relief at Home
A cold compress (ice cubes wrapped in a towel) placed on the lower abdomen for 5-10 minutes may provide relief. Do not apply ice directly to the skin.
It is important to take in plenty of fluids.
Scented soaps, bath products and other similar products that may irritate the skin should be avoided. The best results are obtained by gently washing the genital area with a cotton swab and water. You cannot share towels, washcloths, or sponges. This minimizes the risk of infection to other family members.
Sexual abstinence is recommended until the blisters and ulcers disappear.
Why both partners need to treat genital herpes
One partner may have persistent manifestations of the disease.
Another may be a carrier.
To avoid constant relapses of the disease, both partners should receive treatment.
A complete cure is impossible.
Once infection occurs, the virus remains in the body forever.
It is imperative to receive treatment in order to:
- no active infection has developed
- there were no constant relapses
- do not infect the fetus if pregnancy is planned
This virus is extremely dangerous for a child who is in utero.
Genital herpes and sexual intercourse
If partners are carriers of the same virus, the possibility of re-infection is excluded. It is recommended to avoid intimate relationships from the moment the first symptoms appear until they disappear completely.
The herpes simplex virus is highly contagious when blistered. Sexual activity in this state is accompanied by a maximum risk of transmitting the virus to a partner. If there are no symptoms of genital herpes, the likelihood of transmitting the virus is reduced. However, this is possible because the virus is present on the surface of the skin of the genitals.
Using a condom during every sexual intercourse helps protect yourself from infection. However, it should be remembered that a condom does not guarantee complete protection against transmission of the virus to a partner, because it only protects the covered area of the body.
People who take antiviral medications for a long time are also less likely to contract the virus.
How to recover
Treatment of genital herpes in women is quite long and complex. Many gynecologists believe that it is generally impossible to completely cure HSV types 1 and 2, and the most that can be counted on is a stable remission for several years.
Until recently, it was traditionally believed that virus damage to the upper part of the body was caused by herpes of the first type, and the lower part by the second. However, the sexual revolution and the fashion for oral sex in both directions changed this idea. Today, type 1 virus can cause genital herpes, and type 2 can cause fever on the lips, and types 1 and 2 can cause blisters on the anus. That is, each type feels quite free in the human body and manifests itself where direct infection occurred.
By the way, in 80-90% of people, a blood test for herpes infections reveals antibodies that protect against infection or exacerbation. The initial encounter of a person with these viruses apparently occurs in childhood and in the vast majority of cases is asymptomatic. But the body produces IgG antibodies, which makes it quite resistant to infection. This balance can only be disrupted by provoking external factors.
It should also be remembered that various medical tests for herpes virus types 1 and 2 can detect it in saliva, tears, blood, urine, vaginal secretions, anal folds, semen and cerebrospinal fluid. Therefore, you can “catch” it not only through sexual contact, but also through a towel, cream, shared utensils, cosmetics, etc. The disease cannot be treated independently, at home.
Our clinic in Moscow treats herpes in women with good therapeutic results thanks to the presence of competent specialists and preliminary diagnosis. Good gynecologists, any tests and effective treatment regimens for genital herpes! We invite you to make an appointment with a gynecologist right now!
Genital herpes during pregnancy
To prevent genital herpes from developing in a child, a woman who has ever had symptoms of the disease should see a doctor (sometimes delivery by cesarean section is recommended). Sexual intercourse is prohibited from the third trimester of pregnancy if the woman’s partner not only has signs of genital herpes, but also suffered from the disease in the past. During this period, the risk of fetal infection is very high.
For many years, the development of an effective vaccine against genital herpes has been underway, unfortunately, so far to no avail.
ONLINE REGISTRATION at the DIANA clinic
You can sign up by calling the toll-free phone number 8-800-707-15-60 or filling out the contact form. In this case, we will contact you ourselves.
Prevention
Preventive measures to prevent the occurrence of this disease include:
- quitting smoking, caffeine and alcoholic beverages;
- reviewing your diet, enriching it with vitamins A, C, E;
- avoid overheating and hypothermia;
- the microflora of the digestive system should be normal;
- maintaining physical activity;
- do not neglect massage and physiotherapy;
- consumption of bee products.
Vaginal herpes is a rather unpleasant and quite dangerous disease. To prevent its occurrence, it is necessary to follow the rules of personal hygiene and promptly contact a gynecologist when the first symptoms appear.
Is it possible to become infected with genital herpes in a bathhouse or swimming pool?
Outside the human body and at very high temperatures, the virus will not survive in the environment.
Therefore, infection with a virus in a bathhouse is very rare.
But still, it happens, this is possible when using someone else's towel that has viruses on it.
The owner of the towel must have an active infection.
The same applies to the pool; infection is possible, but it occurs extremely rarely.
Advice for patients in the active stage of infection: do not visit public places.
Do not be afraid of contracting any infections.
If you follow the rules of hygiene and use your personal accessories, there is practically no risk of infection.