Recurrent herpes of the external genitalia
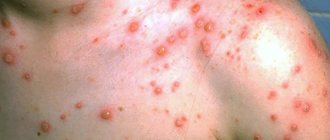
Typical recurrent herpes on the skin and mucous membranes of the genital organs, usually in the same place, subjective: burning, itching manifested by repeated blistering rashes.
Atypical forms of recurrent herpes, which greatly complicate the diagnosis.
In atypical forms, either one of the stages of development of the inflammatory process in the lesion predominates (erythema, blistering), or one of the components of inflammation (edema, hemorrhage, necrosis), or subjective symptoms (itching), which give the corresponding name to the atypical form (erythematous, bullous, hemorrhagic, necrotic, itchy, etc.).
Atypical forms of herpes of the external genitalia are more common in women than in men.
The subclinical (asymptomatic) form is manifested by microsymptoms: short-term (less than a day) appearance of one or several microcracks, accompanied by slight itching. Sometimes there are no subjective sensations, which reduces the number of patients visiting medical institutions and complicates diagnosis.
The subclinical form is detected mainly during virological examination of sexual partners of patients with any sexually transmitted infection, or during examination of married couples with impaired fertility.
Clinical diagnosis of abortive course, atypical and subclinical forms of RGG is difficult and can only be made using virological research methods.
A feature of genital herpes is multifocality. The pathological process often involves the lower part of the urethra, the mucous membrane of the anus and rectum.
Organs of the genitourinary system in women and men that may be affected:
- entrance to the vagina;
- vagina;
- vaginal part of the cervix;
- cervical canal;
- urethra;
- bladder;
- anus;
- rectal ampulla;
- mucous membrane of the uterine cavity;
- body of the uterus;
- the fallopian tubes;
- ovaries;
- prostate;
- seminal vesicles;
Ways of infection with herpes
Infection with herpes in the intimate area in men occurs in the following situations:
Classic vaginal intercourse with a woman infected with the genital herpes virus, with the pathogen localized in the vagina.
Anal contact - in the presence of a virus in the rectal mucosa or the skin of the perianal area.
Oral sex very often causes the appearance of herpes on the penis, because many people suffer from the so-called “cold on the lips,” that is, labial herpes, which very easily spreads to the man’s penis.
Infection of a child during childbirth in the presence of a large amount of virus in the vagina of the woman in labor.
Such herpes can occur not only after contact with an infected person who currently has clinical manifestations of a herpes infection (ulcers, spots, blisters, crusts). Infection occurs even in the absence of these signs of the disease, because the genital herpes virus can be present in the skin and mucous membrane during remission of the disease, but transmission to a healthy person is also possible during this period.
Clinical features of herpetic infection in women
Herpes of the urethra and bladder
Herpetic urethritis in women is subjectively manifested by pain and cramping at the beginning of urination, and a frequent urge to urinate. With herpetic cystitis, hematuria, pain at the end of urination, blood in the urine, and pain in the bladder area appear.
Herpetic cystitis
In a woman, the first and only sign of HSV infection may be in the genitourinary tract. It often occurs in the first 1-3 months after the start of sexual activity or a change of sexual partner.
Herpes of the anal area and rectum
The lesion in the anal area usually represents a recurrent fissure, which is often a reason for diagnostic errors. Such patients with an erroneous diagnosis of “anal fissure” end up with surgeons. The itchy form of herpes anus and herpetic lesions of hemorrhoids are also difficult to diagnose.
The list of diseases etiologically associated with HSV is constantly growing. According to the literature, in 3.6% of women suffering from treatment-resistant colpitis and cervical leukoplakia, HSV is one of the etiological factors of the disease. A new form of latent intrauterine HSV-II infection with localization of the pathological process in the glandular epithelium of the endometrium is described. It has been proven that HSV can cause the development of endometritis and salpingoophoritis.
The asymptomatic form of herpes of the internal genitalia is detected in 20-40% of women suffering from herpes of the buttocks and thighs. This important circumstance must be taken into account when planning pregnancy in women with this form of GC due to the existing likelihood of developing complications of HSV infection during pregnancy.
The etiopathogenetic role of HSV in cervical cancer has been established. The above emphasizes the growing etiological role of HSV in the structure of diseases of the pelvic organs in women.
Herpes and pregnancy
The prevalence of HSV among pregnant women in the United States is 22-36%, in Europe 14-19%. Viremia in women during pregnancy can cause fetal death, stillbirth, and premature birth. Herpes viruses cause up to 30% of spontaneous abortions in early pregnancy and over 50% of late miscarriages; they are second only to the rubella virus in terms of teratogenicity (the development of fetal deformities).
The most severe forms of neonatal herpes develop when a newborn is infected with the herpes simplex virus during childbirth. With primary herpes in the mother, from 30% to 80% of children are infected, with recurrent herpes – 3–5%. Infection of the fetus during delivery, if the mother had herpetic eruptions at the end of pregnancy, occurs in 50% of women with RGG; however, 60–80% of infected children develop encephalitis.
Symptoms of herpes in the intimate area
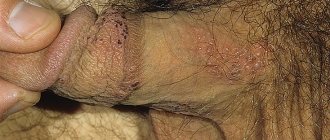
Herpes on the penis usually manifests itself in the form of successive rashes on the skin of the shaft, glans penis, at the base of the penis, on the urethral sponges and inside the urethra, on its mucous membrane.
Herpes begins in the intimate area in men with the appearance of itching, burning, and redness of the skin of the penis. Next, against the background of the spot and slight swelling, grouped bubbles appear, filled with transparent contents. The blisters either burst with the formation of erosions and ulcers, or dry out into a crust, which falls off after a few days with the formation of a pink post-inflammatory spot. When the rash is localized on the urethral mucosa, there may be pain when urinating and discharge from the canal mixed with blood.
Diet
When doing treatment at home, you must follow a diet. This will help prevent the herpes from getting worse. The principle of the diet is a high content of lysine, a small amount of arginine.
- Allowed foods include low-fat dairy products, beef, chicken, various fish and seafood.
- For dessert you can eat ice cream or drink coffee with cream.
- Blackberries, black currants, peaches, apples, bananas help cleanse the body.
- Additionally, your daily diet should include garlic and brewer's yeast (you can use pharmaceutical preparations in the form of capsules).
- You can eat a little green onion salad dressed with olive oil three times a day. The dish is rich in retinol and ascorbic acid, which helps strengthen the body.
Alcohol should be avoided completely. Minimize consumption of sugar, sweets and nuts.
Which doctor should I contact if I have herpes in the intimate area?
A venereologist has the greatest knowledge and experience in treating genital herpetic infections. At the appointment, the doctor will determine the localization, stage of the viral process, and the condition of the regional lymph nodes. Material is taken from the surface of the rash and from the urethra for PCR analysis to determine the type of herpes and related sexually transmitted infections.
To clarify the diagnosis and develop a treatment plan, blood is taken to determine antibodies to various types of herpes viruses and the state of the immune system.
Prevention
In order to prevent genital herpes, experts recommend constantly taking measures to strengthen the immune system, as well as directing your efforts to preventing possible infection.
usually occurs sexually) from a sick person to a healthy person. Manifested by the following symptom complex: rash (vesicles) on the genitals – purulent pustules – purulent ulcers – scabs. The duration of the disease is 30 days. Discharge, problems with urination, and enlarged or inflamed lymph nodes in the groin are also observed.
Currently, many developed countries are actively developing preventive herpetic vaccines that protect against infection, and therefore we can hope that in a few years humanity will be able to receive an effective vaccine against herpes.
How is herpes on the genitals in men treated?
Treatment of genital herpes, or, as it is more correctly called, genital herpes, is a difficult task. The fact is that at the moment there are no drugs that can completely remove the virus from the body. And therefore, relapses of the disease are possible even after complete therapy.
Herpes on the head of the penis requires complex treatment. Such treatment includes the prescription of antiviral drugs in the form of injections, tablets, suppositories, and topically in the form of creams. To correct the state of antiviral immunity, interferon inducers, immunomodulators, and herpes vaccine are prescribed. Classic methods of administering antiherpetic drugs externally, orally, intravenously, as well as an innovative method of electrophoresis of abnormal nucleosides and interferon into an organ affected by herpes are used. This gives maximum effect in case of protracted herpetic infection of the male and female reproductive systems, especially the prostate, bladder and fallopian tubes. The option of “just anointing it with something” is not suitable for the treatment of viral lesions of the genitals. This will certainly lead to the formation of a chronic process with frequent exacerbations, when sexual life becomes impossible in principle.
For the initial episode and rare relapses, the disease is usually treated within 7–14 days. If a chronic herpetic infection has developed with exacerbations more than 6 times a year, then the patient needs longer therapy up to 3-6 weeks, and sometimes taking medications for 6-12 months.
Our clinic has developed complex treatment regimens that not only stop this relapse, but also create the prerequisites for a long, relapse-free course of genital herpes without exacerbations, complications or a decrease in a man’s quality of life.
Atypical form
The atypical form of the pathological process is characterized by an erased abortive course, which affects not only the external genitalia, but also the internal genital organs. As a rule, this form of infection is characteristic of chronic recurrent herpes, but at the same time, it can also occur with primary lesions.
It's no secret that many chronic pathologies of the genital organs are diagnosed as diseases of unknown etiology. This is due to the inability to identify the cause of the disease, and therefore the prescribed treatment is very often ineffective. It is in such cases that good specialists suspect the development of an atypical form of herpesvirus infection.
Treatment of herpes type 1
Herpes virus type 1 (HSV-1) is a type of herpes virus that affects the trigeminal nerve. Most people know this common virus as a cold sore. Manifestations of the virus appear on the skin around the lips and directly on the red border and wings of the nose. They look like bumps against a background of redness, which then transform into blisters, erosions, and crusts. The course of the infection consists of periods of exacerbations and remissions; the virus is constantly located in the nervous tissue and is activated under favorable conditions (hypothermia, weakened immunity, various diseases, stress). Complications of a viral infection are possible, such as damage to other areas of the skin and internal organs.
Treatment of herpes type 1 during exacerbation
- The use of drugs whose action suppresses the further development of viral infection. Both external (creams, ointments) and internal (tablets, injections) and combined treatment are possible. Therapy with antiviral drugs is necessary during exacerbation of the disease.
- The use of immunomodulators, prostaglandin inhibitors, interferon inducers: this is necessary to activate the immune defenses to fight the virus.
Treatment during an exacerbation period lasts on average no longer than 10–14 days.
Treatment of herpes after remission
After the disappearance of external manifestations of infection, immunomodulatory drugs, physiotherapy, ozone therapy, and plasmapheresis are used. The patient is advised to reconsider his lifestyle, give up bad habits, and eat right. When 2–3 months have passed after recovery, vaccine therapy is carried out in order to form an immune response. Special vaccines used:
- live weakened
- inactivated (“dead”)
- split vaccines (“divided” into proteins and nucleic acids)
Due to the proven oncogenicity of the herpes simplex virus, the use of vaccines is a rather controversial method of treatment. Thus, live and inactivated vaccines are considered dangerous in terms of the risk of developing cancer pathologies, and split vaccines, despite their apparent superiority and novelty, may have low effectiveness.
Based on the above, it is obvious that the herpes simplex virus type 1 must be suppressed during exacerbations, and it is better to prevent the development of exacerbations as such.
Treatment of herpes type 2
The herpes virus, once entering the human body, remains there forever, periodically disturbing with its manifestations on the skin and mucous membranes. Consequently, treatment of type 2 herpes or genital, genital herpes cannot guarantee complete healing, but only reduces or stops its recurrence and the severity of clinical manifestations.
Prescribing treatment for herpes should be preceded by a deep and detailed diagnosis aimed at clearly determining the type of virus, the state of the immune system, especially the body’s antiviral defense, the presence of complications of herpes infection and concomitant diseases.
The cost of determining the herpes virus type 2 is 300 rubles using the polymerase chain reaction method, which takes one day.
Dermatovenereologists at our clinic develop treatment for herpes only after a final diagnosis has been established and are never guided by a formal approach in prescribing antiviral chemotherapy.
There are several types of therapy for herpes type 2, which are prescribed depending on the frequency of relapses and the severity of symptoms.
- Episodic treatment of genital herpes is carried out each time a relapse occurs and aims to relieve the clinical manifestations of the disease.
- Anti-relapse treatment or suppressive therapy is prescribed for frequently recurrent herpes type 2 and has the task of stopping the activation and manifestation of the virus for a long time.
Very often, in the treatment of genital herpes, we use drugs from different pharmacological groups, that is, complex therapy for type 2 herpes is carried out. This helps both relieve this relapse and protect against the reappearance of herpetic eruptions.
- Abnormal nucleosides are purely antiviral drugs that block viral enzymes and prevent the reproduction of herpes.
- Antibiotics are prescribed when a secondary bacterial infection occurs. They have no effect on the virus itself.
- Immunomodulators, interferon inducers are drugs that enhance the fight against the virus by the person’s own immune system.
- Herpetic vaccine - used to develop specific immunity against herpes type 2 by forming a large number of antibodies to it.
- Vitamins, ozone therapy and other restorative procedures can reduce the number of relapses in patients with frequently recurrent herpes.
- Local treatment - antiviral creams, gels, ointments and simply drying and disinfectants such as fucorcin and brilliant green solution.
The duration of treatment for herpes type 2 depends on many factors and ranges from 10 days to a year.
Doctors involved in the treatment of genital herpes work in our clinics, where you can undergo any diagnosis of this viral infection and receive the necessary therapy depending on your specific situation related to type 2 herpes.
The cost of treatment for genital herpes depends on the duration of the course prescribed to you and the drugs used and is generally 500-1500 per day of injection therapy.
The price of tablet treatment for herpes type 2 is low, but it is ineffective.
Our specialists will help you choose the most adequate therapy so that you feel absolutely healthy, even if you have this type of herpes simplex virus in your body.
Diagnostic methods
Herpetic infection with a typical course is easily recognized. A vaginal examination reveals typical rashes located in the vagina, on the cervix.
Laboratory diagnosis requires an atypical form.
The following methods are used:
- 1 PCR diagnostics - determination of viral DNA in discharge from the vagina, urethra, and erosions on the skin.
- 2 Growing the virus in cell culture is used less frequently due to the long duration of the study.
- 3 Enzyme immunoassay can detect antibodies and determine the form of infection.
Differential diagnosis is carried out with an atypical form, which sometimes looks like:
- 1Streptococcal infection.
- 2Lichen planus.
- 3Candidiasis.
- 4Behçet's disease.
- 5 Pemphigus.
If complications develop or the disease is poorly controlled, consultation with an immunologist, dermatologist and related specialists may be required.
Treatment of herpes type 3
Herpes simplex virus type 3 (HSV-3) is the cause of infectious diseases such as varicella (chickenpox) and shingles.
Most people experience a viral infection during preschool age, but cases of infection in adulthood are also not rare. Herpes zoster most often occurs in adulthood and old age.
This type of herpesvirus is also characterized by a lifelong existence in the human body: it is impossible to completely recover from the virus; throughout life, the virus “dormants” in the tissues of the nervous system.
Symptoms of chickenpox include fever, rash on the skin and mucous membranes, itching; in mild forms of the disease, a small amount of elements may form on the skin; body temperature does not rise.
Shingles is also characterized by skin rashes, general weakness, itching, and fever.
Treatment of viral herpetic infection type 3 is multi-stage, complex. Since it is not possible to get rid of the virus, the goals of therapy are as follows:
- Reduce pain during acute illness
- Shorten the regeneration period of skin manifestations
- Reduce the likelihood of complications such as postherpetic neuralgia
- Etiotropic (directed at the cause of the disease) therapy: antiviral drugs are used in the first three days from the onset of symptoms. These drugs can suppress the spread of the virus; they reduce the activity of viral particles. The duration of treatment is on average 7–10 days.
- Symptomatic therapy: due to severe pain, itching and discomfort accompanying skin manifestations of HSV-3, analgesics and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (ibuprofen-based drugs) are prescribed; At elevated temperatures, antipyretics are recommended. Anticonvulsants prescribed for acute HSV-3 (carbamazepine) also reduce the severity of pain. Treating skin rashes with antiseptic solutions prevents the risk of developing infectious complications.
- Increasing the body's defenses with the help of interferon inducers and immunomodulators.
- Specific immunotherapy: it is necessary for infection with HSV-3 during pregnancy; such therapy consists of the administration of specific immunoglobulin in the early postpartum period.
- Antidepressants: this component of therapy is aimed at reducing discomfort and correcting the psychological state.
- Physiotherapy: successfully used due to positive treatment results. Methods of influence such as electrical neurostimulation, magnetic therapy, laser therapy, hyperbaric oxygenation, and reflexology are used.
The duration of treatment for herpes zoster is from 7 to 14 days for an uncomplicated process and up to 3-4 weeks for a process complicated by pustular infection or neuritis.
Treatment of herpes type 4
Among herpes viruses, type 4 is extremely widespread, also known as the Epstein-Barr virus. Just a few years ago they didn’t write about him as much as they do now; Meanwhile, the diversity of its manifestations should not give reason to take this type of herpesviruses lightly. The virus is the cause of diseases such as infectious mononucleosis, multiple sclerosis, lymphogranulomatosis, Burkitt's lymphoma, oncological diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, nasopharynx, etc.
Treatment of herpes type 4 can be called multi-stage, complex, individual: everything depends on various factors, such as, first of all, the course of the disease, the severity of symptoms, as well as the state of the immune system, the presence or absence of diseases.
It should be noted that the course of the infection can be both latent and pronounced. Mild forms of viral infection, reminiscent of a common acute respiratory viral infection (often even without a rise in temperature) are subject to outpatient treatment and do not require medication, with the exception of symptomatic remedies.
If the disease occurs with a rise in temperature, deterioration of condition and general well-being, hospitalization is often required.
Therapy can be described as follows:
- Bed rest, drink plenty of fluids.
- Mobilization of the body's immune forces with the help of immunomodulators (Viferon, Cycloferon), alpha interferon (Roferon, Reaferon). The administration of immunoglobulin (Sandoglobulin, Polygam, etc.) is also indicated.
- Nonspecific antiviral treatment with abnormal nucleotides, acyclovir (in severe cases, administered intravenously).
- Symptomatic remedies: painkillers, antipyretics, vasoconstrictor drops, gargling.
- Antibiotics for infectious complications.
- For swelling of the pharynx, hormones (corticosteroids) are prescribed.
- Adaptogens, B vitamins, and nootropics are also used. In some cases, the prescription of antidepressants and psychostimulants is indicated.
The infection is not completely cured, so improving health is of great importance to prolong the period of remission. You should give up bad habits, including food habits, treat diseases in a timely manner, and get rid of foci of chronic infection.
Herpes: questions and answers
Is it possible to treat teeth with herpes?
Dentists say that it is possible to treat teeth with herpes, but they strongly advise against doing so. If it is possible to postpone the procedure, it is better to postpone it for 1-2 weeks, when the blistering rashes completely disappear. If the toothache is mild or moderate, specialists will help relieve it with safe medications, and the therapy itself will begin after the exacerbation of herpes has passed. In critical cases, if you need urgent surgical intervention, you will be helped in any dental clinic, despite the presence of concomitant diseases.
We recommend monitoring the condition of your teeth and undergoing regular preventive examinations so that in the future there is no reason for urgent dental treatment during the period of herpes. We advise the same regarding viral infections. This pathology is difficult to control. Often its symptoms appear at the most inopportune moment. If you are tired of discomfort on your lips, spoiled appearance and constant itching, contact our medical center and get rid of this problem.
Can you drink alcohol if you have herpes?
In this case, alcohol does not have a negative effect directly on the affected area. However, drinking it during an exacerbation of herpes is still not recommended, since alcohol has a bad effect on the body as a whole. When it is consumed, the body begins to spend energy on eliminating alcohol and turns on compensatory mechanisms, which leads to even greater fatigue and a decrease in protective reactions. Medicine has long recognized that there are no safe doses of alcohol. There are no direct contraindications to drinking alcohol during an exacerbation of herpes, however, specialists at our Private Practice clinic strongly do not recommend this for the following reasons:
- Alcohol can worsen existing allergic reactions or provoke new ones in response to one of the medications you are taking.
- Alcohol increases the load on the liver, which at this moment is already working on the biotransformation of drugs and the removal of infectious toxic products.
- The likelihood of developing side effects with any treatment regimen for alcohol intake increases significantly.
- Alcohol further suppresses the immune system, which complicates the treatment of herpes and delays the moment of recovery.
- Alcoholic drinks retain fluid in the body, which slows down the removal of toxins and cleansing of the bloodstream.
Of course, if there is an important reason, drinking alcohol in small quantities is allowed even while treating herpes. In the absence of abuse, the possible risks are minimal. At the same time, we try to convey to each patient the importance of following the prescribed treatment regimen and the need for dedication, since the patient himself is primarily interested in a successful result.
Thus, our medical doctor takes the position that you can drink alcohol if you have herpes, but you shouldn’t do it. Following a correct lifestyle and a competent treatment regimen drawn up by our specialists guarantee the achievement of the desired and quick result.
Is it possible to wet herpes?
The common belief that herpes cannot be wetted is incorrect. The water itself does not have a negative effect on rashes and damaged skin. It does not increase the symptoms of the disease and does not contribute to its progression. On the contrary, it is recommended to keep the skin affected by blisters clean to prevent secondary infection and speed up healing.
You can wash your face if you have blisters on your lip, and you can also take a shower if you have rashes on your body. In this case, you should follow some precautions:
- during an exacerbation, take a shower rather than a bath;
- the water temperature should be comfortable, and prolonged bathing and the use of hot water should be avoided;
- It is better to simply wash off dirt and sweating with water using the palm of your hand, rather than using a washcloth. During the period of exacerbation, the use of hygiene products that contain added dyes and fragrances is also subject to restrictions;
- After swimming, it is better to pat your skin with a towel rather than dry yourself with it. We recommend using two towels, one of which should be in contact with the affected areas of the skin, and the other with healthy areas.
Is it possible to take baths if you have herpes?
We do not recommend taking baths if you have herpes. To maintain hygiene, it is enough to take a shower every day. Hot baths and prolonged swimming can reduce the skin's protective properties and also contribute to the spread of infection to neighboring areas. The exception is short-term therapeutic baths after the acute stage of the disease with the addition of agents with bactericidal properties.
Is it possible to go to the pool with herpes?
Herpetic blisters periodically burst, and the affected area of skin turns into an open wound. This area should be protected from possible infection and any damaging factors. We do not recommend going to the pool if you have herpes, as the likelihood of skin damage increases. The main reasons are the addition of aggressive disinfectants, as well as prolonged exposure to water. In addition, you must remember that during the period of exacerbation of herpes infection you are very contagious and should not attend open groups.
Is it possible to give birth with herpes?
The birth process is quite complex and is accompanied by rupture of blood vessels and bleeding. Open blood flow significantly increases the likelihood of the baby contracting infections that the mother has. When preparing for the upcoming birth, the question becomes relevant: is it possible to give birth with herpes and what is the best method to do this. According to American studies, herpes during pregnancy is transmitted from mother to child in less than 1% of cases. If a woman had relapses of herpes before pregnancy, then the child is reliably protected from infection by maternal antibodies to the virus. The woman chooses the method of delivery together with the gynecologist, and natural childbirth is also possible.
Is it possible to breastfeed if you have herpes?
Everyone knows that during an exacerbation of herpes, it is better for the patient to protect himself from any contact with others - shaking hands, using common household items, etc. This is due to the fact that the blistering rash contains a high concentration of the virus and there is a high risk of infecting other people. Considering this, the question arises whether it is possible to breastfeed with herpes, because this process involves the closest possible contact between the child and the young mother.
According to American studies, breastfeeding during exacerbation of herpes virus infection is possible. Specialists at our Private Practice clinic recommend not interrupting breastfeeding even if there is a relapse of a viral infection in the mother, since breast milk is the best nutrition for a newborn. In addition, antibodies to the virus enter the child’s body with mother’s milk, thereby providing the baby with stable antiherpetic immunity.
Is it possible to smear herpes with brilliant green?
Zelenka is not an antiviral agent. Its benefits for herpetic rashes include drying the wound, accelerating cell regeneration and preventing bacterial infection. You can smear herpes with brilliant green, but this should be an addition to the main treatment, and not monotherapy. Our Private Practice clinic offers everyone to undergo a detailed diagnosis of virus carriage, as well as receive an individual treatment regimen to reduce the frequency of relapses.
Is it possible to smear hydrogen peroxide on herpes?
Peroxide is an antiseptic that, when it gets into a wound, causes virtually no pain, unlike iodine and brilliant green. Thanks to this, the remedy has become quite popular, including in the fight against herpetic rashes. In their practice of treating herpes, our doctors do not discourage the use of peroxide externally, but we need to clarify why this should be done. Peroxide is used for its intended purpose (as an antiseptic) and is not an antiviral agent. Free oxygen, which is released from the peroxide when interacting with the virus, has a detrimental effect on the cell wall of the pathogen. An additional benefit is the ability to expel dead organisms and cleanse the wound. However, modern medicine, which is followed by highly qualified specialists at our clinic, suggests using antiviral drugs with proven effectiveness instead of peroxide. We will select an individual treatment regimen for each patient and help avoid relapses.
Is it possible to smear herpes with iodine?
We can confidently answer: only two methods are effective in the fight against viral infections. The first is the use of antiviral drugs, the second is an increase in the immune response. Iodine is an antiseptic and acts as an oxidizing agent. The popularity of its use for herpes is explained by its ability to dry out blisters, destroy cells damaged by the virus and prevent secondary infection. The product can be used to accelerate wound healing and cell regeneration. It is possible to cauterize herpes with iodine, but you need to understand that the procedure is not done to kill the virus, but rather is a way to prevent bacterial infection. It is strictly not recommended to use concentrated iodine solutions to cauterize herpes with iodine if rashes appear in the genital area, since these areas of the skin are very sensitive.
Can you treat herpes with toothpaste?
Toothpaste is one of the popular folk remedies for combating herpetic rashes. If you smear toothpaste on herpes, unfortunately, you will not be able to kill the virus. It lives inside the body, and symptoms of the disease appear only when immunity decreases. The secret to the effectiveness of toothpaste is its fluoride content (other toothpastes are not suitable for such purposes). This element destroys the membranes of damaged cells, accelerates tissue renewal and wound healing, which leads to faster disappearance of symptoms and recovery. Our medical center offers a more modern approach to the treatment of herpes viral diseases. If you believe in the power of toothpaste, try to choose products based on herbal ingredients, as they will additionally have an anti-inflammatory and drying effect.
Is it possible to cauterize herpes?
When characteristic rashes appear, many patients try to immediately cauterize the blisters with iodine, brilliant green or alcohol. However, a virus is an infectious agent that penetrates inside a human cell and, thanks to it, continues to live and multiply. It is possible to cauterize herpes, but it is recommended to do this to prevent the development of a secondary infection, and not to destroy the virus. Our Private Practice clinic advises all patients to use non-alcohol-based antiseptic solutions for these purposes to avoid unnecessary injury and burns to the skin.
Sex and herpes
Herpes is a chronic viral infection. Once HSV has entered the body, it will never leave it. How then can you have sex if you or your partner have this disease? Is it possible to have sex with herpes?
It is reliably known that the herpes virus can be present in the mucous membrane of the genitals or oropharynx and lips even in the absence of rashes. That is, infection is possible without exacerbation of the disease.
Transmission of the herpes simplex virus occurs when the mucous membranes of a healthy person come into contact with an infected person. This happens both during classic vaginal contact and during oral and anal sex.
The chief physician of the Private Practice clinic, urologist-dermatovenereologist, doctor of the highest category, Evgeniy Aleksandrovich Volokhov, talks about herpes on the penis.
Pathogenesis
Genital herpes is defined in ICD-10 under code A60.0. According to WHO, men are infected 2 times less often than women. When infected, the virus primarily attacks epithelial cells, affecting large areas of the genitals, passing further into the genitourinary system.
In cells, viruses reproduce by budding; already 10 hours after infection, herpes is ready to create “daughter” virions - full-fledged viral particles. They penetrate various tissues, blood, lymph. The period of subsidence of the virus depends on the level of immunity. Usually it is 14-21 days.
Acellular organisms infect nerve ganglia (clusters, nodes), remaining there for life, since they cannot survive without a cell. Here they do not manifest themselves in any way until so-called trigger situations occur, which serve as an impetus for the activation of pathogenic microflora.
MAKE AN APPOINTMENT WITH A UROLOGIST
Klokov Andrey Nikolaevich
Urologist-andrologist, doctor of the highest category
Make an appointment