Objective grounds
Itching is a sensation accompanied by the need to scratch the skin. There are several opinions about its occurrence:
- irritation of certain pain receptors;
- occurs independently under the influence of mediators - histamine, serotonin, adrenaline, opioids and others.
The second theory is supported by the fact that itching sensations appear only in the superficial layers of the dermis and the mucous membranes adjacent to it, while pain occurs anywhere in the body. In addition, pain and itching can occur in isolation from each other.
Itching can be localized or spread throughout the body. Due to its occurrence, it is divided into:
- propriocevtive - appears due to a violation of the structure of the dermis;
- neuropathic – observed when the nervous system is damaged;
- neurogenic – without damage to the NS;
- psychogenic – mental disorders.
All types of symptoms differ in intensity, duration and place of occurrence.
Itching of the skin of the body often has objective causes and accompanies any disease. First of all, these include skin diseases :
| Type of disease | Cause | Why does it itch? | Localization of sensations |
| Dermatitis | Nervous stress, exposure to cold, allergens | Small rashes, peeling of the dermis. | Any part of the body |
| Dermatophytosis | Fungus | The vital activity of fungi in the upper layers of the skin | Scalp, smooth skin |
| Lichen | Fungi and viruses against the background of reduced immunity | Peeling of the epidermis | Scalp |
| Pediculosis | Lice | Parasite bite | Head, pubis |
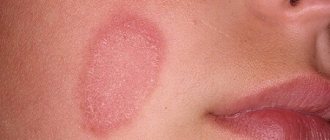
| Psoriasis | It is not completely clear. Presumably: low immunity, heredity, infections | Dry, scaly rashes | Elbows, head, lower back, genital mucosa |
| Scabies | Mite | Parasite bite and blisters. Accompanied by severe itching, which intensifies in the evening | Interdigital area |
| Xerosis | Infections, hepatitis, liver cirrhosis, kidney disease | Coarsening and peeling of the skin | Any parts of the body |
| Neurodermatitis | Stress, allergies, hormonal and digestive disorders | Damage to the top layer of skin | Neck, skin folds, bends of knees, elbows |
Another skin condition that causes "scabies" is eczema . It is believed that it occurs against the background of reduced immunity. It can be triggered by stress, nervous tension, as well as hormonal imbalances and allergic reactions.
Eczema is characterized by the formation of foci of rashes in the form of “wet” blisters and pimples, and in some cases dry ones. The itching in this condition is simply unbearable; it is the main symptom of the pathology. The elements are localized on the neck, head, flexor surfaces of the elbows, ankles and knees.
The skin may itch if there are diseases of the internal organs :
- Kidney - a symptom manifests itself on the skin and in the genital area.
- Liver - spreads to the face and hands, while the skin turns yellow.
- Thyroid – dry, flaky and itchy skin on the hands and face.
- Anemia.
- Diabetes – the skin and mucous membranes of the genital organs begin to itch due to increased blood glucose levels.
- Oncological diseases.
- Hormonal disorders - menopause, pregnancy, menstrual syndrome.
- Viral infections - herpes, AIDS.
- Dehydration.
Treatment
Treatment for itchy skin
Therapy for skin itching is carried out taking into account the established causes and associated factors. For this purpose, pharmacotherapy, local therapy, physiotherapy, and psychotherapy are used. Patients with itchy skin need to change their eating and daily household habits: giving up sweet foods, wearing clothes made of synthetic and coarse fabrics, and using detergents that dry out the skin. It is recommended to avoid stress, avoid scratching the skin, and use neutral moisturizers.
Direct treatment for itchy skin consists of the following components:
- Topical therapy.
Among local antipruritic drugs, topical steroids, cooling lotions, local anesthetics, antihistamines, and calcineurin inhibitors are recommended. The drugs are available in the form of creams, solutions, powders, and ointments. - Systemic pharmacotherapy.
Taking into account the etiological factor of skin itching, antihistamines, glucocorticosteroids, vitamins, immunosuppressants, antimicrobials, and in some cases antidepressants and opioid analgesics are prescribed. - Physiotherapy.
Among the methods of physiotherapy for various forms of skin itching, PUVA therapy and PUVA baths, ultraviolet irradiation, laser therapy, ultraphonophoresis, electrosleep, etc. can be effective. Exercise therapy, acupuncture, general baths with a sedative effect (pearl, pine, valerian) are useful. - Psychotherapy.
Psychotherapeutic techniques (autogenic training, group psychotherapy, cognitive behavioral therapy) help reduce the subjective perception of the severity of itching, stop scratching the skin, improve sleep and quality of life.
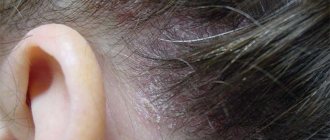
Treatment for itchy scalp
The problem of itchy scalp often resolves when the underlying disease goes into remission. In all cases, the selection of pharmaceutical cosmeceutical hair care products is important: shampoos, masks, oils. For complex treatment of the identified problem, a trichologist may suggest mesotherapy, cryomassage, darsonvalization, and laser treatment of the scalp. For dandruff and seborrheic dermatitis, use antifungal shampoos. For pediculosis, the scalp is treated with special products.
Treatment for itchy eyes
Treatment of itching in the eye area has its own specifics and is carried out mainly using local remedies. During treatment, you must stop using cosmetics and wearing contact lenses in favor of glasses. To eliminate the causes of itching, the following are prescribed:
- instillation of eye drops: antihistamines, steroids, antibacterials, “artificial tears” preparations;
- placing ointments behind the eyelid;
- shading of the conjunctiva with antiseptic and astringent agents (for conjunctivitis);
- treatment of the ciliary edge of the eyelids (for demodicosis, blepharitis);
- washing the conjunctival sac (for eye burns, foreign bodies);
- physiotherapy: UHF, magnetic therapy, magnetophoresis, laser therapy.
If necessary, surgical interventions are performed: opening the stye of the eyelid, removing foreign bodies of the conjunctiva and cornea, anti-glaucoma operations, phacoemulsification of cataracts, etc.
Burning sensation and its origin
A burning sensation in the body and limbs manifests itself in the form of tingling, a sensation of heat. It is constantly present throughout the day or has a wave-like character, but, as a rule, does not bother you at night.
The appearance of this symptom is facilitated by damage to the peripheral nerves. This is observed, for example, in diabetes mellitus . In this case, the burning sensation is concentrated primarily in the extremities, followed by tingling and numbness.
Sciatica is an inflammation of the sciatic nerve, accompanied by a burning sensation in the legs up to the foot.
With multiple sclerosis, the burning sensation is combined with tingling. Such an alliance extends to the limbs. One should be wary of their simultaneous occurrence with problems of speech and coordination.
Radiculopathy is damage to the nerve roots of the spinal nerves. In this case, a pathological feeling of heat also occurs in the arms and legs.
Dangerous is the appearance of a burning sensation in one half of the body. Along with other signs, such as unclear speech, headache, blurred vision, delirium, hallucinations, it can be a sign of a stroke .
Heat in the legs often indicates vascular pathology .
Other conditions that can cause this sensation include:
- spider and snake bites;
- poisoning by chemical compounds;
- avitaminosis;
- calcium deficiency;
- burns.
Particular discomfort is caused by itching and burning in a woman’s intimate area (vagina, vulva and perineum).
A burning sensation in the vagina, along with dryness, are manifestations
of menopausal changes or atrophic inflammation . If the cause of the burning sensation is various kinds of discharge, then this indicates candidiasis, inflammatory processes or sexually transmitted diseases .
Moderate itching in the vaginal area may indicate an allergic reaction to latex or medications. The discussed symptoms in the vulva (external genitalia) also appear against the background of sexually transmitted infections . Other reasons may be:
- lice;
- eczema and mycoses;
- tumor-like formations;
- helminthic infestations;
- kidney and liver diseases.
The perineum includes the area around the genitals and anus. The occurrence of unpleasant sensations in it indicates the presence of such conditions :
- helminthic infestations;
- allergy to powder or linen;
- haemorrhoids;
- rectal tumors;
- systemic diseases;
- sexual infections;
- herpes, candida;
- incorrect hygienic approach.
Itchy skin
Itching is one of the most common dermatological complaints, and it can occur not only in patients with dermatoses, but also in a wide range of general diseases. This is an unpleasant sensation, which is accompanied by a continuous need for response mechanical irritation of the skin. Itching can significantly affect the general condition and quality of life of patients, causing insomnia, anxiety, and in severe cases even lead to depression and suicidal thoughts.
Itching is one of the forms of the skin analyzer, close to other types of skin sensation (touch, pain). Unlike pain, which causes a “withdrawal, avoidance” reflex, with itching a “processing” reflex occurs. Scratching, rubbing, kneading, warming, pinching itchy areas leads to instant, but not long-term, satisfaction. This is due to the fact that during the scratching process, stronger impulses are simulated in the nerve endings, which suppress the conduction of weaker itching signals from the affected areas. Severe itching is relieved only through severe self-harm, leading to the replacement of the sensation of itching with a feeling of pain. If itching exists for a long time, then a focus of pathological excitation is formed in the cerebral cortex and itching from a defensive reaction turns into a standard skin reaction to various external and internal stimuli. At the same time, in response to prolonged scratching, the state of peripheral nerve receptors also changes, which leads to a decrease in the threshold for the perception of itching. Thus, a “vicious circle” is formed, the presence of which explains the difficulties in treating itching.
Itching is caused by mechanical, thermal, electrical or chemical stimulation of unmyelinated nerve fibers, the free nerve endings of which lie at the border of the epidermis and dermis. They are excited either directly or indirectly, through the release of various mediators (histamine, serotonin, proteases, neuropeptides, etc.).
Physiological itching occurs in response to environmental irritants (crawling insects, friction, temperature changes, etc.) and disappears after the cause is eliminated. Pathological itching is caused by changes in the skin or throughout the body and causes a strong need to get rid of the itching by scratching or other means.
Itching can be a symptom of various dermatoses (scabies, pediculosis, atopic dermatitis, allergic dermatitis, eczema, mycoses, psoriasis, lichen planus, etc.) or occur on intact skin due to diseases of the internal organs. Endogenous causes of skin itching are very diverse:
- endocrine and metabolic disorders (diabetes mellitus, hyperthyroidism, hypothyroidism, menopause, hyperparathyroidism);
- liver diseases (biliary cirrhosis, extrarenal cholestasis, hepatitis of various etiologies, etc.);
- chronic renal failure;
- blood diseases (iron deficiency anemia, polycythemia vera, lymphogranulomatosis, leukemia, mastocytosis);
- tumors of internal organs, melanoma;
- autoimmune diseases;
- infectious and parasitic (HIV infection, helminthiasis);
- neurological diseases;
- psychoneuroses;
- pregnancy;
- taking medications;
- age (senile itching).
If the cause of the itching, even with a thorough examination, cannot be identified, then it is defined as itching of unknown origin (pruritus sine materia).
To accurately assess itching, it is necessary to carefully collect anamnesis and question the patient. You should pay attention to the following characteristics of itching: time of occurrence, provoking factors, intensity, course, localization, character.
The intensity of itching can vary - from mild to very severe. For a more objective assessment, you should clarify: does itching interfere with falling asleep; whether the patient wakes up from itching; Does itching interfere with daily work? Itching leading to sleep disturbance is considered severe.
Depending on the time of occurrence, they are distinguished - nocturnal, daytime, permanent, seasonal. For example, with scabies and widespread eczema, the itching intensifies when patients go to bed; anal itching caused by pinworms occurs between two and three o'clock in the morning; in psychoneuroses - permanent.
Limited itching of the skin in one anatomical area, as a rule, is caused by local causes. The presence of widespread and symmetrical itching suggests its internal nature.
The itching sensation can be “deep” or “superficial”, it can have a hint of burning, tingling (for example, dermatitis herpetiformis is characterized by burning itching, especially of the scalp). Itching - parasthesia is a feeling of tingling, mild burning, crawling, etc., develops with increased pain sensitivity of the skin and decreases with stroking or light pressure on the itching area. Biopsy itch leads to deep damage to the skin.
As a result of prolonged itching and scratching, excoriation, pigmentation, scars, lichenification, and pyoderma occur. The free edge of the nail plates wears off, leaving the nails looking polished. Objective signs are not necessary to make a diagnosis of itchy skin.
Features of itching in syndromes of different origins
Cholestatic (liver) itching is one of the most painful and persistent symptoms of chronic cholestasis. It occurs in 100% of patients with primary biliary cirrhosis and in almost 50% is a reason to consult a doctor. Most often precedes all other symptoms of cirrhosis. Usually generalized, more pronounced on the limbs, thighs, abdomen, and with obstructive jaundice - on the palms, soles, interdigital folds of the hands and feet, under tight clothing.
Uremic itching, in chronic renal failure, can be local or diffuse, more pronounced on the skin of the neck, shoulder girdle, limbs, genitals, and nose. Intense, worse at night or immediately after dialysis, as well as in the summer months.
Diabetic itching most often occurs in the anogenital area, ear canals, and in some patients it is diffuse in nature.
Hyperthyroid itching is observed in 4–10% of patients with thyrotoxicosis, diffuse, faint, and inconsistent.
Hypothyroid itching is caused by dry skin, generalized, sometimes very intense, even excoriation.
Menopausal itching is observed mainly in the anogenital area, in the axillary folds, on the chest, tongue, palate, and often has a paroxysmal course.
Itching in hematological and lymphoproliferative diseases . Generalized or local: Hodgkin's disease - above the lymph nodes, anogenital - with iron deficiency anemia, with polycythemia - on the head, neck, limbs. With polycythemia, stabbing, burning, aquatic itching may precede the disease by several years.
Paraneoplastic itching sometimes appears several years before the onset of the disease. Can be local or generalized, of varying intensity. For some forms of cancer, a specific localization of itching is observed: for prostate cancer - itching of the scrotum and perineum; for cervical cancer - vaginal itching; for rectal cancer - perianal area; with a brain tumor infiltrating the bottom of the fourth ventricle, itching in the nostril area.
Psychogenic itching is often associated with depression and anxiety. It is characterized by: absence of skin changes, widespread or limited to some symbolic, significant area for the patient, intensifies in stressful situations, conflicts, sleep, as a rule, is not disturbed, patients often describe their sensations in a whimsical, exaggerated manner. Itching is relieved by taking sedatives or antipruritic drugs, and is much less easily relieved by external means. The presence of deep excoriations, bizarre self-harm, and parasitophobia is more likely to indicate the presence of psychosis rather than neurosis. A conclusion about the psychogenic cause of itching is possible only after excluding skin and systemic diseases.
Senile itching occurs in almost 50% of people over 70 years of age, more often in men and occurs in the form of night attacks. The causes of senile itching are mainly endocrine disorders, atherosclerosis, and dry skin. Senile itching is a diagnosis of exclusion; to make it, you must reject another cause of itching.
Localized itching
Itching of the anus is an extremely painful suffering, observed almost exclusively in men, especially after 40 years. It is often complicated by the appearance of painful cracks, streptococcal or candida intertrigo, the formation of boils, and hidradenitis. Causes: untidiness, hemorrhoids, helminthic infestation (enterobiasis), diabetes mellitus, constipation, proctitis, prostatitis, vesiculitis, intestinal dysbiosis.
Genital itching . It occurs in women over 45 years of age in the area of the external genitalia, less commonly in the vagina. The itching is painful, accompanied by the appearance of excoriations and skin dyschromia. Causes: leucorrhoea, urogenital infections, endocrine disorders (menopause), inflammatory diseases of the genital organs, sexual neuroses. In girls, genital itching is observed with enterobiasis.
Itching of the scalp is often a manifestation of seborrheic dermatitis or psoriasis, and can also be a sign of diabetes. Excoriation and bloody crusts, as well as impetiginous elements as a result of a secondary infection, are usually observed on the scalp.
Itching of the ears and external auditory canals can be observed with eczema, seborrheic and atopic dermatitis, and psoriasis.
Itching of the eyelids can occur when exposed to volatile irritants, allergic dermatitis to cosmetics, and also as a result of parasitism of the Demodex mite in the hair follicles of the eyelashes.
An itchy nose can be a manifestation of hay fever, as well as intestinal helminthiasis in children.
Itching of the fingers is observed with eczema, scabies, and bird mite infestation.
Itching of the skin of the lower extremities can be caused by varicose veins, varicose eczema, and dry skin.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of skin itching requires special attention, since it can precede the manifestation of serious diseases. At the first stage, a physical examination is carried out with an in-depth study of the skin condition and, in the presence of skin manifestations, an in-depth dermatological examination. Every patient suffering from itching should be tested for dermatozoonoses. In cases where itching cannot be associated with any dermatosis, other causes should be sought. Screening for a patient with pruritus should include:
- clinical blood test, ESR;
- general urine analysis with determination of protein, sugar, sediment;
- biochemical blood test (functional liver tests: ALT, bilirubin, alkaline phosphatase; fasting glucose level; cholesterol level; urea, uric acid, creatinine, acid phosphatase; determination of total protein and protein fractions; iron level and iron-binding capacity of serum, saturation of erythrocytes with iron) ;
- stool analysis for occult blood, helminths and their eggs;
- chest x-ray;
- functional examination of the thyroid gland, thyroxine level.
At the second stage, additional laboratory, ultrasound, X-ray, endoscopic, and histological studies are carried out, based on feasibility.
Patients with unexplained itching should be re-evaluated periodically, as the disease causing the itching may appear later.
Treatment
The most effective treatment for itching is to treat the underlying condition. Unfortunately, this is not always possible, so in such cases symptomatic therapy is prescribed. General therapy includes the use of sedatives, antihistamines, mast cell membrane stabilizers (ketotifen), hyposensitizing agents (calcium preparations and sodium thiosulfate), sequestrants and enterosorbents, salicylates. A wide range of physiotherapeutic methods are used: electrosleep, adrenal inductothermy, contrast showers, sulfur and radon baths, sea bathing. External therapy plays a major role in the treatment of itching, but most local drugs act for a short time. They are prescribed in the form of powders, alcohol and aqueous solutions, shaken mixtures, pastes, and ointments. For dry skin, antipruritic agents based on ointments and oils are more suitable. Antipruritic effects have: corticosteroid ointments, 5–10% anesthesin, 1–2% phenol, 5–10% Diphenhydramine solution, water with table vinegar (3 tablespoons of vinegar per 1 glass of water), lemon juice, chamomile infusion (10 –20 flowers per 1 glass of water), etc.
Also, for itching of any origin, it is necessary to eliminate provocative factors, such as dry skin, contact with irritating substances, degreasing the skin (rough, alkaline soap), consumption of certain products (alcohol, spices), as well as environmental temperature changes.
In conclusion, I would like to emphasize that, despite the wide range of therapeutic methods and agents, treating itching remains a difficult task.
Literature
- Adaskevich V.P., Kozin V.M. Skin and venereal diseases. M.: Med. lit., 2006, p. 237–245.
- Romanenko I.M., Kulaga V.V., Afonin S.L. Treatment of skin and venereal diseases. T. 2. M.: Medical Information Agency LLC, 2006, p. 342–34.
- Skin itching. Acne. Urogenital chlamydial infection. Under. ed. E. V. Sokolovsky. SPb: Sotis. 1998, p. 3–67.
I. B. Mertsalova , Candidate of Medical Sciences
RMAPO, Moscow
Contact information for authors for correspondence
Psychogenic nature of burning and itching
The term “psychosomatics” is quite common these days. It is defined as the occurrence of bodily manifestations based on psychological factors.
If during the examination of the patient it is not possible to find objective reasons causing such impressions, the matter is most likely in the mental sphere of the person. Or rather, in its negative manifestations.
For example, itching and burning sensations in the body develop against the background of a stressful situation . If it was a one-time problem, then after it is eliminated, the unpleasant manifestations also disappear.
As for chronic stress , these symptoms may persist or even intensify. This, in turn, increases nervous tension and aggravates the situation. It turns out to be a vicious circle.
There is an understandable explanation for the appearance of skin paresthesias in psychological disorders. With negative emotions, the body increases the production of serotonin and dopamine. It is these neurotransmitters that provoke the occurrence of itching and burning, usually without visible skin elements. But sometimes a rash, dryness and peeling may appear.
Senestopathies
Burning, itchy feelings provoked by mental disorders are classified as simple thermal senestopathies.
Senestopathies are a variety of unpleasant, intrusive and exhausting impressions that are concentrated on the surface or inside the body. This concept was first learned about in 1907 thanks to the scientists P. Camus and Dupre.
The peculiarity of this condition from true burning and itching is the rich and elaborate way of describing them. For example, “there is a fire in the head”, “the chest is on fire”. The localization is characterized by an unusual presentation: “itching in the stomach area”, “a vessel in the abdomen is pulsating”.
Such episodes can be isolated, constant or paroxysmal. Sometimes they are so intrusive that they literally drive the patient crazy.
Their characteristic feature is tactile hallucinations. They often manifest themselves in terms of itching and tingling. A person claims that bugs or mites are crawling under his skin. In some cases, he even sees them, or it seems to him that crumbs or sand are stuck to his body.
Such hallucinations provoke obsessive actions. The patient persistently visits doctors or tries to get rid of intrusive parasites on his own: he constantly washes himself and disinfects his body.
Mental disorders that lead to similar senestopathies:
- hypochondria;
- neuroses and depression;
- psychoses and psychopathy;
- oneiroid;
- paranoia;
- affective and delusional disorders, etc.
Itchy and “hot” sensations in neuroses
Neurosis is a psychogenic nervous disorder associated with emotional, behavioral and somatovegetative disorders. What distinguishes it from other mental illnesses is that the patient is fully aware of the severity of his condition and strives to get rid of it.
A distinction is made between mental and physical neurosis. Physical neurosis, along with psychogenic disorders, also has physical symptoms. There are several varieties of it.
Skin neurosis is manifested by burning and itching of the skin against the background of its bluish, marbled tint. The skin of the joints and legs becomes rough and tightens.
This condition is characterized by changes in sensitivity. It can be reduced or, conversely, increased when unpleasant sensations appear at the slightest touch. With physical neurosis, the skin itches and “burns” in certain areas or throughout the body, becomes wet or dry. Tactile hallucinations are characteristic.
The patient is so bothered by these manifestations that he scratches his body until it bleeds, leaving wounds and abrasions.
The reasons for this condition are:
- mental and physical stress;
- stress;
- conflict situations;
- brain injuries;
- hormonal disorders;
- infections.
Muscular neurosis . This condition is preceded by physical overexertion, as well as prolonged monotonous activity.
The disease is accompanied by a burning sensation throughout the body or in certain areas against a background of muscle tension and spasms. Another characteristic symptom is pain in the chest, neck and face.
Neurosis of the genital organs . The main manifestations of this syndrome are itching and burning in the genital area, which occur after sexual intercourse, during the menstrual period and for a number of other reasons.
The culprits of the disease are:
- mental infantility;
- chronic fatigue;
- conflicts in the family.
Other mental and nervous disorders
It is worth noting that these unpleasant sensations in the intimate area also appear with other types of neurosis.
Here is a case described in psychotherapeutic practice. A young woman aged 22 went to a psychiatric hospital. Because of this, their sexual and marital life is destroyed, the couple is on the verge of divorce.
During the survey, it was found that the girl got married at the insistence of relatives at the age of 19. And her husband is 18 years older than her. She developed normally, and at the time of coming to the center she was physically healthy, including gynecologically.
Conclusion: hysterical psychopathy , a symptom of hysterical genitalgia. This symptom developed due to the girl’s negative attitude towards her husband and sex life in general. Pain and burning in the vagina in this case act as an unconscious pathological adaptation mechanism for avoiding sexual intimacy with the husband. The symptom was eliminated with the help of hypnosis, but the dislike of sexual relations remained.
Thus, in this situation, a burning sensation in the intimate area became a manifestation of exclusively mental disorders, despite physical health.
Vegetative-vascular dystonia can also be accompanied by sensations of heat and itching in the body. The reason for this is an imbalance in the functioning of the nervous system. This disorder leads to changes in cardiac activity, which is why the condition is often accompanied by a burning sensation in the chest. It is accompanied by other symptoms such as arrhythmia, shortness of breath, heart pain, pressure surges, dizziness and loss of consciousness.
Causes of chapping facial skin
There can be several reasons for chapping of facial skin. The main ones:
- Dehydration of the dermis. The skin can peel off due to the fact that a person spends a large amount of time in rooms with excessively dry air (where radiators and split systems operate). Peeling also occurs when you ignore the complete cleansing and moisturizing of any type of dermis, even oily ones. In 20% of people, the epidermis is predisposed to dehydration from birth due to a reduced supply of moisture and glycerol substances from the deep layers of the skin to the surface. Dehydration often occurs due to a deficiency of protein synthesis, a lack of so-called fillagrin.
- Poor quality care for combination and oily dermis. If you have combination skin, dry areas on the cheekbones and corners of the lips are located next to the oily T-zone, and they need to be taken care of differently. Lubricating with greasy cream is not a good idea.
- Thinned, hypersensitive skin. Usually observed in people suffering from allergic reactions. Experienced allergy sufferers know which cream will protect their skin. However, closer to 50 years, the dermis becomes drier and more capricious, as the amount of hormones decreases. And if there is no full hydration, the fabric easily loses moisture, becomes dull, peeling and signs of aging appear.
- Freezing. Dry, cold climate conditions provoke moisture loss in the epidermis, and severe frosts can negatively affect the hydrolipid protection of the skin.
- "Re-cleaning". If you cleanse your face with soap, even the oiliest and densest skin will peel off. Therefore, one of the basic rules of care is not to wash your face until it squeaks and use a special toner after washing. This will preserve the pH of the dermis and the integrity of the hydrolipidic barrier that retains water.
- Frequent exfoliation. Exfoliation is an important step in skincare. However, we are talking about dead cells of the stratum corneum. If you peel more often than the instructions on the product packaging recommend, this will destroy the stratum corneum, and the skin will peel and become chapped. Homemade scrubs are considered more gentle than professional scrubs.
- Hypovitaminosis. If the skin on your face becomes chapped or becomes dry, this may indicate a vitamin deficiency. You can find out which substance is insufficient by taking a blood test. Vitamins A, B, C, D, E, F are recommended to be taken internally, as well as applied externally (as part of anti-chapping products for the face).
- Dry decorative cosmetics. Almost any make-up can cause peeling - contact dermatitis. But the problem with dry cosmetics (even useful ones based on minerals) is that they take away moisture. Therefore, if the dermis is excessively dry and prone to peeling, cosmetics should be applied only after complete hydration.
- Allergic reactions and other diseases. Any allergy, from skin reactions (dermatitis) to runny nose and asthma, can occur in both children and adults. When the cause is not identified, it is important to consult a specialist. In addition to an allergic reaction, the skin may peel and become chapped due to certain diseases of the epidermis, or be a manifestation of internal problems in the body.
Whatever the cause of skin chapping, it can be prevented, the main thing is to follow the recommendations of cosmetologists.
What can itching and feeling of heat in the body lead to?
These symptoms are so uncomfortable that it is simply impossible to ignore them. All attention is concentrated on them, which is why a person becomes inattentive, absent-minded, disruptions appear in his professional activities, and his performance decreases.
Irritability and tension reach a peak state. Depression and nervous breakdowns are possible. Such overexertion leads to mental imbalance. The patient's sleep is disturbed and insomnia develops. As a result, during the day he feels exhausted and sleep-deprived.
Severe itching in the intimate area sometimes leads sufferers to the point that they use various objects that injure the mucous membrane and skin in this area.
Scratches on the skin and mucous membranes can become infected, inflamed and suppurate, spreading the process to larger areas.
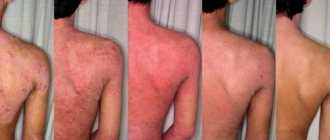
Weeping eczema
Systemic therapy
Therapy for weeping eczema is selected individually, taking into account the presumed causes of the disease, the severity of clinical manifestations, and the presence of concomitant pathologies or complications in the patient.
To reduce sensitization of the body, patients are recommended to follow a hypoallergenic diet, from which fatty fish and meats, oysters and other seafood, coffee and cocoa products, citrus fruits, tomatoes, and legumes are excluded. If the exacerbation of the disease is associated with the influence of exogenous factors, their elimination is a necessary condition for the success of treatment. Given the specific situation, patients may need to change their place of work, eliminate household allergens, or move to more suitable climatic conditions. Complex treatment of weeping allergic dermatosis requires the use of a number of drugs:
- Antihistamines
. To eliminate skin itching in the acute phase, first-generation histamine blockers are used, and after relief of symptoms, it is possible to continue treatment with second- and third-generation medications. - Desensitizing drugs
. Solutions of calcium and sodium thiosulfate are used. The treatment reduces vascular permeability, has an anti-inflammatory effect, and normalizes metabolic reactions in the dermis. - Cell membrane stabilizers
. To enhance the effectiveness of antihistamines, treatment with mast cell membrane stabilizers is indicated. Some authors recommend the use of omena-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids to normalize the structure of cell membranes. - Glucocorticosteroids
. For generalized forms of weeping eczema and no effect from other treatment options, hormones are used in pulse therapy or long-term use. - Immunocorrective agents
. Rational immunocorrection is prescribed to alleviate the condition of a continuously recurring form of weeping eczema. Treatment includes thymus preparations and leukopoiesis stimulants. - Antibiotics
. Treatment with antibacterial agents is required for the microbial form of dermatosis and the proven infectious-allergic nature of the disease.
Since various somatic disorders play a role in the pathogenesis of weeping eczema, treatment includes the correction of these pathologies. To normalize the functioning of the digestive tract, it is advisable to use enzyme replacement therapy, probiotics and synbiotics, and vitamin and mineral complexes. To balance the state of the central nervous system, mild sedatives are included in the treatment regimen; tranquilizers and antidepressants are prescribed for certain indications.
Local therapy
In the weeping phase, lotions with astringents are used, which reduce exudation, promote faster appearance of crusts and regression of the disease. In the acute stage, daily procedures lasting 1-1.5 hours are prescribed, which involve constant changing of the dressings as they dry. Then they proceed to applying ointments with topical corticosteroids, antiseptics, and calcineurin inhibitors.
Of the physiotherapeutic methods of treatment, the most effective is selective ultraviolet therapy, during which irradiation is carried out with light of a narrow range (311 nm). Low-intensity laser irradiation of the red or infrared spectrum, electropuncture of biologically active points, and local hyperthermia are also performed. At the stage of remission, ozone therapy, balneotherapy, and peloid therapy have a good effect.