Dermatovenerologist
Khasanova
Alina Rashidovna
9 years experience
Make an appointment
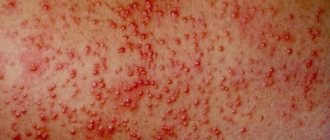
Ring-shaped erythema is a multiform lesion of the skin, a characteristic feature of which is the appearance of ring-shaped spots and rashes on the skin. The skin color of the affected areas changes and becomes red, bright pink or bluish. Depending on the causes of the disease, swelling, local fever and other manifestations of the disease may be observed. Changes in skin color occur due to the expansion of the lumen of the blood capillaries penetrating the connective tissue and the associated stagnation of blood.
Types of pathology
Doctors distinguish several types of annular erythema, depending on the causes of the disease:
- centrifugal erythema Daria - most often affecting middle-aged men, less often - children and the elderly, related to infectious-allergic manifestations;
- migratory - a disease of an infectious nature that occurs as a result of a tick bite infected with Borrelia;
- rheumatic, or ring-shaped anular erythema is one of the symptoms accompanying rheumatism, characteristic of children and adolescents.
According to external signs, ring erythema can occur:
- in flaky form - with peeling of dead skin along the edges or the entire surface of the spots;
- in vesicular form - with the appearance of small liquid-filled bubbles along the edge or entire surface of the spots;
- in a garland-shaped form - with the easiest flow, which is characterized by pale pink spots, arranged in chains or garlands and disappearing after a few days;
- in a microgarland-shaped form - with small spots, up to 1 cm in diameter, sometimes accompanied by peeling or the formation of bubbles, with a long course.
The medical literature also mentions other, very rare types of annular erythema - telangiectatic, purpuric or indurated.
Symptoms
The main manifestation of the disease is the appearance on the skin of characteristic rashes in the form of irregular rings with a bright border raised above the surface of the skin. With Dardieu's centrifugal erythema, they appear, as a rule, on areas of the skin usually covered by clothing - on the back, abdomen and chest, and forearms. Ring-shaped erythema after a midge bite is a single spot spreading from the site of infection, and in its final form it can reach 20-25 cm in diameter. The spots may be accompanied by itching or burning. With the rheumatic form of the pathology, there are no unpleasant sensations.
Are you experiencing symptoms of erythema annulare?
Only a doctor can accurately diagnose the disease. Don't delay your consultation - call
Why does inflammation of the skin vessels develop?
There are several factors that provoke the onset of the inflammatory process in the vessels of the epidermis:
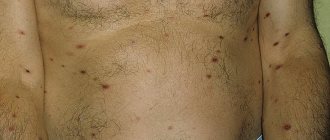
- bacterial infectious diseases caused by streptococci - scarlet fever, tonsillitis, pharyngitis, otitis media, etc., after which erythema nodosum of the lower extremities develops as a complication of the disease;
- long-term systemic disease - tuberculosis, lymphogranulomatosis, trichophytosis, yersiniosis;
- long-term course of treatment with antibiotics, bromides, salicylates, iodides or sulfonamides;
- vaccination;
- ulcerative colitis;
- cancer;
- Behçet's disease;
- pregnancy and the associated hormonal changes in the female body, and the risk of developing erythema nodosum increases significantly if the pregnant woman has a history of chronic infectious foci;
- hereditary predisposition to the disease: it is often diagnosed in several generations of the same family or in close relatives;
- allergies, which contribute to the development of a chronic form of pathology.
Erythema nodosum most often affects young people 20-30 years of age. Before the onset of puberty, the incidence is the same in boys and girls, but starting from adolescence, the disease occurs mainly in women, among whom the incidence is 3-6 times higher than in men. There is a certain seasonality: in winter and spring, the number of visits to the doctor about this increases significantly due to decreased immunity and an increase in the number of infectious diseases, including streptococcal infections.
Causes of the disease
There are many diseases and conditions that can cause erythema annulare, since it is not an independent disease and always occurs against the background of some pathological process. Skin manifestations most often develop against the background of:
- accumulation of toxins in the body;
- rheumatism;
- fungal, viral or bacterial infections;
- chronic inflammatory diseases;
- dysfunction of the endocrine gland;
- tuberculosis;
- borreliosis;
- reducing the protective function of the immune system;
- allergic reaction;
- cancer;
- helminthic infestation;
- taking certain medications.
In addition, in many cases, Darier's annular erythema occurs for no apparent reason in completely healthy people.
Erythema nodosum - symptoms and treatment
Erythema nodosum is an inflammation of the subcutaneous fat, which is accompanied by the appearance of painful, palpable red or purple subcutaneous nodules. Most often they appear on the legs, sometimes in other areas.
This disease is caused by an increased immune response of the body to the pathogen [1][3]. Despite numerous studies of this pathology, the causes of erythema nodosum and the mechanism of its development have not been sufficiently studied. However, there is a theory that the main cause of erythema nodosum may be various infectious diseases.
Table 1. Causes of erythema nodosum.
| Main reasons | Diseases that may cause erythema nodosum | Other |
| — B-hemolytic streptococcus of group A — Tuberculosis bacillus — Chlamydia — Hepatitis B and C — Herpesvirus family — Various fungi — Protozoa — Lymphogranuloma venereum — Psittacosis — Measles — Cat scratch disease — HIV, etc. | — Sarcoidosis — Ulcerative colitis — Regional ileitis — Hodgkin's disease (Hodgkin's lymphoma) — Lymphosarcoma — Leukemia — Rheumatoid arthritis — Behcet's disease — Malignant neoplasms — Chronic hepatitis — Ankylosing spondylitis — Granulomatous mastitis — Takayasu's arteritis — Vogt's disease — Koyanagi — Granuloma Wegener's ematosis - APS syndrome - Systemic lupus erythematosus, etc. | — Taking medications: sulfonamides, bromides, clomiphene, codeine, co-trimoxazole, D-penicillamine, dapsone, diclofenac, dicloxacillin, estrogens, ibuprofen, indomethacin, interleukin-2, etc. — Pregnancy — Jellyfish burns — Smoke inhalation in firefighters and etc. |
Risk factors for the appearance of erythema nodosum include fungal diseases, inflammatory diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, hormonal imbalances, tuberculosis, and taking various medications [2]
An important role is played by provoking factors , such as climate change, transitional seasons, stress, temperature changes (hypothermia), varicose veins of the lower extremities, etc. The disease is seasonal, usually appears in early spring and late autumn, which is due to frequent colds, sore throats, and decreased immunity.
The incidence of erythema nodosum in different countries can vary from 1 to 5 cases per 100,000 population per year [12]. This depends on the prevalence of diseases that can cause erythema nodosum in a particular area. Mostly, erythema nodosum is detected in people 20-30 years old [2][12]. It is at this age that a person first encounters many infections.
Women who have the HLA B8 gene are more susceptible to erythema nodosum, which may confirm the fact of a hereditary predisposition to this disease [4]. HLA (Human Leukocyte Antigen - human leukocyte antigen) is responsible for recognizing foreign cells and activating the immune response to them. When this mechanism is triggered, we see a clinical picture of inflammation, which is caused by the reaction of the immune system.
It is known that HLA B8 is associated with several groups of diseases, including erythema nodosum. And it is so programmed that it occurs more often in women [11]. This is why women get sick much more often than men (about 3-6 times) [12]. If we do not take into account changes in the genome, then erythema nodosum occurs proportionally equally in men and women, since they are equally susceptible to streptococcal infections and other diseases.
Erythema nodosum is more often detected in the European population, particularly in Scandinavia, while it is rarely diagnosed in Asians, since the HLA B8 gene is almost never found in them [11][13].
Diagnostics
When annular erythema appears, diagnosis is based on data from a dermatological examination and anamnesis. The main task of the examination is to determine the cause that caused the pathological changes in the skin. For this, the patient is prescribed:
- analysis of skin scrapings for fungus;
- clinical blood test;
- testing for treponematosis;
- skin biopsy for histological analysis;
- serological blood test;
- allergy tests.
Based on the results obtained, specific studies can be prescribed to determine the condition of certain organs and identify the underlying disease.
Therapy of the inflammatory process
Treatment of erythema nodosum is aimed, first of all, at getting rid of foci of chronic infection or other causative pathology. It includes:
- antibiotic therapy if the inflammatory process is infectious;
- desensitizing therapy if the cause of the disease is an allergic reaction of the body;
- taking anti-inflammatory drugs to relieve inflammation and relieve pain;
- plasmapheresis, cryopheresis or hemosorption to quickly eliminate intoxication;
- corticosteroid and anti-inflammatory ointments for inflamed joints and erythema nodes;
- physiotherapeutic treatment - ultraviolet irradiation, laser therapy, background cutter, magnetic therapy, etc.
For pregnant patients, clinical recommendations for erythema nodosum are significantly limited, since many drugs are undesirable to use. Previously, this disease served as a justification for artificial termination of pregnancy, but it has now been proven that it does not affect the development of the fetus.
Treatment
The basic principle of treating annular erythema is to stop the action of the factor that provokes the pathology. Depending on the diagnostic results, the patient may be prescribed oral medications:
- antibiotics, antivirals to treat infections;
- antiallergic and hyposensitizing agents;
- cytostatics;
- anthelminthic drugs;
- glucocorticoids.
In addition, external agents may be useful - antihistamines, steroids or zinc-containing ointments to reduce discomfort and reduce symptoms. For annular erythema, clinical recommendations may include limiting certain foods that cause an allergic reaction: confectionery, mushrooms, nuts, canned food, smoked meats, citrus fruits, etc. You should be prepared for the fact that the treatment process will last several months, as well as the possibility relapses.
Diagnostic methods
Laboratory test results do not provide a basis for definitively diagnosing erythema nodosum in a child or young person. They are aimed, first of all, at identifying the causes of the disease and its accompanying pathologies. The patient may be prescribed:
- clinical blood test;
- bacterial culture of nasopharyngeal mucus microflora to identify streptococci;
- stool culture for suspected yersiniosis;
- tuberculin diagnostics;
- skin allergy tests;
- blood test for rheumatoid factor and consultation with a rheumatologist;
- tissue biopsy of the nodular formation and histological examination of the sample to identify the inflammatory process in the walls of the capillaries.
After clarifying the etiological factor, concomitant vascular pathologies or foci of chronic infection, the patient may need consultation with a specialized specialist - an infectious disease specialist, pulmonologist, otolaryngologist, phlebologist, etc., as well as additional instrumental studies.