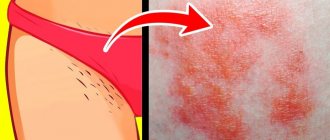
The skin is a protective barrier that prevents pathogenic bacteria and viruses from entering the body. In the genital area, the epidermis is especially sensitive, so it is here that rashes and redness often occur. An infectious rash is dangerous to a woman’s life and sexual health. Therefore, at the first signs of damage to the skin and mucous membranes in the groin, you should consult a doctor as soon as possible.
Medical specialists will help identify the cause and prescribe effective treatment for rashes in the genital area.
Causes of rashes in the intimate area
The content of the article
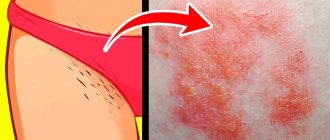
In women, rashes of various types most often appear on the pubis, genitals, and perineum. These can be ulcers, spots, pimples and other visually noticeable skin lesions. These manifestations may be associated with frequent shaving, mild allergies, and poor hygiene. However, quite often rashes in the intimate area require medical attention, as they become a response to infection.
The appearance of an unpleasant rash in the intimate area is associated with the following factors:
- Infection
. The nature of the rash depends on the type of infection that is actively multiplying in the body. Infection with a sexually transmitted infection is usually accompanied by additional symptoms. This may include purulent discharge, itching in the groin, and menstrual irregularities. - Weakening of the immune system
. This factor allows opportunistic flora to actively reproduce. Chronic diseases, antibiotic treatment, chemotherapy, childbearing, and hypothermia seriously weaken the immune system. - Chemical burn
. Aggressive substances destroy the upper layers of the epidermis. The body responds to this with the appearance of small, painful pimples. - Synthetic underwear
. Sometimes it causes genital allergies. Poor quality fabric does not allow the skin to “breathe”, which leads to the proliferation of pathogenic flora; - Ignoring hygiene rules
. This creates favorable conditions for viruses and bacteria to enter the body. It is especially important to carefully observe intimate hygiene during menstruation.
Treatment methods
How groin redness is treated is determined by the doctor on an individual basis based on information obtained during a medical examination. Therapy is complex, including the use of medications and adherence to personal hygiene rules. Physiotherapy treatments such as ultraviolet therapy may also be recommended.
Self-medication in this case can be extremely dangerous, since some diseases accompanied by redness in the groin require immediate medical attention and professional assistance. Therefore, having noticed suspicious spots and other alarming, unpleasant symptoms on her husband, the woman should convince him of the need to visit a doctor.
In some situations, no special treatment is required. This is acceptable if irritation occurs as a result of wearing tight synthetic underwear. In this case, a man should give preference to loose models made from natural materials.
Much attention is paid to hygiene issues, water procedures using softening hypoallergenic detergents and aftershave gels. It is recommended to shower twice a day, and then treat the groin area with baby powder.
If redness and irritation are caused by serious diseases, a comprehensive treatment is developed to eliminate them.
Types of rashes in women
Skin rashes manifest themselves in different ways. There are such types of rashes that affect the skin in the intimate area:
- A pimple
is a small bump or nodule protruding above the general layer of skin. The formation is often filled with serous fluid; - An abscess
is a large pimple with a watery texture. The formation is filled with purulent fluid; - Erythema
- bright red spots with clear boundaries. They stand out strongly against the background of healthy skin; - A blister
is a formation filled with fluid. Occurs due to mechanical injuries, burns; - An ulcer
is a non-healing wound that most often forms on the mucous membranes; - Condyloma
is a small formation of the papillary type on a stalk. Localized on the mucous membrane of the genital organs. - A node
is a dense formation in the deep layers of the epidermis. It appears in the form of a tubercle that protrudes above healthy tissues; - Plaque
– multiple formations in the form of small spots. They rise above healthy skin.
A rash in the groin area in women can simultaneously manifest itself in several types of skin lesions. Each type of rash is a signal of developing pathology, poor hygiene, unsafe sex life or other intimate problems.
Dermatophytosis
This is a pathology caused by mold fungi. The disease is most often diagnosed in men, women and children; the disease affects very rarely.
The infection is transmitted from animals, infected people and through the soil in which the pathogen lives. In this regard, the risk group includes the following categories of people:
- with a weakened immune system;
- paying insufficient attention to compliance with hygiene rules;
- regularly ride horses;
- agricultural workers;
- frequently using other people's personal items (for example, bath towels).
Symptoms of the disease:
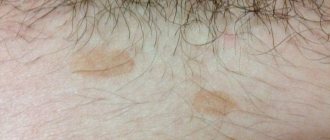
- Red spots on the pubis. In both men and women, they can be localized in the groin, thighs and buttock folds. The rashes are highly inflamed and symmetrical. The boundaries between them and healthy skin are roller-shaped.
- Pronounced itching and burning.
- Pustules and blisters often form.
To treat the disease, the use and external use of antifungal agents is prescribed. In addition, the skin must be treated with antiseptics. An important step in the treatment of dermatophytosis is regular adherence to hygiene rules.
Rash due to syphilitic infection in women
Syphilis is an infectious disease that is sexually transmitted. This is a dangerous and serious disease that affects the genital organs, liver, and nervous system. Without adequate medical care, a person becomes disabled or dies.
Sexual infection appears 1-2 months after infection. Its first sign is the formation of a dense, hard chancre on the labia or vaginal mucosa. This is the main symptom of the onset of the inflammatory process. After 4-6 weeks, the solid formation disappears. An imaginary feeling of recovery appears.
In fact, at this time the infection is already spreading throughout the body. This is evidenced by a small pink rash in the groin area in women, which appears after 5-10 days. The rash also affects the mucous membranes of the mouth and eyes. With syphilis, small dense condylomas also appear in the intimate area. They are located mainly on the labia and anus.
The rash with syphilis in women does not itch or hurt. The infection is accompanied by abnormal vaginal discharge. Leucorrhoea contains impurities of pus, becomes thicker, and has an unpleasant odor. Whitish papules, ulcers and purulent discharge are characteristic signs of the second stage of syphilis.
In the third stage, the characteristic rash spreads throughout the body. Sometimes the rash goes away, but after a couple of weeks the syphilitic rash in women again covers the entire body.
HIV rash in women
HIV is a virus that destroys blood cells, which leads to atrophy of the immune system. A rash with HIV infection in women becomes an early sign of infection. Papules and vesicles appear throughout the body, including on the genitals. The nature of the rash is always different, since it can be fungal, bacterial, or papillomavirus in nature. The main symptom is the appearance of pathological elements on the skin, which differ in color, structure, density from healthy tissue.
How does an HIV rash appear in women? At the initial stage, large and small erythemas or papular, compacted areas in the intimate area are observed. An erythematous rash on the genitals in women quickly spreads from the perineum to other parts of the body. The rashes do not peel, do not hurt or itch. This type of rash is characteristic of the active development of common infectious diseases (influenza, measles, rubella). Skin pathologies at the initial stage of immunodeficiency are accompanied by candidiasis and fever.
As the disease progresses, the rash takes on a different character. The circulatory system is weakened, so pinpoint hemorrhages appear in place of the capillaries. In the acute stage of the disease, a rash in the groin area in women manifests itself in the form of vesicles and papules. Often they merge, forming large lesions and weeping wounds. Such rashes are characteristic of sexually transmitted infections (genital herpes, gonorrhea). Sometimes a rash on the labia in women manifests itself in the form of folliculitis, which looks like teenage acne.
With immunodeficiency, other types of rashes may appear (seborrheic dermatitis, pityriasis versicolor). The nature of the rash always depends on the type of pathogen.
Prevention measures
To prevent the appearance of redness and irritation in the groin area, men should listen to the following recommendations from experts:
- take a hygienic shower daily;
- wear high-quality, natural underwear;
- do not use washcloths, towels, personal hygiene items of other people;
- fight excessive sweating, which causes irritation;
- Keep the skin in the groin dry and clean.
Spots between the legs in the groin, especially with accompanying itching and inflammation, are a serious reason to consult a specialist. In some situations, this phenomenon may be a sign of a violation of hygiene standards, but often indicates the development of dangerous pathologies that require competent, timely treatment.
Rash between the legs in women: sexually transmitted infections
Sexual diseases often cause an alarming symptom - rashes in the intimate area. Pimples, vesicles, ulcers, and erythemas accompany the progression of the following sexually transmitted infections:
- Genital herpes
. This virus is present in the body of 99% of women. When the immune system is weakened, herpes type 2 actively affects the skin and mucous membranes of the genital organs. The woman's groin becomes covered with small whitish blisters filled with liquid. On the 2-3rd day of illness, the pimples burst, and in their place weeping ulcers form. The rash from genital herpes can last for months. Therapy helps achieve remission, but it is impossible to cure the disease. - Gonorrhea .
Affects the internal and external genitourinary tract. When infected with gonorrhea, women develop small ulcers on the mucous membranes. Often the first ulcers form on the labia minora. An ulcerative rash is accompanied by purulent vaginal discharge, itching and burning in the perineum. Sometimes a woman develops a fever. The gonorrhea rash is red and hurts when in contact with clothing; - Gardnerellosis
. This is a bacterial infection of the vulvar mucosa. The disease is accompanied by ulcerative rashes on the mucous membranes of the groin. Small ulcers cover the labia, vulva, and sometimes spread to the anus. Additional symptoms are itching, burning, swelling of the external genitalia, watery vaginal discharge. - Molluscum contagiosum
. This is a viral skin disease. Appears after infection with the smallpox virus. In this case, small nodules and compactions form on the pubic part of women, which are located singly or in groups. The skin of the genitals takes on a pink color. Seals and nodules are practically not felt to the touch. When pressing on the rash, a white liquid appears. The rash does not hurt or itch. With this disease, rashes affect the pubis, genitals, inner thighs, and anus.
Ftiriaz
This term refers to a parasitic pathology that belongs to the group of sexually transmitted infections. Another name for the disease is pediculosis pubis.
Typically, lice are spread through close contact with an infected person. The risk group includes the following categories of people:
- Leading a promiscuous lifestyle.
- Adult film actors.
- Homeless.
- Workers of saunas, baths and dry cleaners.
- People who are serving sentences in prison.
- Workers of child care institutions.
- Military personnel who live in barracks.
It is important to know that from the area of primary infection, pubic lice can easily move to the intimate part of the body. As a rule, the pathogen affects the pubis, anus and perineum.
The main symptom of phthiriasis is severe itching. Red spots appear in places where scratching occurs. On the pubic area you can also notice a large number of skin flakes resembling dandruff.
The treatment regimen for lice pubis includes the use of insecticides that destroy lice, preventive measures and treatment of the skin of people who have been in close contact with the patient.
Rash due to hormonal imbalance in women
Hormonal imbalance is dangerous for a woman’s health. Reproductive function, metabolism, hair, nails, and skin suffer from improper hormone production. Active acne that is difficult to treat is a clear sign of hormonal imbalance.
Hormonal rash in a woman manifests itself in the form of acne and pimples, characteristic of adolescence. The formation of acne is promoted by clogging of the sebaceous glands with dead epithelium. Moreover, in case of hormonal imbalance, sebum is produced more actively. This provokes the appearance of new acne. The clogged ducts begin to fester. Often, ulcers are accompanied by a secondary infection, which further complicates treatment.
Hormonal acne occurs throughout a woman's body. But more often acne is observed on the face, back, and back of the head. Sometimes acne appears in the pubic area in women. This happens due to blockage of the pubic hair follicles. Hormonal rash spreading to the intimate area requires a comprehensive diagnosis. Unlike adolescence, hormonal acne in an adult woman does not go away on its own. It is necessary to start treatment.
Seborrheic dermatitis
If the red spots on the pubis are peeling, the doctor may suspect this pathology. Externally, the disease manifests itself as plaques, which are covered with scales of different sizes. Inflammations are localized in areas where the sebaceous glands are most developed.
The causative agent is a fungus. The process of its active reproduction is triggered by the following factors:
- Long-term use of certain medications.
- Living or staying for a long time in a region with high humidity.
- Overwork.
- Regular exposure to stressful situations.
- Unbalanced diet.
The treatment regimen for seborrheic dermatitis on the pubis includes taking antifungal drugs, as well as topical use of zinc pyrithione-based products. Additionally, medications of other effects may be prescribed. The choice of remedy depends on the form of seborrheic dermatitis.
Rash due to thrush in women
Candidiasis or thrush is an infectious and inflammatory disease caused by the proliferation of fungi of the genus Candida. Pathology occurs in almost every woman, because Candida is part of the opportunistic flora of the genital tract. Decreased immunity allows microorganisms to actively multiply, which leads to the appearance of characteristic symptoms.
The main symptom of the development of thrush is a cheesy white discharge from the vagina. Then an unpleasant red rash appears on the skin and mucous membranes of the genital organs. The rashes often itch, which is very irritating and provokes scratching of the affected areas. The woman also feels a burning sensation, which intensifies during sexual intercourse and urination. Pimples on the genitals with thrush are always covered with a white coating. This is the main sign of the development of a fungal infection.
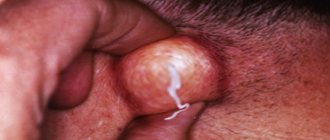
Yellow discharge in women and purulent rash
Purulent rashes may appear on the labia and mucous membranes of the vulva. This is a sign of a bacterial infection. The clinical picture is usually complemented by yellow vaginal discharge. Gradually, acne spreads to the pubic area, causing folliculitis (ulcers on the hair follicles).
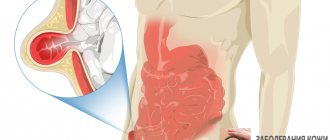
The pathology is easily treated - antibiotics, local antiseptics, drugs for immunity. However, the disease is dangerous because the infection spreads to the deeper layers of the skin. A boil forms at the site of damage to the fatty tissue. The formation is dense and painful. The pain radiates to the abdomen and rectum.
Often the formation of a subcutaneous boil ends in bartholinitis. This is an inflammation of the reproductive gland in the vestibule of the vagina. With bartholinitis, a large formation appears at the vaginal vault, which hurts and interferes with movement. Bartholinitis is treated surgically - the formation is opened, the pus is removed and washed with an antiseptic.