Stomatitis is an inflammation of the mucous membrane in the oral cavity. It is believed that children are most vulnerable to stomatitis. In adults, stomatitis does not occur as often. The instability of children to stomatitis is explained by the fact that they have a more delicate mucous membrane; children tend to constantly put something in their mouth and taste it, which contributes to the entry of microbes and accidental injuries. In addition, children's immunity is at the stage of formation, and therefore they are becoming acquainted with many bacteria and viruses for the first time. The first encounter with bacteria or, for example, with the herpes virus can be accompanied by a fairly violent reaction from the body.
Causes and risk factors
The mucous membrane of the child's oral cavity is often injured. The appearance of ulcers can be caused by temperature effects (hot food and drinks), biting the inner surface of the cheeks or lips; damage by sharp edges of the filling, braces or the tooth’s own tissues in case of chipped enamel. Normally, the immune response allows the pathological process to be quickly eliminated, the mucous membrane heals, and bacteria do not have time to cause severe inflammation and ulceration.
Weakened children's immunity cannot cope with this task, which leads to the development of aphthous stomatitis. A small number of opportunistic bacteria that populate the oral cavity begin to actively multiply. Often the disease occurs against the background or as a result of a severe infection: influenza, ARVI, acute tonsillitis, infectious mononucleosis, etc.
Main risk factors:
- food allergies, allergic reactions to hygiene products, such as toothpaste;
- deficiency of vitamins and microelements due to a strict diet or impaired digestion of food;
- hereditary predisposition;
- foci of infection in the oral cavity: caries, chronic periodontitis, periodontitis, gingivitis;
- frequent respiratory diseases;
- severe systemic diseases: pathologies of the endocrine system, blood vessels, metabolic disorders, etc.
Ask a Question
Causes of childhood stomatitis
The immediate causes of stomatitis are bacteria, viruses and fungi. These microorganisms may be present in small quantities in a healthy child, but they begin to multiply and cause disease in the presence of certain factors.
Factors contributing to the occurrence of stomatitis
- Failure to comply with hygiene rules (the child may touch the mouth with dirty hands), hard plaque on the teeth;
- Weakened immunity;
- Long-term use of medications (especially antibiotics). Antibiotics disrupt the natural microflora, promoting the growth of fungus and the occurrence of fungal stomatitis.
Forms of the disease
According to the ICD, aphthous stomatitis is assigned code K12.0. There are two forms of the disease - acute and chronic. The second is characterized by frequent relapses and may be a consequence of inadequate or untimely treatment of acute inflammation.
An acute disease is characterized by severe symptoms. It begins quickly, severe pain occurs at the site of mucosal damage, and the child may refuse to eat. In some cases, body temperature rises, weakness and lethargy occur.
The chronic form is characterized by a sluggish course; the child’s general well-being does not suffer. The disease can recur up to several times a year.
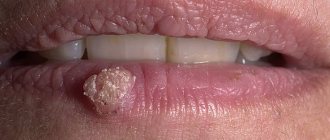
The appearance of a pimple on the tongue: diseases and treatment
The most harmless reason for the appearance of a pimple on the tip of the tongue is mechanical damage. Regular antiseptic treatment is enough to get rid of the problem. To relieve inflammation, you can use decoctions of sage and chamomile. A prerequisite is not to touch the wound with your hands, as you risk causing a more serious infection.
Allergy
It usually manifests itself as a scattering of small pimples throughout the tongue plate; if treatment is not addressed immediately, the pathology penetrates the root of the tongue, the frenulum and affects the larynx.
Symptoms of aphthous stomatitis
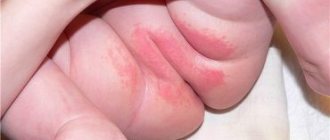
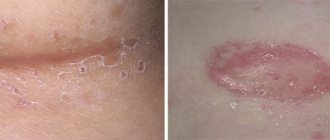
The onset of acute aphthous stomatitis in children may resemble ARVI: there is malaise, increased body temperature, and more profuse salivation may appear. The main symptom of the disease is the appearance of ulcers in the mouth: first, a red dot appears on the mucous membrane, which subsequently becomes an ulcer (aphtha) within 2-3 days. Accidental touching causes pain. The child refuses food and hygiene procedures.
Single erosions occur more often, but there are cases of multiple aphthae formed in groups. They usually measure up to several millimeters, but in severe cases the diameter of the ulcer reaches one centimeter. The disease is characterized by the appearance of a bright red rim around the aphthae; a grayish or yellow film-like coating forms on it.
There are also general symptoms that accompany aphthous stomatitis. These include:
- sleep disturbances (due to pain or discomfort);
- decreased appetite;
- pain while talking;
- increased fatigue, lethargy;
- whims, irritability.
Early treatment of aphthous stomatitis in children can prevent complications, shorten recovery time, and prevent further development of the disease.
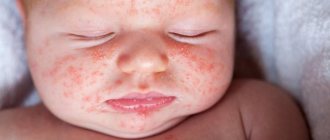
Enteroviral vesicular stomatitis (arm - leg - mouth)
Caused by enteroviruses. It also occurs in adults, but in 95.7% of cases children are affected.6 It is characterized by seasonal occurrence (summer - autumn) and group incidence.4 It is observed mainly in children under 10 years of age. Vesicular stomatitis is contagious, so it is recommended to use separate utensils and hygiene products. Characteristics for this disease: temperature 37.5-38, weakness, headache, muscle pain, rash on the palms, soles, as well as blisters on the hard palate and pharynx, which then turn into erosions that are almost not painful.
Features of treatment
To diagnose a disease, only a visual examination is often sufficient, but in some cases laboratory diagnostics are required to determine the causative agent of the inflammatory process and the sensitivity of bacteria to antibiotics. Treatment should be carried out by a dentist, and the treatment regimen is developed individually, taking into account test results, the age and well-being of the child, the causes of the disease, the area of mucosal lesions and other conditions.
If the question of how to treat aphthous stomatitis in children is decided individually, then recommendations regarding eating behavior and hygiene are general for all cases. Such recommendations include the following:
- avoidance of too hot or cold drinks and foods;
- following a hypoallergenic diet;
- refusal of food that irritates the mucous membrane. This list includes fatty, salty and spicy foods, marinades, solid foods;
- adding pureed and soft foods to the menu. This includes cream soups, porridges, pre-boiled meat;
- drinking enough liquid;
- careful adherence to oral hygiene: using brushes with soft bristles, rinsing the mouth after each meal.
Local drug treatment consists of the use of such agents as:
- rinses or irrigation solutions (for children who do not yet know how to rinse their mouths) with an antiseptic effect;
- ointments and gels that stimulate the restoration of mucous membranes;
- drugs for pain relief and burning sensation.
It is important to test the product before use: apply a small amount to the crook of your elbow. If there is no redness, burning, or rash, we can say there is no allergy - the product can be used for treatment.
In some cases, systemic drug therapy is indicated. Your doctor may prescribe antihistamines to combat the allergic reaction and relieve swelling. In order to increase the resistance of the child's body, immunomodulators may be recommended. The decision on the need for antibacterial therapy is made in the case of an extremely severe course of the disease, a persistent increase in body temperature, and identification of a bacterial pathogen in a smear.
Elevated body temperature and pain are indications for symptomatic therapy. The doctor may recommend non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in a dosage and form appropriate to the age of the young patient. Sometimes it is advisable to use suppositories if taking the medicine in the form of a tablet or syrup causes pain or anxiety.
Treatment of infants additionally includes disinfection of toys and teethers that the baby may put in his mouth. A nursing mother should pay attention to breast hygiene: thoroughly wash her breasts after feeding using warm water and special products.
Sometimes it is advisable to use folk remedies. Thus, rinsing the mouth with chamomile can soothe inflamed mucous membranes and speed up the healing process. However, it is important to remember that such prescriptions can only complement the main course of treatment. Don't forget to consult your doctor about the possibility of using them. Some herbs are strong allergens, so it is important to ensure that you are not hypersensitive to them.
Warming, the use of honey and alcohol tinctures are prohibited, as all this can lead to a worsening of the condition and lead to serious complications. It is better not to self-medicate, but to show the child to a qualified specialist.
Treatment of aphthous stomatitis in children usually takes no more than 7–12 days. It all depends on the state of the child’s immune system, the severity of inflammation, the number and depth of ulcers.
Treatment of herpes sore throat in children
There is no specific antiviral treatment. Treatment of the cause of herpetic disease should be carried out according to the following scheme:
- isolation of the patient
- drinking plenty of fluids, bed rest
- actions aimed at relieving and alleviating symptoms.
At the moment, no drug has yet been invented that can kill the causative agent of the disease. You can only alleviate or remove the symptoms. A person recovers completely only when the body develops immunity to the virus. Usually the body takes a week to do this.
First of all, it is advisable to isolate the child from other family members - separate dishes, linen and towels - the disease is contagious. For herpetic sore throat, children are prescribed antihistamines to relieve swelling and irritation. "Claritin", "Suprastin" and others are suitable. To reduce the temperature, use antipyretics: Nurofen, Efferalgan, Paracetamol, etc. To relieve pain in the throat, gargle with decoctions of sage, chamomile, calendula, salt or soda solution. Rinsing should be done every hour. You can use special sprays and aerosols: Hexoral, Ingalipt, Tantum-Verde. Tablets and lozenges relieve pain. It is advisable to use the antiseptic agents Miramistin and Chlorhexidine.
For successful recovery it is necessary to create favorable conditions for the child. It is necessary to provide conditions for sleeping in a well and frequently ventilated room. The diet should consist of soups, purees, and cereals. Food should not be hot so as not to irritate a sore throat. Don't forget about drinking plenty of warm drinks. The patient can be given rosehip decoction, tea with jam or honey.
Note to parents! In case of herpes sore throat, do not inhale, warm up or apply compresses under any circumstances. Such measures will only activate viruses, and the disease will drag on.
Some parents mistakenly lubricate the bubbles in the larynx with iodine or brilliant green. This measure is absolutely ineffective, does not bring any practical benefit, but causes severe pain to the baby.
There is no need to give your child antiherpetic drugs such as Acyclovir and its analogues. As we have already mentioned, the course of the disease has nothing to do with the herpes virus.
Prevention
The development of the disease can be prevented with the help of general strengthening measures: it is important to adhere to a daily routine, provide nutrition taking into account the body’s needs for vitamins and minerals, and pay attention to the prevention of infectious diseases.
The development of stomatitis can be avoided using simple measures, such as:
- regular oral hygiene, which should begin from the moment the baby’s first tooth appears;
- use of toothpastes without sodium lauryl sulfate. This component increases the risk of developing the disease;
- routine examinations by a pediatric dentist;
- rinsing the mouth after every meal;
- limited consumption of sweets.
Pediatric dentists at STOMA clinics are ready to help a child of any age. By contacting us, you can be confident in the professionalism of our specialists. We have developed effective treatment regimens for aphthous stomatitis in children. Doctors will talk in detail about preventing relapses and give recommendations on maintaining oral health.
Diagnostics
A patient suspected of having this disease is examined by a dentist. He asks the child’s parents about how the disease progressed. The diagnosis is established on the basis of the characteristic clinical picture of stomatitis, revealed during examination, anamnesis and characteristic complaints. Upon examination, typical mucosal lesions are revealed.
To confirm the diagnosis, laboratory testing of scrapings of the oral mucosa, the contents of ulcers, the patient’s saliva and blood is used.
The following are used for research:
- cytopolymerase chain reaction;
- immunofluorescence method;
- serological blood tests (RSC, ELISA, immunoglobulin M test);
- HSV test for the detection of immunodot G-specific glycoprotein.
These methods are used only for severe infections, as they are quite expensive.
Treatment of white spots on gums
The first thing parents need to do is visit a pediatrician. If necessary, the child will be referred to a dentist. Pediatric dentistry is a department where the factors that provoke the disease are determined. Depending on your age, the doctor will carry out therapeutic measures.
- In case of improper hygiene, the mother will receive professional recommendations.
- When pimples are a consequence of vitamin deficiency, the nutrition of the mother and child is adjusted. You should drink enough liquid.
- Congenital masticatory organs, if they are mobile, are removed.
- Pathological diseases are treated with modern methods.
- The toddler should be protected from anxiety and stress.
- Stomatitis is treated with antiseptics, for example, Miramistin. The drug is prescribed by a doctor.
- Candida fungus is eliminated with drugs such as Flucostat. The baby's mouth is treated with chlorhexidine.
- If there is a lack of calcium, the necessary minerals are prescribed.
You cannot puncture the blisters yourself. The gum tissue may be damaged. After all, with such a procedure, infection can easily occur.
Course of herpetic sore throat
The diagnosis of herpetic sore throat can be made by an otolaryngologist, therapist or pediatrician after examining the patient and clarifying his complaints. To monitor changes characteristic of a viral infection, the doctor may prescribe a general blood test, and to confirm enteroviral sore throat, a specialist may prescribe a pharyngeal smear and a blood test for specific antibodies. The pathogen can also be detected in stool or inflammatory fluid that is released from vesicles1,4.
Manifestations of herpetic sore throat can go away on their own in less than 10 days. But in any case, at the first symptoms of the disease, you should definitely consult a doctor. You cannot self-medicate2,3.
In some cases, herpetic sore throat can cause complications from the nervous system. In this case, 1 appears:
- severe spasm of the neck muscles, due to which the child cannot bend his head;
- weakness of the muscles of the limbs;
- disturbance of consciousness.
A severe complication of herpetic sore throat is damage to the soft membranes of the brain, brain and spinal cord1,3.
Newborns are at highest risk of developing complications, so they need careful treatment and care3. It is important to maintain hydration and give your child enough fluids1.
Up to contents