Many mothers face the problem of rashes on their face in the first month of their baby’s life. The first thought that comes to mind is that it is an allergy. Often, unfortunately, the nurse who comes to visit can also “erroneously” convince that mommy has eaten forbidden chocolate or oranges. The young mother goes on a diet, leaving only buckwheat and chicken breast, excluding all colored foods.
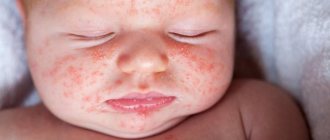
In the first three weeks of a baby’s life, a rash usually appears that is absolutely not related to the foods consumed by the mother. This is neonatal acne, or newborn acne, which is more common than allergies.
What is newborn acne and what causes it?
Between two and five weeks of age, small pimples may appear on your baby's face (usually on the cheeks, nose, eyelids, chin and/or forehead). According to statistics, acne of newborns (or infant acne, neonatal pustulosis) occurs in 30% of babies. Experts do not agree on why acne occurs, but it may be due to one of the following reasons:
- inflammation of the skin caused by fungi of the genus Melassezia, which are part of the normal human microflora and colonize the skin in the first weeks after birth
- overactive sebaceous glands on the baby’s skin, caused by the specific action of maternal hormones (androgens)
Pimples on a newborn's face have nothing in common with acne in teenagers.
Dermatologist Anna #a_medclinic_Bolshakova talks about newborn acne. ⠀ The popular name “infant bloom”, “hormonal rash”, “newborn acne” or dermatologically transient neonatal pustular melanosis is a variant of the physiological norm. One of the reasons is considered to be fluctuations in hormonal levels, which affect the activity of the baby’s still imperfect sebaceous glands (due to an increased concentration of estrogen from the mother). ⠀ Usually, “newborn bloom” begins to appear in the second or third week of life, and passes without a trace by the 3rd month. ⠀ Small red elements (pustules) with whitish or white-yellow spots, similar to pustules, appear on the baby’s skin. The rashes may merge into groups.
They are absolutely sterile! That is, they have nothing to do with bacterial pustules.
The predominant localization of the rash is the face (cheeks, forehead, eyelids, chin); it can also be found on the neck, behind the ears, and upper torso, and in boys also on the genitals. ⠀ In contrast to allergic and pseudo-allergic appearances of newborn acne:
- do not bother the child (no itching, sleep or appetite disturbances)
- characterized by “white tips” in the center
- never peels off
- rashes do not merge into weeping lesions!
That is: if the rash spreads throughout the body, bothers the child, merges into weeping lesions or peels off - this is no longer neonatal acne. ⠀ “Hormonal rash” must be distinguished from prickly heat. ⠀ Since flowering of newborns is, in fact, a completely normal phenomenon, in most cases no specific therapy is necessary. By 2-2.5 months of the baby’s life, the rashes disappear on their own, and not even the slightest trace remains in their place. Treatment is required only for very severe types of hormonal rash. In such situations, the help of a dermatologist or endocrinologist is required.
You should never squeeze white spots on your baby's skin, as such actions can lead to infectious complications and cause scars. There is also no need to treat pustules with alcohol solutions and other antiseptics (potassium permanganate, furatsilin, etc.).
Proper care for the delicate skin of a newborn involves only ensuring its dryness and cleanliness. The use of fat-based ointments is also contraindicated for newborn acne, since they create an airtight film on the baby’s skin, which only worsens the situation. ⠀
How to get rid of acne in newborns
There are no home remedies to get rid of newborn pimples on the face. You need to wait until they disappear on their own. Typically, newborn acne goes away in about three to four months without leaving any traces. Here's how to take care of your baby's delicate skin if he has pimples:
- Wash him every day with warm water and mild baby soap, then pat dry.
- Try to avoid any rubbing of the affected areas of the skin, as this can make the process worse or even lead to infection.
- Do not apply lotions or oils to your baby's face.
- There is no need to follow a diet, since neonatal acne has nothing to do with the mother’s diet
Peeling
On the second or third day after birth, the newborn’s skin begins to peel off. Peeling is observed in everyone, but to varying degrees of severity. Most severe if the baby is post-term. The reason is the same restructuring of the body to exist in the air. The skin loses moisture, and the top layer gradually peels off. Physiological peeling does not require treatment and goes away on its own within a few days.
If the peeling is profuse and leads to deep cracks, the skin is lubricated with special moisturizers - emollients. In case of pronounced peeling, it is necessary to exclude congenital skin diseases such as ichthyosis, hyperkeratosis and others.
When to see a doctor
If you are concerned about your baby's complexion or if you are concerned that the condition is not improving after three to four months, consult your pediatrician. Your doctor may prescribe a special cream to treat acne in a newborn. Do not use over-the-counter creams or any other medications for acne without first consulting your pediatrician as they may harm your baby. Contact your pediatrician if your newborn has any of these symptoms:
- blisters on the skin
- peeling skin
- heat
- uncharacteristic tearfulness
- poor appetite
Causes
- Excess hormones from the mother that are still present in the baby
- Restructuring the child's hormonal system
- Excess secretion from the baby's sebaceous glands
- Blocked skin pores and follicles
- Excessive proliferation of lipophilic yeast leading to inflammation
- Hormonal imbalance (in teenagers)
- Gastrointestinal problems (in teenagers)
Neonatal and juvenile acne develop during periods of physiological natural hormonal changes. Infant acne is rare, mainly in boys; rashes become noticeable from the second half of life and continue to appear for 2-3 years, sometimes up to 5 years. In all forms, additional exogenous provoking factors can play a significant role.
Diagnostics
If your teen has acne, a dermatologist can diagnose acne by looking at the breakouts. During your appointment, your dermatologist will also note what types of acne they are and where the breakouts appear on the skin. This will help your dermatologist create an effective treatment plan. Sometimes what looks like pimples is another problem. For example, some people mistake hidradenitis suppurativa, also called acneinversa, for everyday acne. Treatment for this condition is different from that for acne. Another disease that can be mistaken for acne is perioral dermatitis. This often causes rashes that look like pimples around the mouth. Whether your teen has stubborn acne or another condition, a dermatologist can accurately diagnose acne vulgaris and create a treatment plan tailored to your teen's needs.
Treatment and prevention of allergies
According to the latest WHO recommendations, the basis for the prevention of food allergies in children is breastfeeding. Children who receive exclusively breast milk in the first months of life are much less likely to suffer from food allergies. At the same time, mothers of healthy children who are breastfed do not require special diets. Their diet should be complete and varied, including proteins, fats, and carbohydrates. As well as microelements and vitamins. Mothers of children who are at risk for food intolerance are advised not to limit their diet too much. It is necessary to completely exclude those foods to which the mother herself has a reaction and keep a food diary.
If artificial feeding is necessary, children prone to allergies choose special hypoallergenic formulas. To treat existing manifestations, the mixture should be selected by a specialist. According to the latest clinical recommendations, if you are intolerant to cow's milk protein, choose mixtures with fully hydrolyzed protein or amino acid composition. In this case, it is not correct to prescribe hypoallergenic mixtures and mixtures based on goat’s milk protein. Soy-based mixtures themselves can cause an allergic reaction.
Another important step for the prevention and treatment of food allergies is the correct introduction of complementary foods. Complementary foods should be introduced in a timely manner - no earlier than 4 months and no later than 6. To begin with, hypoallergenic foods are selected - white and green vegetables, gluten-free cereals. On one day, the baby is given only one complementary food product, in small quantities, and the possible reaction is observed. At the beginning, a new product should be introduced no more than once a week. Mothers of babies who are predisposed to allergies or already have allergic manifestations are recommended to keep a food diary. There, the mother writes down all the foods she fed the child during the day and possible reactions to them.
The doctor, if necessary, can prescribe medications to the baby. They can be either for oral administration or for skin treatment. Children with chronic allergic rashes require special skin care. It is necessary to use special children's detergents with a neutral pH. And after washing, use special care products - emollients. It is better to consult a doctor about which emollient to choose. If there are manifestations from the gastrointestinal tract or respiratory system, the child needs specific treatment, which can only be prescribed by a doctor during an in-person examination.
Online consultation with a pediatrician
Online consultation
During the consultation, you will be able to voice your problem, the doctor will clarify the situation, interpret the tests, answer your questions and give the necessary recommendations.
Diaper rash
A more serious skin reaction to overheating is diaper rash. Occurs in natural folds. It looks like redness, sometimes with weeping and erosion. With a long process, a bacterial or fungal infection may develop, then the surface of the affected skin is moist, bright red, with clear or purulent discharge. Prevention measures are the same as for prickly heat.
The skin in the folds is treated with powders. If normalizing the microclimate and caring for the newborn does not lead to a reduction in diaper rash, you should see a doctor. If complications occur, antibiotic therapy or topical steroid ointments may be needed.
Vascular abnormalities
Congenital anomalies of vascular structure are varied
- A simple nevus is a capillary anomaly. It appears as a pale pink spot or several small spots. The common name “stork bite” or “angel kiss” arose due to its location on the back of the neck and head, on the forehead, bridge of the nose and upper eyelids. The spots fade by the age of two, but can appear when crying or physical activity. No treatment required.
- Port wine stain or flaming nevus. A dark red spot that looks like a hemangioma. It may be one of the manifestations of pathological syndromes. Lasts for a long time. Treatment is not necessary, but can be done if the spot creates a cosmetic defect.
- Venous anomaly - blue-violet painful nodules under the skin. They can also masquerade as a hemangioma. Occur alone or in combination with other anomalies. The danger lies in the possibility of thrombosis of the altered veins. Treatment consists of wearing compression clothing and using aspirin to prevent blood clots. Surgical excision is possible.
- More rare lymphatic, arteriovenous and combined anomalies are found as part of various pathological syndromes.
Hormonal ointments for diathesis
A special group of local drugs used for diathesis are hormonal ointments. They are used if non-hormonal drugs do not help. Hormonal drugs have a more serious composition, including hormonal components - glucocorticoids. These are steroid hormones synthesized by the adrenal cortex. The most common among them are:
- Natural glucocorticoids: cortisol, hydrocortisone. Their effect lasts for 8-12 hours.
- Synthetic analogues: prednisolone, prednisone, methylprednisolone, mometasone, clobetasol. The substances act within 12-36 hours.
- Synthetic analogues containing fluoride: dexamethasone, betamethasone, paramethasone, fluprednisolone. The effect of the substances lasts up to 3 days.
Such substances have the following effects:
- Antiallergic. Hormones reduce the level of basophils - substances activated during allergies.
- Anti-inflammatory. Substances reduce the level of inflammatory mediators in the blood.
Hormonal drugs have a faster effect, but also have a more impressive list of side effects. For this reason, few hormonal ointments are approved for children, and they try to resort to them in extreme cases, when the child’s condition is advanced and he suffers from itching, large lesions and other unpleasant symptoms.
The list of hormonal drugs used for diathesis includes:
- Advantan (methylprednisolone) – from 4 months;
- Lokoid (hydrocortisone) – from 6 months;
- Afloderm (alclomethasone) – from 6 months;
- Beloderm (betamethasone) – from 6 months
- Dermovate (clobetasol) – from 1 year;
- Elokol (mometasone furoate) – from 2 years.
What are the dangers of using hormonal ointments for diathesis?
Because children have a larger surface area to weight ratio than adults, they are at greater risk for side effects from hormonal medications. With long-term use there is a risk of growth and development disorders. For this reason, children are prescribed minimal doses of ointments, as well as short courses. For example, Advantan cannot be used for longer than 4 weeks.
There are other features of the use of hormonal ointments associated with the small surface area of the child’s body. For example, Beloderm ointment is used very carefully and should never be applied under a diaper, since due to the increased absorption of the active components, the risk of developing serious side effects increases.
It is equally important to apply hormonal ointment with caution in the area of body folds. In these places, the ointment is absorbed more actively and can have a systemic effect on the body, that is, enter the bloodstream and influence from the inside.
In the case of hormonal ointments, it is also important:
- do not exceed the prescribed dosage;
- use the amount of ointment prescribed by the specialist;
- do not extend the period of use (in most cases no longer than 5 days);
- Apply only to the affected areas.
Are there vaccines for children? Is there a coronavirus vaccine for children?
Currently, none of the available Russian coronavirus vaccines is approved for use in children under 18 years of age, as studies have not been conducted among this age group.
However, on June 22, 2022, the World Health Organization announced for the first time that some coronavirus vaccines may be safe and approved for children. For example, the WHO Strategic Advisory Group of Experts (SAGE) concluded that the Pfizer/BionTech is suitable for use in people aged 12 years and over .
In Russia, clinical studies of the COVID-19 vaccine for adolescents 12-17 years old are planned to be conducted by the Center named after. N.F. Gamaleya. The corresponding tests must be approved by the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation.
What is the most common allergen in infants?
1. The first place is occupied by intolerance to cow's milk protein. It should be noted that most modern formulas for feeding infants are based on cow's milk proteins. This is the reason why the baby is allergic to the formula. In addition, a breastfed baby can also have a reaction to cow's milk protein if the mother has an excess of dairy products in her diet. We are not talking about a specific component of milk or formula. Cow's milk contains many different proteins: albumins, globulins, casein. Some of them cause an allergic reaction more often, others less often. Casein makes up about 80% of all milk proteins. Its composition in cow's milk is identical to that of goat's. This explains the cross-reaction in babies to cow's and goat's milk. Therefore, if you are intolerant to cow's milk, it is not recommended to replace it with goat's milk, or mixtures based on goat's milk, in the child's diet. Some proteins are destroyed by heat treatment. This is due to the lower reactogenicity (ability to cause reactions) of boiled milk. There is a protein similar in composition to the protein of beef or veal meat. If the baby is intolerant to this type of protein, there will be a cross-reaction to milk and meat products.
2. The next most common cause of allergies in an infant is a chicken egg. The egg also contains a protein called ovalbumin that is an allergen. Therefore, it is recommended to start introducing eggs into the diet with the yolk and in small portions. Watch your baby's reaction to this product carefully. When feeding eggs and protein for the first time, you should also carefully monitor the reaction. Don't forget that eggs are found in some pasta and baked goods.
3. Gluten is a common cause of food intolerance. This is a protein found in some grains. In order to prevent an undesirable reaction, it is recommended to start complementary feeding with gluten-free cereals. These include: buckwheat, corn, rice. Cereals rich in gluten, such as semolina, millet, and oatmeal, should be introduced closer to the age of one. In the first year, a reaction to gluten is less common than intolerance to cow's milk protein or egg white.
4. In addition, brightly colored fruits and vegetables can cause food reactions. Such as carrots, beets, pumpkin, peach. It is better to postpone their introduction into the diet and give preference to green and white vegetables - such as zucchini, cauliflower and broccoli. It’s best to start introducing your baby to fruits with green apples and pears. It is also better not to rush with exotic fruits such as mango or kiwi.
Do not forget that an allergic reaction is possible to any product. When giving a treat to a baby for the first time, a mother should remember the risk of intolerance. Try not to rush, especially with the introduction of the very first complementary foods. Give unfamiliar foods to the child in small portions in the morning so that it is possible to control the reaction to them throughout the day.
Diaper dermatitis
The distinctive feature of this rash is that it appears only in the area under the diaper, other areas of the body remain clean. The reason is increased humidity and irritating feces.
The rash is found in the buttocks, thighs, lower abdomen in the form of individual elements or continuous areas of changed skin. The elements of the rash are varied: red spots, bumps, pustules or peeling.
To alleviate the condition, you need to change the diaper and wash the baby immediately after bowel movement. While changing clothes, you can arrange air baths, that is, leave the child to lie naked, you can cover it with a regular dry diaper. Lubricate the skin with a special diaper cream.
Change the diaper every 3 hours, even if it is only slightly full. More often when very full. If these measures are ineffective, you should consult a doctor. Local glucocorticoid agents may be needed.