A lipoma of the spermatic cord is a benign tumor consisting of adipose tissue cells. The tumor does not hurt, so in men it is detected more often during examinations associated with other pathologies - infertility, prostatitis, etc. Lipoma causes complications and can degenerate into cancer.
What are spermatic cord lipomas and why are they dangerous?
The content of the article
The spermatic cord is a complex organ, 15-20 cm long, located in the groin - inside the scrotum in men. The cord stretches from the inguinal ring to the top of the testicle and consists of several structures: the vas deferens, arteries and veins of the testicle and vas deferens, lymphatic vessels and nerve plexuses. The organ performs a reproductive function by connecting the testicles, which produce sperm, and the penis.
Statistics indicate that neoplasms in the spermatic cord are registered less frequently than others. Moreover, in 70% of cases the tumor turns out to be benign. Doctors consider lipoma to be one of the most popular and at the same time most predictable types of tumor affecting the spermatic cord.
Lipomas, called wen, can develop on any part of the human body, including in the area of the spermatic cord, which contains loose connective tissue. Neoplasms are benign tumors, but without proper control or treatment they can cause a lot of problems for their carrier.
From a tumor of the spermatic cord the following can develop: myoma and fibromyoma, sarcoma (cancer), myxoma, dermoid, lymphangioma. There is no point in describing these pathologies - they all have unpleasant consequences and require surgical treatment, therefore, having discovered a neoplasm, you should not allow complications to develop.
Lump in the testicle
The most common symptom of testicular cancer is a lump in one or both testicles. Often, the area where the tumor can be felt does not cause pain upon palpation. Seals come in different sizes. A small nodule is palpated in them, harder than the main lump, but painless.
The epididymis, which has an oblong shape and is located at the back, on top of the testicle, should not be confused with the seal. Sperm mature and accumulate in it; it has nothing to do with cancer.
As cancer progresses, the testicles become deformed and become noticeably denser. The boundary between the epididymis and the testicles themselves is erased. Fluid begins to accumulate between the membranes of the testicle.
An important point: if a lump is detected, this is not yet an indisputable sign of testicular cancer in men. In most cases, similar symptoms are characteristic of another disease. A similar compaction may appear after an injury. But if a formation is detected, you must consult a doctor immediately. He will prescribe the necessary examination and tests.
Causes of lipoma formation in men
The cause of lipoma development has not yet been precisely established. Doctors are confident that there is a genetic predisposition to the pathology, since wen in this area is often found in most men from the same family.
It is believed that the tendency to form lipomas is established in men during embryonic development, so the pathology is congenital. In the embryo, cells are formed in the scrotum area that can accumulate fat in the future. When the process starts, these cells quickly divide, turning into a wen.
Contributing factors:
- metabolic disease;
- injuries to the scrotum and groin;
- diseases of the liver and pancreas associated with the processing of fats;
- disruption of the thyroid gland and pituitary gland - organs that produce hormones involved in metabolism;
- diabetes mellitus, which inhibits all metabolic functions in the body;
- alcohol abuse;
- excessive physical activity leading to the formation of an inguinal hernia.
Despite the fact that the wen grows from fat cells, obesity does not put a person at risk. Lipomas can also occur in thin people.
Often this type of tumor is registered in people with Cowden's syndrome (hereditary genetic autoimmune disease).
Spermatocele: definition
A spermatocele (seminal cyst) is a cavity filled with a clear or yellowish fluid. Most often, this pathology is detected in boys during the period of growing up and puberty, as well as in men over 40. In both cases, this is due to age-related changes occurring in the body. A congenital cyst may form. This is a minor malformation that can result from pregnancy complications in the mother.
Symptoms of lipoma in the spermatic cord
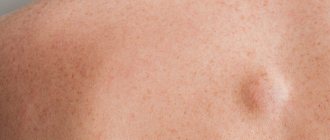
Benign and malignant tumors at the first stage reveal themselves by the appearance of a small compaction. Externally, a lipoma looks like a small ball filled with fat. At the initial stages, it is difficult to identify pathology, which is due to the peculiarities of its localization and development.
Features of the development of lipoma and other tumors in this area:
- Benign tumors grow slowly. Some of them take several years to reach a size of 3 cm in diameter. Others (fibroids and lipomas) can grow to enormous sizes. Due to the expansion of tissues, a man may be bothered by the feeling of the presence of a foreign body.
- Over time, the wen grows, so the scrotum changes size, increasing on one side. Unpleasant sensations arise when touching underwear.
- At first, nothing hurts; pain in the inguinal-scrotal area occurs a little later. The resulting pain is not constant, tending to intensify with pressure and movement. The growth of the tumor leads to a constantly pursuing feeling of heaviness and constant pain. It can radiate to the sacrum, lower back and lower abdomen.
- A large wen compresses the testicle and pinches the veins of the spermatic cord, they expand and become deformed. Due to heat exchange disturbances, spermatogenesis is disrupted, so lipoma is often accompanied by male infertility. Problems with blood flow make themselves felt by a burning sensation in the groin and scrotum.
- Malignant tumors are very insidious. They prefer to grow in the groin area, gradually infiltrating surrounding tissues and organs and forming metastases in the pelvic lymph node. Sarcoma grows slowly until a certain time, which can mislead a man. A sharp increase in tumor with the formation of multiple metastases begins suddenly.
The appearance of pain in the groin area and increased temperature require immediate contact with a urologist to receive a referral for examination. There is a small chance that the tumor will degenerate into cancer.
Treatment methods
After diagnosis, the doctor prescribes treatment, which varies depending on the severity of the patient's condition. If the formation is infected, antibiotics are prescribed. Wen, atheromas and other benign neoplasms, as well as malignant tumors, are removed surgically.
For varicocele, first there is a wait-and-see approach, and then venotonics are prescribed. These drugs help increase the elasticity of blood vessels. If this treatment does not work, it is recommended to use laser or nitrogen.
In case of hematomas, it is necessary to remove the accumulated blood.
Diagnostics
The symptoms of spermatic cord lipoma are similar to other urological diseases: lymphadenitis, varicocele, cancer, so the diagnosis can only be clarified by undergoing diagnostics.
- Palpation.
Decent-sized tumors can be palpated. To the touch, the tumor is defined as a heterogeneous tissue formation. Men discover large lumps on their own before seeking medical help. But with palpation it is impossible to determine the type of tumor, so additional studies must be carried out. - Ultrasound of the scrotum
. This is the primary examination method - it is inexpensive, accurate and painless. Ultrasound is necessary to determine the size of the tumor and its exact location. - Dopplerography
. Ultrasound with a Doppler sensor showing the quality of blood flow. On an ultrasound, the wen is visible as a knot-shaped formation. - X-ray of the scrotum
. Inexpensive, but hazardous to health method. During the examination, soft x-rays are used, but repeated diagnosis in this way in the next few months is contraindicated. On an X-ray, a lipoma appears as a bright spot of regular shape, since fat does not absorb X-rays well. - Diaphanoscopy.
Transillumination helps to exclude hydrocele of the spermatic cord, which is much more common than lipoma; - CT, MRI
. If there are any doubts about the diagnosis, the urologist will send you for an MRI or CT scan - such an examination involves radiation and costs several times more than an ultrasound. - Biopsy.
If cancer is suspected and the diagnosis cannot be made using other means, tumor tissue is removed with a thin needle for careful examination under a microscope. If the lipoma degenerates into cancer or is initially an oncological tumor, atypical (modified) cells are found in tissue samples taken for biopsy.
In addition to instrumental methods, you need to undergo tests. Laboratory tests include: general blood and urine tests, blood biochemistry tests. These tests allow us to screen out other diagnoses associated with inflammatory processes and infections.
Diagnostic capabilities of the clinic
Diagnosis is carried out quickly and efficiently, which allows you to start treatment in a timely manner and avoid negative consequences. Basic and modern research methods completely exclude errors in diagnosis and recreate the complete clinical picture of the disease. The doctor examines the wen, determines whether it is a cosmetic defect, or whether a malignant tumor called liposarcoma is hidden under its mask.
Based on the size and shape of the formation, the feasibility of surgery is considered. Large lipomas are recommended to be removed. Samples of excised tissue are subjected to histological examination under a microscope. Additionally, an ultrasound is prescribed, based on the results of which a conclusion is drawn about the internal contents of the wen capsule and the presence of pathogenic flora.
What symptoms do you see a surgeon for:
- Presence of hernial protrusion
- Daggering pains in the abdomen
- Bloating
- Pain in the right hypochondrium
- Bitterness in the mouth
- Nausea
- Presence of neoplasms on the skin
- Swelling and redness of the skin
- Bone fractures and bruises
- Wounds of any location
- Vomit
- Enlarged and painful lymph nodes
Treatment of lipomas in men
Attempts to treat spermatic cord lipoma with folk remedies are unsuccessful. Herbal medicine is not able to affect adipose tissue, therefore it is useless in the treatment of this pathology. There are no medications that give a significant effect.
The only way to deal with spermatic cord lipoma is surgery. A small lipoma does not require removal provided it is painless, lacks growth and has stable consistency. Violation of any of these conditions is considered an indication for surgery. The intervention is carried out in one of three ways.
- The surgical method
is traumatic, but cheap. The tissue that has undergone the change is excised, and then the wound is sutured. The operation is performed under local anesthesia. Recommended only for large lipomas. - Liposuction
. In this case, a needle is inserted into the lipoma and all its contents are pumped out. The method is unreliable because it does not guarantee ideal removal of fat cells and, therefore, does not protect against subsequent relapses. - Laser exposure
. This method is the most gentle, but is used only for tumors not exceeding 3 cm in diameter. - Radio wave technique is the newest method of treatment that does not cause complications. It is also carried out if the wen is still small.
In some cases, the spermatic cord lipoma reaches very large sizes, which makes its isolated removal impossible. Doctors recommend that such patients agree to radical removal of the tumor along with the testicle and cord.
How to treat wen on the testicles
You can get rid of lipoma forever, as well as atheroma, only through surgical removal.
Is it possible to remove the wen yourself? You cannot remove a lipoma yourself. It has no duct and cannot be squeezed out like atheroma. Some try to open the wen with punctures or incisions, but in this case inflammation cannot be avoided. If you puncture a lipoma yourself, there is a risk of getting phlegmon - extensive inflammation. Inflammation may progress to the testicles with the development of orchitis and subsequent infertility. Independent actions are pointless and dangerous, since only a doctor can correctly remove the formation on the male testicles along with its bed.
A typical example of the consequences of independent attempts to remove a lipoma from the site https://doktor.ru/q/7r576m/:
Traditional methods
Traditional methods for removing testicular lipomas can be used only at your own peril and risk. The skin of the scrotum is delicate and easily injured.
Vishnevsky ointment
There are articles on the Internet that describe the process of removing wen using Vishnevsky ointment. The point is this: you need to apply the ointment, cover it with gauze on top, and secure it with a band-aid. After 8-10 hours, make a dressing. After 3-4 days, the wen, according to the authors, should resolve.
An ointment based on birch tar has an irritating effect and accelerates blood circulation, but there are no lipomas in the instructions for use. Only purulent wounds and boils. It makes sense to use the product for inflamed atheroma. The compress will actually draw out the pus through the widened mouth. The lipoma does not have an opening, it does not fester, and there is no particular point in applying ointment in this case. As an example, here is a review from the site https://otzovik.com/review_1287866.html:
The author did not have a lipoma, but an atheroma. Vishnevsky's ointment opened the pore, the contents came out, but the capsule remained. After a while it will fill up again.
Dermatovenerologist Makarchuk Vyacheslav Vasilyevich talks about means for eliminating lipomas at home
other methods
Popular folk methods of getting rid of wen:
- “Fukortsin”, “Levomekol”, sulfur ointment, ichthyol ointment. You need to smear the wen, cover it with a cotton swab, and secure it with a band-aid. Change dressings 3-4 times a day.
- Aloe and Kalanchoe. Clear the sheet of film, grind it into a paste, apply it to the lipoma, insulate it with a piece of polyethylene on top and secure it with a band-aid. Change dressings three times a day.
- Balm Karavaev. Apply a thin layer once a day for a month.
The herbs and essential oils that make up Karaev's Vitaon balm have anti-inflammatory, analgesic, regenerating, and antimicrobial properties. Price from 140 rubles
Cases of spontaneous resorption of small lipomas due to changes in metabolic processes, for example, under the influence of heat, have been recorded. However, it is not worth warming up the scrotum to resolve the lipoma - there is a risk of damaging the testicles and disrupting spermatogenesis.
Surgical removal
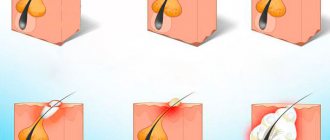
Lipomas are removed routinely. Only ulcers require urgent intervention within 1-2 days. Their removal should not be delayed, otherwise pus may get under the skin and cause phlegmon.
Removal is performed under local anesthesia. Progress of the operation:
- The doctor gives an injection in the area of the lipoma.
- Makes a linear cut from above.
- Removes the wen from the bed. The process is called enucleation.
- Places sutures or strips.
Removing a lipoma
When removing a suppurating lipoma, the connective tissue that forms the capsule is not cut out. Due to inflammation, it is too tightly fused with the surrounding tissue; upon excision, a large wound surface is formed. Sutures are also not required so that the wound can completely clean itself. After the inflammation subsides, the capsule can be permanently removed to avoid relapses.
- Incision – https://prntscr.com/xfl3oy.
- Husking – https://prntscr.com/xfl48s.
In most clinics, technically, laser or radio wave removal of fatty tissues is not very different from conventional surgery. The incision is not made with a scalpel, but with a laser or radio knife, the underlying tissues and vessels are processed. This makes it possible to avoid blood loss and reduces the risk of infection, since the capillaries are immediately sealed. If you make the main incision with a laser, the cosmetic result may be worse. The choice is made by the doctor based on the clinical picture.
Laser treatment of fabrics – https://prntscr.com/xfl6kv.
Liposuction
Liposuction is the suction of the contents of the wen through a needle. The method is only suitable for removing formations with unchanged fatty tissue. Pros: no recovery period and no marks on the skin. Disadvantages: high probability of relapse.
Recovery period after surgery
Removing a lipoma is a simple operation that does not require hospital observation. The patient is sent home the same day. For a week you will need to treat the seam with antiseptic agents and avoid physical activity.
The sutures are removed after 10-14 days, or they completely dissolve on their own within a month. There is no need to pull out the threads yourself to avoid inflammation of the holes. If swelling or bleeding occurs, you need to water the seam with chlorhexidine three times a day and lubricate it with a thin layer of Levomekol. This ointment is a strong antiseptic, is water-based and does not create a film under which pathogenic bacteria develop.
If there is severe inflammation and swelling of the scrotum, you should consult a doctor. Symptoms mean that the infection has already penetrated into the deeper layers of tissue. The wound may need to be opened, cleaned and drained.
Prevention
To prevent the formation of lipomas, provoking factors should be eliminated:
- Avoid excess cholesterol levels in the blood: reduce consumption of smoked and canned foods, fatty foods, and fried foods.
- Monitor your hormonal levels.
- Do not abuse alcohol, do not smoke.
- Avoid injury and overexertion.
Regular, not too intense physical activity and a balanced diet help maintain normal fat metabolism.
Causes of pathology
A ball on the skin of the scrotum can form due to active secretion of the sebaceous glands and metabolic disorders. Sometimes such neoplasms develop as a result of slag deposits due to pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract or endocrine system. Equally important are various hormonal imbalances or excessive sweating. Fatty skin can occur after injury, mechanical damage to the skin, as a consequence of acne, with a sedentary lifestyle or poor diet.
Other causes of balls
If a ball appears in the scrotum, this may indicate not only a benign neoplasm. The causes may be various pathologies, for example, oncology, dropsy, hernia, inflammation of the lymphatic ducts, varicocele, hematocele. A red or white subcutaneous ball, single or multiple boils, and lumps can be caused by sexually transmitted diseases, allergic reactions or infections. In some cases, the reason for the appearance of white balls on the scrotum is a banal failure to comply with the rules of personal hygiene.
With sexually transmitted diseases, neoplasms on the genitals resemble a rash or pimples with watery contents, small purulent ulcers, and cone-like growths. Most likely, these are signs of syphilis, herpes or HPV. Multiple red pimples may appear due to the activation of a fungal infection. This pathology is accompanied by discomfort when urinating and a strong burning sensation in the perineum.
A ball in the scrotum can appear when wearing synthetic underwear, using harsh detergents or due to the use of latex condoms. In this case, the appearance of red blisters or pimples that are very itchy and flaky is typical. These are symptoms of contact allergies, which can be eliminated by eliminating allergens from everyday life.
White balls on the scrotum may indicate cancer. The tumor can be benign or malignant. The pathological process is accompanied by heaviness and swelling in the damaged area, severe pain.
Diagnosis and treatment of atheroma of the scrotum
Diagnosis of atheroma is usually limited to visual and physical (palpation) examination, while treatment of atheroma requires mandatory removal of the cystic neoplasm.
In medical practice, several methods are used to eliminate atheroma of the scrotum:
- surgical opening and cleaning;
- electrocoagulation using an electric loop;
- laser destruction (destruction);
- Radio wave excision is the latest method using a radio wave knife.
Laser and radio wave treatment make it possible to remove atheroma very quickly without affecting healthy tissue. In addition, after using these devices there is no bleeding, since both the laser and radio waves seal the vessels. There is no residue left after removal of tumors or scars—everything heals very quickly. Since the urologist applies anesthesia, the patient does not feel anything.
To delete or not to delete
As we said above, such a disease is not dangerous for the human body, but it is worth finding out the reasons for its occurrence.
The doctor may prescribe removal in the following cases:
- the neoplasm is continuously increasing in volume;
- is located in places of vascular connections and interferes with the full supply of blood to the male genital organs;
- nearby tissues are inflamed;
- sharp or aching pain when pressing on the sore area;
- unpleasant sensations, namely itching and burning;
- the neoplasm is filled with purulent discharge;
- an unaesthetic appearance that causes a number of complexes in men.
Before treating this disease, it is necessary to undergo a complete diagnosis, which includes instrumental and laboratory methods. The most common and effective type of therapy is surgery. If the cystic formation is small, then doctors may choose a wait-and-see approach. It’s just that sometimes the pathological process goes away on its own. If the doctor diagnoses a large tumor and it is growing progressively, then a surgical treatment method is necessary. There are four main types of operations.
Open surgery to remove atheroma
In this case, the patient is given local anesthesia. Doctors make an incision and remove everything that is under the skin pouch, and then remove the capsule itself. In this case, infection is possible. If doctors have the opportunity, they make a large incision and carefully remove the capsule itself. After this, the incision is sutured. The disadvantage of this procedure is the scar that may remain after the operation.
Laser removal
This technique is minimally invasive. Removal occurs due to the fact that the affected area of the skin is subject to thermal influence.
As a rule, laser removal is used when the tumor is small in size.
At the time of the operation, the skin is dissected using a laser, and the thermal effect begins to evaporate the contents of the skin pouch. As a result of such an operation, the doctor does not use any instruments other than a laser. This technique is excellent for patients who have difficulty clotting their blood. After such treatment, the patient has virtually no scars.
Removal using the Surgitron device
Best materials of the month
- Coronaviruses: SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19)
- Antibiotics for the prevention and treatment of COVID-19: how effective are they?
- The most common "office" diseases
- Does vodka kill coronavirus?
- How to stay alive on our roads?
Removal occurs as a result of exposure to radio waves. This technique is considered the fastest and safest. Thanks to high-frequency radiation, the outer cover and internal capsule of the formations die off. During removal, the patient does not experience pain. After the procedure, there are completely no scars and the patient recovers quickly.
Electrocoagulation
The technique uses electric current, as a result of which the tumor is destroyed. The operation involves removing not only the cyst, but also the vessels that surround it. Therefore, there is no need to worry about possible bleeding. This technique is used only when the atheromas are not inflamed and are small in size.
During the operation, the skin is cut using a scalpel-like electrode, the doctor presses on the affected area and everything comes out. Doctors remove the capsule itself using a spoon and tweezers. The advantage of the procedure is the complete absence of scars.
Symptoms of pathological processes
The course of pathological processes in the scrotum has a number of features determined by its anatomical structure. Therefore, when identifying symptoms of a particular disease in a patient, the doctor will pay attention to some manifestations of scrotal diseases:
- The pain can vary in nature. Its intensity, as a rule, depends on the individual characteristics of the patient - pain threshold, characteristics of perception, psychological factors. It accompanies almost any pathological process in the scrotum - inflammatory processes, varicocele (varicose veins of the scrotum), trauma and testicular torsion.
- Compaction in the scrotum - part of the organ is palpated as a harder formation than other tissues. Palpation of the compaction can be painless (atheroma) or cause sharp pain (hematoma or varicocele). The cause of compaction may be a skin abnormality (atheroma, wart), hematoma due to injury, tumor, vascular disorders, or inflammatory process.
- Itching. This is one of the most intolerable types of itching because, unlike most other areas, it is not always possible to scratch the scrotum. The cause of itching can be allergic skin reactions, some sexually transmitted infections, prickly heat, irritation caused by uncomfortable underwear and clothing, poor hygiene, skin irritation from shaving or other procedures.
- Edema. It can be uniform or uneven, which indirectly indicates the localization of the lesions. The swollen scrotum increases in size, its sensitivity changes, and itching may appear. The cause of swelling may be injury, varicocele, or allergic reactions.
- Redness (hyperemia) of the scrotum. It appears most often during inflammatory processes, less often - during disorders in the circulatory system. Most often combined with other signs of the disease, indicating its nature. With an inflammatory process in the scrotum, a characteristic combination of symptoms is hyperemia, compaction, pain, swelling, and increased local temperature.
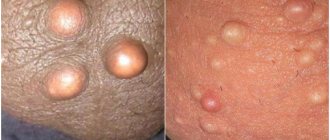
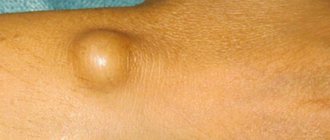
What does a lipoma look like?
Lipoma has several typical features that allow it to be distinguished from other neoplasms. This is a painless spherical formation, which is located under the skin and is characterized by mobility, as well as a fairly dense consistency. Wen can be only 0.5 cm in size, but in some cases it grows quite large. In general, such a tumor tends to grow. With constant pressure or friction, the wen can become injured, inflamed and suppurate.
Most often, small wen does not cause any discomfort to its owner, except aesthetic.
Relapse Prevention
To prevent the problem from recurring, you need to get tested for hormones - it is especially important to measure testosterone and undergo treatment to normalize hormonal levels. You also need to constantly take care of the cleanliness of your genitals and wear loose cotton underwear. This is enough to avoid relapse and another operation on the scrotum.
The choice of the optimal technique, as well as the appropriateness of a particular method of pain relief, is determined by the doctor. Medical offers the services of a highly qualified specialist in the field of urology and andrology. Urologists will perform a full diagnosis and treatment of atheroma of the scrotum. Removal of any tumors is carried out with a laser or radio knife.
Structural features
As mentioned above, the scrotum creates and maintains the optimal temperature for spermatogenesis (34.5ºC). Stable maintenance of this temperature is achieved due to the sequential arrangement of several layers of the scrotal wall:
- Dermis (inner layer of skin). Its structure is no different from the skin of other parts of the body. It may have more pronounced pigmentation than the rest of the skin and is slightly more elastic.
- Fleshy shell. A connective tissue structure located just under the skin of the scrotum. Unlike most parts of the body, there are practically no fat cells in the musculature, it consists mainly of muscle fibers.
- Outer leaf of the spermatic fascia. This is a connective tissue formation that continues the superficial fascia of the abdomen.
- The levator testis muscle and its fascia. This is a rudiment of a formation found in some animals. The contraction of this muscle causes the testicle to be removed from the scrotum into the abdominal cavity. Thus, it is protected from injury. In humans, this muscle does not perform its function and is a rudiment.
- The inner layer of the spermatic fascia is a continuation of the fascia of the abdominal wall. It is fused with the surface layer of the tunica vaginalis of the testicle.
- The tunica vaginalis of the testicle is an analogue of the peritoneum and in embryogenesis is formed from its protrusion. It consists of two layers - the superficial (parietal), which fuses with the internal spermatic fascia, and the internal (visceral), directly adjacent to the testicle. Between them is a cavity filled with water.
Such a complex structure is not just a repetition and modification of the abdominal wall, it provides optimal conditions, gives the testicle a certain mobility, and protects it from injury. In addition, the scrotal tissue is rich in blood vessels and nerves, making it one of the most sensitive places on a man’s body.
Based on the anatomical structure, there are several general patterns of pathological processes in the scrotum. In particular, purulent inflammations are well contained by numerous fasciae; they usually take on a localized character.