Approximately 95% of the world's population is affected by the herpes virus.
If a person has good immune defense, the infection is in a “dormant” state.
If immunity decreases, the virus will immediately make itself known with rashes in the mouth and nose.
Anyone infected with the virus may develop cold sores on their lips and nose.
Some people may not have a rash, but the presence of the herpes virus in the body cannot be ruled out.
Causes of herpes
The causative agent of herpes is the type 1 virus of the same name, which provokes the appearance of a blistering rash on the lips.
You should know that the pathogen is highly contagious.
The virus is present in the body of most people, but not every person develops symptoms.
Those infected with a pathogen, but unaware that they are sick, are carriers of the disease and pose a serious danger to others.
Transmission of the herpes virus can occur:
- as a result of contact with the mucous membrane of an infected person with a rash
- when kissing
- by airborne droplets (during sneezing and coughing)
- when a pathogen enters damaged skin from objects contaminated with viruses
The probability of contracting the virus is 100% even in the absence of close contact.
The disease manifests itself in people with weakened immune defenses, with insufficient intake of vitamins and minerals (iron and zinc) into the body, and suffering from pathologies of the digestive and endocrine systems.
Initially, the pathogen enters the cell, where it begins to actively multiply and infect healthy cells.
As a result, characteristic signs of infection by the herpes virus appear.
Damage to the nasal mucosa occurs with episodes of exacerbation and subsidence of the inflammatory process.
After the first episode of the disease ends, antibodies begin to form.
As immunity decreases, symptoms of infection reappear.
Exacerbations of herpes occur in the following cases:
- as a result of hypothermia
- with exacerbation of existing chronic infections
- as a result of stress and depression
- for colds caused by a viral infection: ARVI, influenza
- for sore throat
- if the body is deficient in vitamins and minerals
- with long-term uncontrolled use of antibacterial drugs and cytostatics
Frequent relapses (more than three times during the year) indicate that a person has reduced immunity.
This condition requires additional examination and specific therapy.
If you leave everything as it is, the infection can lead to damage to various organs and systems.
Herpes on the nose: causes of manifestation and exacerbation
As with herpes on the lips, manifestations in the nasal area are caused by viruses of types 1 and 2. The infection may go unnoticed and appear weeks or even months later.
Typically, an exacerbation of infection is provoked by the following circumstances:
- overheating (on the beach in summer) or hypothermia;
- viral or bacterial diseases;
- unbalanced diet;
- stress, destructive situations;
- alcohol abuse, smoking;
- lack of vitamins;
- exacerbation of chronic diseases;
- long course of antibiotics;
- Women may experience infection during menstruation.
Symptoms of herpes in the nose
Depending on how long you have been infected, certain symptoms will appear.
The consequences of primary infection have more pronounced symptoms.
The symptoms of relapses depend on the state of the immune system.
In some patients, an exacerbation of the process may occur in the form of mild itching and slight redness of the skin and mucous membranes.
Signs of relapse are characterized by:
- hyperemia of the skin and nasal mucosa
- swelling
- presence of tingling and itching in the affected area
- runny nose
If the infection is primary and the immune system is weakened, then the period of exacerbation is accompanied by:
- presence of headache
- temperature rise
- presence of pain in the affected area
- enlarged nearby lymph nodes may be noted
- malaise and weakness
If such symptoms appear, doctors recommend applying antiviral drugs to problem areas.
If this is not done, then in a couple of days herpetic rashes will begin to appear.
During this period, the symptoms of intoxication of the body begin to manifest themselves more acutely.
When a rash occurs, the manifestation of a runny nose intensifies.
The vesicles mature over several days and ulcers remain in their place.
The liquid that flows from the bubbles contains high concentrations of pathogens, and therefore poses a danger to people with whom the patient comes into contact.
Therefore, the affected areas should be treated several times during the day to prevent the spread of infection not only to nearby tissues, but also to others.
Healing of ulcers on the mucous membrane occurs faster than on the skin.
It will take up to three days for the affected tissue to recover.
To exclude the possibility of complications of herpes and the addition of a secondary infection, it is recommended to carry out therapy until the symptoms completely disappear.
If you stop treatment before the relapse ends, then the formation of purulent wounds inside the nose is possible.
- Stress or emotional distress;
- Various somatic diseases, in particular colds, flu, diabetes, HIV;
- Poisoning or intoxication;
- Drinking alcohol, caffeine and smoking;
- Excessive ultraviolet radiation;
- Hypothermia or overheating;
- The arrival of menstruation;
- Overwork and exhaustion;
- Inadequate nutrition (diet) or stomach upset;
- Other factors individual to each person.
After activation, the virus travels along nerves from the trigeminal ganglion back to the skin.
It is important to know that the trigeminal plexus gives off branches that innervate the lips, oral mucosa, gums, skin on the earlobe and part of the cheek. Lesions on the skin will be located in accordance with the exiting nerves. As the virus travels through a nerve, it causes inflammation of the nerve tissue, which causes pain along the nerve fiber. In its development, herpes on the lips goes through stage IV:
Stage I of herpes - tingling. This is when most people feel like they are getting sick. Before a cold sore appears on the lips, the skin in the corners of the mouth or the inner surface of the lips, or on the tongue, or even all over the face begins to itch. In the place where a relapse of herpes will soon develop, harbingers of the disease appear: pain, tingling, tingling, itching. The skin over the site of future relapse turns red. The development of herpes can be prevented if acyclovir-based drugs are used at this stage. If you are experiencing severe itching, you can take an aspirin or paracetamol tablet.
Stage II of herpes - the stage of inflammation, begins with a small painful vesicle, which gradually increases in size. The bubble is tense and filled with a clear liquid, which later becomes cloudy.
Stage III of herpes is the ulceration stage. The bubble bursts and a colorless liquid oozes out, filled with billions of viral particles. An ulcer forms in its place. At this moment, the sick person is very contagious, as he releases a huge amount of viral particles into the environment. Due to the pain and sores on the face, this stage is the most annoying for a person.
Stage IV of herpes - scab formation. A crust forms over the ulcers, and if damaged, it can cause pain and bleeding.
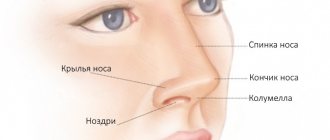
Herpes rashes are most often located on the red border of the lips, but can also be on the nose, on the cheeks, in the ears, on the forehead, in the oral cavity: on the gums, the inner surface of the lips and cheeks.
Strictly observe the rules of personal hygiene. “Colds” on the lips are contagious! Always wash your hands with soap and water before and after touching cold sores, including after applying antiviral cream.
Don't touch your eyes! (especially women while applying makeup). Do not use saliva to wet contact lenses. Despite the itching and pain, you should not touch the rash, kiss, especially with children, use someone else's lipstick or borrow your own, or smoke one cigarette with a friend. Do not attempt to remove blisters or scabs to avoid spreading the infection to other parts of the body or causing a bacterial infection.
Avoid oral sex! Oral sex during a “cold” on the lips of an “active” partner can cause genital herpes in a partner passively participating in oral sex. In this case, herpes from the lips of the “active” partner can be transferred to the genitals of the partner receiving caresses.
If you have a cold on your lips, use individual dishes or a towel, and do not drink from someone else’s glasses.
Stages of herpes development
| Stages herpes | I | II | III | IV |
| Peculiarities | The appearance of precursors of the disease in the form of hyperemia and itching | Blistering rash formation | Opening of blisters and formation of ulcers | Scab formation and tissue regeneration |
| Duration | From 1 to 2 days | 2-3 days after infection | On the 3rd day | From 4 to 10 days |
If the immune system is able to cope with the virus, then the healing stage proceeds faster than usual.
If the immune system is weakened, complications may develop in the form of the formation of ulcers, and if left untreated, the infection can penetrate the tissues of the organ of vision and brain.
In a child, compared to an adult, the clinical manifestations are more pronounced.
2. Reasons
Erysipelas is a bacterial infection, the causative agent of which is almost always group A beta-hemolytic streptococci. This tendency, however, is not absolute: a similar inflammation can be caused by staphylococcus, especially in cases of a long-term chronically recurrent process, as well as other pathogens. In general, we have to take into account the fact that in recent decades in the clinic of infectious diseases, incl. skin, there is a steady tendency towards an increase in combined invasions (for example, bacterial and fungal), developing according to the mechanism of super- or coinfection.
The main risk factor is microtraumatization of the skin of the nose in combination with weakened local immunity and non-compliance with sanitary and hygienic rules.
The risk increases in the presence of foci of chronic coccal infection in adjacent tissues and organs (otitis, tonsillitis, sinusitis, and many others). One of the widespread causes of erysipelas is the practice of self-squeezing out elements of acne and/or pustular (pustular) rash in unsterile or frankly unsanitary conditions. In some cases, nasal erysipelas is iatrogenic in nature, i.e. the launch of the pathological process is caused by medical procedures or surgical intervention on the ENT organs.
Visit our Otolaryngology (ENT) page
What do herpetic rashes in the nose look like?
In the nose, the pathology looks slightly different than when localized on the tip of the nose, on the lips or genitals.
With exacerbation, a rash resembling abscesses appears.
Small, watery blisters filled with transparent contents appear on the nasal mucosa, around which the mucous membrane becomes red.
After some time, the rashes thicken and burst.
In their place, very painful ulcers form.
When the blisters rupture, they release viruses that can spread to the lips and areas around the nose.
Therefore, during this period, it is imperative to use antiviral gels and other drugs prescribed by a doctor for treatment.
3. Symptoms and diagnosis
As shown above, typical manifestations of erysipelas of the nose include erythema and inflammatory swelling of the soft tissues, clearly demarcated by a roller from healthy skin. The swelling can be so severe that the patient’s face becomes deformed and changes beyond recognition. Blisters filled with mucopurulent exudate (bullous form of erysipelas) are often observed.
As a rule, the general symptoms of infectious intoxication are pronounced: malaise, fever, hyperthermia (up to 40° and above), headache, weakness, soreness and swelling of the nearest lymph nodes. After a few days, body temperature may drop just as sharply.
It should be noted that in the absence of timely adequate therapy, erysipelas tends to expand to neighboring areas (skin of the face, neck, chest, ear, etc.); with the involvement of the mucous membranes and submucosal layers of the pharyngeal structures, the development of such serious complications as abscess formation, phlegmon, sepsis, and intracranial inflammation is possible.
The clinical picture of erysipelas is quite specific and usually does not create any difficulties in diagnosis. Examination of the ENT organs reveals hyperemia of the mucous membranes of the nasal cavity. Laboratory diagnostic methods are used to identify the pathogen(s) and assess drug sensitivity. In more complex cases, they resort to instrumental imaging diagnostics (endoscopy, ultrasound, etc.).
About our clinic Chistye Prudy metro station Medintercom page!
Diagnosis of herpes
Even if the patient has characteristic signs of infection, additional studies will be required to confirm the diagnosis of HSV.
The statement becomes possible based on:
✔ Cytological examination of biomaterial. For analysis, swabs are taken from the affected areas.
✔ PCR allows you to detect the genetic material of the virus in the test sample (saliva, blood).
✔ ELISA allows you to detect Ig to the herpes simplex virus in the blood, as well as determine the duration of the disease.
Blood tests can identify herpes from other infections with similar symptoms.
Herpes in the nose: features of therapy
Drug treatment of herpetic rashes in the nose involves the prescription of systemic and local drugs.
Depending on the severity of symptoms, treatment can be carried out comprehensively or medications can be prescribed separately.
At the initial stage of development of the pathological process, when only precursors are present, local therapy with Zovirax, Levomekol, and Acyclovir is carried out at home.
Fenistil Pencivir cream can also be used.
The drug Erazaban prevents the development of complications.
Panavir deserves special attention; it helps cope with advanced forms of herpes, relieves pain, has an anti-inflammatory effect, and also helps increase local immunity.
Regardless of the location of the process: at the tip of the nose, in the cavity or near it, the affected areas require treatment.
Timely application of ointments to the affected areas can reduce the spread of infection to the areas surrounding the nose.
They are recommended to be applied in a thin layer to clean skin every 4 hours.
According to doctors, the effectiveness of therapy will be maximum if the affected area is treated in the first two days.
During the treatment process, you should try to touch the rashes with your hands as little as possible and under no circumstances squeeze them out.
Treatment should be carried out very carefully with a disposable cotton swab, after which it must be disposed of.
As soon as a blistering rash appears, the doctor should prescribe complex therapy.
The treatment regimen is supplemented by taking tablets with antiviral effects.
These include Famvir, Valacyclovir, Acyclovir, Valtrex.
Medicines with antiviral effects are not prescribed to be taken orally by children, during pregnancy, or by women during lactation.
Based on the test results, the doctor will determine what types of virus have been identified, calculate the required dosage of the medicine, and also tell you how long to take the pills and what to apply to the resulting ulcers.
Typically, zinc or tetracycline ointment is used to treat ulcers.
Their use will prevent re-infection and spread of infection to nearby areas of the face.
If complications arise and the disease is accompanied by an increase in body temperature and symptoms of intoxication in the patient’s body, then the oral medication regimen is supplemented with Paracetamol or Ibuprofen.
To improve the functioning of the immune system, drugs to strengthen the immune system are prescribed.
In order to accelerate tissue regeneration and prevent the spread of infection, antiseptics are used.
They treat wounds and areas of skin and mucous membranes around the affected areas.
In order to make the body’s recovery process more effective, the following are prescribed:
● Amiksin . The drug helps increase the body's resistance to viruses;
● Polyoxidonium has a stimulating effect on the immune system, which allows the body to effectively cope with infection;
● Neovir . Takes part in the synthesis of interferons aimed at fighting pathogens.
All these measures will be effective and will prevent relapses only if the patient observes the requirements of personal hygiene.
That is, use only personal items when in contact with your face (use only your towel), etc.
As a rule, to assess the effectiveness of drugs, tests must be taken before and after the course of treatment.
How to treat a nose infection?
Like any other disease, herpes requires consultation with a specialist. If rashes often appear on the wings of the nose, under the nose or inside, you should contact an immunologist.
Traditionally, there are two approaches to treating rashes. The first approach is to prescribe acyclovirii or its derivatives. This group of drugs has its pros and cons. Before use, you must carefully study the instructionsiii, since there are a sufficient number of contraindications and side effects on the body. For example, it is prescribed to pregnant or lactating women with close supervision by a doctor. There are restrictions for use in patients with health problems (for example, kidney or liver failure).
Over time, resistance to these drugs may develop (that is, the herpes adapts or does not respond to this drug at all). The principle of action of acyclovir is the destruction of the DNA of the virus and its ability to reproduce.
The second approach is control over relapses, that is, the use of drugs that can have both an antiviral effect and support the immune system, keeping herpes in a “dormant” state. Various immunomodulatory or antiviral drugs can be used to carry out therapy. One of these drugs is the drug VIFERON. It simultaneously has antiviral and immunomodulatory effects. It is also important to know that this drug is recommended by the standards (protocols) of medical care for the treatment of herpes infection.
How to treat herpes in a child's nose
It is worth remembering that when choosing a drug to relieve symptoms such as herpes on the nose, you should consult a doctor, since many antiviral drugs, especially those based on acyclovir, have contraindications for children under 12 years of age. With frequent relapses of the disease in a child, doctors prescribe complex treatment, always with courses of antiviral drugs. For example, the drug VIFERON can be used in suppositories, which is approved for children from the first days of life. VIFERON in the form of rectal suppositories should be administered to the child into the rectum (that is, rectally). According to the instructions, the treatment regimen is as follows: for 5 days, a suppository in a dosage of 150,000 IU is administered once every 12 hours.
For premature newborns with a gestational age of less than 34 weeks, it is recommended to use the drug VIFERON suppository 150,000 IU daily, 1 suppository 3 times a day after 8 hours.
Treatment of herpes in pregnant women
During pregnancy, it is more difficult to cure herpes on the nose, since many anti-inflammatory and antiviral drugs are prohibited due to the possibility of unwanted side effects during pregnancy and effects on the fetus. Therefore, before using any product, you should consult a doctor. Most often during pregnancy, she prescribes local antiviral ointments or gels.
Viferon Gel
For example, VIFERON gel. It is better to start therapy at the first signs (itching and burning). Squeeze out a strip of gel no more than 0.5 cm long, apply it with a cotton swab or cotton swab onto the previously dried affected surface, apply 3-5 times a day. Treatment lasts 5-6 days and can be continued until clinical manifestations disappear. Treatment can and should be started even if the rash has already begun. For rashes on the nasal mucosa, the gel is applied after cleansing the nasal passages.
Viferon Candles
If herpes manifests itself frequently, then systemic treatment using VIFERON rectal suppositories is recommended. Their use, according to the instructions, is possible from the second trimester of pregnancy (starting from the 14th week of gestation). Course: VIFERON 500,000 IU, 1 suppository 2 times a day. after 12 hours every day for 10 days, then 1 suppository 2 times a day. after 12 hours every fourth day for 10 days. Then every 4 weeks until delivery - 150,000 IU, 1 suppository 2 times a day. every 12 hours every day for 5 days. If necessary, it is indicated before delivery (from the 38th week of gestation) 500,000 IU, 1 suppository 2 times a day. every 12 hours every day for 10 days.
Thus, the inclusion of the drug VIFERON Rectal Suppositories in the complex therapy of pregnant women with HSV-1 HSV-2 helps reduce the duration of the disease from 10.2 to 6.8 days; reducing the number of pregnancy complications (threat of miscarriage from 62% to 31.9%; polyhydramnios from 30.3% to 10%; oligohydramnios from 28.4% to 9% and preeclampsia from 40% to 16.7%), reducing the frequency of relapses of concomitant bacterial vaginosis by more than 1.5 times (mycoplasma and ureaplasma) vi.
Herpes on the nose: treatment in adults
If the frequency of manifestations of the disease in an adult is high, then doctors will recommend complex treatment for such a patient, including immunomodulatory drugs, including, as mentioned above, the drug VIFERON. It is worth noting that the form of delivery of the active substance to the body (rectal suppositories) does not create additional stress on the stomach and liver, which is important for patients who are already taking other drugs to treat concomitant diseases. This is especially true for older people.
The recommended dose for adults is 1,000,000 IU, 1 suppository 2 times a day every 12 hours every day for 10 days or more for recurrent infections. According to clinical indications, therapy can be continued. It is better to start treatment immediately when the first signs of damage to the skin and mucous membranes appear (itching, burning, redness). For recurrent infections, it is advisable to begin treatment in the prodromal period.
The article “New aspects in the treatment of herpes simplex” vii noted that during therapy with the drug VIFERON, there was a rapid relief of clinical manifestations of exacerbation of the disease. The time for regression of rashes decreased on average by 5–7 days. As a result of clinical observation of patients for 1 year after the end of therapy, it was noted that VIFERON, with long-term use, also has a preventive effect. A 3–4-fold reduction in the relapse rate was recorded in 69% of patients.
If signs of infection appear, treatment with suppositories can be accompanied by the use of VIFERON gel, which alleviates the symptoms and improves the quality of life.
How is herpes treated in children and women during pregnancy?
During pregnancy, a woman's body undergoes hormonal imbalance, resulting in decreased immunity.
Therefore, in this state, their body is susceptible to viral infection.
Most medications - antiviral drugs are no exception - have a toxic effect.
So their use during pregnancy and breastfeeding is extremely undesirable.
In this regard, the most rational option would be to use folk remedies, but only with the permission of the attending physician.
Treatment for herpes infection in children is similar to treatment for adults.
Ointments are used as local therapy, and Viferon and Acyclovir are used for systemic treatment.
Another feature of the treatment of pathology in childhood is the presence of age restrictions.
In most cases, the use of systemic agents is contraindicated for children under 12 years of age.
According to experts, the child’s body must overcome the virus itself so that it can easily withstand exacerbations in the future.
With immunodeficiency, the body will not be able to fight the infection, and the progression of the disease will provoke complications.
Therefore, the prescription of antiviral therapy in this situation will be justified.
WHAT YOU NEED TO KNOW ABOUT HERPES SIMPLE
Key Facts
There are two types of herpes simplex virus: herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-I) and herpes simplex virus type 2 (HSV-II).
HSV-I herpes on the lips and facial area
transmitted primarily through oral contact and causes oral herpes (symptoms of which may include a “fever sore”), but can also cause genital herpes.
HSV-II herpes in the genital area
is one of the sexually transmitted infections and causes genital herpes.
More than 90% of the world's population are carriers of the herpes virus. Infection with both HSV-I and HSV-II lasts for life.
The frequency of herpes on the lips varies from person to person and can recur from 2 to 12 times a year. Most cases of herpes are oral and genital.
Typically, the virus settles in the body at 3-5 years of age, but does not appear until puberty.
Transmission routes:
- Autoinfection.
The virus is transmitted from infected areas of the body to uninfected areas. For example, contact lens wearers can transfer the herpes virus to the eye area by wetting the lenses with infected saliva instead of a solution.
- When contacting another person through a kiss
For infection to occur through a kiss, the virus needs 2 conditions:
so that the carrier has an active phase of herpes (moreover, it can be asymptomatic)
so that the partner has a predisposition to infection: an abundance of saliva, small wounds.
- Upon contact with a contaminated surface
The virus is able to survive for some time outside its host: in a humid environment, at a temperature of 37°. That is, it is possible to become infected by drinking from the same glass or using the same lipstick. It is theoretically possible, but rare, to become infected with genital herpes when sitting on plastic surfaces (toilet, locker room bench), because On plastic surfaces under favorable conditions, the virus survives for about 4 hours.
Stages of herpes
Precursor stage
It usually begins with a tingling, itching and burning sensation on the lips. Duration from several hours to 1 day.
Hyperemia stage
Literally on the same day as the tingling sensation, swelling and redness of the lip occurs. The condition is usually accompanied by itching and lasts on average 1-2 days.
Bubble stage
A group of several bubbles is formed, which merge with each other into one painful bubble filled with lymph. This usually happens on the second day and is accompanied by very painful sensations.
Stage of erosion formation
On day 3, the blisters transform into ulcers and pustules, which then form a sore. Usually it is gray in color with a bright red ring around it. The liquid released from the sore contains virus particles in a concentration of 1 million per 1 ml. and is highly contagious
Crust formation stage
From days 4 to 9, the sore dries out and crusts over. In this case, the pain becomes less, but severe itching appears. The sore may fall off in parts and bleed. Herpes begins to heal from the inside, the sore becomes smaller.
Healing stage
On days 9-11, the wound heals and heals. However, redness may persist for another two days. During this period, the virus returns to a dormant state, in which it can remain until it is activated again by risk factors.
Treatment
The most effective medications for people infected with HSV are antiviral drugs such as acyclovir, famciclovir and valacyclovir. They help relieve symptoms and reduce the frequency of their occurrence, but do not lead to a complete cure.
Prevention
HSV-I herpes on the lips and facial area
HSV-I is most contagious during the onset of oral herpes symptoms, but it can also be transmitted when no symptoms are felt or observed. Individuals with active symptoms of oral herpes should avoid oral contact with others and sharing objects that have come into contact with saliva. They should also abstain from oral sex to prevent herpes from spreading to their partner's genitals. People with symptoms of genital herpes should avoid sexual intercourse while they are experiencing symptoms.
Consistent and correct use of condoms can help prevent the spread of genital herpes. However, condoms can only reduce the risk of infection, since symptoms of genital herpes can appear in areas not protected by a condom.
Individuals already infected with HSV-I cannot become infected again, but they remain at risk of infection with HSV-2, which affects the genital area.
Pregnant women with symptoms of genital herpes should inform health care providers. Preventing new infections with genital herpes virus is especially important for women in late pregnancy, since this is the period when the risk of developing neonatal herpes is highest.
HSV-II herpes in the genital area
People with a genital infection caused by HSV should abstain from sexual activity while symptoms of genital herpes appear. HSV-II is most contagious when lesions appear, but it can also be transmitted when no symptoms are felt or observed.
Systematic and correct use of condoms can help reduce the risk of spreading genital herpes. However, condoms provide only partial protection because HSV can be found in areas not protected by a condom. Medical male circumcision can provide men with lifelong partial protection against HSV-II, as well as HIV and human papillomavirus (HPV).
Individuals with symptoms suggestive of genital HSV infection should be tested for HIV infection, and those living in areas with high HIV prevalence should be offered more focused HIV prevention interventions, such as pre-exposure prophylaxis.
Pregnant women with symptoms of genital herpes should inform health care providers. Preventing new infections with genital herpes virus is especially important for women in late pregnancy, since this is the period when the risk of developing neonatal herpes is highest.
Where to go if your child has herpes
If signs of infection with a herpes infection appear, the child’s parents should contact their local pediatrician at the clinic at their place of residence so that the doctor can immediately prescribe treatment.
To prevent recurrence of infection caused by the herpes simplex virus, a specialist may suggest vaccination.
The doctor will also prescribe medications whose action is aimed at increasing immune defense - interferon and immunostimulants.
If your herpes symptoms don't go away
To understand why the symptoms of the virus remain, you will need to undergo a series of tests so that a specialist can assess the state of the immune system.
What kind of doctor cares for such patients?
The role of immunity, in this case, is of paramount importance, and in its absence, consultation with an immunologist is necessary.
The doctor will conduct the necessary examination and determine the reason for the lack of effectiveness of the therapy.
After this, the immune system will be corrected.