Anatomy of the nose
The visible part of the nose consists of: the back, wings, tip and nostrils.
Anatomy of the visible part of the nose
The internal structure of the nose is a little more complex.
The nasal bone consists of 2 segments, connects in the middle and forms the bridge of the nose in its upper part.
The cartilage continues the nasal bone, forming the tip and wings of the nose. The septum is a cartilaginous plate that internally divides the nose into two halves.
The tip of the nose meets the columella , which forms and separates the nostrils. It consists of skin and cartilage.
If you hold the tip of your nose, you can move it in different directions. The cartilages of the nose are quite mobile and plastic.
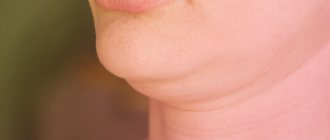
How to remove widow's hump at home
The first thing that is recommended when deciding how to remove a widow’s hump is exercise. Taking into account the main reason for its development (stooping, prolonged static position), regular loads on the neck and shoulders, upper back and abs will help normalize posture. But it is important to remember that exercises for widow’s hump at home can be performed only after the doctor’s permission, after undergoing an examination that excludes osteoporosis and more serious causes of the development of the defect.
There are quite simple and effective exercises to eliminate the widow's hump. By strengthening the right muscles, you can prevent and correct this terrible condition. The exercises use the body's own resistance to strengthen and tone the key muscles of the upper back. When these muscles are strong, they keep the cervical vertebrae level and prevent the head from moving forward. And the exercises themselves stimulate the growth and density of bones in the vertebrae.
The workouts work the posterior deltoid, rhomboid and middle trapezius muscles. To straighten your hump, you will need only two light weights: for example, 2 dumbbells of 2 kg each or plastic bottles of water.
- Stand with your feet shoulder-width apart and hold one weight in each hand.
- Lean forward at your hips at about a 45-degree angle. Extend your arms in front of you.
- Squeezing your shoulder blades, raise both arms up and out to shoulder level. Your elbows should be slightly bent. Slowly lower your arms back to the starting position. Repeat 8 times in 1 set.
- Do 3 sets of 8 reps or as many as you can.
During exercises, do not raise your arms above shoulder level. You can do this exercise seated if you prefer - just keep your back straight and lean forward at the hips, bringing your chest down to your knees.
Hump of nose
The hump is formed at the junction of the nasal bone and cartilage and is clearly visible in profile.
A hump can appear for three reasons:
- The bones and cartilage of the nose have grown together incorrectly after a bruise or fracture
- The hump of the nose is genetically determined and inherited
- Unsuccessful rhinoplasty – a hump may appear due to an incorrectly planned operation
Anatomy of the nasal hump
Operation process
Preparation for surgery occurs as follows:
- A consultation with a surgeon is carried out.
- The patient takes tests at the clinic or at his place of residence (tests are considered valid for 10 days).
Carrying out the operation:
- The patient comes to the clinic, enters into a treatment agreement and pays for it.
- The patient is placed in the ward.
- The doctor applies the necessary markings and photographs the patient to compare the result after the nose job is performed.
- Intravenous anesthesia is administered.
- The operation is performed and lasts 60-120 minutes.
- The patient is left in the ward for a day (the time spent in the clinic can be increased to several days, if necessary).
How to get rid of a hump nose
There are two ways to get rid of a hump in the nose: with fillers or rhinoplasty.
Fillers are an injectable drug for the correction of cosmetic defects.
Nose correction with fillers is a quick and easy option that can help improve the appearance of your nose for a short period of time. Using fillers, you can straighten the bridge of the nose, correct the tip of the nose, and fill in uneven spots.
Rhinoplasty is a plastic surgery to correct the shape of the nose and change the anatomy to improve breathing.
Unlike fillers, with the help of rhinoplasty you can solve all problems at once and forever:
- Remove hump
- Make your nose smaller
- Align the nasal septum
- Improve nasal breathing
- Change the shape of the tip of the nose
How to cure widow's hump with liposuction
For most patients with withers, neck liposuction is the most suitable technique to achieve an ideal result. Typically, neck liposuction can only be performed under local anesthesia, which reduces the likelihood of possible complications from general anesthesia. However, for some patients, the doctor may decide to use general anesthesia. Liposuction cannula can be inserted through very small incisions, which leave minimal residual scarring after the healing process is complete.
In some cases, the doctor may perform a second liposuction procedure at a later date to improve results and achieve an optimal appearance. Because the skin on the upper back/neck is quite thick and the fat can be quite fibrous, the surgeon uses special lipocannulas to improve the shape, define the area, and facilitate shrinkage of the skin. Although there are some doctors who may use an “open technique,” many plastic surgeons prefer to approach the area in a minimally invasive manner to avoid scarring.
Recovery depends on the technique used during surgery.
Liposuction patients usually recover quickly and can return to their normal activities in about a week after surgery. Sometimes drainage may be required for proper healing. After full plastic surgery, a longer stay in the clinic and a long recovery period may be required. Information materials on the site are posted for informational purposes, not self-medication. Any plastic surgery is a surgical intervention. When deciding to have surgery, be sure to consult with a qualified professional.
Open or closed hump surgery?
Open and closed rhinoplasty
From the patient’s point of view , the only difference is in the incision. With open rhinoplasty, the incision passes through the nasal passages inside the nose and along the columella, and with closed rhinoplasty, only through the nasal passages.
Many people are convinced that after open rhinoplasty there will be visible scars on the columella. But in fact, scars are practically invisible, and over time they disappear without a trace.
From the surgeon’s point of view , the difference is that with closed rhinoplasty, the surgeon acts blindly, but with open rhinoplasty, he sees and controls everything.
Open rhinoplasty provides predictable results and allows for precise changes to the internal anatomy of the nose. That's why I only perform open rhinoplasty.
Look at my case, take a special look at the columella.
Scar 2.5 months after open rhinoplasty ©Dikarev Alexey Sergeevich
Rhinoplasty with fillers – how is the procedure performed?
This method involves the introduction of special preparations containing hyaluronic acid into the nasal area. The product fills in unevenness, so that the nose is leveled, acquiring symmetry. The fillers themselves are either absorbable (their effect wears off over time) or permanent (continuous action). Doctors do not recommend the use of permanent products, as their use can cause complications.
The procedure itself takes approximately 45 minutes. First, the face is treated with an antimicrobial agent, then with a mild anesthetic. After this, points are placed for future injections, then the drug itself is administered. As soon as the skin becomes sensitive, the patient can go home.
It is important to note that these manipulations will not help with severe defects. The duration of the procedure’s effectiveness is 9-12 months, then it can be repeated.
Septoplasty
Septoplasty is an operation to correct the nasal septum.
For most people, the nasal septum is initially uneven. Even if you think you have a perfectly straight nose, your septum may be slightly shifted, bent or pinched. Because of this, nasal breathing is limited.
Nasal septum
Septoplasty helps improve nasal breathing and get rid of various problems caused by a deformed nasal septum:
- chronic runny nose
- nasal congestion
- snore
Possible consequences
The postoperative period largely depends on the work of the plastic surgeon.
Click to enlarge
Possible complications include:
- Deformation of the septum;
- Loss of smell;
- The beginning of the inflammatory process;
- Breathing disorders;
- Dry mucous membranes.
With complications, heavy bleeding is most often observed, swelling increases, body temperature rises, and headaches are possible. The appearance of any symptoms of complications requires urgent medical attention.
Often, any complications can be avoided if you follow the recommendations of the plastic surgeon.
Alignment of the nasal bridge
In order to remove the hump, I use a scalpel and an osteotome.
An osteotome is a surgical instrument used to cut bone.
I remove the cartilage tissue with a scalpel, and excise the nasal bone with an osteotome.
Removal of nasal hump
In this case, we make the back even by removing the hump, i.e. we lower it. But if you have a snub nose, removing the hump is not enough. For such cases I use a special technique.
Preparation for rhinoplasty
Consultation with a plastic surgeon, 3D modeling
In plastic surgery, the preparatory period for surgical intervention is important. It starts with an initial consultation. At the appointment, the surgeon examines the patient, takes photographs, listens to wishes for the future nose, and makes recommendations. After examination and assessment of the condition of the nasal tissues, the surgeon determines to what extent the desired rhinoplasty can be performed and how to correct the shape.
3D modeling helps you visualize what your nose will look like after correction. To do this, photographs of the face are taken in three projections: full-face, half-profile and profile. The photographs are entered into a program that models a three-dimensional image of the face. On it you can “design” according to size and clearly demonstrate not only the new nose, but the entire appearance. However, plastic surgeons warn that in reality the result may differ, because the program does not take into account the internal structure of the nasal passages and the individual characteristics of the body during recovery. Using 3D modeling, the volume of surgical intervention is determined.
Often, when correcting a hump, plastic surgery of the tip of the nose is additionally required. This is necessary so that a straight nose looks aesthetically more attractive and does not appear long.
If the patient has initial breathing problems, hump correction is performed together with septoplasty - restoration of a deviated nasal septum.
Analyzes and research
Before surgery, you must undergo examinations and tests:
- blood for biochemistry, Rh factor and group;
- general blood analysis;
- blood test for prothrombin;
- tests for hepatitis B, C, RW (syphilis), HIV;
- ECG;
- radiography of the paranasal sinuses.
The surgeon must know about all chronic diseases, allergies, and bad habits. This information is collected by the doctor during a history or interview. If you have chronic diseases, he may prescribe other tests.
When preparing for plastic surgery, the surgeon develops an operation plan.
Restrictions
- For a month before rhinoplasty, avoid sun exposure and do not visit the solarium.
- Do not do deep mechanical or chemical peeling for a month.
- Give up alcohol and smoking in two weeks.
- Stop taking medications, blood thinners, hormonal drugs, and antibiotics for two weeks.
- Buy contact lenses if you wear glasses.
- 24 hours before surgery, eat only light meals.
On the day of surgery you should not drink or eat. In the morning, take a warm shower and wash your face thoroughly. Decorative cosmetics cannot be applied. Remove all jewelry. If you have eyelash extensions, you need to remove them.
“Turkish delight” technique – for straightening the back of a snub nose
The essence of the technique is to straighten the bridge of the nose by raising it.
If you simply cut off the hump, the nose will look unnatural, the back will be concave - this is called a saddle nose.
Saddle nose surgery
In order to raise the bridge of the nose, I use grafts - grafts from the cartilage of the nasal septum.
I cut the nasal septum cartilage into small pieces and form a graft. It turns out to be a kind of “sausage” made from your own tissues. I attach the graft to the back of the nose.
Nasal dorsum graft
This method is vaguely reminiscent of correction with fillers. The essence is the same - filling in irregularities and raising the bridge of the nose.
Only correction with fillers needs to be performed every year, and the graft from your own tissues will be securely fixed and will not go anywhere.
What's next?
After plastic surgery of the nasal hump is performed, a special plaster bandage is applied to the nose, thanks to which the cartilage and bone fragments are fixed in the new position.
The recovery period after rhinoplasty lasts several months. During this time, swelling of the nose may persist, and breathing may be difficult. After the operation, it is prohibited to take hot baths, visit swimming pools, saunas, perform intense physical activity, or wear glasses with oppressive or heavy frames. Airplane travel is also prohibited.
After rhinoplasty, it is important to protect your nose from external influences as much as possible, since the fused cartilage and bone tissues remain fragile during the healing process and can be easily damaged.
The shape of the nose will take 6-12 months to form, during which time all swelling will subside and final healing will occur. The results obtained will last a lifetime; no additional procedures are needed.
Stabilization of the nasal bridge and improvement of breathing - the “Spreader graft” technique
To fix the nasal septum, widen the nasal passages and improve nasal breathing, I use grafts.
Most often, during primary rhinoplasty, nasal septum cartilage is used for grafts. If rhinoplasty has already been performed and there is not enough septal cartilage, auricular or costal cartilage is used.
Cartilage of the nasal septum, auricle, costal
Two strips of cartilage must be cut out to form grafts.
Grafts to improve breathing
Grafts are placed and sutured between the septum and the upper lateral cartilages.
Choosing the right exercise
To reduce your nose, there is no need to perform all existing exercises; 2-3 aimed at eliminating existing defects will be enough. If your nose is beautifully shaped, it is recommended to perform Carol Maggio’s multifunctional exercise to maintain it.
If there are no flaws, it will not allow them to appear, and will also shorten a long nose and make its tip narrower, the upper lip sharper, and help disguise a small hump.
The sequence of actions includes 5 steps:
- Take a starting position - any comfortable one: sitting, standing, lying down, and even while walking. The main thing is that the stomach should be pulled in, the muscles of the buttocks and the front of the thighs should be tense, and the rest of the body should be as relaxed as possible. It is not advisable to hold or lose your breath; it should be measured.
- Using your thumb and forefinger, squeeze the bridge of your nose like a clothespin; your fingers should be straight and positioned vertically. If it becomes more difficult to breathe, your fingers are probably resting on the cartilage; you need to move them a little higher on the bone.
- Place the tip of the index finger of the second palm against the nasal septum from below.
- Close your lips and, without opening your mouth, lower your lower jaw so that your upper lip stretches and pulls the tip of your nose, while holding it in place with your finger.
- Freeze in this position for a second, return to the starting position and relieve tension. Do one set of 40 repetitions daily. When performed correctly, a tingling and slight burning sensation should appear in the area adjacent to the nose.
If the redness of the nose bothers you, massaging the ears can successfully cope with it.
You need to grab them so that your index fingers are in front and your thumbs are in back. Massage the edges of the ears in a circular motion for half a minute, moving from bottom to top. There is no need to stretch your ears. At the top, for convenience, you can swap your fingers. Perform 2-3 sets daily until the problem disappears, and when it returns, resume manipulations.
Stabilization of the nasal tip - “Extended septal graft” technique
To stabilize the tip of the nose, I again use a nasal septum graft. The essence is the same as with grafts to improve breathing.
The graft is placed between the cartilages of the nasal wings and sewn to the septum to add strength.
Nasal tip stabilization graft
Installation of this graft helps to securely fix the tip of the nose to avoid changes in its position in the future. With age, the soft tissues of the nose begin to sag and the nose ages.
Aging nose
If necessary, I correct the wings and tip of the nose.
In what cases will the surgeon refuse correction?
Like any other surgical intervention, rhinoplasty has a number of contraindications. They are divided into absolute and relative.
The surgeon will refuse surgery in the following cases:
- diseases of the heart and blood vessels;
- hemophilia, other blood clotting problems;
- hypertension;
- age - up to 18 and after 40 years;
- liver, kidney failure;
- diabetes;
- pustular formations in the operated area (boils, acne);
- malignant neoplasms;
- mental illness.
Correction is not performed until the age of 18, since the formation of bone tissue is not yet complete until this age. However, there are exceptions. A nose job may be performed earlier in the event of injury.
After 55 years, rhinoplasty is not performed, since after this age the regenerative abilities of tissues decrease, healing progresses worse, and the risk of complications is high.
Relative contraindications include viral and bacterial respiratory tract infections, as well as pregnancy and lactation.
Reviews about hump rhinoplasty
Reviews from social networks and instant messengers
Video reviews
Independent reviews
Anonymous
I would like to express my deep gratitude to Alexey, even though he did not operate on me. I have a young daughter. Several years ago she had a serious accident, recovered, everything was fine, she was cured. But something terrible happened to her nose (during the accident there was a fracture and apparently something went wrong). The girl is still very young, but she has become so insecure and downtrodden. I kept saying that everything was fine, but I see it. I’ve already taken her to psychologists, but I see that it’s not helping (now I don’t understand what I was thinking, I can’t imagine how a psychologist would help). I started thinking about plastic surgery about a year ago, but for some reason I thought it was a pleasure only for the rich. I started looking at prices, doctors in the city and found Alexey. Moreover, I noticed him in some program, and there he was described like this! When I told my daughter about the idea, she burst into tears with joy, and we almost immediately went to the reception. Everything went very well! Alexey is a very sensitive, understanding and competent specialist. Thank you so much for restoring the girl’s self-confidence!
Diana
I always wanted to make my wide nostrils a little smaller, and I was terribly complex about this. An opportunity arose, including a financial one, and only thanks to Alexey did I regain confidence in my beauty. A knowledgeable doctor, polite and prudent staff at the Line clinic. The operation went quickly, unlike the preparation for it, here as everywhere else - tests, examination, consultations. After a month, the seams were completely worn out, and did not become inflamed, as in some people. Now I’ve forgotten that I once suffered with my nose. I recommend
https://www.tecrussia.ru/plasticheskie-hirurgi/krasnodar/2291-dikarev.html
Anonymous
In April I had rhinoplasty with Dikarev. The operation was successful, then she was under the supervision of medical staff for 2 days. Discharged for 3 - then a week of rehabilitation. I thought it would take longer. The doctor is a professional. You can really trust your face and not be afraid that it will warp))
https://23med.ru/doctors/plastic-surgeon/dikarev-aleksey-sergeevich
View all reviews
We care about your health
Epithelial tumors
Papillomas. There are papillomas of the vestibule and the nasal cavity. The first ones are gray in color, dense, villous surface, small in size, not malignant. It is believed that papillomas are caused by viruses from the family of papillomoviruses types 6, 11 and 16. Papillomas of the nasal cavity primarily affect the mucous membrane. They often recur after surgical removal. With anterior rhinoscopy or endoscopy, papillomas are gray-white in color, soft in consistency, single or multiple, bleed when touched, and resemble cauliflower. Treatment of nasal papillomas is predominantly surgical or cryodestruction. Surgically removed material should be sent for histological examination due to the possibility of malignant degeneration (transitional cell carcinoma). Another problem in the treatment of these patients is the frequent recurrence of papillomas. To prevent it, it is recommended to prescribe interferon drugs - domestic Laferon or foreign intron A. The method of treatment with Laferon consists of inhalation administration at the beginning of therapy (1 million Laferon is diluted in 20 ml of 0.9% NaCl solution). Inhalations continue for the first 10 days, then Laferon is prescribed intramuscularly once a day, at a dose of 1 million units, for 20 days. Some clinics determine the titers of antibodies to it to monitor the presence of the virus in the blood serum. When the levels increase above 1:200 in the blood of patients, antiviral drugs (Zoverax or others) are prescribed. Papilloma viruses also infect the cervix, which leads, in less pathogenic types, to the occurrence of condylomas.
Inverted papilloma. Called due to the ability of squamous epithelium to invaginate in the form of a wide ribbon into the connective tissue, these tumors have destructive growth, recur and become malignant. They are also known as columnar cell papillomas.
Adenoma is a benign tumor of the glandular epithelium of the nasal mucosa. It mainly affects the lower parts of the nasal cavity on a broad base with a smooth surface. Characterized by slow growth. The tumor is erysipelas-gray in color, no more than 2 cm in size, and is accompanied by rapid growth, germination into adjacent tissues, and changes in the histological structure. Its treatment is surgical. The removed material should be examined histologically.
Nonepithelial tumors
Hemangioma is a tumor developing from blood vessels, similar in nature to developmental defects. What it has in common with other tumors is rapid growth, during which hemangioma destroys surrounding tissue and causes a cosmetic and sometimes functional defect. In 1863, Vikhrov published a macro-microscopic classification of hemangiomas, dividing them into capillary, cavernous and racemose (branched). Subsequently, this principle was included in many classifications.
Today, this classification is used, which includes additional data on tumor growth, its spread, blood supply characteristics and relationship with large blood vessels.
True hemangiomas: 1) capillary (simple): exophytic (venous and arterial type); 2) cavernous: mucous-submucosal; diffuse (spreading into depth); 3) branched (angiodysplasia); 4) mixed (angiofibromas, hemlymphangiomas, branched with cavernous, branched with Barre-Mason glomusangiomas, etc.).
Diagnosis of tumors in the nose
- Routine external examination of the patient. Palpation of the tumor.
- Anterior and posterior rhinoscopy.
- Examination of the nasal cavity and paranasal sinuses using an endoscope. Diaphanoscopy.
- Comprehensive X-ray examination.
- CT and MRI.
- Cytological examination of discharge obtained during puncture, sinus lavage, as well as nasal discharge.
- Histological examination of pieces of the neoplasm.
Treatment of nasal tumors
- Surgical removal of the tumor (if it is of significant size with preliminary embolization of the vessels feeding the tumor).
- Cryodestruction of the tumor.
- Sclerosis therapy.
- Radiation therapy in combination with surgical removal (for tumor malignancy).
Bleeding polyps of the cartilaginous part of the nasal septum are red, round in shape with a smooth surface. They are characterized by frequent bleeding. Treatment is surgical.
Fibromas, myomas, lipomas are rarely found in the cavity and paranasal sinuses. Angiofibroma, fibromyoma, osteofibroma, adenofibroma, neurofibroma, histiocytoma may occur. The treatment of these tumors is surgical.
Osteomas. They are most common among benign tumors of the paranasal sinuses, in people 20-40 years old. According to some authors, osteomas are localized in the area of bone sutures in 50% of patients. Histologically, three forms of osteomas are distinguished: compact (ivory), spongy and compact-spongy. Osteomas are extremely slow growing and predominantly asymptomatic. They are often discovered incidentally during X-ray or CT scanning. With large tumors or localization in the main sinus, a headache may be observed; with osteomas of the frontal sinus, exophthalmos, diplopia, and visual impairment may be observed.
Treatment of osteomas is exclusively surgical. The sooner it is carried out, the better success will be achieved. Mandatory histological examination of the removed tumor. Sometimes, with compact osteomas of the main sinus, when there is a risk of serious complications (damage to the cavernous sinus, internal carotid artery), surgical intervention should be carried out jointly with neurosurgeons.
Chondromas. They develop from the remains of the primordial cartilaginous skeleton and can be attributed to developmental anomalies. Tumors are characterized by slow expansive growth with penetration into the orbit or cranial cavity. They often recur and, in addition, can become malignant. Osteochondromas can occur in the nasal cavity. Neurogenic tumors
Paragangliomas (glomus tumors, chemodectomas) grow from small cell groups of the nasal mucosa. Rarely found in the nasal cavity. The tumor has infiltrative growth, often recurs, and malignantly degenerates. In such cases, it often grows into the skull and brain.
Tumor-like lesions
Tumor-like diseases are described in the relevant sections of the reference book, but fibrous dysplasia deserves special attention.
Fibrous dysplasia. Refers to tumor-like lesions of the nose and paranasal sinuses and is a defect in the formation of osteogenic mesenchyme. Characterized by the replacement of bone with fibrous tissue. Some authors consider the disease to be a developmental anomaly of unknown origin. Diagnosis of the disease is radiological but mainly histological confirmation is the main motive for choosing treatment. This lesion is also known as fibrous osteodystrophy, osteitis fibrosa. The bones of the upper jaw, main and frontal bones are predominantly degenerated. Treatment is surgical. The affected bone areas are removed. Relapses are possible. Sometimes such patients are treated in dental hospitals. V.
Malignant tumors of the nose and paranasal sinuses
The incidence of malignant tumors is steadily increasing by 2.6-3.0% per year. Malignant tumors of the nose and paranasal sinuses account for about 0.5% of cancer incidence statistics. In 2002, per 100 thousand population of Ukraine, the incidence of malignant tumors of this localization was 0.59, 287 patients were diagnosed for the first time. For comparison, in Belarus in the same year it was 0.7, 70 patients were identified. In Russia, 832 patients were detected for the first time, the incidence was 0.6. In the United States, 2,000 patients with cancer of the nasal cavity and paranasal sinuses are diagnosed annually.
Localization of tumors in the nose and paranasal sinuses, which are a system of narrow thin-walled cavities rich in nerves, blood and lymphatic vessels, promotes growth and rapid spread to adjacent formations, which significantly complicates treatment and leads in many cases to death.
Among the factors that cause malignant growth in this area are wood dust, petroleum products, professions associated with exposure to potent compounds - benzenes, acids, alkalis, nickel ores, varnishes and smoking. Among the factors that contribute to the growth of these tumors, chronic diseases are also noted - rhinitis, polypous sinusitis, ethmoiditis, frontal sinusitis, viral agents. The Epstein-Bar virus is considered the etiological factor of malignant lymphomas, papillomovirus types 11, 16, leads to the occurrence of transitional cell carcinoma and papillomas in the area of the nasal epithelium.
In most cases, the disease affects people of working age. Early clinical manifestations in people with tumors of this localization are insignificant and therefore the disease is more often detected in stages III – IV, when the walls of the cavities are already destroyed and penetration into adjacent anatomical areas begins.
According to most authors, malignant tumors are most often localized in the maxillary sinus (75-80%), in second place are the cells of the ethmoidal labyrinth and the nasal cavity (10-15%), less often the sphenoid and frontal sinuses are affected (1-2%).
When treating people with malignant tumors of the nose and paranasal sinuses, surgical, radiation and chemotherapy methods are used, but the results remain unsatisfactory, while the number of patients with this pathology does not decrease.
It should be noted that the palette of morphological forms of malignant tumors of the nose and paranasal sinuses is diverse.
Basal cell carcinoma occurs more often in various areas of the skin of the nose. Trichoepithelioma also belongs to basal cell malignant neoplasms.
Melanoma is observed in 2-3% of malignant tumors of this location. Most often it is located in the nasal cavity. The tumor is characterized by polymorphism. However, the sarcomatous form predominates. Early symptoms include bleeding and difficulty breathing. Melanoma metastasizes in 60% of cases to the cervical lymph nodes.
Clinical picture of tumors in the nose
Clinical manifestations of malignant tumors depend on the stage of the disease, localization, growth form, as well as the morphological structure of the tumor.
Symptoms:
- Pain. They appear sharply when localized in the upper jaw along the n. trigeminus. When the tumor is localized or grows into the area of the pterygopalatine fossa, shooting pain appears in the area of the eyeball or temple, which indicates irritation of the n.auriculotemporalis. Pain as the first sign of the disease was observed in 17% of patients.
- Impaired nasal breathing. When the tumor was localized in the nose, similar complaints were noted in 62.8% of patients. Patients whose tumor did not spread beyond the paranasal sinuses, or those whose tumor grew towards the cheek, temporal bone, alveolar process, or orbit did not complain of nasal breathing disorder.
- Nasal discharge. More often they are unilateral mucopurulent with an admixture of blood.
- Headache of various types, often with various paresthesias in the facial area on the side of the tumor. Often in such cases neuralgia is diagnosed. If they are not treatable, you should always remember about the possible development of a malignant disease.
- Pain in the teeth, deformation of the face, nose, lacrimation, exophthalmos, deformation of the hard and soft palate - these symptoms can occur to varying degrees with malignant tumors of the nose and paranasal sinuses.
Malignant tumors of the mucous membrane of the maxillary sinus occur without symptoms for a long time. Clinical manifestations depend on the starting point and size of the tumor. Tumors arise on all walls of the sinus, from the superomedial part of the sinus they quickly cause bleeding, swelling of the eyelids, lacrimation, exophthalmos; when they grow forward, they grow into the anterior wall and then in the cheek area they can be identified by palpation. As the tumor grows downward, it grows into the hard palate and changes its configuration. The growth of a tumor from the medial wall into the nasal cavity makes breathing difficult and leads to the formation of polyps. If the tumor grows predominantly in the direction of the posterior wall with germination into the fossa, the nasal part of the pharynx, then it causes pain.
When a tumor destroys the orbital wall, the process spreads to the orbital tissue, which is manifested by exophthalmos, decreased visual acuity and diplopia. Malignant tumors of the ethmoid labyrinth. Isolated lesions of the labyrinth cells are observed in 10% of cases.
When the tumor spreads towards the orbit, the thin wall of the latter is destroyed and tumor growth into the orbit is observed.
From the cells of the labyrinth, neoplasms can also spread to the maxillary, sphenoid sinuses, anterior and middle cranial fossa, and nasal pharynx.
Tumors of the sphenoid (main) sinus. Primary cancer of this location is extremely rare. Typically, these are tumors that extend from the maxillary sinus or ethmoid. The earliest symptoms are ocular, often damage to the efferent nerve, less often - decreased vision. Patients seek help from an ophthalmologist or neurologist. Characteristic orbital-superior syndrome (damage to the vessels and nerves that pass through the optic foramen and the superior orbital fissure), visual impairment, up to blindness, ptosis, diplopia, pain in the occipitotemporal and occipital regions.
Tumors of the frontal sinus are rare and have symptoms when affected, which do not extend beyond the sinus, similar to the symptoms of chronic frontal sinusitis. In recent years, CT and MRI have made it possible to differentiate this disease from mucocele, osteomyelitis and sinusitis. Symptoms depend on the direction of tumor growth. Germination downwards and medially leads to penetration into the orbit, ethmoidal labyrinth, exophthalmos appears, germination posteriorly - the anterior cranial fossa is affected, then a sharp headache, convulsions, and mental disorders are possible. Penetration of the tumor through the anterior wall leads to swelling and discoloration of the skin in the frontal area of the head.
Overview video of ENT surgery in Moscow, Kurkino and Khimki:
Here's something else interesting
Surgical treatment of bulging eyes - Olivari operation
How to remove a double chin and tighten your neck?
How to remove bags under the eyes? Lower blepharoplasty or fillers.
How to get rid of jowls? Lifting, SMAS-lifting, MACS-lift.