A callus is a skin lesion small in size and depth that occurs from physical activity, sports, or wearing uncomfortable shoes. Calluses in the form of chafing often occur from tight, new shoes. The skin reacts to exposure with hyperkeratosis - excessive keratinization (thickening).
Dry calluses may not cause discomfort for a while, but usually hurt when pressed. It is advisable to immediately take measures to remove dead skin and heal tissue. If you do nothing, the problem will become deeper and wider in the literal sense of these words. In the future, tissue infection, suppuration, and related problems may arise.
For treatment, doctors can recommend various products in the form of gels, ointments and infusions, but the most effective and simple remedy is considered to be a patch against calluses, the advantages of which are:
- does not require special knowledge or special conditions for dressing;
- securely fixed on the callus;
- protects the skin from further damage, penetration of microbes, and development of infection;
- softens the stratum corneum for painless and quick removal;
- reduces pain;
- stimulates tissue regeneration;
- serves as a prevention of inflammation and cracks;
- the medicinal composition in the form of impregnation remains on the injured area and does not stain clothing, unlike ointment.
The medical supply store offers a wide selection of plasters, including waterproof, clear, and highly specialized ones. All that remains is to choose the appropriate option and follow the instructions for use.
Medical diagnosis of callus
Core-type calluses are fairly easy to diagnose.
After an in-person consultation, a dermatologist can provide a conclusion and diagnosis about the type of skin growth.
The only difficulty may be differentiating an ingrown callus from Verruca plantaris (plantar wart).
Because they have the same location and appearance.
You can distinguish a callus from a wart by the following features:
- An ingrown callus is not accompanied by bleeding even with strong pressure on it.
- A wart, unlike a callus, is not a single formation. Typically, upon examination, several warts that resemble cauliflower can be identified.
- The callus in its central zone has a small depression, which can be seen upon detailed examination. In the case of a wart, the HPV formation consists of thin fibers; petechiae (black dots) are observed on top, which bleed when injured.
- If a wart is present, pain occurs when the lesion itself is palpated; there is no pain when walking. In the case of calluses, pain is observed with any mechanical movement.
To confirm the diagnosis and determine the cause of the disease, the dermatologist prescribes a blood test for diabetes mellitus.
Also an analysis to determine the human papillomavirus, to exclude HPV.
Additionally, the doctor can redirect the patient to other specialized specialists.
See a podiatrist (a doctor who treats foot pathologies), a rheumatologist or an orthopedist.
An important point is to exclude Morton's neuroma.
Morton's neuroma is a benign or non-cancerous growth of fibrous tissue.
Develops in the area of the tibial nerve, most often between the third and fourth fingers.
The pathology is accompanied by thickening of the plantar nerve, pain when walking, and a feeling of numbness in the fingers.
The disease is also known as Morton's metatarsalgia, plantar neuroma, and intermetatasal neuroma.
Formation mechanism
A synovial cyst is formed in this way:
- The elasticity and endurance of damaged tissue decreases.
- The joint is unable to retain joint fluid.
- The contents of the synovial membrane are poured into the surrounding tissues.
As a result, an elastic and dense tumor-like formation appears, filled with thick liquid inside.
Doctors still cannot accurately answer the question of why a synovial cyst occurs. However, they identify several factors that can trigger the appearance of a lump:
- Hereditary predisposition. If close relatives had a hygroma on the finger, then the likelihood of its occurrence in the child also increases.
- Systematic load on the hands.
- Inflammatory diseases and injuries (microtraumas, bruises, sprains, dislocations, fractures) of tendons and joints.
- Metaplasia is the pathological replacement of normal tissues with abnormal ones.
- Excessive tension in the arm muscles.
- Calluses on the fingers that appear regularly.
- Lack of adequate treatment for finger injuries and diseases.
Finger hygromas, which form after injuries, are diagnosed in 30% of patients. Tumors that are inherited occur in 50% of cases. In other cases, growths are formed due to repeated injuries and constant overstrain of the damaged area.
Reference. Tendon ganglion most often appears in women between 20 and 30 years of age. In children and the elderly, pathology is observed extremely rarely.
Methods for treating and removing ingrown calluses
The only and effective method of eliminating this problem on the legs is to remove the stratum corneum of the callus and its root.
In this case, it is important to completely remove not only the surface of the callus, but also the root.
Otherwise, the risk of relapse reaches 100%.
There are various methods for removing calluses; the optimal treatment option is selected individually.
Depending on the clinical signs, the neglect of the case and how deep the root has penetrated into the layers of the dermis.
Causes of calluses
Before getting rid of corns on your feet and fingers, you need to find out the main reasons for their appearance and eliminate them. Most often, calluses occur due to:
- using uncomfortable, narrow shoes or shoes of the wrong size;
- wearing hard shoes on bare feet or a very thin nylon sock;
- a heel that is too high, which causes compression and excessive stress on the forefoot;
- various foot diseases;
- walking barefoot for a long time;
- excessive sweating of the feet;
- wearing shoes with hard seams inside or with rubbing surfaces;
- wearing socks that are too large and cause wrinkles;
- selection of shoe models with thin soles.
Removing callus using drilling
This procedure can be carried out in a pedicure salon.
During the manipulation, a special device resembling a drill is used.
The procedure does not require the use of anesthesia.
Since it is not accompanied by pain.
Drilling/excision of callus areas is carried out using special attachments.
An antibacterial ointment is first placed in the deepening of the callus to prevent the development of the inflammatory process.
For the first few days, the patient may feel minor discomfort, which goes away on its own and does not require treatment.
Dry callus is removed using a similar method, but provided that it is not neglected.
The drilling procedure has certain disadvantages:
- If the rod is located deep enough, this manipulation may be ineffective. Often several manipulations are required to completely remove the callus.
- In the process of drilling out the keratinized area of the dermis, damage to healthy skin is possible. The procedure requires a highly qualified specialist.
- This type of callus removal is a contact type of procedure, which means it is accompanied by an increased risk of infection.
How to choose the right ointment against calluses?
In home treatment, the drug is selected taking into account the type of callosal defect:
- Ointments with a moisturizing, softening, and keratolytic effect will help with corns and dry calluses. Therapeutic agents enhance desquamation - exfoliation of dead skin flakes, activate blood microcirculation, and soften damaged areas.
- For shallow core calluses, keratolytic preparations are used to loosen the keratinized epidermis, and local anesthetics to eliminate pain.
- For water calluses, burst blisters, and areas worn down to the flesh, use antibacterial anti-inflammatory drugs that have a drying and wound-healing effect. And also, reparants and regenerants for skin restoration.
For bloody calluses resulting from tissue compression, treatment with antiseptics is necessary. An infection easily penetrates into a burst blood callus, which can lead to suppuration, inflammation of the lymph nodes, and sepsis (blood poisoning).
Benefits of ointment treatment:
- accessibility (you don’t need a doctor’s prescription to purchase the product);
- therapeutic effect to accelerate the healing of the epidermis;
- wide choice of directional action;
- acceptable price category.
Important!
Medicines for external use do not have direct contact with the digestive organs, which significantly reduces the list of contraindications for their use. When self-treating with topical drugs, you must:
- follow the instructions for use;
- before use, perform an allergy test on the inner bend of the elbow joint;
- After opening the package, store the ointment in the refrigerator.
Removal of callus with liquid nitrogen (cryodestruction)
Cryodestruction is an innovative, highly effective method of removing calluses on the foot, heel or toes using liquid nitrogen.
During the procedure, the keratinized area of the skin is frozen, after which the destruction of the callus is observed.
It has been noted that the procedure is associated with an extremely low rate of callus re-development.
Many dermatologists note that no other method for removing core calluses gives results as favorable as cryodestruction.
Removing callus with liquid nitrogen takes about 10-20 minutes.
It is performed under local anesthesia, so the procedure is completely painless and safe.
Side effects are extremely rare (no more than 3% of cases).
Include callus recurrence, pain, discomfort, bleeding, infection, scarring.
The first few days after the procedure, the formation of a cold bubble is observed, which under no circumstances should be pierced.
Within 10-14 days, the healing process occurs; a crust forms in place of the bubble, which falls off on its own.
The process is not accompanied by the formation of scars.
The procedure is usually well tolerated, with minor discomfort possible.
Some disadvantages of cryotherapy:
- If the rod is extremely deep, cryodestruction is not always able to completely rid the patient of the callus.
- If you do not properly care for the skin after the procedure, there is a risk of an infectious process.
- Freezing the callus with liquid nitrogen is not used when large areas of the epidermis are affected. Cryodestruction used on large calluses can lead to a number of complications. For this reason, in advanced cases, they resort to other therapeutic methods.
Indications and contraindications
Before using a silicone patch for calluses on your feet, you should read the instructions, including indications and contraindications for its use.
The patch should be used in the following cases:
- as soon as the callus is discovered;
- if the formation is accompanied by discomfort and pain;
- at risk of a crack;
- to protect the lesion from infection.
Contraindications for use are the presence near the callus:
- cracks;
- open wounds;
- scratches and bruises;
- papillomas and moles.
Components that impregnate the patch can cause negative reactions on open wounds - pain, burning, swelling, etc.
Laser excision of callus
Laser callus removal remains a priority treatment method.
Allows you to effectively eliminate the problem with minimal risk of recurrence.
The laser penetrates into the deep layers of the dermis, which makes it possible to remove the root completely, rather than partially.
The operation of the device is based on the reproduction of a laser beam with special light properties:
- Monochromatic: Has only one specific wavelength or color.
- Coherence: Vibrates in the same phase or synchronously.
- Divergence: the beam works in a given direction.
During the manipulation, the epidermal layer is “burned out”, one after another.
The manipulation requires the use of an anesthetic.
The average session duration is no more than 10-15 minutes.
Before using the laser, the callus is treated with antiseptic drugs.
After laser irradiation, a dense crust forms, which will disappear after 10-14 days.
Laser treatment to remove calluses leads to cell regeneration.
It has an anti-inflammatory effect and stimulates the local immune system.
Thus, it promotes rapid healing of wounds.
However, the main advantage of the laser is the complete removal of callus even with a deep root location.
Often, one visit to a dermatologist is enough to effectively eliminate the problem.
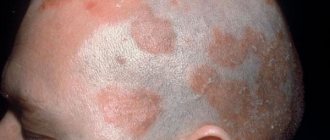
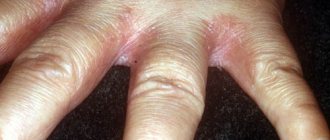
Causes and methods of treating bumps between the phalanges of the fingers
The appearance of bumps on the fingers and subsequent deformation of the terminal phalanx of the finger is a consequence of diseases of the musculoskeletal system. In each specific case, the doctor makes an accurate diagnosis, but in most cases there are two main reasons for the formation of lumps.
For what reason does the disease develop?
The first reason is arthrosis of the joint, which causes inflammation in it. It is inherited and develops due to disruption of metabolic processes in the body, decreased immunity, and hypothermia. The second reason is arthritis. It causes damage to the cartilage in the joint. Healthy cartilage is always smooth, bones slide over it easily without causing pain. If for some reason a metabolic disorder occurs in the body, a joint injury occurs and an infection occurs, autoimmune diseases arise, then this can cause wear and tear of the cartilage, in other words, the development of arthritis. It is worth understanding that a bone growth on the finger is just a side effect of the diseases mentioned. That is, with arthritis or arthrosis, the appearance of cones is possible, but not necessary. There are other reasons why formations appear on the phalanges of the fingers. These include:
- Work that places prolonged stress on the phalanges of the fingers. The range of such work is very wide - from bricklaying to professional piano playing.
- Hygroma, which is a chamber filled with a gel-like liquid. To the touch it is an elastic formation that does not cause pain. It is better to refrain from self-punctures to remove fluid. After such self-medication, the hygroma forms again.
- Fibroma. This problem occurs very rarely and is associated with pinched nerve endings.
- Skin cancer or sarcoma.
- In women, menopause.
You should not hesitate to consult a doctor if alarming symptoms begin to appear in your finger work - crunching or painful sensations when flexing/extending the phalanges.
Typical signs of disease development
The first symptoms of this disease may resemble simple irritations. These include: redness of the skin on the joint with the appearance of a tumor; the inflammatory process in the joint, like any other part of the body, causes an increase in the content of leukocytes in the blood. But the following signs give cause for concern:
- Pain caused by finger movement.
- The need to make extra effort to bend or straighten the finger.
- Beginning of lump formation.
In addition, a decrease in the number of lymphocytes in the patient’s blood can be a warning signal about the development of the disease. These are cells that support the immune system. If there are fewer of them, the likelihood of infections entering the body increases, which can cause arthritis. It has already been mentioned that this is one of the possible reasons for the appearance of bumps. If a patient exhibits at least some of these symptoms, it would be wise to undergo testing.
Diagnosis of finger joint seals
During the first visit with a complaint about such symptoms, a rheumatologist will examine the affected area and take an anamnesis. Sometimes this is enough to accurately determine the cause of pain in the phalanges of the fingers. In other cases, it may be necessary to take a puncture, do an x-ray or magnetic resonance imaging. To verify the presence or absence of a malignant tumor, histology of the lump tissue is prescribed. For this, a biopsy is used.
Treatment of bone formations
Each patient is prescribed his own therapy. But it is still possible to define general methods. In turn, they are distributed for treatment with drugs, traditional medicine, and prevention. The group of drugs includes the following drugs:
- Painkillers.
- Anti-inflammatory action.
- Hormonal.
- Chondroprotectors.
- Vitamins.
Despite the abundance of treatment methods in traditional medicine, you need to exercise caution and consult your doctor before using them. You need to understand that traditional medicine does not replace scientific medicine, but only complements it. Among these additions are the following:
- Mustard powder is mixed with camphor oil. Take 50 grams of both ingredients. Whites from two chicken eggs are added to them, and this entire mixture is diluted with 70% alcohol until a homogeneous mass is formed. The finished medicine is applied in a thin layer to the sore spot and wrapped in a clean piece of natural material. The bandage is not removed for two hours, and the interval between procedures should not exceed four days.
- Squeeze out as much juice as possible from pre-chopped garlic, moisten a clean piece of natural cloth with it and wrap it around the bone growth. Repeat the procedure for a week.
- Dip a fresh cabbage leaf into boiling water, then pull it out and spread it with liquid honey. Coat the bones on your fingers and wrap with cling film. Continue treatment for two weeks and apply the bandage at night.
- Celandine oil can save you from severe pain. This drug is purchased at a pharmacy or obtained by manual processing of the plant. To do this, pass celandine through a meat grinder and infuse the pulp in vegetable oil. This method is not applicable for patients suffering from allergies.
In case of hygroma formation, similar treatment methods are taken.
Apply cabbage leaves or make lotions from celandine juice. The sore spot is steamed in salt water, smeared with honey, and wrapped in woolen cloth. Honey and peeled aloe are added to rye flour. This paste is applied to the sore spot overnight. Before using any type of traditional medicine treatment, you must agree with your doctor. Author: K.M.N., Academician of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences M.A. Bobyr
Radio wave removal of callus
Callus removal by radio wave is carried out using a special device “Surgitron”.
The Surgitron device uses advanced radio wave technology.
Ensures accuracy, versatility and safety of medical procedures.
The surgical electrode, which is a tungsten wire, emits 3.8 MHz radio waves and slides through the tissue without putting pressure on it.
The pathologically changed area is evaporated, which leads to the destruction of the callus.
An important advantage is that the electrode is self-sterilizing during use, which reduces the likelihood of infection after the procedure.
Other benefits of radio wave treatment:
- Excellent cosmetic results; the manipulation is not accompanied by the formation of scar tissue.
- Fast recovery for the patient, since the treatment process does not affect the healthy tissue surrounding the callus.
- Reduced postoperative pain; in addition, the manipulation itself is not accompanied by pain.
After radio wave removal, the callus becomes covered with a crust, which falls off on its own after 7-10 days.
After which a new, healthy layer of new skin appears, which over time blends with the natural color of the epidermis.
Establishing diagnosis
If a patient notices a suspicious tumor on his finger, he should contact a traumatologist, surgeon or orthopedist.
Reference. The specialist will conduct a differential diagnosis to distinguish the hygroma from the leak (capsule with purulent contents), ganglion (nerve ganglion), epithelial cyst, chondroma (cartilaginous tumor), osteoma (bone tumor), aneurysm (protrusion of the artery wall), malignant formations, etc. d.
First, the doctor collects anamnesis, conducts a visual examination, and palpates the neoplasm.
To clarify the diagnosis, the patient is prescribed the following studies:
- Ultrasound helps evaluate the structure of the formation.
- Magnetic resonance imaging and computed tomography are performed if nodular structure is suspected.
- X-ray.
To analyze the contents of the formation, a puncture is performed. During the examination, the pathological formation is punctured, the necessary cellular material is collected, and then it is studied in the laboratory.
To clarify the diagnosis and create an effective treatment regimen, doctors prescribe the following tests:
- Clinical examination of blood and urine.
- Biochemistry of blood.
- X-ray of the lungs.
- Tests to detect sexually transmitted infections, hepatitis, HIV.
- Electrocardiography.
Once the diagnosis is made, treatment is necessary.
Treatment of callus with medications
It is immediately worth noting that drug treatment of calluses has the least therapeutic effectiveness.
This phenomenon is associated with the inability of drugs to penetrate deep into tissues, eliminating the root of the formation.
The products used for core calluses often contain keratolytic components and can be effective at the beginning of callus development.
As a rule, products based on salicylic acid are used.
Salicylic acid is a keratoplastic and keratolytic agent.
In addition, it has an antibacterial and antifungal effect.
Salicylic acid works by softening keratin, a natural protein that is part of the skin's structure and produced by the body.
The drug has a softening effect on the stratum corneum of the dermis, which facilitates its removal.
Salicylic acid is often used in combination with other substances.
Allows for a higher therapeutic effect.
When using salicylic acid preparations, the simultaneous use of the following drugs is not recommended:
- Alcohol-containing medications.
- Any other local medications that contain dibenzoyl peroxide or retinoid.
- Soapy substances that have a drying effect.
- Cosmetics that have an exfoliating effect.
Prevention
To prevent cyst formation, you must follow the following rules:
- If there is a hereditary predisposition to hygroma, you need to avoid injuring your hands, protect your joints, and limit monotonous mechanical loads on your hands.
- During physical work, distribute the load evenly between your hands. If you regularly engage in such activities, then use elastic bandages.
- Treat tendovaginitis (inflammation of the tendon sheath) and bursitis (inflammation of the mucous bursae of the joints) with a chronic course in a timely manner.
The latter pathologies often cause the appearance of a tumor.
As you can see, finger hygroma is not a dangerous pathology. But in order to avoid unpleasant consequences, you need to seek medical help in time and carry out competent therapy. You should not self-medicate, as this will only worsen your condition.
Traditional medicine in the treatment of calluses
Folk remedies cannot affect the development of callus and are not an effective treatment method.
The treatment and removal of callus must be carried out by a qualified specialist.
This will minimize negative consequences and complications.
It is necessary to begin treatment of callus in the early stages of its development.
When there is still a chance to get rid of the problem without resorting to surgical methods.
As it progresses, the root of the callus will penetrate into the deeper layers of the epidermis.
Then it may be necessary to use more radical and expensive methods of therapy.
How to prevent skin problems in the future
A patch for calluses on the heel and other areas will help speed up recovery and relieve discomfort. But it is easier to prevent the formation of calluses than to treat the consequences. Preventive measures include the following:
- regular pedicure, daily foot hygiene;
- moderate skin hydration;
- wearing comfortable shoes of your size with a hard back and wide toe;
- changing and cleaning shoes several times a season;
- therapeutic exercises, foot massage;
- preventing the risk of microtrauma;
- refusal to wear wet socks and gloves.
The listed preventive measures will reduce the risk of callus formation (wet, dry, core). If trouble cannot be avoided, it is advisable to immediately begin treating the calluses and should not cut them off.
1.General information
Calluses are a widespread phenomenon, which in the vast majority of cases does not come to the attention of outpatient or, especially, inpatient surgeons. The exception is rare cases of complications that require surgery and subsequent intensive treatment.
This development of events is mainly due to the fact that “ordinary” calluses are opened at home without observing the basic rules of asepsis and the principles of primary medical self-help. Therefore, it will not be amiss to remember what a skin callus is and what measures need to be taken to eliminate and prevent it.
We emphasize that in this case we are talking only about skin calluses; Bone calluses are a different kind of pathology that should be considered separately.
A must read! Help with treatment and hospitalization!
3. Symptoms and diagnosis
There are several types of calluses, which differ significantly both etiologically and clinically. For example, a core callus is usually formed in response to the introduction of a small foreign body (a splinter, a chip that has gotten under the skin, a piece of stone, etc.) and is a compaction that goes deep, visible from the outside as a cap with a central crater. Corns are also a type of callus - keratinized areas on the soles of the feet, sometimes of a fairly large area, without a clear boundary with the skin of normal elasticity and moisture.
The most obvious and significant difference is between the two main categories of calluses: soft and dry.
Soft (water) calluses at the stage of formation are a locally irritated, reddened, weeping, painful area of skin, which quickly transforms into a blister or sac filled with serous fluid (“dropsy”); if the exposure does not stop at this stage, the soft callus inevitably breaks through to form an open wound. The penetration of pathogenic microorganisms triggers an infectious-inflammatory process, the classic signs of which are swelling, hyperemia, clearly localized pain, and local fever. The most serious of the complications mentioned above include purulent abscesses, cellulitis, and osteomyelitis.
The callus is dry (hard), looks like a local rounded keratinization, usually yellow-gray, with a radius of several millimeters to several centimeters, clearly demarcated from the surrounding skin and rising (sometimes significantly) above its level. Any pain or discomfort occurs, as a rule, only when such a callus is pressed or laterally displaced.
The most common areas for the formation of calluses are the distal, terminal sections of the hands and feet (phalangeal folds, fingertips, interdigital spaces, skin of the palms and soles), as well as elbows and knees. More specific calluses can also occur in other areas: for example, in professional violinists, constant contact with the hard varnished wood of the soundboard causes the skin on the lower jaw bone on the left to become rough.
As a rule, there is no need for additional diagnostics: a dermatologist or surgeon at first glance distinguishes a callus from an inflammatory cyst or abscess, scleroderma skin changes, warts, swelling due to joint inflammation, etc. However, in some cases, a differential diagnostic study (for example, histological or ultrasound) may be necessary.
About our clinic Chistye Prudy metro station Medintercom page!
4.Treatment
When opening a soft callus at home, the first priority is antiseptic measures: the affected area should be thoroughly washed and disinfected, the needle should be sterilized (it is better to use the sterile needle included with any disposable syringe). After opening and expiration of the contents, the wound surface should also be treated with a disinfectant solution, carefully remove flaps of dead skin with a sterilized manicure instrument (do not tear off under any circumstances!), apply antibiotic ointment and, if necessary, a protective bandage or bactericidal patch. There is also a wide range of traditional medicine, the consideration of which is beyond the scope of this article.
To eliminate and prevent dry calluses, therapeutic and hygienic creams, gels, ointments, and liquids are offered; You can also find countless recommendations for steaming, using pumice, softening compresses, etc. However, it is more important to remember the following.
At the first signs of an infectious-inflammatory process, as well as when a rapid change in the size, shape, color of the callus and/or sensations associated with it begins, you should immediately consult a doctor (surgeon or dermatologist). Currently, many methods for the safe removal and treatment of calluses are successfully used, taking into account the individual nuances of each case: radio wave, laser, cryotherapeutic, microsurgical techniques.
Types of calluses
Bone calluses can be of the following types:
- Endosteal.
This callus is localized on the outside of the bones. It is not supplied with blood vessels, so it often thickens and protrudes above the surface of the bone.
- Intermedial.
This callus is concentrated in the area of the injury, between the outer and inner sides of the bone. X-ray examination does not always detect such a callus.
- Periosteal.
This callus grows at the site of bone fusion. Most often it forms in patients who have been completely immobilized for a long time.
- Near the rest
a callus can appear not only after a bone fracture, but even after a severe bruise of soft tissues. The growth often reaches significant sizes, making it difficult to get rid of. In the area where the callus is formed, the muscles swell, and the person complains of pain when trying to make a movement.
- Paraosseous
callus appears on long bones. Treatment for such a growth is long-term. If this callus is localized on spongy bones, then its size is small.