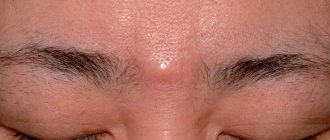
The peritoneum is a serous membrane that covers the inside of the abdominal cavity and the organs located in it. The visceral layer is that part of the peritoneum that surrounds individual organs; the parietal layer of the peritoneum lines the entire cavity as a whole. The peritoneum prevents friction of organs against each other, provides shock absorption, creates mesenteries in which vessels feeding the organs pass, and forms two omentums, which play an important role in inflammatory processes in the abdominal cavity. Between the layers of the peritoneum there is a small amount of fluid.
The anterior abdominal wall limits the abdominal cavity in front, limited above by the lower edge of the costal arch, below by the pubic symphysis, inguinal folds and the iliac crest. The anterior abdominal wall has several layers, the outermost being the skin, the deepest being the peritoneum.
Peritoneal tumors are neoplasms that arise in the tissues of the peritoneum.
- Classification of peritoneal tumors
- Causes of tumors
- Symptoms of peritoneal tumors
- Diagnostics
- Treatment
- Radiation therapy
- Chemotherapy
- Radiosurgery
- Surgery
- Complications
- Survival prognosis and prevention
Classification of peritoneal tumors
Peritoneal tumors are divided into malignant and benign. Benign ones are extremely rare; when large, they can compress the abdominal organs, as a result of which in some cases they need to be removed.
Malignant tumors are divided into primary and secondary. Primary peritoneal tumors originate from the cells of the serous membrane and, according to their histological structure, are mesotheliomas. Secondary, in turn, are divided into tumors that have grown into the peritoneum from organs located in the abdominal cavity, and peritoneal carcinomatosis (damage to the peritoneum by tumor cells of other organs that have metastasized into it).
Symptoms of peritoneal tumors
Benign tumors of the peritoneum, as a rule, are asymptomatic, except in situations where they reach large sizes and compress surrounding organs. Benign tumors are often discovered accidentally.
Symptoms of malignant tumors of the peritoneum include symptoms characteristic of any malignant tumors - intoxication, anemia, weight loss, loss of appetite, which usually appear when the tumor reaches a significant size, and specific ones, due to a specific location. The last group includes pain, dysfunction of organs compressed by the tumor, and the appearance of ascites. With massive tumors that compress the intestines, intestinal patency may be impaired, up to the development of intestinal obstruction, requiring emergency surgical intervention.
Symptoms and possible complications
The development of preperitoneal lipomas occurs asymptomatically. Unpleasant sensations in the area of the white line of the abdomen appear during the period when the formation of the hernia has ended. The latter, upon palpation, causes painful sensations that radiate to different parts of the body. The appearance of this symptom is explained by the fact that the hernia, as it grows, compresses the nerve endings.
What does a wen look like on the body?
A fatty tissue (lipoma) is a benign neoplasm that almost never develops into a malignant tumor.
Compression also causes impaired blood circulation in the peritoneal area, which leads to the gradual death of local tissues.
The nature of the clinical picture is determined by the localization of the hernia. Depending on the location of the tumor, patients experience:
- constipation;
- nausea and vomiting;
- blood in stool;
- bloating;
- dysfunction of the genital organs (usually in women);
- urinary disturbance;
- development of jaundice.
In the absence of adequate treatment, the size of the gap in the peritoneum reaches 10 cm, which contributes to the formation of multiple hernias.
In extreme cases, wen degeneration into liposarcoma occurs. If the neoplasm has managed to metastasize, then the clinical picture is complemented by signs of damage to other organs.
It is possible to differentiate between benign and malignant tumors only on the basis of the results of a histological examination performed after surgery.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of peritoneal tumors includes a classic interview and examination of the patient, ultrasound examination of the abdominal cavity, computer, magnetic resonance and positron-emitron tomography. X-ray contrast studies and scintigraphy are also used. In some cases, it is necessary to resort to diagnostic laparoscopy (examination of the abdominal cavity through small incisions in the anterior abdominal wall using special equipment). Diagnosis is facilitated by biopsy and analysis of ascitic fluid. Other laboratory methods (in particular biochemical and clinical blood tests) are of auxiliary value, because are not specific.
Types of operations:
Plastic surgery using your own tissues
- The incision is made in the midline above the hernial protrusion.
- The hernia defect is sutured with a non-absorbable thread, thereby eliminating the possibility of separation of the abdominal muscles.
This type of operation is used for small hernial orifices and the patient does not have conditions and diseases that cause failure of the connective tissue structures of the body.
The disadvantages of this type of operation include the need to create tension in the tissues of the anterior abdominal wall, which can lead to relapse of the disease. Another disadvantage is the long incision along the midline and a long rehabilitation period with limited physical activity.
Plastic surgery using synthetic prostheses and meshes
This is also a traditional (open) intervention performed through an incision over the hernial protrusion. However, with this type of operation, tension is not created on the native tissues of the abdominal wall, and the defect is closed using a prosthesis made of synthetic material. Artificial implants and meshes grow over time with a person’s own tissues and create a strong support; in this regard, the possibility of recurrence of the disease is reduced to almost zero.
Laparoscopic hernia repair of the linea alba.
With the advent of high-tech devices, this technique in the treatment of hernias is becoming increasingly popular. The operation does not require a long skin incision.
Several punctures are made in the abdominal wall, located mainly in the lateral sections, through which the hernial sac is exposed, adhesions are separated, if any, and a special mesh prosthesis is installed.
Laparoscopic surgery involves fewer traumatic factors than open surgery. The period of rehabilitation and recovery after laparoscopy is much shorter than with other techniques. Even with large hernias, after a month you can return to your usual rhythm of life and usual loads. In addition, the postoperative period does not require wearing a bandage. The distance of skin punctures from the site of installation of the mesh prosthesis reduces the risk of purulent-inflammatory complications, which can be of great importance in people with reduced immunity (for example, diabetes, obesity) and significantly reduces the risk of hernia recurrence.
A relative disadvantage of laparoscopic hernia repair of the linea alba can be considered the lack of correction of diastasis of the rectus muscles and, consequently, incomplete restoration of the shape of the anterior abdominal wall, especially in thin people. The widespread use of this technique is also limited by the significant cost of the implant, which has a special coating that prevents adhesions, and instruments for its laparoscopic installation. Such operations are also not suitable for patients with severe diseases of the cardiovascular and respiratory systems. All surgical interventions are performed under general anesthesia. Postoperative hospital stay depends on many factors and concomitant diseases and ranges from 2 to 10 days.
Rehabilitation after surgery
With traditional plastic surgery methods, wearing a bandage is recommended in the postoperative period. In addition, during the period of convalescence, it is important to follow all the recommendations of the attending physician: follow a special gentle diet and avoid any physical activity. Ignoring a disease such as a hernia and a lax attitude towards one’s health can lead to life-threatening conditions and, in the future, to serious complications. Despite the fact that the only method of treating this disease is surgery, the variety of types of operations that currently exist makes it possible to select the optimal type of plastic surgery for each patient, taking into account his individual characteristics.
Radiation therapy
The goal of radiation therapy is to slow tumor growth. Applicability in the treatment of mesothelioma is limited due to the large area of tumor spread, the proximity of other organs and the difficulty of local action. For tumors of other organs that grow into the peritoneum, the advisability of using radiation therapy is determined by the histological type of the tumor and the sensitivity of its tissues to radiation.
Radiation therapy is used both independently and in combination with other treatment methods.
To make a diagnosis, cytological examination of punctate is necessary.
Microscopically lipoma
It is built like regular adipose tissue and differs from it in the size of the lobules and fat cells. The latter are either very small or reach gigantic sizes. In some cases, between the lobules and individual fat cells there is a proliferation of connective tissue, sometimes significant, and a fibrolipoma is formed. If there are a large number of vessels in it, the tumor is called angiolipoma.
For Dercum's disease
the histological picture is often similar to that described above, however, in some cases an angiolipoma structure or granulomatous structure with the presence of giant cells of foreign bodies is observed.
For benign symmetrical lipomatosis
the nodes have the structure of a regular lipoma. In the systemic form of multiple lipomatosis, in addition to mature fat cells, undifferentiated mesenchymal cells are found, as well as intermediate cells containing varying amounts of lipids in their cytoplasm. In well-differentiated areas, mature fat cells are visible, usually located in the mucoid stroma; in less differentiated areas there are lipoblasts of varying degrees of maturity containing lipids, as well as areas consisting of fibroblastic elements.
For familial lipomatosis
Histologically, mature adipose tissue is revealed, separated by connective tissue layers.
Histologically with angiolipoma
the ratio of adipose tissue, vascular and stromal elements can vary widely. From the shell, loose fibrous septa penetrate into the tumor, overgrown with vessels, the walls of which do not contain elastic and muscular elements. The intervascular space is filled with a substance with the histochemical properties of glycosaminoglycans. The cellular component, in addition to fat cells, is represented by vascular endothelial cells, erythrocytes, fibrocytes, lymphocytes and, rarely, polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Signs of inflammation or necrosis are usually not observed. Angiolipomas are characterized by minimal mitotic activity, slow growth, differentiation of elements, and lack of germination into surrounding tissues.
Anhymyolipoma
consists of adipose tissue, proliferating blood vessels and smooth muscle fibers that form a node in the subcutaneous tissue or deep parts of the reticular layer of the dermis. Data from IHC studies in cutaneous angiomyolipomas are contradictory: in some cases, tumors express HMB-45, in others the staining is negative.
Fibrous component in fibrolipoma
can be represented either by extensive fibrous fields or narrow layers between accumulations of fat cells. The fibrous part resembles a soft fibroma with a small number of cellular forms - fibroblasts, histiocytes, located in the loose intercellular substance. Less commonly, the fibrous component is represented by coarse fibrous connective tissue. Along the fibers there are spindle-shaped and stellate cells that contain neither glycogen nor fat, how they differ from the cells of embryonic adipose tissue. The fatty component included in these neoplasms is represented by mature fat cells. The latter have different sizes and shapes, some are flattened, some are signet-shaped. Small or large fat vacuoles are detected in the cytoplasm. The number of vessels in both the fibrous and fatty parts of the tumor is usually small. Along the course of the vessels, focal lymphoid infiltrates are detected.
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy treatment for peritoneal tumors can be used both as the main method of treatment and as a precursor to or subsequent to surgery. The type of drug is selected according to the type of tumor. In addition to classical chemotherapy, for peritoneal tumors, the technique of administering drugs directly into the abdominal cavity and prolonged rinsing with solutions is used. This technique allows the use of large concentrations of drugs without introducing them directly into the bloodstream, and also ensures the closest possible contact of the drug with the tumor tissues. Injecting chemotherapy drugs directly into the abdomen can reduce complications associated with chemotherapy. Currently, this method is actively being developed.
Can it be cured with folk remedies?
A small wen in the preperitoneal cavity will help to remove folk remedies. You should not try to treat an inflamed, painful, or rapidly growing tumor on your own. Be prepared for relapses. The capsule of the cone remains under the skin, this causes the growth of new, often multiple cones larger in diameter than the first.
At home, compresses and masks made from food products, herbs, vodka, and spices are used. Pharmacy products: iodine, hydrogen peroxide, antiseptic ointments, absorbable balms. Home therapy usually lasts several months. No one guarantees a good result or excludes harm.
Folk remedies will only help in the treatment of subcutaneous preperitoneal lipoma. It will not be possible to cure retroperitoneal disease on your own.
Radiosurgery
Radiosurgical method is one of the types of radiation therapy, in which, using special equipment, high doses of radiation are targeted, causing the death of tumor cells. The aggressiveness and radicality of the method was the reason for its name and its separation into a separate section of radiation therapy. The possibility and feasibility of use for peritoneal tumors is determined individually, taking into account the type of tumor, its size, location, and the possibility of using other techniques.
Surgery
Surgical treatment, or, as patients call it, abdominal surgery, is performed in 2 ways - laparotomically (i.e., with a large full incision) and laparoscopically (with small incisions through which instruments for performing the operation and a video camera are inserted, obtaining an image from which , the surgeon controls his actions). The applicability of surgical treatment, as well as the choice of method, depend on the size of the tumor, its prevalence, and various accompanying circumstances. In some cases, surgery is impossible, sometimes it is possible, but not advisable. In these situations, the choice falls on other treatment methods. If surgery is performed, it may be supplemented with radiation therapy and (or) chemotherapy. The operation is performed under general anesthesia in a hospital setting.
Features of treatment
Factors for removal in the preperitoneal area are:
- Rapid tumor growth to a diameter of more than 10 cm.
- Compression of internal organs, nerves, blood vessels, muscles.
- Soreness.
- Aesthetic effect.
- Damaged, causing inflammation.
- Increased body temperature, malaise.
There are surgical and medicinal methods for treating a preperitoneal lump.
Surgical removal is not always indicated. If the tumor size does not exceed one centimeter, the doctor may prescribe drug treatment.
Need advice from an experienced doctor?
Get a doctor's consultation online. Ask your question right now.
Ask a free question
The drug is injected into the lipoma or applications are applied to the affected area.
When injecting into the preperitoneal space, Dispropane is often used in combination with lidocaine. After three sessions within two months, it is possible to get rid of 80% of the formations.
Applications are considered an auxiliary method of disposal. Absorbable balm is applied to the affected area: Viaton 2-3 times a day (for half an hour).
The main disadvantage of drug treatment of a preperitoneal tumor is the high probability of relapse - the capsule remains under the skin.
Large or dangerous lipomas are removed surgically in a hospital. Varieties of such operations:
- Traditional excision.
- Puncture-aspiration method.
- Laser removal.
- Radio wave method.
- Endoscopic method.
- Liposuction.
Laser and radio wave methods are rarely used for lipoma in the preperitoneal abdominal cavity. Wen with a diameter of up to 3 cm can be removed in this way.
During liposuction, the surgeon removes the contents of the capsule using a needle; endoscopically, the contents of the lump are removed using a microscopic hole. A similar method is puncture-aspiration excision: a small incision is made on the side, the contents of the capsule are removed.
These methods allow you to avoid scars and rehabilitation in the clinic. The consequence of the first will be a high risk of recurrence of a preperitoneal lump of even larger size.
Traditional excision of the formation is effective and traumatic. Suitable for large wen, eliminates the development of relapses. There is a danger of scarring and requires rehabilitation. Subcutaneous formations are removed under local anesthesia. For more complex cases, general anesthesia is provided. After the operation, the patient attends dressings for 10-14 days.
Survival prognosis and prevention
Unfortunately, with secondary damage to the peritoneum, carcinomatosis, the diagnosis is most often made when the disease has already entered the stage at which it is impossible to completely defeat the disease. However, the treatment methods used can significantly prolong the patient's life and alleviate symptoms.
For primary peritoneal tumors, the prognosis depends on the location of the tumor, the type of cellular structure and size. Under favorable circumstances and the right choice of treatment tactics, complete removal followed by remission is possible.
Prevention of peritoneal tumors is compliance with the general rules for the prevention of cancer, as well as specific attention to persons in contact with asbestos. In particular, compliance with production standards, monitoring the environmental situation in settlements at risk, timely examination of persons in contact with asbestos.
Book a consultation 24 hours a day
+7+7+78