The most common method for detecting CMV (cytomegalovirus infection) is a blood test for cytomegalovirus. There are various pathogen detection techniques that can reliably determine the presence of the pathogen. Most tests are based on the detection of specific antibodies produced by the body in response to the pathogen. PCR diagnostics are also possible, which provides information about the presence of pathogen DNA in the blood, allows one to assess the activity of the infectious process and the degree of spread of the pathogen in the body.
The most common method for detecting CMV (cytomegalovirus infection) is a blood test for cytomegalovirus. There are various pathogen detection techniques that can reliably determine the presence of the pathogen. Most tests are based on the detection of specific antibodies produced by the body in response to the pathogen. PCR diagnostics are also possible, which provides information about the presence of pathogen DNA in the blood, allows one to assess the activity of the infectious process and the degree of spread of the pathogen in the body.
Human cytomegalovirus infection is a viral anthroponotic disease that affects almost the entire body. It is characterized by a wide variability of forms and symptoms - from asymptomatic carriage to severe damage to the respiratory, excretory and other body systems.
Causative agents of infection, its sources
Cytomegalovirus (Cytomegalovirus hominis) belongs to the genus of DNA viruses, is distinguished by its large virion size (up to 300 nm), and is part of the herpesvirus family. Several strains of the pathogen have been registered:
The source of infection is the patient or the carrier. The pathogen is detected in biological fluids and secretions. Routes of entry of the virus:
- Davis.
- Kerr.
- AD-169.
- Towne 125.
Most strains are little studied, but it is reliably known that all of them can reproduce without destroying the host cell. The virus can survive for a long time at room temperature, but is sensitive to heat and the action of disinfectants.
- Airborne.
- Contact.
- Food.
- Parenteral and transplacental.
According to statistics, the infection rate is up to 95%, depending on the region and country.
Classification
There is no globally accepted classification system for cytomegalovirus infection (CMVI). In practice, the classification developed in 1980 is used. According to this system, CMVI is divided into:
- Congenital, can be acute, chronic.
- Acquired, can be acute, latent, generalized.
CMV infection is classified according to the duration of its course:
- Spicy.
- Protracted
- Chronic
- Recurrent.
Depending on the severity of the course, there are mild, moderate, and severe forms of the course.
The mechanism of the onset and development of the disease
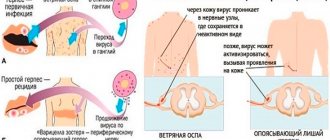
The virus enters the body through the mucous epithelium of various organs. The free presence of viral particles in the bloodstream quickly ends with the introduction of the pathogen into mononuclear-type phagocytes. The initial replication of cytomegalovirus occurs in them.
Infected cells enlarge, and large intranuclear inclusions, which are accumulations of viral bodies, can be found in them. An increase in the number of affected cells is manifested by the development of multiple nodular infiltrates or calcifications in the tissues. The pathogen reproduces especially actively in the salivary glands , where it is easiest to detect.
The pathogen can persist in cells for a long time; the only manifestation of infection is suppression of cellular immunity. In most, the disease proceeds latently and becomes an asymptomatic carrier.
Exacerbation of CMV infection occurs in patients with suppressed immunity. The most common reasons for weakening the body's defenses:
- Taking immunosuppressants.
- HIV infection.
- Pregnancy.
As a result, the virus is activated, active reproduction of the pathogen begins in all organs and tissues, and the clinic of one of the forms of the disease develops. Severe CMV infections are in most cases associated with HIV infection.
When to treat and how
Therapy for cytomegalovirus infection should be complex and multicomponent.
To do this, drugs are used that directly affect the pathogen.
These include:
- Virus replication blockers
- Drugs that destroy viral particles
From the first group, Ganciclovir is used.
Megalotect is used to destroy the cell wall.
Additional treatments for patients with cytomegalovirus include immunomodulators, painkillers and anti-inflammatory drugs.
To carry out full monitoring, treatment of patients with the acute form occurs in a hospital setting.
This makes it possible to isolate the patient and prevent further spread of infection.
Outpatient treatment is also possible.
For pregnant women and children, the use of antiviral drugs is of particular importance.
Ganciclovir can inhibit the process of hematopoiesis and cause bleeding.
Skin rashes appear while taking it.
Disturbances from the gastrointestinal tract appear less frequently.
Self-medication or use of drugs without the supervision of a physician can harm the body.
Any therapy should be prescribed after an examination and a range of laboratory tests.
Clinical picture
The duration of the incubation period remains unclear since the initial forms of CMV infection occur latently. Characteristic clinical symptoms develop as a result of exposure to factors that weaken the immune system.
Congenital CMV infection in children in early periods of life also occurs as an asymptomatic carriage. Then it manifests itself in the form of various severe complications, the most common:
- Deafness.
- Chorioretinitis.
- Cytomegalovirus syndrome.
In particularly severe cases, congenital CMV infection leads to secondary pathologies and death in the first weeks of life. You can avoid these consequences by doing a blood test for cytomegalovirus before conceiving a child.
Acute congenital CMV
It is a consequence of primary infection of the mother during pregnancy. Develops in approximately 5% of children infected with CMV infection in utero. In other cases, it occurs hidden and does not lead to serious consequences. The mortality rate of acute congenital CMV infection is high, accounting for up to 30% of cases. Surviving children often suffer severe consequences, including:
- Delay in physical and mental development.
- Chronic jaundice.
- Hydrocephalus.
- Polycystic pancreas.
If a child is infected in the early stages of embryogenesis, the fetus is highly likely to die. Survivors have serious defects and developmental anomalies:
- Microcephaly.
- Lung hypoplasia.
- Defects in the structure of the kidneys of the heart and aorta.
- Esophageal atresia.
- Chronic congenital CMV
Mortality during the development of this form of infection is low; it is characterized by the development of severe pathologies of the child’s organs and systems. These include: hydro- and microcephaly, lens opacity, deafness, microgyria (underdevelopment of the convolutions of the brain).
Complexes with this research
TORCH infections.
Avidity of IgG antibodies Diagnosis of TORCH infections with determination of avidity of IgG antibodies 9,260 ₽ Composition Entry into IVF Examination when a woman enters the IVF procedure 23,500 ₽ Composition
IVF planning Examination for preliminary preparation of a woman for the IVF procedure 13,260 ₽ Composition
IN OTHER COMPLEXES
- Examination during pregnancy. 1st trimester 17,040 RUR
- Pregnancy planning. Diagnosis of infections 8,800 ₽
- Miscarriage RUB 40,440
Acquired CMV infection
In the majority of infected people, it occurs without a pronounced clinical picture, in the form of a subclinical form or latent virus carriage. The transition to a clinically expressed disease is observed with various disturbances in the functioning of the immune system arising under the influence of various risk factors.
In this case, acute acquired CMV infection develops, the symptoms of which are similar to viral hepatitis or infectious mononucleosis. It can occur secretly and is detected accidentally during a screening blood test for cytomegalovirus.
Another common form of acquired CMV infection is mononucleosis-like syndrome. The clinical manifestations of this form are almost identical to another disease caused by the Epstein-Barr herpesvirus - infectious mononucleosis.
The incubation period can last up to 60 days. The active phase of the disease begins with flu-like symptoms: prolonged fever, chills, severe muscle and joint pain, severe fatigue. Patients often complain of a sore throat, enlarged regional lymph nodes, and skin rashes.
Rarely, symptoms of hepatitis such as jaundice may occur. Blood tests show an increase in liver enzymes (ALAT, AST). Pneumonia may develop, the probability of lung damage is 5-6%.
The duration of the disease can be up to 1-2 months, after which most patients experience a complete recovery. Some symptoms last longer, for example, enlarged lymph nodes can persist for up to six months.
Cytomegalovirus (CMV) (IgM antibodies)
In response to the introduction of cytomegalovirus (CMV) into the body, immune restructuring of the body develops. The incubation period ranges from 15 days to 3 months. With this infection, non-sterile immunity occurs (that is, complete elimination of the virus is not observed). Immunity to cytomegalovirus infection (CMV) is unstable and slow. Reinfection with an exogenous virus or reactivation of a latent infection is possible. Due to long-term persistence in the body, the virus affects all parts of the patient’s immune system. The body's protective reaction manifests itself, first of all, in the form of the formation of specific antibodies of the IgM and IgG classes to CMV. Specific antibodies are responsible for the lysis of the intracellular virus and also inhibit its intracellular replication or spread from cell to cell. Sera from patients after primary infection contain antibodies that react with internal proteins of CMV. The serum of recovered people contains mainly antibodies that react with membrane glycoproteins.
The greatest diagnostic significance is the determination of IgM as an indicator of the activity of the process, which may indicate an acutely ongoing disease, reinfection, superinfection or reactivation. The appearance of anti-CMV IgM antibodies in a previously seronegative patient indicates a primary infection. During endogenous reactivation of an infection, IgM antibodies are formed irregularly (usually in fairly low concentrations) or may be completely absent. Detection of class G immunoglobulins also makes it possible to determine primary cytomegalovirus infection (CMVI), monitor over time individuals with clinical manifestations of infection, and help with retrospective diagnosis. In severe CMV disease, as well as in pregnant women and young children, the production of antibodies to CMV is slowed down. This is manifested by the detection of specific antibodies in low concentrations or the absence of positive dynamics of antibodies.
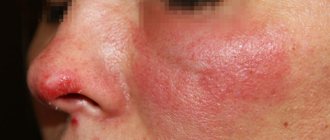
Features of infection . Cytomegalovirus (CMV) infection is a widespread viral infection of the body, which belongs to the so-called opportunistic infections, which usually occur latently. Clinical manifestations are observed against the background of physiological immunodeficiency states (children of the first 3 - 5 years of life, pregnant women - more often in the 2nd and 3rd trimester), as well as in persons with congenital or acquired immunodeficiencies (HIV infection, use of immunosuppressants, oncohematological diseases, radiation, diabetes and so on.).
Cytomegalovirus is a virus of the herpes virus family. Like other members of the family, after infection it remains in the body almost for life. Stable in humid environments. The risk group includes children 5-6 years old, adults 16-30 years old, as well as people who practice anal sex. Children are susceptible to airborne transmission from parents and other children with latent forms of infection. For adults, sexual transmission is more common. The virus is found in semen and other body fluids. Vertical transmission of infection (from mother to fetus) occurs transplacentally and during childbirth.
CMV infection is characterized by a variety of clinical manifestations, but with full immunity it is clinically asymptomatic. In rare cases, a picture of infectious mononucleosis develops (about 10% of all cases of infectious mononucleosis), clinically indistinguishable from mononucleosis caused by the Epstein-Barr virus. Replication of the virus occurs in the tissues of the reticuloendothelial system, epithelium of the urogenital tract, liver, mucous membrane of the respiratory tract and digestive tract. When immunity is reduced after organ transplantation, immunosuppressive therapy, HIV infection, as well as in newborns, CMV poses a serious threat, since the disease can affect any organ. the development of hepatitis, pneumonia, esophagitis, gastritis, colitis, retinitis, diffuse encephalopathy, fever, leukopenia is possible. The disease can be fatal. Cytomegalovirus infection in pregnant women, examination during pregnancy. When a pregnant woman is initially infected with cytomegalovirus (in 35–50% of cases) or the infection is reactivated during pregnancy (in 8–10% of cases), an intrauterine infection develops. If an intrauterine infection develops before 10 weeks, there is a risk of developmental defects and possible spontaneous termination of pregnancy. When infected at 11-28 weeks, intrauterine growth retardation and hypo- or dysplasia of internal organs occur. If infection occurs at a later stage, the lesion may be generalized, involve a specific organ (for example, fetal hepatitis) or appear after birth (hypertensive-hydrocephalic syndrome, hearing impairment, interstitial pneumonitis, etc.). Manifestations of infection also depend on maternal immunity, virulence and localization of the virus. It is impossible to completely cure this disease: cytomegalovirus cannot be removed from the body. But if you promptly, at the slightest suspicion of infection with this virus, consult a doctor and carry out the necessary tests, then you can keep the infection in a “dormant” state for many years. This will ensure a normal pregnancy and the birth of a healthy child.
Acquired cytomegalovirus infection in newborns
It develops as a result of infection of a newborn during the passage of the birth canal or in the initial stages of life - during breastfeeding, contact with carriers of the virus. Most children are asymptomatically converted to the carrier form.
Clinical symptoms appear in cases of severe prematurity or low birth weight. The infection occurs in the form of long-term pneumonia, often accompanied by bacterial damage to the respiratory system. The development of hepatitis, enlarged lymph nodes, and delays in mental and physical development are possible. During pregnancy, it is necessary to undergo a lot of tests that help identify the presence of not only CMV infection, but also toxoplasmosis.
Symptoms of CMV
The content of the article
CMV may be accompanied by the following symptoms:
- chronic weakness;
- temperature rise;
- sore throat, sore throat;
- pain in the right and left hypochondrium;
- enlarged lymph nodes.
Generalized form of CMV infection
Develops in infected people with extremely weakened immune systems. It is characterized by serious damage to the liver, nervous system, gastrointestinal tract, and lungs. The severity of the pathology depends on the state of the immune system; especially severe manifestations are observed in those taking immunosuppressants and patients with AIDS.
The main clinical manifestations of generalized CMV infection:
- Subacute onset. It is characterized by: severe loss of strength, fever, increased sweating at night, patients complain of pain in the joints and muscles.
- Ulcers of the stomach, intestines and esophagus manifest themselves in the form of abdominal pain and dyspeptic symptoms. They can lead to internal bleeding and perforations in the walls of the gastrointestinal tract.
- Hepatitis. There is jaundice, tenderness and enlargement of the liver.
- Pneumonia. Chest pain, cough, and respiratory rate increase.
- Encephalitis. Main manifestations: nystagmus (rhythmic twitching of the eyes), drowsiness, damage to one or more pairs of cranial nerves, disorientation. People who are HIV positive may develop AIDS dementia syndrome.
- Retinitis. Leads to complete or partial blindness.
- Multiple organ failure. The most common cause of death in a generalized infectious process. It manifests itself in the form of dysfunction of all organs and systems of the body affected by the virus.
Cytomegalovirus - symptoms of CMV
Congenital form of cytomegalovirus infection
Most children with congenital cytomegalovirus infection never show symptoms or have any health problems. However, some may have health problems that appear at birth or may develop later.
Some children may have the following signs of congenital cytomegalovirus infection at birth:
- problems with the liver, lungs and spleen;
- low birth weight;
- small head size (microcephaly);
- convulsions.
About 1 in 10 babies with CMV will have noticeable signs at birth, such as jaundice or an enlarged liver. They may also have long-term health problems such as hearing and vision loss and developmental delays.
About 40-60% of infants born with signs of congenital cytomegalovirus infection will have long-term health problems, such as:
- mental retardation;
- lack of coordination;
- muscle weakness.
Because signs of cytomegalovirus infection at birth are similar to other medical conditions, the diagnosis should be confirmed by laboratory tests within 2 to 3 weeks after birth.
Acquired form of cytomegalovirus infection
Most healthy people who acquire CMV after birth have an insidious disease and are unaware that they have been infected. In this case, there are no long-term health consequences.
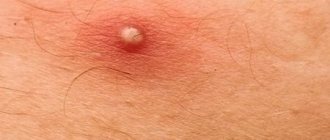
In some cases, cytomegalovirus infection in healthy people can cause the following symptoms:
- fever;
- redness of the throat;
- muscle pain;
- fatigue;
- enlarged lymph nodes.
Once a person becomes infected, the virus establishes a lifelong latency and can recur periodically. Illnesses caused by CMV rarely occur unless a person's immune system is weakened due to therapeutic drugs or illness.
People with weakened immune systems may experience more severe symptoms, affecting the eyes, lungs, liver, esophagus, stomach and intestines.
Make an appointment with a gynecologist
Mononucleosis-like syndrome
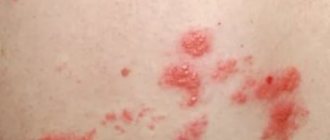
People with normal immunity who become ill with cytomegalovirus infection may experience a syndrome similar to mononucleosis. In this case, lymphomonocytosis is observed in the blood with the appearance of atypical mononuclear cells. The symptoms resemble a cold:
- high body temperature and chills (up to 1 month);
- headache, aches in muscles and joints;
- fatigue, malaise and weakness;
- enlargement of the salivary and lymph glands;
- skin rash resembling rubella rash.
In some cases, with mononucleosis-like syndrome, hepatitis develops - jaundice and an increase in liver enzymes in the blood. In 6% of cases, pneumonia develops as a complication.
Mononucleosis syndrome lasts for 6-90 days. After this, complete recovery occurs. Residual effects may persist for a month (enlarged lymph nodes, weakness, malaise).
Symptoms of cytomegalovirus in men and women
In men, CMV can affect the prostate and testicles. In women, the inner layer of the uterus, ovaries, cervix and vagina.
Symptoms of chronic cytomegalovirus infection
If CMV remains in the body for a long time, the immune system loses the ability to resist it. In this case, there is a prolonged increase in body temperature to 37.1-38.0 degrees. There is an enlargement of lymph nodes of different groups and an enlargement of the liver or spleen (rarely). Myocarditis (inflammation of the muscle tissue of the heart) also develops, and eye damage occurs.
Cytomegalovirus infection in people with normal immunity
It is not characterized by significant deviations, so a person’s life activity remains unchanged. The body's protective functions independently cope with CMV.
Cytomegalovirus infection in AIDS
An extremely severe course of the disease is noted. It is possible that a generalized form of infection may develop, in which damage to internal organs is observed:
- brain (dementia, encephalitis, meningitis);
- lungs (pneumonia, pneumonitis);
- kidneys (renal failure, nephritis with necrosis);
- eye (retinitis, complete blindness).
Damage to the liver (hepatitis), heart, adrenal glands, spleen, intestines, esophagus, etc. is less common. The prognosis in most cases is unfavorable.
Cytomegalovirus during pregnancy
If primary infection with cytomagalovirus occurs in pregnant women, they may experience the following complications:
- premature birth;
- spontaneous miscarriage;
- polyhydramnios;
- frozen pregnancy;
- intrauterine infection of the fetus, severe damage to its nervous system;
- fetal death.
Particularly severe consequences occur when the fetus is infected in the 1st trimester of pregnancy. In the case of pregnancy against the background of a pre-existing cytomegalovirus infection, in the chronic course of this pathology, when there are already protective antibodies in the woman’s blood, the probability of infection of the fetus does not exceed 10%. That is why, even at the stage of planning conception, it is necessary to be examined for the presence of TORCH infection (toxoplasmosis, rubella, cytomegalovirus, herpes, other infections).
If intrauterine infection of the fetus occurs, the risk of death of newborns is high. Survivors are often diagnosed with serious abnormalities:
- lack of vision and/or hearing;
- microcephaly;
- brain calcification;
- impaired growth and formation of the musculoskeletal system;
- hepato- and splenomegaly;
- pneumonia;
- frequent hemorrhages in parenchymal and hollow organs;
- delayed mental and physical development;
- heart diseases.
Cytomegalovirus infection during pregnancy is, of course, an alarming and dangerous factor. However, this is not a verdict. You need to see a doctor and follow medical recommendations, minimizing the risk of possible complications.
- The use of antiviral drugs in 80% of cases helps to stop the exacerbation - the virus and antibodies indicating its activity (IgM) disappear from the blood of patients.
- The use of human immunoglobulin for the treatment of the manifest form of CMV in pregnant women stops the reproduction of the virus and its elimination from the body in 75% of cases.
Classification and stages of development of cytomegalovirus infection
Acquired CMV can be latent or manifest. In the first case, we are talking about the absence of clinical signs. Diagnosis can only be made by laboratory tests. The manifest form of cytomegalovirus can be localized - sialoadenitis, and generalized - damage to the stomach and intestines, development of hepatitis, etc. In the congenital form, acute (death is often inevitable when a newborn is infected) and chronic course of the disease is possible. Cytomegalovirus infection is isolated separately in HIV-infected people.
According to the severity of CMV, there are:
- mild – there is no obvious damage to internal organs and no change in function;
- moderate - dysfunction of internal organs is moderate, no critical changes are observed;
- severe - damage to internal organs is pronounced (catastrophic functional failures are observed and complications develop).
Make an appointment with a gynecologist
Diagnosis of infection
In a routine blood test, patients suffering from CMV infection observe:
- Severe lymphocytosis.
- Atypical mononuclear cells (up to 10% or more).
- The total number of white blood cells rarely falls outside the normal range. In newborns, thrombocytopenia and a decrease in the number of red blood cells may be detected. In a biochemical blood test, an increase in the activity of liver enzymes is observed.
In samples of cerebrospinal fluid from patients with central nervous system damage, an increase in protein components, neutrophilic pleocytosis and a significant decrease in glucose levels are detected.
Treatment
It is based on conducting serological blood tests for cytomegalovirus - antibodies specific to this infection are detected. These include:
- Immunoglobulin M. These are markers of an acute infectious process during primary infection or the development of an exacerbation. They go beyond normal limits only 1-2 months after the virus enters the body. Increased rates can persist for up to six months. A high IgM titer in pregnant women means that there is a risk of infection of the embryo.
- Immunoglobulin G. An unimportant type of immunoglobulin. It rises quite late, during the period of attenuation of the infectious process. Serves to detect cytomegalovirus in the body.
- PCR. Allows you to accurately identify the genetic material of the virus in blood, other biological fluids, and tissues. Its variety, quantitative PCR, makes it possible to monitor the activity of the development of the infectious process as it provides data on the magnitude of virion reproduction.
- Direct microscopy. Based on direct observation of infected cells with a specific morphology. Materials obtained from biopsy, urine sediment, saliva, and blood are suitable for analysis. They are distinguished by their enormous size, large intranuclear inclusion, which is surrounded by a light rim, this is the so-called “owl's eye”. Microscopy is the simplest and most accessible method for detecting CMV infection.
Prevention
Subclinical forms of CMV infection and latent carriage are extremely common, and therefore in most cases do not require specific treatment, even if specific antibodies are detected. Treatment of such forms of cytomegalovirus is aimed at strengthening the body's defenses with the help of immunomodulators and preventing risk factors that lead to exacerbation of the disease.
To treat clinically active forms of CMV infection, 3 drugs are used that are quite effective:
- Ganciclovir. Administered by intravenous infusion twice a day. The course of treatment lasts 2-3 weeks. It is especially effective in combination with Citotect, a specific immunoglobulin, which is also administered intravenously.
- Foscarnet. Used if treatment with ganciclovir was not effective enough. It is administered intravenously three times a day, by slow administration (infusion duration is at least 2 hours).
- Cidofovir. Another drug of choice for CMV infection, which is used for resistance to ganciclovir. Administered intravenously, 1 time per week.
These drugs are contraindicated for use by pregnant women. In this case, pathogenetic therapy is prescribed. It includes a variety of interferon preparations (viferon, roferon) as well as inducers of the production of their own interferons - cycloferon, neovir.
The administration of interferons and other immunomodulatory drugs occurs under the control of the immunological status. If immunomodulators are ineffective, it is possible to prescribe a course of human immunoglobulin, which is administered by intramuscular injection in an amount of 3 to 5 with an interval of 2-3 days.
Various forms of CMV infection can masquerade as diseases with similar symptoms. Therefore, differential diagnosis is required with:
- Sepsis.
- Infectious mononucleosis.
- Bacterial meningitis.
Is it possible to completely get rid of
Cytomegalovirus infects cells and penetrates their genotype.
Even after intensive and varied treatment, it is not possible to completely get rid of the virus.
Any therapy in his case is aimed at preventing the development of complications and stimulating the immune system.
It is this that serves as the main barrier between illness and a healthy state.
How to remove immunoglobulin from blood
Unfortunately, this cannot be done completely.
Immune memory persists throughout life.
Specific diagnostics
The main direction in the prevention of CMV is compliance with the rules of personal hygiene, individual protection when in contact with patients with cytomegalovirus. It is especially important to follow preventive recommendations for people at risk:
- Patients who have undergone transplantation.
- Pregnant women.
- HIV-infected.
- Patients suffering from immunodeficiencies.
Means for specific prevention are under development. The only drug that allows prophylaxis in patients after transplantation is letermovir. It has not yet found widespread use; it is recommended for use only in the USA.
Examination for cytomegalovirus infection at Medart
The laboratory of the Medart clinic is equipped with modern high-precision equipment that allows you to perform any type of diagnosis of cytomegalovirus infection and other types of serological diagnosis of infectious diseases (diagnosis for HIV, syphilis, hepatitis, giardiasis, Helicobacter pylory, toxoplasmosis).
A blood test for cytomegalovirus is included in a set of tests for STIs (sexually transmitted infections). It is also possible to diagnose CMV infection based on individual indicators, for example, when planning pregnancy.
If necessary, test results can be obtained on the day the material is submitted. This is especially important in severe forms of CMV infection, when the speed of diagnosis and effective treatment is critical. Advantages of the clinic:
- Ability to perform a full range of diagnostic procedures.
- Optimal pricing policy.
- Qualified specialists.
Patients of the Medart clinic receive a full range of medical services - from preliminary consultation and laboratory diagnosis of cytomegalovirus to the prescription of effective therapy and receiving recommendations for prevention and rehabilitation after the disease.
What to do before taking tests?
Correct behavior before donating blood for analysis will help you obtain reliable diagnostic results.
There are no strict recommendations for cytology or ELISA.
The patient is asked to refrain from drinking alcohol and smoking.
Avoid fatty, fried or spicy foods.
The PCR method requires clearer rules.
To obtain an accurate result, you need to stop taking antibacterial or antiviral agents a few days before the test.
Abstain from sexual intercourse for a week.
The period of menstruation in women can influence the survey data.